Lab_1:练习2——使用qemu执行并调试lab1中的软件
一、实验内容
为了熟悉使用qemu和gdb进行的调试工作,我们进行如下的小练习:
(一)从CPU加电后执行的第一条指令开始,单步跟踪BIOS的执行。
(二)在初始化位置0x7c00设置实地址断点,测试断点正常。
(三)从0x7c00开始跟踪代码运行,将单步跟踪反汇编得到的代码与bootasm.S和 bootblock.asm进行比较。
(四)自己找一个bootloader或内核中的代码位置,设置断点并进行测试。
二、实验步骤
补充材料:
我们主要通过硬件模拟器qemu来进行各种实验。在实验的过程中我们可能会遇上各种各样的问题,调试是必要的。qemu支持使用gdb进行的强大而方便的调试。所以用好qemu和gdb是完成各种实验的基本要素
默认的gdb需要进行一些额外的配置才进行qemu的调试任务。qemu和gdb之间使用网络端口1234进行通讯。在打开qemu进行模拟之后,执行gdb并输
target remote :1234
即可连接qemu,此时qemu会进入停止状态,听从gdb的命令
另外,我们可能需要qemu在一开始便进入等待模式,则我们不再使用make qemu开始系统的运行,而使用make debug来完成这项工作。这样qemu便不会在gdb尚未连接的时候擅自运行了。
gdb的地址断点
在gdb命令行中,使用b *[地址]便可以在指定内存地址设置断点,当qemu中的cpu执行到指定地址时,便会将控制权交给gdb。
(一)从CPU加电后执行的第一条指令开始,单步跟踪BIOS的执行
1.修改gdbinit文件
首先,在 /moocos/ucore_lab/labcodes_answer/lab1_result/tools 目录下,修改gdbinit文件
进入目录:
cd ./moocos/ucore_lab/labcodes_answer/lab1_result/tools
修改方法为:
输入vim gdbinit
用D删除gdbinit中原有的内容(D为删除整行,x或X为删除单个字符)
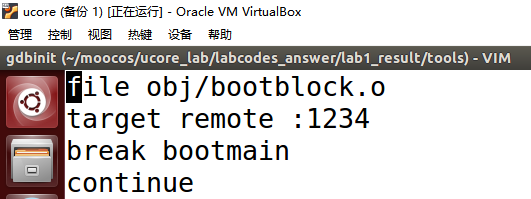
