【Codeforces-707D】Persistent Bookcase DFS + 线段树
D. Persistent Bookcase
Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent data structures: they are data structures that always preserves the previous version of itself and access to it when it is modified.
After reaching home Alina decided to invent her own persistent data structure. Inventing didn't take long: there is a bookcase right behind her bed. Alina thinks that the bookcase is a good choice for a persistent data structure. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf.
The bookcase consists of n shelves, and each shelf has exactly m positions for books at it. Alina enumerates shelves by integers from 1to n and positions at shelves — from 1 to m. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf in it.
Alina wrote down q operations, which will be consecutively applied to the bookcase. Each of the operations has one of four types:
- 1 i j — Place a book at position j at shelf i if there is no book at it.
- 2 i j — Remove the book from position j at shelf i if there is a book at it.
- 3 i — Invert book placing at shelf i. This means that from every position at shelf i which has a book at it, the book should be removed, and at every position at shelf i which has not book at it, a book should be placed.
- 4 k — Return the books in the bookcase in a state they were after applying k-th operation. In particular, k = 0 means that the bookcase should be in initial state, thus every book in the bookcase should be removed from its position.
After applying each of operation Alina is interested in the number of books in the bookcase. Alina got 'A' in the school and had no problem finding this values. Will you do so?
Input
The first line of the input contains three integers n, m and q (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 103, 1 ≤ q ≤ 105) — the bookcase dimensions and the number of operations respectively.
The next q lines describes operations in chronological order — i-th of them describes i-th operation in one of the four formats described in the statement.
It is guaranteed that shelf indices and position indices are correct, and in each of fourth-type operation the number k corresponds to some operation before it or equals to 0.
Output
For each operation, print the number of books in the bookcase after applying it in a separate line. The answers should be printed in chronological order.
input
2 3 3
1 1 1
3 2
4 0
output
1
4
0
input
4 2 6
3 2
2 2 2
3 3
3 2
2 2 2
3 2
output
2
1
3
3
2
4
input
2 2 2
3 2
2 2 1
output
2
1
Note
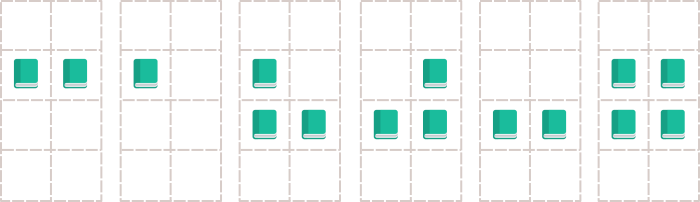
This image illustrates the second sample case.
Solution
题目大意:
给出一个矩阵,要支持如下操作
1.(x,y)位置变成1
2.(x,y)位置变成0
3.整行取反,0变成1,1变成0
4.退回到第k次操作后的状态
一共Q次询问,每次询问后输出矩阵中1的个数
首先,把矩阵展成序列,对其建线段树,这样,1,2,3操作就是简单的单点修改,区间修改
操作4的难处在于空间不允许保存历史状态,
考虑离线。
首先假设我们得到$i$之前的所有操作的答案,$i+1$次操作是退回操作,显然$i+1$次操作的答案,可以通过以前的答案得到,但问题涉及状态的变化
很显然,一次退回操作就相当于将这个操作之后的,到下一次退回操作之前的所有操作,从其退回到的状态开始修改
这显然是个树形的结构,于是我们的方法就非常直观了
对于所有的操作,我们假定$i$操作是向$i+1$操作连一条单向边的,那么对于一个退回操作$k$,它所退回到的操作是$x$,就相当于从$x$也向$k+1$连一条单向边,然后我们用$x$把$k$的答案更新,去掉$k$既可
那么从一号操作为根的树上DFS,每次修改,记录答案,修改完后回溯,直到遍历整棵树
而这样,状态不能记录的问题就被解决了,只需要一棵线段树,不过是修改2Q次
一个操作,可能不合法,这时候需要记录一下,回溯的时候特判
