自己实现HashMap
一载体
HashMap是由数组组成,数组元素为哈希链。
数组
public class MyHashMap<K, V> {
transient Node<K, V>[] table;
}
数组元素
@SuppressWarnings("hiding")
class Node<K, V> implements Map.Entry<K, V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K, V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
@Override
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
@Override
public V setValue(V value) {
V tempValue = value;
this.value = value;
return tempValue;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [ key=" + key + " , value=" + value + " , " + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?, ?> e = (Map.Entry<?, ?>) o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) && Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
二属性
private static int initCount = 16;//初始化长度
private static float loadFator = 0.75f;//加载因子
private int size;
private static int threshold;//扩容临界值
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
添加构造方法初始化属性
public MyHashMap(){
this(initCount, loadFator);
}
public MyHashMap(int initCount){
this(initCount, loadFator);
}
public MyHashMap(int initCount, float loadFator){
if(initCount < 0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("初始化长度不合法 : " + initCount);
}
if(initCount > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY){
initCount = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
}
if(loadFator <0 || Float.isNaN(loadFator)){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("加载因子不合法 : " + loadFator);
}
this.loadFator = loadFator;
this.threshold = (int) (initCount * 2 * loadFator);
}
三方法
1增加元素
1.1如果没有哈希碰撞,HashMap就相当于一个数组,而且查找无需遍历。
public Object put(K key, V value){
if(table == null || table.length == 0){
//此时真正创建数组
table = new Node[initCount];
}
int hash = hash(key);
int len = table.length;
int index = hash % len;// (len-1) & hash
if(table[index] == null){
table[index] = new Node<>(hash, key, value, null);
}
return null;
}
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
1.2哈希碰撞的情况。
如果按jdk8的实现方式,哈希碰撞的情况分为两种情况,首先是形成一个链表,当链表长度大于8时,会分裂成红黑树。这里只按链表实现。
else{//哈希碰撞
MyHashMap<K, V>.Node<K, V> e = p;
do{
if(e.hash == hash && ((e.key == key) || (key != null && key.equals(e.key)))){
V oldValue = p.value;
//用新值覆盖旧值
p.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
p = e;
}while((e = p.next) != null);
//将元素放在链表最前面
table[index] = new Node<K, V>(hash, key, value, p);
if(++size > threshold){//扩容
resize();
}
public void resize(){
//TODO
}
2获取元素
根据key得到数组索引,再判断有无链表。如有,判断链表长度。为1直接返回。大于1,需循环链表。
public V get(K k){
int hash = hash(k);
int len = table.length;
int index = hash % len;
Node<K,V> node = table[index];//找到链表
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
Node<K,V> p;
if ((p = node.next) == null) {//如果链表只有一个元素,直接返回
return node.value;
} else {//如果有多个元素,循环比较key
p = node;
do {
if (p.key == k || p.key.equals(k)) {
return p.value;
}
node = p;
} while ((p = node.next) != null);
}
return null;
}
3删除元素
首先得找到元素。同样是根据key得到数组索引。判断链表是否有值。无值直接返回。有值分两种情况,一种是被删除元素在链表最前面,那么直接将最前面的指针断掉。否则需要将前一个的指针指向后一个元素。由于链表结构只有next,没有前后左右,所以在循环的时候需要随时保存前一个元素,在找到被删除元素的时候,直接将前一个与后一个连接即可。
public void remove(K k){
int hash = hash(k);
int len = table.length;
int index = hash % len;
Node<K,V> node = table[index];
Node<K,V> prev = node;
while (node != null) {
if(node.hash == hash && (node.key == k || node.key.equals(k))){
if(node == prev){//被删除元素在链表第一位
table[index] = node.next;
}else{
prev.next = node.next;//node 为当前元素 prev为前一个元素 将前一个元素的指针next指向下一个元素
}
size--;
}
prev = node;
node = node.next;
};
}
四扩容
扩容的触发条件是属性threshold大于HashMap元素个数size。在put元素的时候需要判断。
在增加,删除的时候,会对元素个数进行增减。
注意这里的size并不是指数组长度。而是指链表的总长度。
初始化一个HashMap,在put入第一个值的时候,会初始化一个数组,长度为16,算上负载因子,实际使用长度为12。但并不是说这个数组必须要每个索引都有值才会扩容。如下图所示,只有3个索引有值,但3个索引处的链表总长度达到12,也就达到了扩容的临界点。
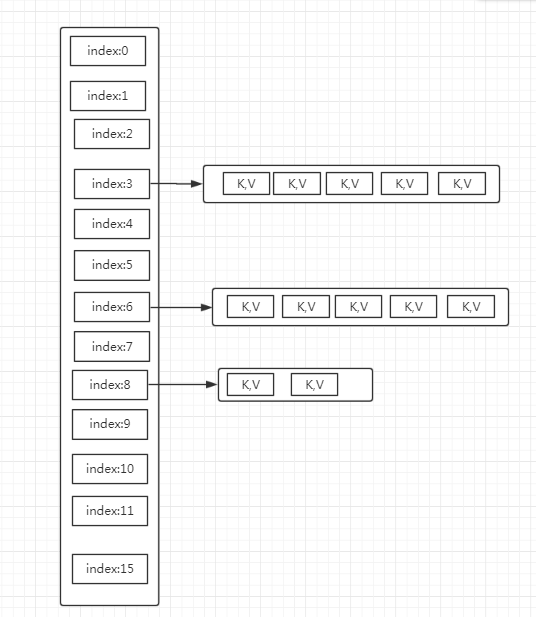