将以下内容粘贴入gdbinit中
set architecture i8086
target remote :1234

2.make debug
输入cd ..,退回到./moocos/ucore_lab/labcodes_answer/lab1_result
输入make debug
随后执行make debug,将弹出gdb窗口,如图所示:
在gdb窗口中使用si命令即可单步追踪
(注意:你不必每次输入si,输入一次si后,只要按回车即可执行上次的指令)

在gdb界面下,可通过如下命令来看BIOS的代码
x /2i $pc(显示当前eip处的汇编指令)

(二)在初始化位置0x7c00设置实地址断点,测试断点正常。
1.修改gdbinit文件
进入目录:
cd ./moocos/ucore_lab/labcodes_answer/lab1_result/tools
修改方法与(一)相同,
修改的内容如下:
target remote :1234 //连接qemu,此时qemu会进入停止状态,听从gdb的命令
set architecture i8086 //设置当前调试的CPU是8086
b *0x7c00 //在0x7c00处设置断点。此地址是bootloader入口点地址,可看boot/bootasm.S的start地址处
c //continue简称,表示继续执行
x/10i $pc //显示当前eip处的汇编指令
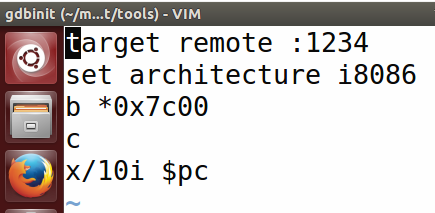
2.make debug
输入cd ..,退回到./moocos/ucore_lab/labcodes_answer/lab1_result
输入make debug
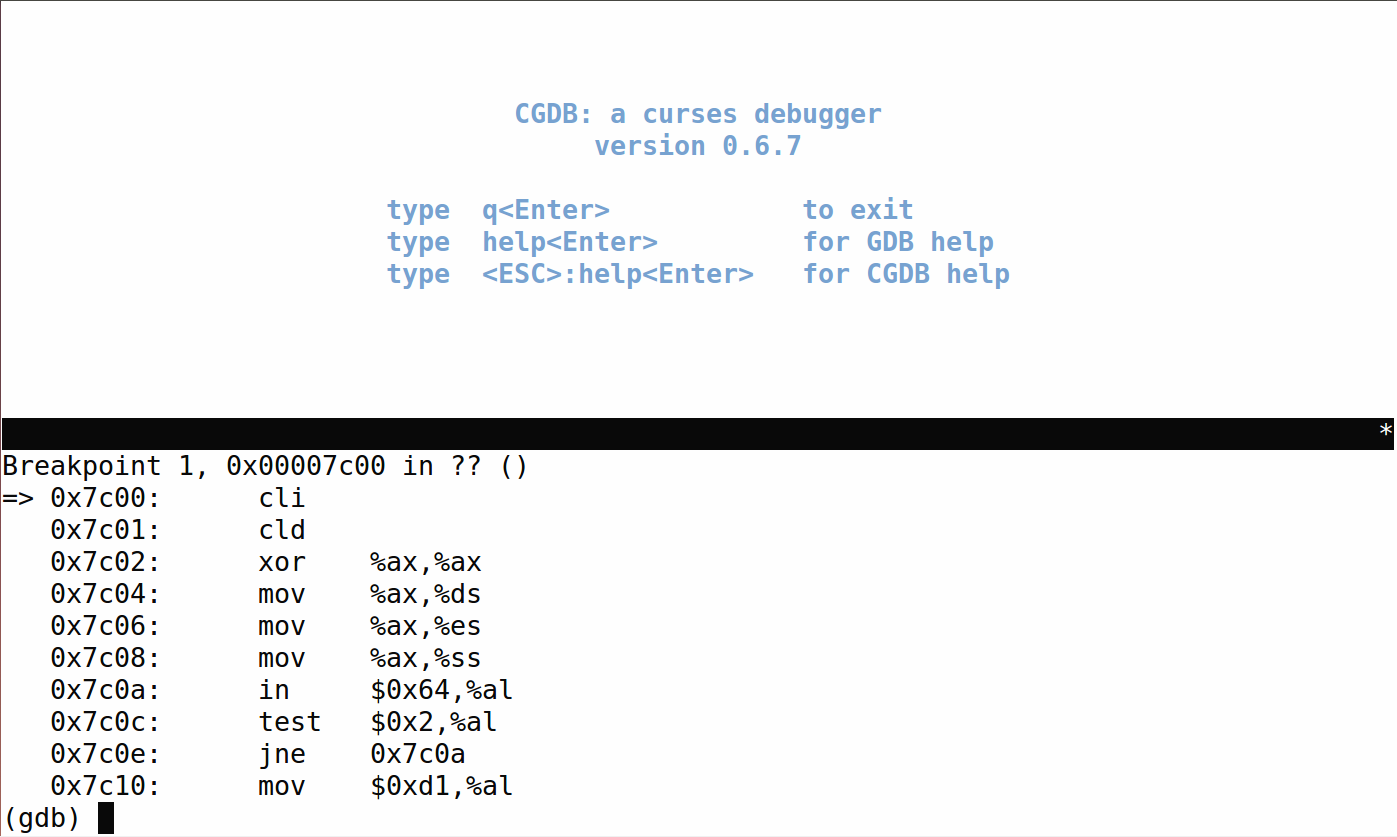
(三)从0x7c00开始跟踪代码运行,将单步跟踪反汇编得到的代码与bootasm.S和 bootblock.asm进行比较
bootasm.S的完整代码为:
#include <asm.h> # Start the CPU: switch to -bit protected mode, jump into C.
