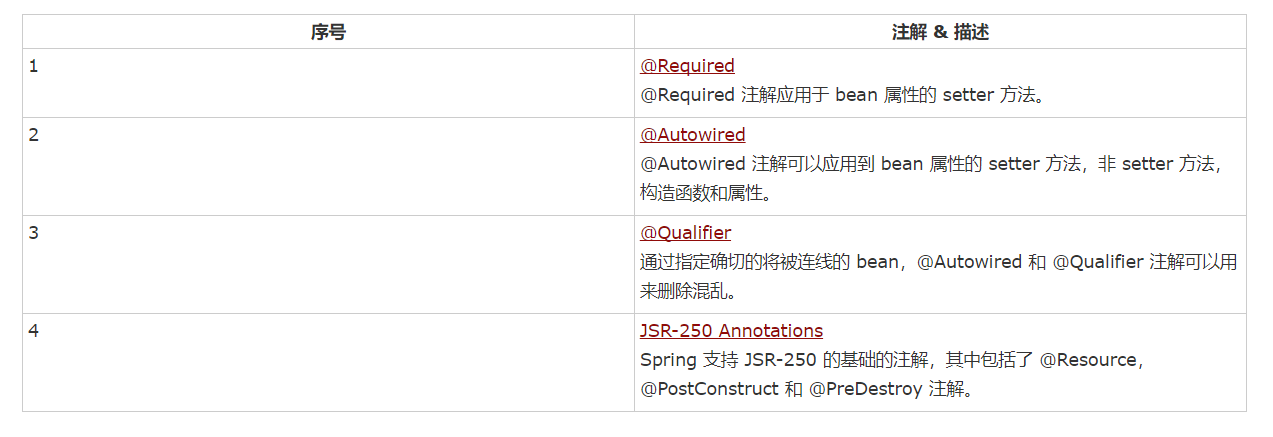
Spring(七)之基于注解配置
基于注解的配置
从 Spring 2.5 开始就可以使用注解来配置依赖注入。而不是采用 XML 来描述一个 bean 连线,你可以使用相关类,方法或字段声明的注解,将 bean 配置移动到组件类本身。
在 XML 注入之前进行注解注入,因此后者的配置将通过两种方式的属性连线被前者重写。
一、@Required注解
@Required 注解应用于 bean 属性的 setter 方法,它表明受影响的 bean 属性在配置时必须放在 XML 配置文件中,否则容器就会抛出一个 BeanInitializationException 异常。下面显示的是一个使用 @Required 注解的示例。
(1)编写Student.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Required;
public class Student {
private Integer age;
private String name;
@Required
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
@Required
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
(2)编写MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println("Name : " + student.getName() );
System.out.println("Age : " + student.getAge() );
}}
(3)编写Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <context:annotation-config/> <!-- Definition for student bean -->
<bean id="student" class="com.tutorialspoint.Student">
<property name="name" value="Zara" /> <!-- try without passing age and check the result -->
<property name="age" value="11"/>
</bean> </beans>
(4)运行MainApp.java中的main方法
如图:
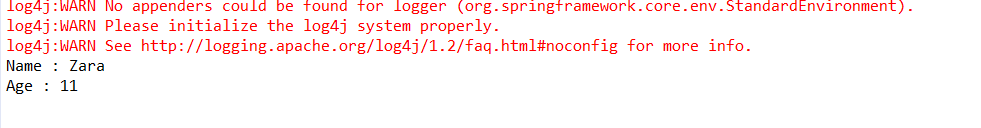
这是正常流程
异常流程只需将Beans.xml改成如下,再运行main方法:
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <context:annotation-config/> <!-- Definition for student bean -->
<bean id="student" class="com.tutorialspoint.Student">
<property name="name" value="Zara" /> <!-- try without passing age and check the result -->
<!--<property name="age" value="11"/>-->
</bean> </beans>
控制台最后的结果如下:

我想大家应该明白了,@Required注解的作用,其实这个注解与input中的required属性倒有其相同点,必填不能为空。
二、AutoWired注解
@Autowired 注释对在哪里和如何完成自动连接提供了更多的细微的控制。
@Autowired 注释可以在 setter 方法中被用于自动连接 bean,就像 @Autowired 注释,容器,一个属性或者任意命名的可能带有多个参数的方法。
演示示例:
1.编写TextEditor.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class TextEditor {
private SpellChecker spellChecker;
@Autowired
public void setSpellChecker( SpellChecker spellChecker ){
this.spellChecker = spellChecker;
}
public SpellChecker getSpellChecker( ) {
return spellChecker;
}
public void spellCheck() {
spellChecker.checkSpelling();
}
}
2.编写SpellChecker.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class SpellChecker {
public SpellChecker(){
System.out.println("Inside SpellChecker constructor." );
}
public void checkSpelling(){
System.out.println("Inside checkSpelling." );
}
}
3.编写Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <context:annotation-config/> <!-- Definition for textEditor bean without constructor-arg -->
<bean id="textEditor" class="com.tutorialspoint.TextEditor">
</bean> <!-- Definition for spellChecker bean -->
<bean id="spellChecker" class="com.tutorialspoint.SpellChecker">
</bean> </beans>
4.编写MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
TextEditor te = (TextEditor) context.getBean("textEditor");
te.spellCheck();
}
}
5.运行MainApp.java中的main方法
结果如下:
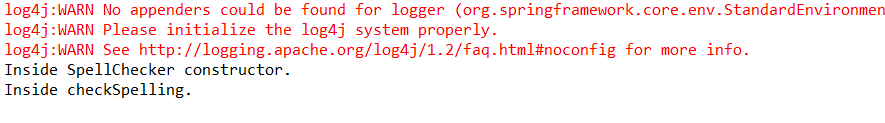
@AutoWired 自动装配 它的一个属性叫required,属性值是boolean类型,默认为true,必须,也可以修改为false,非必须。
三、Qualifier注解
可能会有这样一种情况,当你创建多个具有相同类型的 bean 时,并且想要用一个属性只为它们其中的一个进行装配,在这种情况下,你可以使用 @Qualifier 注释和 @Autowired 注释通过指定哪一个真正的 bean 将会被装配来消除混乱。下面显示的是使用 @Qualifier 注释的一个示例。
