spark MLlib Classification and regression 学习
二分类:SVMs,logistic regression,decision trees,random forests,gradient-boosted trees,naive Bayes
多分类: logistic regression,decision trees,random forests, naive Bayes
归回: linear least regression, decision tress,random forests,gradient-boosted trees, isotonic regression。
一。Linear models
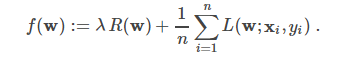

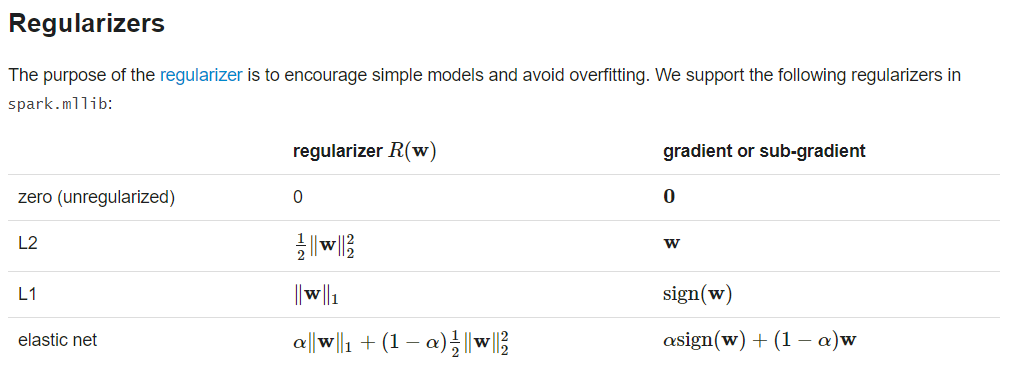
classification (SVMs, logistic regression)
package ML.ClassificationAndRegression; import org.apache.spark.SparkConf;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaSparkContext;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.SVMModel;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.SVMWithSGD;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.BinaryClassificationMetrics;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.optimization.L1Updater;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils;
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD;
import scala.Tuple2; /**
* TODO
*
* @ClassName: SVMClassifier
* @author: DingH
* @since: 2019/4/9 10:28
*/
public class SVMClassifier {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("SVM Classifier Example").setMaster("local");
JavaSparkContext jsc = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
String path = "D:\\IdeaProjects\\SimpleApp\\src\\main\\resources\\data\\mllib\\sample_libsvm_data.txt";
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(jsc.sc(), path).toJavaRDD(); // Split initial RDD into two... [60% training data, 40% testing data].
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> train = data.sample(false, 0.6, 11L);
train.cache();
final JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> test = data.subtract(train); //Run training algorithm to build the model
int numsIterations = 100;
SVMWithSGD svm = new SVMWithSGD();
svm.optimizer().setNumIterations(200).setRegParam(0.01).setUpdater(new L1Updater());
final SVMModel model1 = svm.run(train.rdd());
// final SVMModel model1 = SVMWithSGD.train(train.rdd(), numsIterations); model1.clearThreshold(); JavaRDD<Tuple2<Object, Object>> scoraAndLables = test.map(new Function<LabeledPoint, Tuple2<Object, Object>>() {
public Tuple2<Object, Object> call(LabeledPoint p) throws Exception {
double predict = model1.predict(p.features());
return new Tuple2<Object, Object>(predict, p.label());
}
}); BinaryClassificationMetrics metrics = new BinaryClassificationMetrics(scoraAndLables.rdd()); double areaUnderROC = metrics.areaUnderROC(); System.out.println("Area under ROC = " + areaUnderROC); model1.save(jsc.sc(),"D:\\IdeaProjects\\SimpleApp\\src\\main\\java\\MLModel");
SVMModel model = SVMModel.load(jsc.sc(), "D:\\IdeaProjects\\SimpleApp\\src\\main\\java\\MLModel"); }
}
SVMClassifier
package ML.ClassificationAndRegression; import org.apache.spark.SparkConf;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaSparkContext;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function;
import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.MultiClassSummarizer;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.LogisticRegressionModel;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.LogisticRegressionWithSGD;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.MulticlassMetrics;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils;
import scala.Tuple2; /**
* TODO
*
* @ClassName: LogistiRegression
* @author: DingH
* @since: 2019/4/9 11:08
*/
public class LogistiRegression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("LogisticRegression");