# The BIOS loads this code from the first sector of the hard disk into
# memory at physical address 0x7c00 and starts executing in real mode
# with %cs= %ip=7c00. .set PROT_MODE_CSEG, 0x8 # kernel code segment selector
.set PROT_MODE_DSEG, 0x10 # kernel data segment selector
.set CR0_PE_ON, 0x1 # protected mode enable flag # start address should be :7c00, in real mode, the beginning address of the running bootloader
.globl start
start:
.code16 # Assemble for -bit mode
cli # Disable interrupts
cld # String operations increment # Set up the important data segment registers (DS, ES, SS).
xorw %ax, %ax # Segment number zero
movw %ax, %ds # -> Data Segment
movw %ax, %es # -> Extra Segment
movw %ax, %ss # -> Stack Segment # Enable A20:
# For backwards compatibility with the earliest PCs, physical
# address line is tied low, so that addresses higher than
# 1MB wrap around to zero by default. This code undoes this.
seta20.:
inb $0x64, %al # Wait for not busy( input buffer empty).
testb $0x2, %al
jnz seta20. movb $0xd1, %al # 0xd1 -> port 0x64
outb %al, $0x64 # 0xd1 means: write data to 's P2 port seta20.:
inb $0x64, %al # Wait for not busy( input buffer empty).
testb $0x2, %al
jnz seta20. movb $0xdf, %al # 0xdf -> port 0x60
outb %al, $0x60 # 0xdf = , means set P2's A20 bit(the 1 bit) to 1 # Switch from real to protected mode, using a bootstrap GDT
# and segment translation that makes virtual addresses
# identical to physical addresses, so that the
# effective memory map does not change during the switch.
lgdt gdtdesc
movl %cr0, %eax
orl $CR0_PE_ON, %eax
movl %eax, %cr0 # Jump to next instruction, but in -bit code segment.
# Switches processor into -bit mode.
ljmp $PROT_MODE_CSEG, $protcseg .code32 # Assemble for -bit mode
protcseg:
# Set up the protected-mode data segment registers
movw $PROT_MODE_DSEG, %ax # Our data segment selector
movw %ax, %ds # -> DS: Data Segment
movw %ax, %es # -> ES: Extra Segment
movw %ax, %fs # -> FS
movw %ax, %gs # -> GS
movw %ax, %ss # -> SS: Stack Segment # Set up the stack pointer and call into C. The stack region is from --start(0x7c00)
movl $0x0, %ebp
movl $start, %esp
call bootmain # If bootmain returns (it shouldn't), loop.
spin:
jmp spin # Bootstrap GDT
.p2align # force byte alignment
gdt:
SEG_NULLASM # null seg
SEG_ASM(STA_X|STA_R, 0x0, 0xffffffff) # code seg for bootloader and kernel
SEG_ASM(STA_W, 0x0, 0xffffffff) # data seg for bootloader and kernel gdtdesc:
.word 0x17 # sizeof(gdt) -
.long gdt # address gdt
bootasm.S
bootblock.asm的完整代码为:
obj/bootblock.o: file format elf32-i386 Disassembly of section .text: 00007c00 <start>: # start address should be :7c00, in real mode, the beginning address of the running bootloader
.globl start
start:
.code16 # Assemble for -bit mode
cli # Disable interrupts
7c00: fa cli
cld # String operations increment
7c01: fc cld # Set up the important data segment registers (DS, ES, SS).
xorw %ax, %ax # Segment number zero
7c02: c0 xor %eax,%eax
movw %ax, %ds # -> Data Segment
7c04: 8e d8 mov %eax,%ds
movw %ax, %es # -> Extra Segment
7c06: 8e c0 mov %eax,%es
movw %ax, %ss # -> Stack Segment
7c08: 8e d0 mov %eax,%ss 00007c0a <seta20.>:
# Enable A20:
# For backwards compatibility with the earliest PCs, physical
# address line is tied low, so that addresses higher than
# 1MB wrap around to zero by default. This code undoes this.
seta20.:
inb $0x64, %al # Wait for not busy( input buffer empty).
