Bean Definition从加载、解析、处理、注册到BeanFactory的过程。
为了弄清楚Bean是怎么来的,花费了大把功夫,现在要把Bean Definition的加载、解析、处理、注册到bean工厂的过程记下来。这只是bean definition 的加载、解析、处理、注册过程中的一种。
好记性不如烂笔头。
首先我已经知道bean definition 存在了哪里:它就存在一个Map对象中,如果使用的是DefaultListableBeanFactory的话,它就存在一个ConcurrentHashMap对象中。
/** bean 的名字为键,BeanDefinition为值,初始容量为256 */
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>(256);
现在将BeanDefinition是如何一步步走到这个Map对象中的。
一、BeanDefinition的加载
过程比较长,得对着源码慢慢看。
这里讲的是使用xml配置文件的方式来配置bean.
既然是使用的xml配置文件的方式来配置bean,那么首先要读取xml文件。
一)、AbstractBeanDefinitionReader类中
这一步只是说加载bean definition,但是这里方法参数resources 所指的资源并不确定是什么样的,有可能是xml文件,也有可能是属性文件,或者是脚本。
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null");
int counter = 0;
for (Resource resource : resources) {
counter += loadBeanDefinitions(resource);//这个方法有几个实现,如下
}
return counter;
}
上面的代码中的一行 counter += loadBeanDefinitions(resource); 这行代码有好几个实现类都实现了它。如下图:
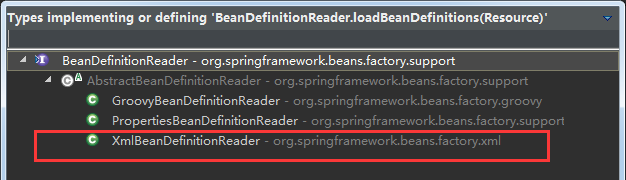
我这里使用实现类XmlBeanDefinitionReader中的实现,所以这里的资源是xml文件。
二)、XmlBeanDefinitionReader类中
从指定的xml文件中加载bean definition,但是他这里只是将Resource转化为EncodedResource对象。然后把这个任务递交给它的重载方法来做。

三)、XmlBeanDefinitionReader类中
从指定的XML文件中加载bean definition。但还不是真正的加载bean定义,只是做准备。
/**
* Load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the XML file,
* allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
} Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
四、XmlBeanDefinitionReader类中
这里是真正的从xml 文件中加载的bean definition 。主要有两个步骤:①、加载指定的文档,得到一个Document对象。②、将Document对象和Resource交给registerBeanDefinitions(...)方法来完成注册
/**
* Actually load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param inputSource the SAX InputSource to read from
* @param resource the resource descriptor for the XML file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
* @see #doLoadDocument
* @see #registerBeanDefinitions
*/
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
//省略捕获异常的代码
}
}
五)、XmlBeanDefinitionReader类中
注册指定的Document对象中的bean definition。这里实际上是创建了一个BeanDefinitionDocumentReader对象然后让它来完成。
/**
* Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document.
* Called by {@code loadBeanDefinitions}.
* <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes
* {@code registerBeanDefinitions} on it.
* @param doc the DOM document
* @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information)
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions
* @see #setDocumentReaderClass
* @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions
*/
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
二、BeanDefinition的解析
六)、DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类中
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader是BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的一个实现类。这一步主要是解析文档解析的是<beans/>。比如xml文件是XSD的还是DTD的。
这里主要是获得一个Element对象。这个对象就代表xml文件中的<beans/>节点。在这个节点下包含着文件中的所有<bean/>节点。然后将这个Element对像交给的doRegistrerBeanDefinitions(Element)方法来处理。

七)、DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类中
这个方法将</beans>节点下的每一个<bean/>相对应的bean definition注册。但是真正做这件事的是另一个方法 parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
不过在调用parseBeanDefinitions(root,this.delegate)方法之前和之后都可以对这个这个方法参数中的Element对象进行处理。
/**
* Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element.
