在树莓派上实现numpy的LSTM长短期记忆神经网络做图像分类,加载pytorch的模型参数,推理mnist手写数字识别
这几天又在玩树莓派,先是搞了个物联网,又在尝试在树莓派上搞一些简单的神经网络,这次搞得是LSTM识别mnist手写数字识别
训练代码在电脑上,cpu就能训练,很快的:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision
import numpy as np
import os
from PIL import Image # 定义LSTM模型
class LSTMModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, num_classes):
super(LSTMModel, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, batch_first=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, num_classes) def forward(self, x):
h0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_size).to(x.device)
c0 = torch.zeros(self.num_layers, x.size(0), self.hidden_size).to(x.device) out, (h_n,c_n) = self.lstm(x, (h0, c0))
out = self.fc(out[:, -1, :])
return out # 设置超参数
input_size = 28
sequence_length = 28
hidden_size = 128
num_layers = 2
num_classes = 10
batch_size = 100
num_epochs = 1
learning_rate = 0.001 # 加载MNIST数据集
train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), download=True)
test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=False, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()) # 创建数据加载器
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False) # 创建LSTM模型
model = LSTMModel(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, num_classes) # 定义损失函数和优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) # 训练模型
total_step = len(train_loader)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(train_loader):
images = images.reshape(-1, sequence_length, input_size)
outputs = model(images)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels) predictions = torch.argmax(outputs,dim=1)
# acc = torch.eq(predictions,labels).sum().item()
# print(acc)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step() if (i + 1) % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch [{}/{}], Step [{}/{}], Loss: {:.4f}'.format(epoch + 1, num_epochs, i + 1, total_step, loss.item())) # 保存模型
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model.pth') # 加载模型
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model.pth'))
with torch.no_grad():
for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(test_loader):
images = images.reshape(-1, sequence_length, input_size)
outputs = model(images)
predictions = torch.argmax(outputs,dim=1)
acc = torch.eq(predictions,labels).sum().item()
print(acc) # folder_path = './mnist_pi' # 替换为图片所在的文件夹路径
# def infer_images_in_folder(folder_path):
# with torch.no_grad():
# for file_name in os.listdir(folder_path):
# file_path = os.path.join(folder_path, file_name)
# if os.path.isfile(file_path) and file_name.endswith(('.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png')):
# image = Image.open(file_path)
# label = file_name.split(".")[0].split("_")[1]
# image = np.array(image)/255.0
# image = np.expand_dims(image,axis=0)
# image= torch.tensor(image).to(torch.float32)
# logits = model(image)
# predicted_class = torch.argmax(logits)
# print("file_path:",file_path,"img size:",image.shape,"label:",label,'Predicted class:', predicted_class)
# break # infer_images_in_folder(folder_path) # 保存模型参数为numpy的数组格式
model_params = {}
# print(list(model.parameters()))
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
model_params[name] = param.detach().numpy()
print(name,param.shape) np.savez('model.npz', **model_params)
然后需要自己在dataset里导出一些图片:我保存在了mnist_pi文件夹下,“_”后面的是标签,主要是在pc端导出保存到树莓派下
树莓派推理端的代码,需要numpy手动重新搭建网络,并且需要手动实现双层的LSTM神经网络,然后加载那些保存的矩阵参数,做矩阵乘法和加法
import numpy as np
import os
from PIL import Image # 加载模型参数
model_data = np.load('model.npz') '''
weight_ih_l[k] : the learnable input-hidden weights of the :math:`\text{k}^{th}` layer
`(W_ii|W_if|W_ig|W_io)`, of shape `(4*hidden_size, input_size)` for `k = 0`.
Otherwise, the shape is `(4*hidden_size, num_directions * hidden_size)`. If
``proj_size > 0`` was specified, the shape will be
`(4*hidden_size, num_directions * proj_size)` for `k > 0`
weight_hh_l[k] : the learnable hidden-hidden weights of the :math:`\text{k}^{th}` layer
`(W_hi|W_hf|W_hg|W_ho)`, of shape `(4*hidden_size, hidden_size)`. If ``proj_size > 0``
was specified, the shape will be `(4*hidden_size, proj_size)`.