7c0a: e4 in $0x64,%al
testb $0x2, %al
7c0c: a8 test $0x2,%al
jnz seta20.
7c0e: fa jne 7c0a <seta20.> movb $0xd1, %al # 0xd1 -> port 0x64
7c10: b0 d1 mov $0xd1,%al
outb %al, $0x64 # 0xd1 means: write data to 's P2 port
7c12: e6 out %al,$0x64 00007c14 <seta20.>: seta20.:
inb $0x64, %al # Wait for not busy( input buffer empty).
7c14: e4 in $0x64,%al
testb $0x2, %al
7c16: a8 test $0x2,%al
jnz seta20.
7c18: fa jne 7c14 <seta20.> movb $0xdf, %al # 0xdf -> port 0x60
7c1a: b0 df mov $0xdf,%al
outb %al, $0x60 # 0xdf = , means set P2's A20 bit(the 1 bit) to 1
7c1c: e6 out %al,$0x60 # Switch from real to protected mode, using a bootstrap GDT
# and segment translation that makes virtual addresses
# identical to physical addresses, so that the
# effective memory map does not change during the switch.
lgdt gdtdesc
7c1e: 0f lgdtl (%esi)
7c21: 6c insb (%dx),%es:(%edi)
7c22: 7c 0f jl 7c33 <protcseg+0x1>
movl %cr0, %eax
7c24: c0 and %al,%al
orl $CR0_PE_ON, %eax
7c26: c8 or $0x1,%ax
movl %eax, %cr0
7c2a: 0f c0 mov %eax,%cr0 # Jump to next instruction, but in -bit code segment.
# Switches processor into -bit mode.
ljmp $PROT_MODE_CSEG, $protcseg
7c2d: ea 7c b8 ljmp $0xb866,$0x87c32 00007c32 <protcseg>: .code32 # Assemble for -bit mode
protcseg:
# Set up the protected-mode data segment registers
movw $PROT_MODE_DSEG, %ax # Our data segment selector
7c32: b8 mov $0x10,%ax
movw %ax, %ds # -> DS: Data Segment
7c36: 8e d8 mov %eax,%ds
movw %ax, %es # -> ES: Extra Segment
7c38: 8e c0 mov %eax,%es
movw %ax, %fs # -> FS
7c3a: 8e e0 mov %eax,%fs
movw %ax, %gs # -> GS
7c3c: 8e e8 mov %eax,%gs
movw %ax, %ss # -> SS: Stack Segment
7c3e: 8e d0 mov %eax,%ss # Set up the stack pointer and call into C. The stack region is from --start(0x7c00)
movl $0x0, %ebp
7c40: bd mov $0x0,%ebp
movl $start, %esp
7c45: bc 7c mov $0x7c00,%esp
call bootmain
7c4a: e8 b1 call 7d00 <bootmain> 00007c4f <spin>: # If bootmain returns (it shouldn't), loop.
spin:
jmp spin
7c4f: eb fe jmp 7c4f <spin>
7c51: 8d lea 0x0(%esi),%esi 00007c54 <gdt>:
...
7c5c: ff (bad)
7c5d: ff incl (%eax)
7c5f: add %al,(%eax)
7c61: 9a cf ff ff lcall $0x0,$0xffff00cf
7c68: cf add %dl,0x1700cf(%edx) 00007c6c <gdtdesc>:
7c6c: pop %ss
7c6d: 7c add %dl,0x0(%esp,%edi,)
... 00007c72 <readseg>:
/* *
* readseg - read @count bytes at @offset from kernel into virtual address @va,
* might copy more than asked.
* */
static void
readseg(uintptr_t va, uint32_t count, uint32_t offset) {
7c72: push %ebp
7c73: e5 mov %esp,%ebp
7c75: push %edi
7c76: push %esi
7c77: c6 mov %eax,%esi
7c79: push %ebx
uintptr_t end_va = va + count;
7c7a: 8d lea (%eax,%edx,),%eax // round down to sector boundary
va -= offset % SECTSIZE;
7c7d: d2 xor %edx,%edx
/* *
* readseg - read @count bytes at @offset from kernel into virtual address @va,
* might copy more than asked.