HashMap扩容首先需要将数组扩容。数组长度改变,那么所有元素的链表必须重新组合。不然,查找就会乱套。这是比较耗时的。所以,在使用HashMap的时候,如果能预估长度,最好在初始化的时候指定,避免频繁扩容。
public void resize(){
int len = size << 1;
threshold = (int)(len * loadFator);
size = 0;
Node<K,V>[] newTable = new Node[len];
Node<K,V>[] tempTable = table;
table = newTable;
int tempSize = tempTable.length;
for(int i=0; i<tempSize; i++){
Node<K,V> node = tempTable[i];
while(node != null){
put(node.key, node.value);
node = node.next;
}
}
}
五迭代
1通过keyset来迭代
keyset得到所有的键的set集合。再通过set的迭代器来迭代。
首先定义一个set集合。
Set<K> keySet;
定义获取keyset的方法
public Set<K> keySet(){
return keySet == null ? (keySet = new KeySet()) : null;
}
每次keySet为空,需要通过一个内部类KeySet获取。
class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K>{
@Override
public Iterator<K> iterator() {
return new newKeyIterator();
}
@Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
}
继续定义newKeyIterator
final class KeyIterator extends HashIterator implements Iterator<K> {
public final K next() {
return nextNode().key;
}
}
继续定义KeyIterator
public class HashIterator{
Node<K,V>[] nodes;
Node<K,V> prve;
Node<K,V> next;
int index;
public HashIterator(){
nodes = table;
index = 0;
prve = next = null;
do {
prve = next = table[index];
} while((++index < table.length) && next == null);
}
final Node<K,V> nextNode(){
Node<K,V> e = next;
if((next = (prve = e).next) == null && nodes != null){
do {
} while(index < table.length && (next = nodes[index++]) == null);
}
return e;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
}
再执行一个迭代的时候,先得到一个keys的集合,然后根据集合得到迭代器,这时候会执行HashIterator的构造方法,目的是找到第一个链表。
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
Iterator<String> it = keys.iterator();
然后执行,next时会执行HashIterator的hashNext方法和nextNode方法。
while(it.hasNext()){
String key = it.next();
String value = map.get(key);
}
2通过entrySet。
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet(){
return entrySet == null ? (entrySet = new EntrySet()) : null;
}
class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>>{
@Override
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return new EntryIterator();
}
@Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
}
final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final Node<K,V> next() {
return nextNode();
}
}
最终代码
import java.util.AbstractSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.Iterator; public class MyHashMap<K, V> { transient Node<K, V>[] table; private static int initCount = 16;//初始化长度 private static float loadFator = 0.75f;//加载因子 private int size; private static int threshold;//扩容临界值 static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; public MyHashMap(){
this(initCount, loadFator);
} public MyHashMap(int initCount){
this(initCount, loadFator);
} public MyHashMap(int initCount, float loadFator){
if(initCount < 0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("初始化长度不合法 : " + initCount);
} if(initCount > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY){
initCount = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
} if(loadFator <0 || Float.isNaN(loadFator)){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("加载因子不合法 : " + loadFator);
} this.loadFator = loadFator;
this.threshold = (int) (initCount * loadFator);
} public Object put(K key, V value){
if(table == null || table.length == 0){
//此时真正创建数组
table = new Node[initCount];
}
int hash = hash(key);
int len = table.length;
int index = (len-1) & hash;
Node<K,V> p;
if((p = table[index]) == null){
table[index] = new Node<K, V>(hash, key, value, null);
}else{//哈希碰撞
MyHashMap<K, V>.Node<K, V> e = p;
Node<K,V> temp = p; do{
if(e.hash == hash && ((e.key == key) || (key != null && key.equals(e.key)))){
V oldValue = p.value;
//用新值覆盖旧值
p.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
temp = e;
}while((e = temp.next) != null);
//将元素放在链表最前面