bias_ih_l[k] : the learnable input-hidden bias of the :math:`\text{k}^{th}` layer
`(b_ii|b_if|b_ig|b_io)`, of shape `(4*hidden_size)`
bias_hh_l[k] : the learnable hidden-hidden bias of the :math:`\text{k}^{th}` layer
`(b_hi|b_hf|b_hg|b_ho)`, of shape `(4*hidden_size)`
''' # 提取模型参数
lstm_weight_ih_l0 = model_data['lstm.weight_ih_l0']
lstm_weight_hh_l0 = model_data['lstm.weight_hh_l0']
lstm_bias_ih_l0 = model_data['lstm.bias_ih_l0']
lstm_bias_hh_l0 = model_data['lstm.bias_hh_l0']
lstm_weight_ih_l1 = model_data['lstm.weight_ih_l1']
lstm_weight_hh_l1 = model_data['lstm.weight_hh_l1']
lstm_bias_ih_l1 = model_data['lstm.bias_ih_l1']
lstm_bias_hh_l1 = model_data['lstm.bias_hh_l1']
fc_weight = model_data['fc.weight']
fc_bias = model_data['fc.bias'] # print(lstm_weight_ih_l0.shape,lstm_weight_hh_l0.shape)
# print(lstm_bias_ih_l0.shape,lstm_bias_hh_l0.shape)
# 定义LSTM模型
def lstm_model(inputs):
'''
踩到两个坑,一个是矩阵形状都是这种(4*hidden_size, hidden_size)合并的,需要拆分。
另一个坑是,两层的lstm层需要每个时间步的输出都输入到下一层,而不是最后一个时间步的数据给下一层
''' batch_size, sequence_length, input_size = inputs.shape
hidden_size = lstm_weight_hh_l0.shape[1]
num_classes = fc_weight.shape[0] h0 = np.zeros((batch_size, hidden_size))
c0 = np.zeros((batch_size, hidden_size)) # 第一层LSTM
h_l0, c_l0 = np.zeros_like(h0), np.zeros_like(c0)
out_0 = []
for t in range(sequence_length):
x = inputs[:, t, :]
'''
i_t = \sigma(W_{ii} x_t + b_{ii} + W_{hi} h_{t-1} + b_{hi}) \\
f_t = \sigma(W_{if} x_t + b_{if} + W_{hf} h_{t-1} + b_{hf}) \\
g_t = \tanh(W_{ig} x_t + b_{ig} + W_{hg} h_{t-1} + b_{hg}) \\
o_t = \sigma(W_{io} x_t + b_{io} + W_{ho} h_{t-1} + b_{ho}) \\
c_t = f_t \odot c_{t-1} + i_t \odot g_t \\
h_t = o_t \odot \tanh(c_t) \\
'''
# 输入门
i_t = sigmoid(np.dot(x, lstm_weight_ih_l0[:128].T) + np.dot(h_l0, lstm_weight_hh_l0[:128].T) + lstm_bias_ih_l0[:128] + lstm_bias_hh_l0[:128])
# 遗忘门
f_t = sigmoid(np.dot(x, lstm_weight_ih_l0[128:256].T) + np.dot(h_l0, lstm_weight_hh_l0[128:256].T) + lstm_bias_ih_l0[128:256] + lstm_bias_hh_l0[128:256])
# 候选向量
g_t = np.tanh(np.dot(x, lstm_weight_ih_l0[256:256+128].T) + np.dot(h_l0, lstm_weight_hh_l0[256:256+128].T) + lstm_bias_ih_l0[256:256+128] + lstm_bias_hh_l0[256:256+128])
# 输出门
o_t = sigmoid(np.dot(x, lstm_weight_ih_l0[256+128:512].T) + np.dot(h_l0, lstm_weight_hh_l0[256+128:512].T) + lstm_bias_ih_l0[256+128:512] + lstm_bias_hh_l0[256+128:512])