*/
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent); if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
} preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root); this.delegate = parent;
}
八、DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类中
用一个for循环遍历<beans/>节点下的所有子节点,也就是所有的<bean/>,然后对<bean/>节点进行解析。注意,刚才是对<beans/>进行解析。不过这个解析的任务交给parseDefaultElement(Element ele,BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate)方法来完成。
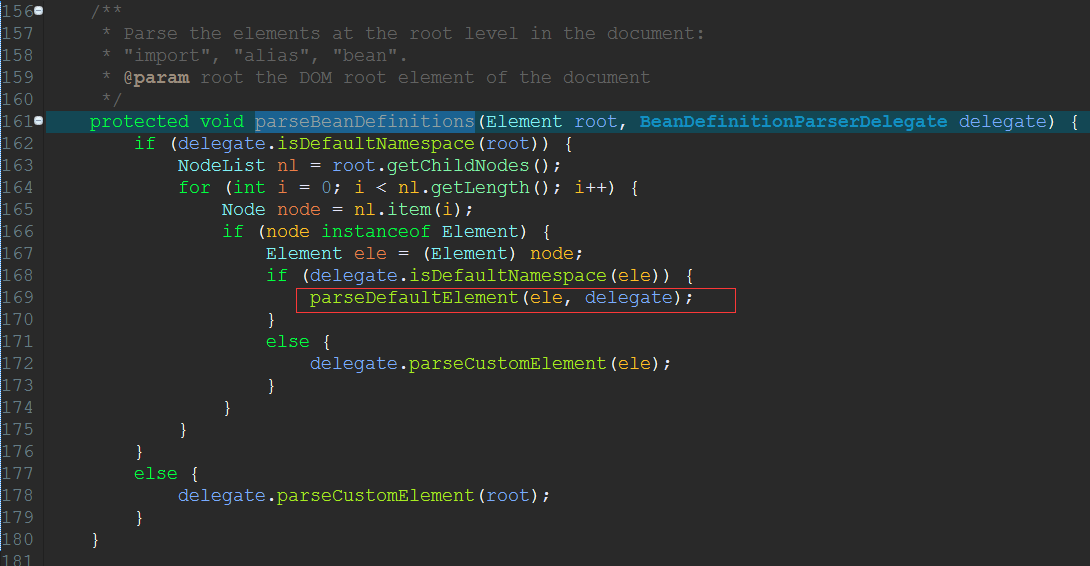
九)、DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类中
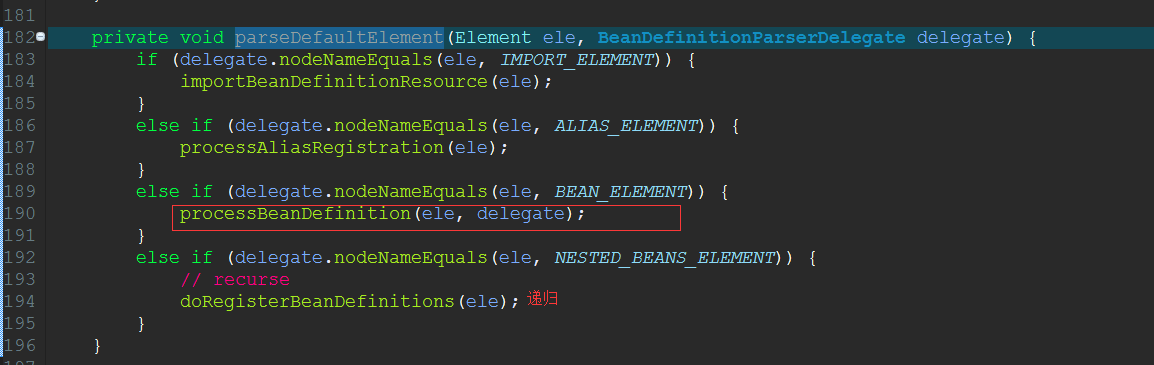
这个方法用到了递归,因为bean是可以嵌套的,所以<beans/>节点下的每一个<bean/>节点都可能在嵌套有很多bean。所以它会判断这个bean是不是嵌套bean,如果不是就进行处理,如果是就进行递归。
处理bean元素的任务交给了三个方法,如图。我这里用processBeanDefinition(ele,delegate)方法举例。
三、BeanDefinition的处理
十)、DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类中
在这个方法中它将的Element对象转化成了BeanDefinitionHolder对象。这个BeanDefinitionHolder对象中持有的BeanDefinition实例的引用,还有beanName,还有bean的别名。
然后将BeanDefinitionHolder对象和特定的bean工厂作为参数交个BeanDefinitionReaderUtils类来处理来进行注册。
第301行代码中如何创建BeanDefinitionHolder的??BeanDefinition的创建

四、BeanDefinition的注册
十一)、BeanDefinitionReaderUtils类中
这个方法先根据BeanDefinitionHolder获取beanName和BeanDefinition,然后将其注册到Bean工厂中Map对象中。比如bean工厂是DefaultListableBeanFactory。
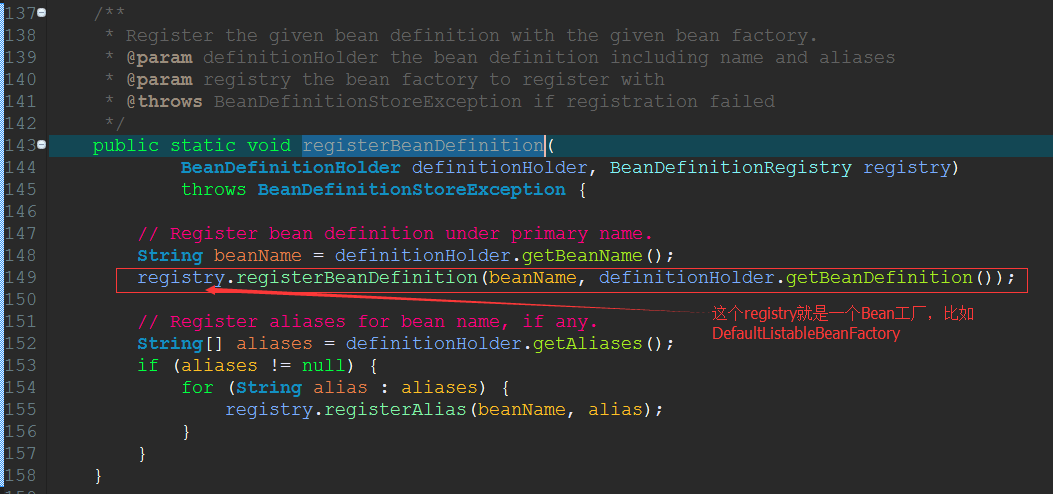
上面红色方框中的代码 registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());这个方法有好几个实现类实现了它,如下图:
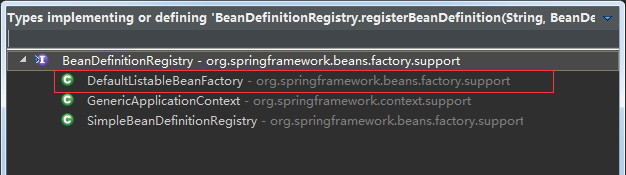
我选择了DefaultListableBeanFactory
十二)、DefaultListableBeanFactory类中,在这个方法中,将BeanDefinition 注册到了开头所说的ConcurrentHashMap对象中了。
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of BeanDefinitionRegistry interface