* */
static void
readseg(uintptr_t va, uint32_t count, uint32_t offset) {
7c7f: push %ebx
uintptr_t end_va = va + count;
7c80: f0 mov %eax,-0x10(%ebp) // round down to sector boundary
va -= offset % SECTSIZE;
7c83: c8 mov %ecx,%eax
7c85: f7 e4 7d divl 0x7de4
7c8b: d6 sub %edx,%esi // translate from bytes to sectors; kernel starts at sector 1
uint32_t secno = (offset / SECTSIZE) + ;
7c8d: 8d lea 0x1(%eax),%ebx // If this is too slow, we could read lots of sectors at a time.
// We'd write more to memory than asked, but it doesn't matter --
// we load in increasing order.
for (; va < end_va; va += SECTSIZE, secno ++) {
7c90: 3b f0 cmp -0x10(%ebp),%esi
7c93: jae 7cfa <readseg+0x88>
static inline void ltr(uint16_t sel) __attribute__((always_inline)); static inline uint8_t
inb(uint16_t port) {
uint8_t data;
asm volatile ("inb %1, %0" : "=a" (data) : "d" (port));
7c95: ba f7 mov $0x1f7,%edx
7c9a: ec in (%dx),%al
struct elfhdr * ELFHDR = ((struct elfhdr *)0x10000) ; // scratch space /* waitdisk - wait for disk ready */
static void
waitdisk(void) {
while ((inb(0x1F7) & 0xC0) != 0x40)
7c9b: e0 c0 and $0xffffffc0,%eax
7c9e: 3c cmp $0x40,%al
7ca0: f3 jne 7c95 <readseg+0x23>
: "memory", "cc");
} static inline void
outb(uint16_t port, uint8_t data) {
asm volatile ("outb %0, %1" :: "a" (data), "d" (port));
7ca2: b2 f2 mov $0xf2,%dl
7ca4: b0 mov $0x1,%al
7ca6: ee out %al,(%dx)
7ca7: 0f b6 c3 movzbl %bl,%eax
7caa: b2 f3 mov $0xf3,%dl
7cac: ee out %al,(%dx)
7cad: 0f b6 c7 movzbl %bh,%eax
7cb0: b2 f4 mov $0xf4,%dl
7cb2: ee out %al,(%dx)
waitdisk(); outb(0x1F2, ); // count = 1
outb(0x1F3, secno & 0xFF);
outb(0x1F4, (secno >> ) & 0xFF);
outb(0x1F5, (secno >> ) & 0xFF);
7cb3: d8 mov %ebx,%eax
7cb5: b2 f5 mov $0xf5,%dl
7cb7: c1 e8 shr $0x10,%eax
7cba: 0f b6 c0 movzbl %al,%eax
7cbd: ee out %al,(%dx)
outb(0x1F6, ((secno >> ) & 0xF) | 0xE0);
7cbe: d8 mov %ebx,%eax
7cc0: b2 f6 mov $0xf6,%dl
7cc2: c1 e8 shr $0x18,%eax
7cc5: e0 0f and $0xf,%eax
7cc8: c8 e0 or $0xffffffe0,%eax
7ccb: ee out %al,(%dx)
7ccc: b0 mov $0x20,%al
7cce: b2 f7 mov $0xf7,%dl
7cd0: ee out %al,(%dx)
static inline void ltr(uint16_t sel) __attribute__((always_inline)); static inline uint8_t
inb(uint16_t port) {
uint8_t data;
asm volatile ("inb %1, %0" : "=a" (data) : "d" (port));
7cd1: ba f7 mov $0x1f7,%edx
7cd6: ec in (%dx),%al
struct elfhdr * ELFHDR = ((struct elfhdr *)0x10000) ; // scratch space /* waitdisk - wait for disk ready */
static void
waitdisk(void) {
while ((inb(0x1F7) & 0xC0) != 0x40)
7cd7: e0 c0 and $0xffffffc0,%eax
7cda: 3c cmp $0x40,%al
7cdc: f3 jne 7cd1 <readseg+0x5f> // wait for disk to be ready
waitdisk(); // read a sector
insl(0x1F0, dst, SECTSIZE / );
7cde: 8b 0d e4 7d mov 0x7de4,%ecx
return data;
} static inline void
insl(uint32_t port, void *addr, int cnt) {
asm volatile (
7ce4: f7 mov %esi,%edi
7ce6: ba f0 mov $0x1f0,%edx
7ceb: c1 e9 shr $0x2,%ecx
7cee: fc cld
7cef: f2 6d repnz insl (%dx),%es:(%edi)
uint32_t secno = (offset / SECTSIZE) + ; // If this is too slow, we could read lots of sectors at a time.