JavaSparkContext jsc = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
String path = "D:\\IdeaProjects\\SimpleApp\\src\\main\\resources\\data\\mllib\\sample_libsvm_data.txt";
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(jsc.sc(), path).toJavaRDD(); JavaRDD<LabeledPoint>[] split = data.randomSplit(new double[]{0.6, 0.4}, 11L);
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> training = split[0].cache();
final JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> test = split[1]; final LogisticRegressionModel model = new LogisticRegressionWithLBFGS().setNumClasses(10).run(training.rdd());
JavaRDD<Tuple2<Object, Object>> predictionAndLabels = test.map(new Function<LabeledPoint, Tuple2<Object, Object>>() {
public Tuple2<Object, Object> call(LabeledPoint labeledPoint) throws Exception {
double predict = model.predict(labeledPoint.features());
return new Tuple2<Object, Object>(predict, labeledPoint.label());
}
}); MulticlassMetrics metrics = new MulticlassMetrics(predictionAndLabels.rdd()); double precision = metrics.precision();
System.out.println("Precision = " + precision); // Save and load model
// model.save(jsc.sc(), "myModelPath");
// LogisticRegressionModel sameModel = LogisticRegressionModel.load(jsc.sc(), "myModelPath");
}
}
LogistiRegression
linear regression (least squares, Lasso, ridge)
package ML.ClassificationAndRegression; import org.apache.hadoop.yarn.webapp.hamlet.Hamlet;
import org.apache.spark.SparkConf;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaDoubleRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaSparkContext;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LinearRegressionModel;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LinearRegressionWithSGD;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils;
import scala.Tuple2; /**
* TODO
*
* @ClassName: Regression
* @author: DingH
* @since: 2019/4/9 11:21
*/
public class Regression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("Regression").setMaster("local");
JavaSparkContext jsc = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
String path = "D:\\IdeaProjects\\SimpleApp\\src\\main\\resources\\data\\mllib\\ridge-data\\lpsa.data";
JavaRDD<String> data = jsc.textFile(path); JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> parsedData = data.map(new Function<String, LabeledPoint>() {
public LabeledPoint call(String line) throws Exception {
String[] split = line.split(",");
String[] features = split[1].split(" ");
double[] v = new double[features.length];
for (int i = 0; i < features.length - 1; i++) {
v[i] = Double.parseDouble(features[i]);
} return new LabeledPoint(Double.parseDouble(split[0]), Vectors.dense(v));
}
}).cache(); final LinearRegressionModel model = LinearRegressionWithSGD.train(parsedData.rdd(), 100); JavaRDD<Tuple2<Double, Double>> valuesAndLabels = parsedData.map(new Function<LabeledPoint, Tuple2<Double, Double>>() {
public Tuple2<Double, Double> call(LabeledPoint labeledPoint) throws Exception {
double predict = model.predict(labeledPoint.features());
return new Tuple2<Double, Double>(predict, labeledPoint.label());
}
}); Double MSE = new JavaDoubleRDD(valuesAndLabels.map(
new Function<Tuple2<Double, Double>, Object>() {
public Object call(Tuple2<Double, Double> dat) throws Exception {
return Math.pow(dat._1 - dat._2, 2.0);
}
}
).rdd()).mean();
System.out.println("training Mean Squared Error = " + MSE); // Save and load model
// model.save(jsc.sc(), "myModelPath");
// LinearRegressionModel sameModel = LinearRegressionModel.load(jsc.sc(), "myModelPath");
}
}
Regression
二。Decision Trees.