//--------------------------------------------------------------------- @Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null"); if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
} BeanDefinition oldBeanDefinition; oldBeanDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (oldBeanDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName +
"': There is already [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] bound.");
}
else if (oldBeanDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
oldBeanDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(oldBeanDefinition)) {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
if (this.manualSingletonNames.contains(beanName)) {
Set<String> updatedSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<String>(this.manualSingletonNames);
updatedSingletons.remove(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames = updatedSingletons;
}
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.manualSingletonNames.remove(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
} if (oldBeanDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}
五、总结
BeanDefinition的加载、解析、处理、注册主要涉及到了四个类。
①、XMLBeanDefinitionReader:主要是的任务是把XML文件加载到内存中以Document对象的形式存在。
②、DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader:完成解析和处理的任务。最后将处理得到的BeanDefinitionHolder交给了BeanDefinitionReaderUtils进行注册。
③、BeanDefinitionReaderUtils:BeanDefinitionHolder有了,Bean工厂也有了,它就负责把BeanDefinitionHolder中的BeanDefinition和BeanName等取出来,然后注册到Bean工厂中。
④、DefaultListableBeanFactory(bean工厂):它有一个ConcurrentHashMap成员变量,以beanName为键,BeanDefinition为值保存注册的bean。
Bean Definition从加载、解析、处理、注册到BeanFactory的过程。的更多相关文章
- spring bean的重新加载
架构体系 在谈spring bean的重新加载前,首先我们来看看spring ioc容器. spring ioc容器主要功能是完成对bean的创建.依赖注入和管理等功能,而这些功能的实现是有下面几个组 ...