(1)编写Student.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class Student {
private Integer age;
private String name;
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
(2)编写Profile.java
package com.tutorialspoint; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; public class Profile {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("student1")
private Student student;
public Profile(){
System.out.println("Inside Profile constructor." );
}
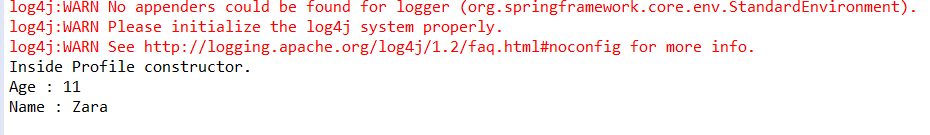
public void printAge() {
System.out.println("Age : " + student.getAge() );
}
public void printName() {
System.out.println("Name : " + student.getName() );
}
}
(3)编写MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
Profile profile = (Profile) context.getBean("profile");
profile.printAge();
profile.printName();
}
}
(4)编写Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <context:annotation-config/> <!-- Definition for profile bean -->
<bean id="profile" class="com.tutorialspoint.Profile">
</bean> <!-- Definition for student1 bean -->
<bean id="student1" class="com.tutorialspoint.Student">
<property name="name" value="Zara" />
<property name="age" value="11"/>
</bean> <!-- Definition for student2 bean -->
<bean id="student2" class="com.tutorialspoint.Student">
<property name="name" value="Nuha" />
<property name="age" value="2"/>
</bean> </beans>
(5)运行MainApp.java对应的main方法
四、Spring JSR-250 注释
Spring还使用基于 JSR-250 注释,它包括 @PostConstruct, @PreDestroy 和 @Resource 注释。因为你已经有了其他的选择,尽管这些注释并不是真正所需要的,但是关于它们仍然让我给出一个简短的介绍。
@PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 注释:
为了定义一个 bean 的安装和卸载,我们使用 init-method 和/或 destroy-method 参数简单的声明一下 。init-method 属性指定了一个方法,该方法在 bean 的实例化阶段会立即被调用。同样地,destroy-method 指定了一个方法,该方法只在一个 bean 从容器中删除之前被调用。
你可以使用 @PostConstruct 注释作为初始化回调函数的一个替代,@PreDestroy 注释作为销毁回调函数的一个替代,其解释如下示例所示。
演示示例:
(1)编写HelloWorld.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import javax.annotation.*;
public class HelloWorld {
private String message;
public void setMessage(String message){
this.message = message;
}
public String getMessage(){
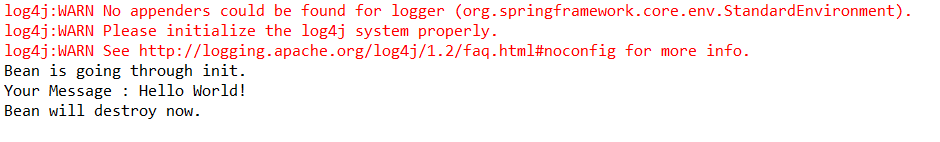
System.out.println("Your Message : " + message);
return message;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("Bean is going through init.");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("Bean will destroy now.");
}
}
(2)编写Beans.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <context:annotation-config/> <bean id="helloWorld"
class="com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld"
init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy">
<property name="message" value="Hello World!"/>
</bean> </beans>
(3)编写MainApp.java并运行对应的main方法
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
HelloWorld obj = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld");
obj.getMessage();
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
}
结果如图:
Spring(七)之基于注解配置的更多相关文章
- Spring 使用AOP——基于注解配置
首先,使用注解实现AOP是基于AspectJ方式的. 创建包含切点方法的类 package cn.ganlixin.test; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.P ...