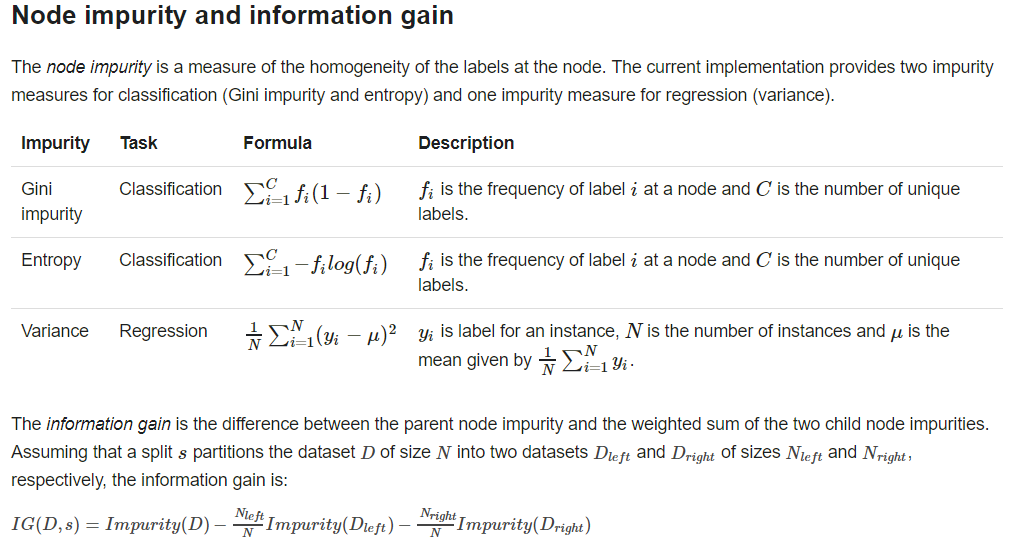
problem specification parameters: algo, numClasses, categoricalFeaturesInfo
stopping criteria : maxDepth, minInfoGain, minInstancePerNode
tunnable parameters: maxBins, impurity,
package ML.DT; import org.apache.spark.SparkConf;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaPairRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaSparkContext;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.PairFunction;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.DecisionTree;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.DecisionTreeModel;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils;
import scala.Tuple2; import java.util.HashMap; /**
* TODO
*
* @ClassName: classification
* @author: DingH
* @since: 2019/4/9 16:11
*/
public class classification {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("DTclassification").setMaster("local");
JavaSparkContext jsc = new JavaSparkContext(conf); String path = "D:\\IdeaProjects\\SimpleApp\\src\\main\\resources\\data\\mllib\\sample_libsvm_data.txt";
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(jsc.sc(), path).toJavaRDD(); JavaRDD<LabeledPoint>[] split = data.randomSplit(new double[]{0.7, 0.3}, 11L);
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> trainningData = split[0];
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> test = split[1]; int numsClasses = 2;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> categoricalFeaturesInfo = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
String impurity = "gini";
int maxDepth = 1;
int maxbins = 32; final DecisionTreeModel model = DecisionTree.trainClassifier(trainningData, numsClasses,categoricalFeaturesInfo, impurity, maxDepth,maxbins);
JavaPairRDD<Double, Double> predictionAndLable = test.mapToPair(new PairFunction<LabeledPoint, Double, Double>() {
public Tuple2<Double, Double> call(LabeledPoint labeledPoint) throws Exception {
return new Tuple2<Double, Double>(model.predict(labeledPoint.features()), labeledPoint.label());
}
}); double testErr = predictionAndLable.filter(new Function<Tuple2<Double, Double>, Boolean>() {
public Boolean call(Tuple2<Double, Double> doubleDoubleTuple2) throws Exception {
return !doubleDoubleTuple2._1().equals(doubleDoubleTuple2._2());
}
}).count() * 1.0 / test.count(); System.out.println("Test Error: " + testErr);
System.out.println("Learned classification tree model:\n" + model.toDebugString()); // Save and load model
// model.save(jsc.sc(), "target/tmp/myDecisionTreeClassificationModel");
// DecisionTreeModel sameModel = DecisionTreeModel.load(jsc.sc(), "target/tmp/myDecisionTreeClassificationModel"); }
}
classification
package ML.DT; import org.apache.spark.SparkConf;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaPairRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaSparkContext;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function2;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.PairFunction;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.DecisionTree;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.DecisionTreeModel;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils;
import scala.Tuple2; import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map; /**
* TODO
*
* @ClassName: Regression
* @author: DingH
* @since: 2019/4/9 16:33
*/
public class Regression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparkConf sparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("JavaDecisionTreeRegressionExample").setMaster("local");
JavaSparkContext jsc = new JavaSparkContext(sparkConf); // Load and parse the data file.