- Spring bean是如何加载的
Spring bean是如何加载的 加载bean的主要逻辑 在AbstractBeanFactory中doGetBean对加载bean的不同情况进行拆分处理,并做了部分准备工作 具体如下 获取原始be ...
- Hibernate懒加载解析
Hibernate懒加载解析 在Hibernate框架中,当我们要访问的数据量过大时,明显用缓存不太合适, 因为内存容量有限 ,为了减少并发量,减少系统资源的消耗,这时Hibernate用懒加载机制来 ...
- Sspring bean被初始化加载2次
Sspring bean被初始化加载2次 spring框架的web项目时,启动的时候发现某个bean被加载了两次,比如使用SchedulingConfigurer或者使用@PostConstruct的 ...
- SpringXML方式配置bean的懒加载lazy-init
lazy-init(懒加载),表示该bean在容器初始化的时候不进行初始化. 例如: <bean name="role1" class="com.fz.entity ...
- Away3D引擎学习笔记(一)资源加载解析块
前文:Away3D断断续续用了一段时间了,三维相关的很多算法,计算转换还是有点绕,整理些自己觉得还有点意思东西,希望大家有用. 三维开始,Away3D构架你场景那几行代码各处都有,这里就不copy了, ...
- Spring Boot 学习系列(09)—自定义Bean的顺序加载
此文已由作者易国强授权网易云社区发布. 欢迎访问网易云社区,了解更多网易技术产品运营经验. Bean 的顺序加载 有些场景中,我们希望编写的Bean能够按照指定的顺序进行加载.比如,有UserServ ...
- <script>标签的加载解析执行
转自原文 <script>标签的加载解析执行 看了很多网上的文章,都是大同小异.总结一下.内部原理还没有搞清楚,有机会再学习. 一.<script>标签的加载解析执行顺序 ht ...
- 一文带你解读Spring5源码解析 IOC之开启Bean的加载,以及FactoryBean和BeanFactory的区别。
前言 通过往期的文章我们已经了解了Spring对XML配置文件的解析,将分析的信息组装成BeanDefinition,并将其保存到相应的BeanDefinitionRegistry中,至此Spring ...
随机推荐
- [转]在windows service中使用timer
本文转自:http://blog.csdn.net/sharpnessdotnet/article/details/7637180 一定要使用System.Timers.Timer timer 而不是 ...
- 注解完成spring json返回数据格式配置
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.module.Simp ...
- jquery 获取 tagName(JQuery如何得到tagName?)
在javascript中要取得tagName十分简单,但在jQuery中官方文档却没有记载,在一通百度和谷歌之后,尝试了不少所谓秘技,都不能正确得到,经过自己的验证,终于找到了方法,于是记录下来以备忘 ...
- 最简单应用的时间日期选择插件---My97DatePicker
最简单的应用:http://www.my97.net/dp/demo/resource/2.1.asp
- 全面了解HTTP和HTTPS
序言 Http和Https属于计算机网络范畴,但作为开发人员,不管是后台开发或是前台开发,都很有必要掌握它们. 在学习Http和Https的过程中,主要是参考了阮一峰老师的博客,讲的很全面,并且通俗易 ...
- git 命令合并分支代码
git 命令合并分支代码 对于复杂的系统,我们可能要开好几个分支来开发,那么怎样使用git合并分支呢? 合并步骤: 1.进入要合并的分支(如开发分支合并到master,则进入master目录) git ...
- sql With(NoLock),With(ReadPast)
--------------- create table tmp1 ( id int primary key, name ) ) ----------- insert into tmp1(id,nam ...
- MathQuill.js
MathQuill.js通过html.css.javascript实现数学公式 <p>Type math here: <span id="math-field"& ...
- vue2 使用 element-ui
看了 http://element.eleme.io/#/zh-CN/component/installation 一些组件和样式够用了 , 试了下 element-ui ,配合到vue中 ...
- 给大家分享下坐标转换的代码的JS和Python两个版本的源码【转】
/** * Created by Wandergis on 2015/7/8. * 提供了百度坐标(BD09).国测局坐标(火星坐标,GCJ02).和WGS84坐标系之间的转换 */ /** * 百度 ...