Code
code from yveh
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
struct edgetype{
int s,t,next;
}e[];
int head[],cnt=;
void addedge(int s,int t)
{
e[cnt].s=s;e[cnt].t=t;e[cnt].next=head[s];head[s]=cnt++;
}
struct Node{
int data,size;
bool rev;
Node()
{
data=rev=;
}
};
bool flag;
namespace Segtree
{
Node tree[];
void pushup(int node)
{
tree[node].data=tree[node<<].data+tree[node<<|].data;
}
void build(int l,int r,int node)
{
tree[node].size=r-l+;
if (l==r)
return;
int mid=(l+r)>>;
build(l,mid,node<<);
build(mid+,r,node<<|);
}
void pushdown(int node)
{
if (tree[node].rev)
{
tree[node<<].data=tree[node<<].size-tree[node<<].data;
tree[node<<].rev^=;
tree[node<<|].data=tree[node<<|].size-tree[node<<|].data;
tree[node<<|].rev^=;
tree[node].rev=;
}
}
void modify_pos(int pos,int l,int r,int node,int val)
{
if (l==r)
{
flag=tree[node].data==val;
tree[node].data=val;
return;
}
pushdown(node);
int mid=(l+r)>>;
if (pos<=mid)
modify_pos(pos,l,mid,node<<,val);
else
modify_pos(pos,mid+,r,node<<|,val);
pushup(node);
}
void modify_rev(int L,int R,int l,int r,int node)
{
if (L<=l&&r<=R)
{
tree[node].data=tree[node].size-tree[node].data;
tree[node].rev^=;
return;
}
pushdown(node);
int mid=(l+r)>>;
if (L<=mid)
modify_rev(L,R,l,mid,node<<);
if (R>mid)
modify_rev(L,R,mid+,r,node<<|);
pushup(node);
}
int query()
{
return tree[].data;
}
}
int n,m,q,opt,u,v,k;
int a[][],ans[];
void init()
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q);
Segtree::build(,n*m,);
}
void dfs(int node)
{
if (a[node][]==)
{
Segtree::modify_pos((a[node][]-)*m+a[node][],,n*m,,a[node][]);
if (!flag)
a[node][]=;
else
a[node][]=;
}
if (a[node][]==)
{
Segtree::modify_pos((a[node][]-)*m+a[node][],,n*m,,a[node][]);
if (!flag)
a[node][]=;
else
a[node][]=;
}
if (a[node][]==)
Segtree::modify_rev((a[node][]-)*m+,a[node][]*m,,n*m,);
ans[node]=Segtree::query();
for (int i=head[node];i!=-;i=e[i].next)
dfs(e[i].t);
if (a[node][]==)
Segtree::modify_pos((a[node][]-)*m+a[node][],,n*m,,a[node][]);
if (a[node][]==)
Segtree::modify_pos((a[node][]-)*m+a[node][],,n*m,,a[node][]);
if (a[node][]==)
Segtree::modify_rev((a[node][]-)*m+,a[node][]*m,,n*m,);
}
void work()
{
memset(head,0xff,sizeof(head));
cnt=;
for (int i=;i<=q;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][]);
if (a[i][]==)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a[i][],&a[i][]);
a[i][]=;
}
if (a[i][]==)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a[i][],&a[i][]);
a[i][]=;
} if (a[i][]==)
scanf("%d",&a[i][]);
if (a[i][]==)
{
scanf("%d",&k);
addedge(k,i);
}
else
addedge(i-,i);
}
dfs();
for (int i=;i<=q;i++)
printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
}
int main()
{
init();
work();
return ;
}
YveH打CF时问我的题...当时蹦出这个想法,但是他没能来得及当场A掉
觉得思路挺有意义的一道题,所以留下了想法...
实际上我还不知道题解是什么.....
【Codeforces-707D】Persistent Bookcase DFS + 线段树的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 707D Persistent Bookcase(时间树)
[题目链接] http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/707/D [题目大意] 给出一个矩阵,要求满足如下操作,单个位置x|=1或者x&=0,一行的数 ...
- 【离线】【深搜】【树】Codeforces 707D Persistent Bookcase
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/707/D 题目大意: 一个N*M的书架,支持4种操作 1.把(x,y)变为有书. 2.把(x,y)变为没 ...