table[index] = new Node<K, V>(hash, key, value, p);
} if(++size > threshold){//扩容
resize();
} return null;
} public V get(K k){
int hash = hash(k);
int len = table.length;
int index = (len-1) & hash;
Node<K,V> node = table[index];//找到链表
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
Node<K,V> p;
if ((p = node.next) == null) {//如果链表只有一个元素,直接返回
return node.value;
} else {//如果有多个元素,循环比较key
p = node;
do {
if (p.key == k || p.key.equals(k)) {
return p.value;
}
node = p;
} while ((p = node.next) != null);
}
return null;
} public void remove(K k){
int hash = hash(k);
int len = table.length;
int index = (len-1) & hash; Node<K,V> node = table[index];
Node<K,V> prev = node;
while (node != null) {
if(node.hash == hash && (node.key == k || node.key.equals(k))){
if(node == prev){//被删除元素在链表第一位
table[index] = node.next;
}else{
prev.next = node.next;//node 为当前元素 prev为前一个元素 将前一个元素的指针next指向下一个元素
}
size--;
}
prev = node;
node = node.next;
}; } Set<K> keySet; public Set<K> keySet(){
return keySet == null ? (keySet = new KeySet()) : null;
} Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet; public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet(){
return entrySet == null ? (entrySet = new EntrySet()) : null;
} class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>>{ @Override
public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return new EntryIterator();
} @Override
public int size() {
return size;
} } final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final Node<K,V> next() {
return nextNode();
}
} class KeySet extends AbstractSet<K>{ @Override
public Iterator<K> iterator() {
return new KeyIterator();
} @Override
public int size() {
return size;
} } final class KeyIterator extends HashIterator implements Iterator<K> {
public final K next() {
return nextNode().key;
}
} public class HashIterator{ Node<K,V>[] nodes;
Node<K,V> prve;
Node<K,V> next;
int index; public HashIterator(){//得到 keys.iterator();的时候执行此构造方法,找到第一个链表
//找到第一个元素
nodes = table;
index = 0;
prve = next = null;
do {
prve = next = table[index];
} while((++index < table.length) && next == null);
} final Node<K,V> nextNode(){
Node<K,V> e = next;
if((next = (prve = e).next) == null && nodes != null){//循环链表
do {
} while(index < table.length && (next = nodes[index++]) == null);//找到下一个链表
}
return e;
} public boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
} public void resize(){
int len = size << 1;
threshold = (int)(len * loadFator);
size = 0;
Node<K,V>[] newTable = new Node[len];
Node<K,V>[] tempTable = table;
table = newTable; int tempSize = tempTable.length;
for(int i=0; i<tempSize; i++){
Node<K,V> node = tempTable[i];
while(node != null){
put(node.key, node.value);
node = node.next;
}
}
} static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
} @SuppressWarnings("hiding")
class Node<K, V> implements Map.Entry<K, V> {
final int hash; final K key;
V value; Node<K, V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
} @Override
public K getKey() {
return key;
} @Override
public V getValue() {
return value;
} @Override
public V setValue(V value) {
V tempValue = value;
this.value = value;
return tempValue;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "[" + key + " : " + value + "]" + " next " + next;
} @Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
} public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?, ?> e = (Map.Entry<?, ?>) o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) && Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
} } }
自己实现HashMap的更多相关文章
- HashMap与TreeMap源码分析
1. 引言 在红黑树--算法导论(15)中学习了红黑树的原理.本来打算自己来试着实现一下,然而在看了JDK(1.8.0)TreeMap的源码后恍然发现原来它就是利用红黑树实现的(很惭愧学了Ja ...
- HashMap的工作原理
HashMap的工作原理 HashMap的工作原理是近年来常见的Java面试题.几乎每个Java程序员都知道HashMap,都知道哪里要用HashMap,知道HashTable和HashMap之间 ...