// We'd write more to memory than asked, but it doesn't matter --
// we load in increasing order.
for (; va < end_va; va += SECTSIZE, secno ++) {
7cf1: e4 7d add 0x7de4,%esi
7cf7: inc %ebx
7cf8: eb jmp 7c90 <readseg+0x1e>
readsect((void *)va, secno);
}
}
7cfa: pop %eax
7cfb: 5b pop %ebx
7cfc: 5e pop %esi
7cfd: 5f pop %edi
7cfe: 5d pop %ebp
7cff: c3 ret 00007d00 <bootmain>: /* bootmain - the entry of bootloader */
void
bootmain(void) {
// read the 1st page off disk
readseg((uintptr_t)ELFHDR, SECTSIZE * , );
7d00: a1 e4 7d mov 0x7de4,%eax
7d05: c9 xor %ecx,%ecx
}
} /* bootmain - the entry of bootloader */
void
bootmain(void) {
7d07: push %ebp
7d08: e5 mov %esp,%ebp
7d0a: push %esi
// read the 1st page off disk
readseg((uintptr_t)ELFHDR, SECTSIZE * , );
7d0b: 8d c5 lea 0x0(,%eax,),%edx
7d12: a1 e0 7d mov 0x7de0,%eax
}
} /* bootmain - the entry of bootloader */
void
bootmain(void) {
7d17: push %ebx
// read the 1st page off disk
readseg((uintptr_t)ELFHDR, SECTSIZE * , );
7d18: e8 ff ff ff call 7c72 <readseg> // is this a valid ELF?
if (ELFHDR->e_magic != ELF_MAGIC) {
7d1d: a1 e0 7d mov 0x7de0,%eax
7d22: 7f 4c cmpl $0x464c457f,(%eax)
7d28: 3a jne 7d64 <bootmain+0x64>
} struct proghdr *ph, *eph; // load each program segment (ignores ph flags)
ph = (struct proghdr *)((uintptr_t)ELFHDR + ELFHDR->e_phoff);
7d2a: 8b 1c mov 0x1c(%eax),%ebx
7d2d: c3 add %eax,%ebx
eph = ph + ELFHDR->e_phnum;
7d2f: 0f b7 2c movzwl 0x2c(%eax),%eax
7d33: c1 e0 shl $0x5,%eax
7d36: 8d lea (%ebx,%eax,),%esi
for (; ph < eph; ph ++) {
7d39: f3 cmp %esi,%ebx
7d3b: jae 7d55 <bootmain+0x55>
readseg(ph->p_va & 0xFFFFFF, ph->p_memsz, ph->p_offset);
7d3d: 8b mov 0x8(%ebx),%eax
struct proghdr *ph, *eph; // load each program segment (ignores ph flags)
ph = (struct proghdr *)((uintptr_t)ELFHDR + ELFHDR->e_phoff);