- CodeForces 707D Persistent Bookcase ——(巧妙的dfs)
一个n*m的矩阵,有四种操作: 1.(i,j)处变1: 2.(i,j)处变0: 3.第i行的所有位置1,0反转: 4.回到第k次操作以后的状态: 问每次操作以后整个矩阵里面有多少个1. 其实不好处理的 ...
- CodeForces 707D Persistent Bookcase
$dfs$,优化. $return$操作说明该操作完成之后的状态和经过操作$k$之后的状态是一样的.因此我们可以建树,然后从根节点开始$dfs$一次(回溯的时候复原一下状态)就可以算出所有状态的答案. ...
- HDU 5877 dfs+ 线段树(或+树状树组)
1.HDU 5877 Weak Pair 2.总结:有多种做法,这里写了dfs+线段树(或+树状树组),还可用主席树或平衡树,但还不会这两个 3.思路:利用dfs遍历子节点,同时对于每个子节点au, ...
- codeforces Good bye 2016 E 线段树维护dp区间合并
codeforces Good bye 2016 E 线段树维护dp区间合并 题目大意:给你一个字符串,范围为‘0’~'9',定义一个ugly的串,即串中的子串不能有2016,但是一定要有2017,问 ...
- Codeforces1110F Nearest Leaf dfs + 线段树 + 询问离线
Codeforces1110F dfs + 线段树 + 询问离线 F. Nearest Leaf Description: Let's define the Eulerian traversal of ...
- dfs+线段树 zhrt的数据结构课
zhrt的数据结构课 这个题目我觉得是一个有一点点思维的dfs+线段树 虽然说看起来可以用树链剖分写,但是这个题目时间卡了树剖 因为之前用树剖一直在写这个,所以一直想的是区间更新,想dfs+线段树,有 ...
- codeforces 707D D. Persistent Bookcase(dfs)
题目链接: D. Persistent Bookcase time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 512 megabytes input ...
随机推荐
- XAMPP部署
1,直接从官网上下载,然后安装即可 2,出现的问题: a,启动Apache服务器的时候,出现打开端口失败,原因80号端口已被占用,解决方案,更改config文件,将端口设置为8090 b,给phpmy ...
- eval的对于验证数学公式的用处
var a=10,b=20; var s=a+b+((a/b)+(a+(a-b)))+(11)/a; var r=eval(s); console.log(r); 只要不报错,说明公式正确, 报错公式 ...
- Spring JDBCTemplate使用JNDI数据源
xml配置: <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverMana ...
- 误人子弟的网络,谈谈HTTP协议中的短轮询、长轮询、长连接和短连接
引言 最近刚到公司不到一个月,正处于熟悉项目和源码的阶段,因此最近经常会看一些源码.在研究一个项目的时候,源码里面用到了HTTP的长轮询.由于之前没太接触过,因此LZ便趁着这个机会,好好了解了一下HT ...
- 知乎日报win10版 - 天天读报【开源】
业余时间写的一个知乎日报win10版客户端,支持收藏,评论,点赞等. 商店地址:https://www.microsoft.com/zh-cn/store/apps/%E5%A4%A9%E5%A4%A ...
- 彻底理解Toast原理和解决小米MIUI系统上没法弹Toast的问题
1.Toast的基本使用 Toast在Android中属于系统消息通知,用来提示用户完成了什么操作.或者给用户一个必要的提醒.Toast的官方定义是这样的: A toast provides simp ...
- Tyk API网关介绍及安装说明
Tyk API网关介绍及安装说明 Tyk是一个开源的轻量级API网关程序. 什么是API网关 API网关是一个各类不同API的前置服务器.API网关封装了系统内部架构,对外提供统一服务.此外还可以实现 ...
- js队列
用指针和数组模拟基本队列 http://blog.csdn.net/zhuwq585/article/details/53177192 js下的事件队列,或者异步队列 http://www.jb51. ...
- ASP.NET mvc异常处理的方法
第一种:全局异常处理 1.首先常见保存异常的类(就是将异常信息写入到文件中去) public class LogManager { private string logFilePath = strin ...
- MATLAB中plot()画图的颜色线型和希腊字母参数设置
y 黄色 · 点线 m 粉红 ○ 圈线 c ...