# 细胞状态
c_l0 = f_t * c_l0 + i_t * g_t
# 隐藏状态
h_l0 = o_t * np.tanh(c_l0)
out_0.append(h_l0) # 第二层LSTM
h_l1, c_l1 = np.zeros_like(h0), np.zeros_like(c0)
out_1 = []
for t in range(sequence_length):
x = out_0[t]
# 输入门
i_t = sigmoid(np.dot(x, lstm_weight_ih_l1[:128].T) + np.dot(h_l1, lstm_weight_hh_l1[:128].T) + lstm_bias_ih_l1[:128] + lstm_bias_hh_l1[:128])
# 遗忘门
f_t = sigmoid(np.dot(x, lstm_weight_ih_l1[128:256].T) + np.dot(h_l1, lstm_weight_hh_l1[128:256].T) + lstm_bias_ih_l1[128:256] + lstm_bias_hh_l1[128:256])
# 候选向量
g_t = np.tanh(np.dot(x, lstm_weight_ih_l1[256:256+128].T) + np.dot(h_l1, lstm_weight_hh_l1[256:256+128].T) + lstm_bias_ih_l1[256:256+128] + lstm_bias_hh_l1[256:256+128])
# 输出门
o_t = sigmoid(np.dot(x, lstm_weight_ih_l1[256+128:512].T) + np.dot(h_l1, lstm_weight_hh_l1[256+128:512].T) + lstm_bias_ih_l1[256+128:512] + lstm_bias_hh_l1[256+128:512])
# 细胞状态
c_l1 = f_t * c_l1 + i_t * g_t
# 隐藏状态
h_l1 = o_t * np.tanh(c_l1)
out_1.append(h_l1) # 全连接层
fc_output = np.dot(h_l1, fc_weight.T) + fc_bias
predictions = np.argmax(fc_output, axis=1)
return predictions # Sigmoid激活函数
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x)) folder_path = './mnist_pi' # 替换为图片所在的文件夹路径
def infer_images_in_folder(folder_path):
for file_name in os.listdir(folder_path):
file_path = os.path.join(folder_path, file_name)
if os.path.isfile(file_path) and file_name.endswith(('.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png')):
image = Image.open(file_path)
label = file_name.split(".")[0].split("_")[1]
image = np.array(image)/255.0
image = np.expand_dims(image,axis=0)
predicted_class = lstm_model(image)
print("file_path:",file_path,"img size:",image.shape,"label:",label,'Predicted class:', predicted_class) infer_images_in_folder(folder_path)
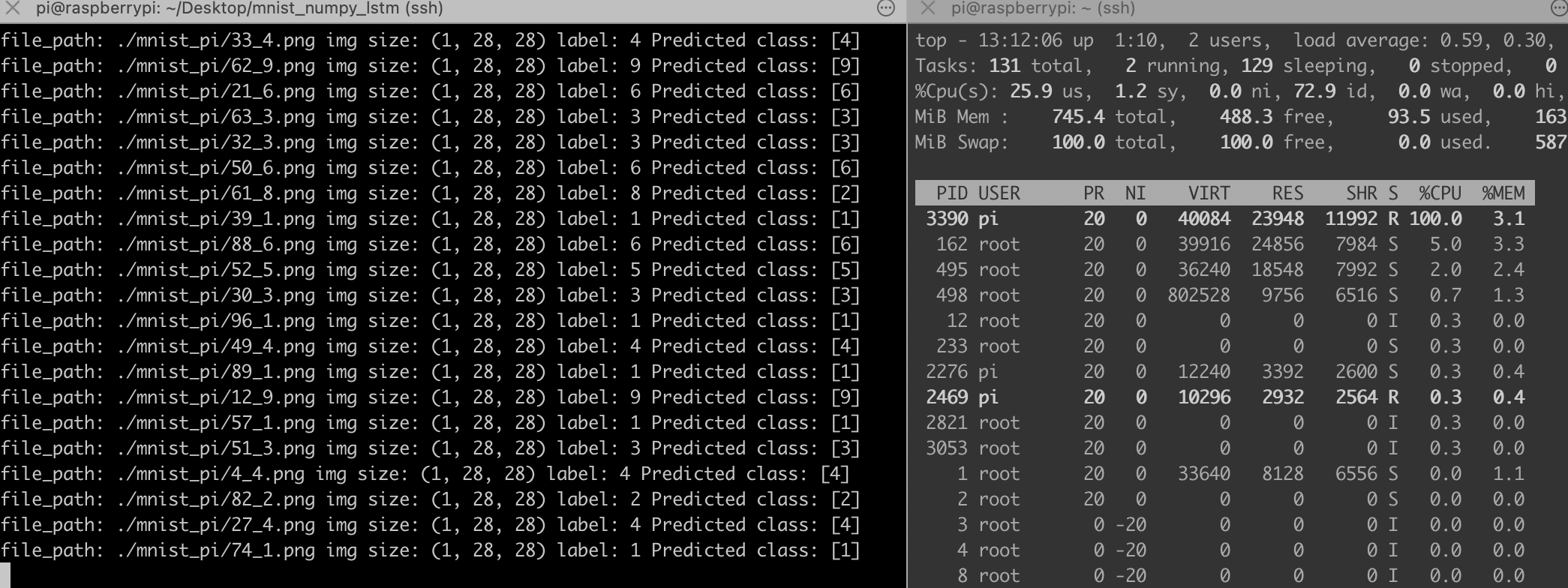
这代码完全就是numpy推理,不需要安装pytorch,树莓派也装不动pytorch,太重了,下面是推理结果,比之前的MLP网络慢很多,主要是手动实现的LSTM网络全靠循环实现。
在树莓派上实现numpy的LSTM长短期记忆神经网络做图像分类,加载pytorch的模型参数,推理mnist手写数字识别的更多相关文章
- TensorFlow——LSTM长短期记忆神经网络处理Mnist数据集
1.RNN(Recurrent Neural Network)循环神经网络模型 详见RNN循环神经网络:https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/6509630.html 2. ...
- 用tensorflow搭建RNN(LSTM)进行MNIST 手写数字辨识
用tensorflow搭建RNN(LSTM)进行MNIST 手写数字辨识 循环神经网络RNN相比传统的神经网络在处理序列化数据时更有优势,因为RNN能够将加入上(下)文信息进行考虑.一个简单的RNN如 ...