String datapath = "D:\\IdeaProjects\\SimpleApp\\src\\main\\resources\\data\\mllib\\sample_libsvm_data.txt";
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(jsc.sc(), datapath).toJavaRDD();
// Split the data into training and test sets (30% held out for testing)
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint>[] splits = data.randomSplit(new double[]{0.7, 0.3});
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> trainingData = splits[0];
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> testData = splits[1]; // Set parameters.
// Empty categoricalFeaturesInfo indicates all features are continuous.
Map<Integer, Integer> categoricalFeaturesInfo = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
String impurity = "variance";
Integer maxDepth = 5;
Integer maxBins = 32; // Train a DecisionTree model.
final DecisionTreeModel model = DecisionTree.trainRegressor(trainingData, categoricalFeaturesInfo, impurity, maxDepth, maxBins); // Evaluate model on test instances and compute test error
JavaPairRDD<Double, Double> predictionAndLabel = testData.mapToPair(new PairFunction<LabeledPoint, Double, Double>() {
public Tuple2<Double, Double> call(LabeledPoint p) {
return new Tuple2<Double, Double>(model.predict(p.features()), p.label());
}
}); Double testMSE = predictionAndLabel.map(new Function<Tuple2<Double, Double>, Double>() {
public Double call(Tuple2<Double, Double> pl) {
Double diff = pl._1() - pl._2();
return diff * diff;
}
}).reduce(new Function2<Double, Double, Double>() {
public Double call(Double a, Double b) {
return a + b;
}
}) / data.count(); System.out.println("Test Mean Squared Error: " + testMSE);
System.out.println("Learned regression tree model:\n" + model.toDebugString()); // Save and load model
// model.save(jsc.sc(), "target/tmp/myDecisionTreeRegressionModel");
// DecisionTreeModel sameModel = DecisionTreeModel.load(jsc.sc(), "target/tmp/myDecisionTreeRegressionModel");
}
}
Regression
三。Random Forests
样本随机,特征随机
featureSubsetStrategy - Number of features to consider for splits at each node. Supported: "auto", "all", "sqrt", "log2", "onethird". If "auto" is set, this parameter is set based on numTrees: if numTrees == 1, set to "all"; if numTrees > 1 (forest) set to "sqrt".
package ML.RF; import org.apache.spark.SparkConf;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaPairRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaSparkContext;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.PairFunction;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.RandomForest;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.RandomForestModel;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils;
import scala.Tuple2; import java.util.HashMap; /**
* TODO
*
* @ClassName: classification
* @author: DingH
* @since: 2019/4/9 16:58
*/
public class classification {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparkConf sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("JavaRandomForestClassificationExample");
JavaSparkContext jsc = new JavaSparkContext(sparkConf); // Load and parse the data file.