- Unit03: Spring Web MVC简介 、 基于XML配置的MVC应用 、 基于注解配置的MVC应用
Unit03: Spring Web MVC简介 . 基于XML配置的MVC应用 . 基于注解配置的MVC应用 springmvc (1)springmvc是什么? 是一个mvc框架,用来简化基于mv ...
- 使用 Spring 2.5 基于注解驱动的 Spring MVC
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-spring25-mvc/ 概述 继 Spring 2.0 对 Spring MVC 进行重大升级后,Sp ...
- 使用 Spring 2.5 基于注解驱动的 Spring MVC--转
概述 继 Spring 2.0 对 Spring MVC 进行重大升级后,Spring 2.5 又为 Spring MVC 引入了注解驱动功能.现在你无须让 Controller 继承任何接口,无需在 ...
- Spring学习之旅(七)基于XML配置与基于AspectJ注解配置的AOP编程比较
本篇博文用一个稍复杂点的案例来对比一下基于XML配置与基于AspectJ注解配置的AOP编程的不同. 相关引入包等Spring AOP编程准备,请参考小编的其他博文,这里不再赘述. 案例要求: 写一 ...
- Spring学习记录(十二)---AOP理解和基于注解配置
Spring核心之二:AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming) --- 面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术.AOP是OOP的延续,是软 ...
- Spring IOC之基于注解的容器配置
Spring配置中注解比XML更好吗?基于注解的配置的介绍提出的问题是否这种途径比XML更好.简单来说就是视情况而定. 长一点的答案是每一种方法都有自己的长处也不足,而且这个通常取决于开发者决定哪一种 ...
- 基于注解配置spring
1 对 bean 的标注基于注解方式有3个注解 @Component @Repository 对DAO类进行标注 @Service 对Service类进行标注 @Controller 对Contro ...
- Spring IOC容器装配Bean_基于注解配置方式
bean的实例化 1.导入jar包(必不可少的) 2.实例化bean applicationContext.xml(xml的写法) <bean id="userDao" cl ...
随机推荐
- 认识Groovy
什么是groovy: Groovy 是 JVM 的一个替代语言 —替代 是指可以用 Groovy 在 Java 平台上进行 Java 编程,使用方式基本与使用 Java 代码的方式相同. 在编写新应用 ...
- springmvc 框架原理
先来个原理图,镇博. (图片出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/selene/p/4658554.html,感谢博主的图) 着重看:处理器映射器,处理器适配器,这两个的配置. 这两个的 ...
- BZOJ1021 [SHOI2008]循环的债务
Description Alice.Bob和Cynthia总是为他们之间混乱的债务而烦恼,终于有一天,他们决定坐下来一起解决这个问题. 不过,鉴别钞票的真伪是一件很麻烦的事情,于是他们决定要在清还债务 ...
- 【MFC】CHtmlView或WebBrowser禁止脚本错误提示
错误展示: 解决办法: 1.CHtmlView类或子类 CHtmlView::SetSilent(TRUE); 2.IWebBrowser2控件 IWebBrowser2::put_Silent(TR ...
- 12 步 30 分钟,完成用户管理的 CURD 应用 (react+dva+antd)
Getting Started https://github.com/dvajs/dva/blob/master/docs/GettingStarted.md -------------------- ...
- 解决API中无法使用session问题
处理API无法使用session的方法,贴图: 1调用如下图 2.需要在Global.asax文件中配置一些东西 protected void Application_PostAuthorizeReq ...
- Android学习笔记(5)----启动 Theme.Dialog 主题的Activity时程序崩溃的解决办法
新建了一个Android Studio工程,在MainActivity的主界面中添加了两个按钮,点击其中一个按钮用来启动 NormalActivity,点击另一按钮用来启动DialogActivity ...
- 经典的 div + css 鼠标 hover 下拉菜单
经典的 div + css 鼠标 hover 下拉菜单 效果图: 源码: <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> ...
- sudo的安装
关于mini版的centos7的是不能直接sudo命令的 下面我来说一下怎么让sudo命令生效 第一步 先切换到root用户: su - 第二步 visudo 给相应用户分配sudo的权限 第三 ...
- 爬虫day03之scrapy安装与使用
参考博客 技术问题不要问,业务问题可以问是不是有一种更好的方法? scrapy windows安装 1. 安装scrapy 参考博客 https://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/a ...