- 手写数字识别 ----在已经训练好的数据上根据28*28的图片获取识别概率(基于Tensorflow,Python)
通过: 手写数字识别 ----卷积神经网络模型官方案例详解(基于Tensorflow,Python) 手写数字识别 ----Softmax回归模型官方案例详解(基于Tensorflow,Pytho ...
- 基于Numpy的神经网络+手写数字识别
基于Numpy的神经网络+手写数字识别 本文代码来自Tariq Rashid所著<Python神经网络编程> 代码分为三个部分,框架如下所示: # neural network class ...
- Tensorflow - Tutorial (7) : 利用 RNN/LSTM 进行手写数字识别
1. 经常使用类 class tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell BasicLSTMCell 是最简单的一个LSTM类.没有实现clipping,projection layer ...
- 神经网络手写数字识别numpy实现
本文摘自Michael Nielsen的Neural Network and Deep Learning,该书的github网址为:https://github.com/mnielsen/neural ...
- LSTM用于MNIST手写数字图片分类
按照惯例,先放代码: import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data #载入数据集 ...
- deep_learning_LSTM长短期记忆神经网络处理Mnist数据集
1.RNN(Recurrent Neural Network)循环神经网络模型 详见RNN循环神经网络:https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/6509630.html 2. ...
- WPF技术触屏上的应用系列(五): 图片列表异步加载、手指进行缩小、放大、拖动 、惯性滑入滑出等效果
原文:WPF技术触屏上的应用系列(五): 图片列表异步加载.手指进行缩小.放大.拖动 .惯性滑入滑出等效果 去年某客户单位要做个大屏触屏应用,要对档案资源进行展示之用.客户端是Window7操作系统, ...
- Android高效率编码-第三方SDK详解系列(二)——Bmob后端云开发,实现登录注册,更改资料,修改密码,邮箱验证,上传,下载,推送消息,缩略图加载等功能
Android高效率编码-第三方SDK详解系列(二)--Bmob后端云开发,实现登录注册,更改资料,修改密码,邮箱验证,上传,下载,推送消息,缩略图加载等功能 我的本意是第二篇写Mob的shareSD ...
随机推荐
- 通过 poe 免费使用ChatGPT、GPT-4
poe 是由美版知乎 Quora 构建的AI 产品,提供实时在线与多个AI 机器人交流.Quora 于去年 12 月首次推出Poe 作为封闭测试版,并于2月份向所有 iOS 用户开放.支持 web 端 ...
- 如何用Python对股票数据进行LSTM神经网络和XGboost机器学习预测分析(附源码和详细步骤),学会的小伙伴们说不定就成为炒股专家一夜暴富了
前言 最近调研了一下我做的项目受欢迎程度,大数据分析方向竟然排第一,尤其是这两年受疫情影响,大家都非常担心自家公司裁员或倒闭,都想着有没有其他副业搞搞或者炒炒股.投资点理财产品,未雨绸缪,所以不少小伙 ...
- es6中clss做了些什么 怎么继承
我的理解是clss实际是一种语法糖 凡是es6中clss能做的 我们通过es5也同样可以完成传统的javascript中只有对象,没有类的概念.它是基于原型的面向对象语言.原型对象特点就是将自身的属性 ...
- .Net Core工作流WorkFlowCore
前言 WorkFlowCore是一个针对.NetCore的轻量级的工作流引擎,提供了FluentAPI.多任务.持久化以及并行处理的功能,适合于小型工作流.责任链的需求开发.支持工作流长期运行,提供了 ...
- 两分钟操作完成用VScode连接MySQL查询数据
第一步:下载一个插件,MySQL Syntax 安装后要是重启或刷新后没有出现 再安装一个MySQL 第二步:下载vscode-database 第三步:把需要的插件下载好后,接下来就开始操作 输入 ...
- axios文件下载!!!!
前端 download(){ debugger; this.loading = true; axios.post('http://localhost:8081/brand_case/dao.do?me ...
- 谈谈selenium中的clear后输入内容异常的处理
谈谈selenium中的clear后输入内容异常的处理 案例 在线考试项目的登录:http://124.223.31.21:9097/#/ 代码 from selenium import webdri ...
- CSS6大种选择器
一.常用的css基本选择器(4种) 1.标签选择器 结构: 标签名{css属性名:属性值}作用:通过标签名,找到页面中所有的这类标签,设置样式 注意:1.标签选择器选择的是一类标签,而不是单独的一个2 ...
- 实现异步操作CompletableFuture
多个线程异步操作后统一返回执行结果AtomicReference<RespVo> event = new AtomicReference<>(); AtomicReferenc ...
- 安装Nodejs,执行npm命令异常
异常现象: 在安装完成Nodejs之后,使用npm install时提示异常: 使用cmd查看npm版本,也报同样的错误. "operation not permitted, mkdir ' ...