String datapath = "D:\\IdeaProjects\\SimpleApp\\src\\main\\resources\\data\\mllib\\sample_libsvm_data.txt";
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(jsc.sc(), datapath).toJavaRDD(); // Split the data into training and test sets (30% held out for testing)
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint>[] splits = data.randomSplit(new double[]{0.7, 0.3});
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> trainingData = splits[0];
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> testData = splits[1]; // Train a RandomForest model.
// Empty categoricalFeaturesInfo indicates all features are continuous.
Integer numClasses = 2;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> categoricalFeaturesInfo = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
Integer numTrees = 3; // Use more in practice.
String featureSubsetStrategy = "auto"; // Let the algorithm choose.
String impurity = "gini";
Integer maxDepth = 5;
Integer maxBins = 32;
Integer seed = 12345; final RandomForestModel model = RandomForest.trainClassifier(trainingData, numClasses,categoricalFeaturesInfo, numTrees, featureSubsetStrategy, impurity, maxDepth, maxBins, seed); // Evaluate model on test instances and compute test error
JavaPairRDD<Double, Double> predictionAndLabel = testData.mapToPair(new PairFunction<LabeledPoint, Double, Double>() {
public Tuple2<Double, Double> call(LabeledPoint p) {
return new Tuple2<Double, Double>(model.predict(p.features()), p.label());
}
}); Double testErr =
1.0 * predictionAndLabel.filter(new Function<Tuple2<Double, Double>, Boolean>() {
public Boolean call(Tuple2<Double, Double> pl) {
return !pl._1().equals(pl._2());
}
}).count() / testData.count(); System.out.println("Test Error: " + testErr);
System.out.println("Learned classification forest model:\n" + model.toDebugString()); // Save and load model
// model.save(jsc.sc(), "target/tmp/myRandomForestClassificationModel");
// RandomForestModel sameModel = RandomForestModel.load(jsc.sc(),"target/tmp/myRandomForestClassificationModel");
} }
classification
package ML.RF; import org.apache.spark.SparkConf;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaPairRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaSparkContext;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function2;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.PairFunction;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.RandomForest;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.RandomForestModel;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils;
import scala.Tuple2; import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map; /**
* TODO
*
* @ClassName: regression
* @author: DingH
* @since: 2019/4/9 17:50
*/
public class regression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparkConf sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("JavaRandomForestRegressionExample");
JavaSparkContext jsc = new JavaSparkContext(sparkConf);
// Load and parse the data file.
String datapath = "D:\\IdeaProjects\\SimpleApp\\src\\main\\resources\\data\\mllib\\sample_libsvm_data.txt";
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(jsc.sc(), datapath).toJavaRDD(); // Split the data into training and test sets (30% held out for testing)
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint>[] splits = data.randomSplit(new double[]{0.7, 0.3});
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> trainingData = splits[0];
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> testData = splits[1]; // Set parameters.
// Empty categoricalFeaturesInfo indicates all features are continuous.
Map<Integer, Integer> categoricalFeaturesInfo = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
Integer numTrees = 3; // Use more in practice.
String featureSubsetStrategy = "auto"; // Let the algorithm choose.
String impurity = "variance";
Integer maxDepth = 4;
Integer maxBins = 32;
Integer seed = 12345;
// Train a RandomForest model.