eph = ph + ELFHDR->e_phnum;
for (; ph < eph; ph ++) {
7d40: c3 add $0x20,%ebx
readseg(ph->p_va & 0xFFFFFF, ph->p_memsz, ph->p_offset);
7d43: 8b 4b e4 mov -0x1c(%ebx),%ecx
7d46: 8b f4 mov -0xc(%ebx),%edx
7d49: ff ff ff and $0xffffff,%eax
7d4e: e8 1f ff ff ff call 7c72 <readseg>
7d53: eb e4 jmp 7d39 <bootmain+0x39>
} // call the entry point from the ELF header
// note: does not return
((void (*)(void))(ELFHDR->e_entry & 0xFFFFFF))();
7d55: a1 e0 7d mov 0x7de0,%eax
7d5a: 8b mov 0x18(%eax),%eax
7d5d: ff ff ff and $0xffffff,%eax
7d62: ff d0 call *%eax
asm volatile ("outb %0, %1" :: "a" (data), "d" (port));
} static inline void
outw(uint16_t port, uint16_t data) {
asm volatile ("outw %0, %1" :: "a" (data), "d" (port));
7d64: b8 8a ff ff mov $0xffff8a00,%eax
7d69: c2 mov %eax,%edx
7d6b: ef out %ax,(%dx)
7d6d: b8 8e ff ff mov $0xffff8e00,%eax
7d72: ef out %ax,(%dx)
7d74: eb fe jmp 7d74 <bootmain+0x74>
bootblock.asm
反汇编得到的代码是:

下图是bootasm.S中14到28行的代码:
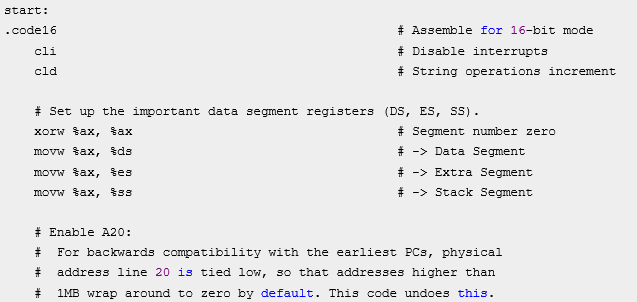
下面是bootblock.asm中10到25行的代码
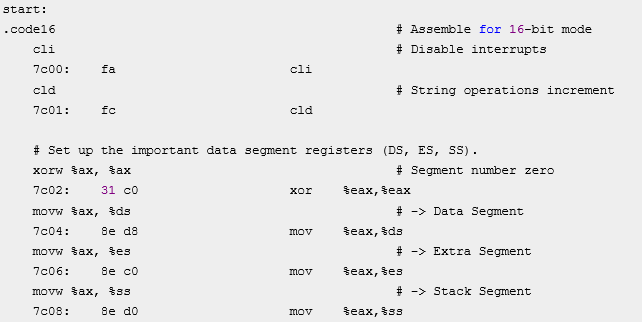
比较可知,三者基本一致。
(四)自己找一个bootloader或内核中的代码位置,设置断点并进行测试
略
Lab_1:练习2——使用qemu执行并调试lab1中的软件的更多相关文章
- 使用 visualstudio code 编辑器调试执行在 homestead 环境中的 laravel 程序
由于之前做 .net 开发比较熟悉 visualstudio,所以自 visualstudio code 发布后就一直在不同场合使用 vscode ,比如前端.node等等.最近在做 laravel ...
- 关于真机调试DDMS中的data文件夹打不开的解决方法
关于真机调试DDMS中的data文件夹打不开的解决方法 今天在开发的时候需要导出程序中的数据库文件查看数据,数据库文件默认就在/data/data/应用包名/databases/数据库名 这个路径下, ...
- 在 Visual Studio 调试器中指定符号 (.pdb) 和源文件
查找并指定符号文件和源文件:指定符号加载行为.使用符号和源服务器上:加载符号自动或在要求. 内容 查找符号 (.pdb) 文件 查找源文件 查找符号 (.pdb) 文件 说明 在之前的 Vis ...
- 转:使用IDA动态调试WanaCrypt0r中的tasksche.exe
逆向分析——使用IDA动态调试WanaCrypt0r中的tasksche.exe 转:http://www.4hou.com/technology/4832.html 2017年5月19日发布 导语: ...