- 计算机程序的思维逻辑 (40) - 剖析HashMap
前面两节介绍了ArrayList和LinkedList,它们的一个共同特点是,查找元素的效率都比较低,都需要逐个进行比较,本节介绍HashMap,它的查找效率则要高的多,HashMap是什么?怎么用? ...
- Java集合专题总结(1):HashMap 和 HashTable 源码学习和面试总结
2017年的秋招彻底结束了,感觉Java上面的最常见的集合相关的问题就是hash--系列和一些常用并发集合和队列,堆等结合算法一起考察,不完全统计,本人经历:先后百度.唯品会.58同城.新浪微博.趣分 ...
- 学习Redis你必须了解的数据结构——HashMap实现
本文版权归博客园和作者吴双本人共同所有,转载和爬虫请注明原文链接博客园蜗牛 cnblogs.com\tdws . 首先提供一种获取hashCode的方法,是一种比较受欢迎的方式,该方法参照了一位园友的 ...
- HashMap与HashTable的区别
HashMap和HashSet的区别是Java面试中最常被问到的问题.如果没有涉及到Collection框架以及多线程的面试,可以说是不完整.而Collection框架的问题不涉及到HashSet和H ...
- JDK1.8 HashMap 源码分析
一.概述 以键值对的形式存储,是基于Map接口的实现,可以接收null的键值,不保证有序(比如插入顺序),存储着Entry(hash, key, value, next)对象. 二.示例 public ...
- HashMap 源码解析
HashMap简介: HashMap在日常的开发中应用的非常之广泛,它是基于Hash表,实现了Map接口,以键值对(key-value)形式进行数据存储,HashMap在数据结构上使用的是数组+链表. ...
- java面试题——HashMap和Hashtable 的区别
一.HashMap 和Hashtable 的区别 我们先看2个类的定义 public class Hashtable extends Dictionary implements Map, Clonea ...
- 再谈HashMap
HashMap是一个高效通用的数据结构,它在每一个Java程序中都随处可见.先来介绍些基础知识.你可能也知 道,HashMap使用key的hashCode()和equals()方法来将值划分到不同的桶 ...
随机推荐
- bzoj5107: [CodePlus2017]找爸爸
Description 小A最近一直在找自己的爸爸,用什么办法呢,就是DNA比对.小A有一套自己的DNA序列比较方法,其最终目标是最 大化两个DNA序列的相似程度,具体步骤如下:1.给出两个DNA序列 ...
- mysql原生分页
select * from table limit (pageNo-1)*pageSize, pageSize; 一:分页需求: 客户端通过传递start(页码),limit(每页显示的条数)两个参数 ...
- Ubuntu16.04下安装Hyperledger Fabric 1.0.0
系统环境 * Ubuntu: 16.04 * Go: 1.9.2 * NodeJS: v6.12.0 * Docker: 17.09.0-ce * HyperLedger Fabric: 1.0.0 ...
- aspose.cells 复制单元格
将第1行至第27行复制到第28行 cells.CopyRows(cells, 0, i*27, 27);
- 干掉win10自带的不给力的应用(转自https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/08b6a591b7398514a8092238.html)
1.右键以管理员身份运行Windows power shell,(怎么找到Windows power shell?按下win键,直接搜索就有了) 2.在应用中输入命令 Get-AppXPackage ...
- 序列化模块_pickle
序列化: 把不能够直接存储的数据变成字节流(bytes)保存在文件, 进行持久化存储 反序列化: 任何数据都可以转成字节流(bytes)进行存储: 1. dumps 把任意对象序列化 li = [1, ...
- MVC JsonResult 结果返回
使用MVC之后, 默认的ActionResult 有很多子类譬如 JsonResult之类, 可以很方便. 基本用法如下: public ActionResult GetVacatio ...
- js对象原型prototype
javascript中的每个对象都有prototype属性,Javascript中对象的prototype属性的解释是:返回对象类型原型的引用. 每一个构造函数都有一个属性叫做原型 1.1. 原型法设 ...
- AND 初识
框架
- 微信小程序从零开始开发步骤-引入框架WeUI
首先来看下WeUI的官方介绍: WeUI 是一套同微信原生视觉体验一致的基础样式库,由微信官方设计团队为微信内网页和微信小程序量身设计,令用户的使用感知更加统一.在微信小程序的开发过程中,涉及到的前端 ...