final RandomForestModel model = RandomForest.trainRegressor(trainingData,categoricalFeaturesInfo, numTrees, featureSubsetStrategy, impurity, maxDepth, maxBins, seed); // Evaluate model on test instances and compute test error
JavaPairRDD<Double, Double> predictionAndLabel = testData.mapToPair(new PairFunction<LabeledPoint, Double, Double>() {
public Tuple2<Double, Double> call(LabeledPoint p) {
return new Tuple2<Double, Double>(model.predict(p.features()), p.label());
}
});
Double testMSE = predictionAndLabel.map(new Function<Tuple2<Double, Double>, Double>() {
public Double call(Tuple2<Double, Double> pl) {
Double diff = pl._1() - pl._2();
return diff * diff;
}
}).reduce(new Function2<Double, Double, Double>() {
public Double call(Double a, Double b) {
return a + b;
}
}) / testData.count(); System.out.println("Test Mean Squared Error: " + testMSE);
System.out.println("Learned regression forest model:\n" + model.toDebugString()); // Save and load model
model.save(jsc.sc(), "target/tmp/myRandomForestRegressionModel");
RandomForestModel sameModel = RandomForestModel.load(jsc.sc(),
"target/tmp/myRandomForestRegressionModel");
}
}
regression
四。Gradient-Boosted Trees

Usage tips: loss, numIterations, learningRate, algo
BoostingStrategy.validationTol
package ML.GradientBoostedTrees; import org.apache.spark.SparkConf;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaPairRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaSparkContext;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.PairFunction;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.GradientBoostedTrees;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.configuration.BoostingStrategy;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.model.GradientBoostedTreesModel;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils;
import scala.Tuple2; import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map; /**
* TODO
*
* @ClassName: classification
* @author: DingH
* @since: 2019/4/9 17:56
*/
public class classification {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparkConf sparkConf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("JavaGradientBoostedTreesClassificationExample");
JavaSparkContext jsc = new JavaSparkContext(sparkConf); // Load and parse the data file.
String datapath = "D:\\IdeaProjects\\SimpleApp\\src\\main\\resources\\data\\mllib\\sample_libsvm_data.txt";
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(jsc.sc(), datapath).toJavaRDD(); // Split the data into training and test sets (30% held out for testing)
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint>[] splits = data.randomSplit(new double[]{0.7, 0.3});
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> trainingData = splits[0];
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> testData = splits[1]; // Train a GradientBoostedTrees model.
// The defaultParams for Classification use LogLoss by default.
BoostingStrategy boostingStrategy = BoostingStrategy.defaultParams("Classification");
boostingStrategy.setNumIterations(3); // Note: Use more iterations in practice.
boostingStrategy.getTreeStrategy().setNumClasses(2);
boostingStrategy.getTreeStrategy().setMaxDepth(5);
// Empty categoricalFeaturesInfo indicates all features are continuous.
Map<Integer, Integer> categoricalFeaturesInfo = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
boostingStrategy.treeStrategy().setCategoricalFeaturesInfo(categoricalFeaturesInfo); final GradientBoostedTreesModel model =
GradientBoostedTrees.train(trainingData, boostingStrategy); // Evaluate model on test instances and compute test error
JavaPairRDD<Double, Double> predictionAndLabel =
testData.mapToPair(new PairFunction<LabeledPoint, Double, Double>() {
public Tuple2<Double, Double> call(LabeledPoint p) {
return new Tuple2<Double, Double>(model.predict(p.features()), p.label());