- @清晰掉 GDB调试器中的战斗机
GDB 的命令很多,本文不会全部介绍,仅会介绍一些最常用的.在介绍之前,先介绍GDB中的一个非常有用的功能:补齐功能.它就如同Linux下SHELL中的命令补齐一样.当你输入一个命令的前几个字符,然后 ...
- 在VisualStudio调试器中使用内存窗口和查看内存分布
调试模式下内存窗口的使用 在调试期间,"内存"窗口显示应用使用的内存空间.调试器窗口(如"监视"."自动"."局部变量" ...
- 异步控制---实现函数asyncAll,在执行完传入数组中func1,func2,func3异步函数后,输出“end”
实现函数asyncAll,在执行完传入数组中func1,func2,func3异步函数后,输出"end" function func1(callback) { setTimeout ...
- 在执行xp_cmdshell的过程中出错,调用'LogonUserW'失败,错误代码:'1909'
在上篇文章Could not obtain information about Windows NT group/user 'xxxx\xxxx', error code 0x5里面,我介绍了SQL ...
- 重新想象 Windows 8 Store Apps (42) - 多线程之线程池: 延迟执行, 周期执行, 在线程池中找一个线程去执行指定的方法
[源码下载] 重新想象 Windows 8 Store Apps (42) - 多线程之线程池: 延迟执行, 周期执行, 在线程池中找一个线程去执行指定的方法 作者:webabcd 介绍重新想象 Wi ...
随机推荐
- Golang中,Aes加解密
今天在用Golang解析php那边用Aes加密的一个key.网上大多是用base64将结果编码一下.而且用到了向量.我php 那边没有用到向量.所以golang这边也是要去掉的.参考网站的改了下.能够 ...
- Android Okhttp POST提交键值对
以前的项目网络连接那块一直坚持使用HttpClient,总是会出现一些莫名奇妙的问题,现在新的项目使用了OKHttp网络框架,发现超级好用,上网再了解下,发现OkHttp口碑真的不错,对比之下Http ...
- Django框架(十二)-- Djang与Ajax
一.什么是Ajax AJAX(Asynchronous Javascript And XML)翻译成中文就是“异步Javascript和XML”.即使用Javascript语言与服务器进行异步交互,传 ...
- MicroK8s及KubeFlow安装文档
安装简单的k8s大约有三种思路:minikube,microk8s,kubeadm.minikube 虽然是官方出品,但主要还是基于虚拟机做的设计.在 Linux 生产环境下,microk8s 可能是 ...
- nginx访问jupyter
现在jupyter已通过k8s安装完成,并通过nodeport暴露出来. 如果不能直接访问这个nodeport(像我在的公司)或是希望能组织好jupyter实例, 那应该如何调通呢? 这里包括两个技术 ...
- Palindrome Mouse(2019年牛客多校第六场C题+回文树+树状数组)
目录 题目链接 题意 思路 代码 题目链接 传送门 题意 问\(s\)串中所有本质不同的回文子串中有多少对回文子串满足\(a\)是\(b\)的子串. 思路 参考代码:传送门 本质不同的回文子串肯定是要 ...
- Nat类型测试
这是一个测试NAT类型的小工具,一般也没太多用处,只有游戏玩家可能需要用来测试你的网络NAT类型是什么.NAT类型一般分为以下4种: 1. Full Cone NAT (完全圆锥型)2. Restri ...
- python面试题以及答案
目录 Python基础篇 1:为什么学习Python 2:通过什么途径学习Python 3:谈谈对Python和其他语言的区别 Python的优势: 4:简述解释型和编译型编程语言 5:Python的 ...
- 【oracle】decode函数
DECODE(参数,值1,翻译值1,值2,翻译值2,...值n,翻译值n,缺省值) 值1:当参数=值1 翻译值1:想要得到的值 值2:当参数=值2 翻译值2:想要得到的值
- Python内置函数---ord()
描述: ord() 函数是 chr() 函数(对于8位的ASCII字符串)或 unichr() 函数(对于Unicode对象)的配对函数,它以一个字符(长度为1的字符串)作为参数,返回对应的 ASCI ...