}
});
Double testErr =
1.0 * predictionAndLabel.filter(new Function<Tuple2<Double, Double>, Boolean>() {
public Boolean call(Tuple2<Double, Double> pl) {
return !pl._1().equals(pl._2());
}
}).count() / testData.count();
System.out.println("Test Error: " + testErr);
System.out.println("Learned classification GBT model:\n" + model.toDebugString()); // Save and load model
// model.save(jsc.sc(), "target/tmp/myGradientBoostingClassificationModel");
// GradientBoostedTreesModel sameModel = GradientBoostedTreesModel.load(jsc.sc(),
// "target/tmp/myGradientBoostingClassificationModel");
}
}
classification
五。naive Bayes
model type : "multinomial","bernouli"
package ML.ClassificationAndRegression.NaiveBayes; import org.apache.spark.SparkConf;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaSparkContext;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.NaiveBayes;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.NaiveBayesModel;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.LabeledPoint;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils;
import scala.Tuple2; /**
* TODO
*
* @ClassName: example
* @author: DingH
* @since: 2019/4/10 10:04
*/
public class example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("naiveBayesExample");
JavaSparkContext jsc = new JavaSparkContext(conf); String path = "D:\\IdeaProjects\\SimpleApp\\src\\main\\resources\\data\\mllib\\sample_libsvm_data.txt";
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> data = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(jsc.sc(), path).toJavaRDD(); JavaRDD<LabeledPoint>[] split = data.randomSplit(new double[]{0.6, 0.4}, 12345L);
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> train = split[0];
JavaRDD<LabeledPoint> test = split[1]; final NaiveBayesModel model = NaiveBayes.train(train.rdd(), 1.0, "multinomial"); JavaRDD<Tuple2<Double, Double>> predictionAndLabel = test.map(new Function<LabeledPoint, Tuple2<Double, Double>>() {
public Tuple2<Double, Double> call(LabeledPoint labeledPoint) throws Exception {
double predict = model.predict(labeledPoint.features());
return new Tuple2<Double, Double>(predict, labeledPoint.label());
}
}); double accuracy = predictionAndLabel.filter(new Function<Tuple2<Double, Double>, Boolean>() {
public Boolean call(Tuple2<Double, Double> doubleDoubleTuple2) throws Exception {
return doubleDoubleTuple2._1().equals(doubleDoubleTuple2._2());
}
}).count() / (double) test.count(); System.out.println("acucuracy is : " + accuracy); NaiveBayesModel model1 = NaiveBayesModel.load(jsc.sc(), ""); }
}
naive Bayes
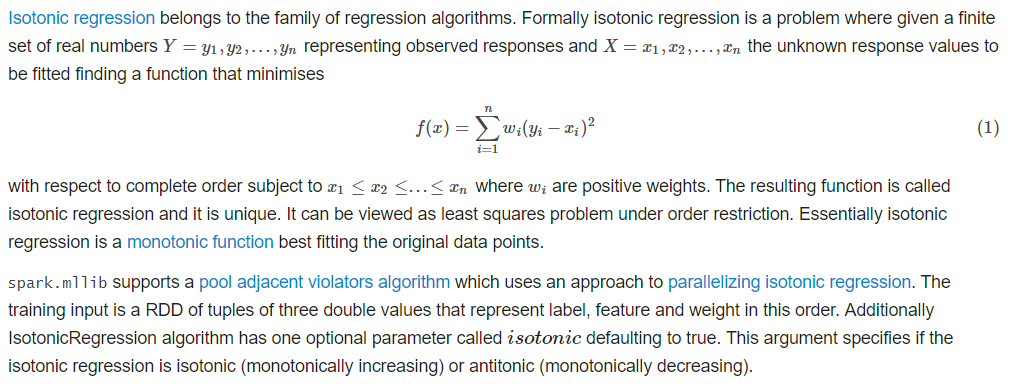
六。isotonic regression
package ML.ClassificationAndRegression.IsotonicRegression; import org.apache.spark.SparkConf;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaDoubleRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDD;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaSparkContext;
import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.IsotonicRegression;
import org.apache.spark.mllib.regression.IsotonicRegressionModel;
import scala.Tuple2;
import scala.Tuple3; /**
* TODO
*
* @ClassName: example
* @author: DingH
* @since: 2019/4/10 10:31
*/
public class example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local").setAppName("isotonicRegressionExample");
JavaSparkContext jsc = new JavaSparkContext(conf); String path = "D:\\IdeaProjects\\SimpleApp\\src\\main\\resources\\data\\mllib\\sample_isotonic_regression_data.txt";
JavaRDD<String> data = jsc.textFile(path); JavaRDD<Tuple3<Double, Double, Double>> parsedData = data.map(new Function<String, Tuple3<Double, Double, Double>>() {
public Tuple3<Double, Double, Double> call(String s) throws Exception {
String[] strings = s.split(",");
return new Tuple3<Double, Double, Double>(Double.parseDouble(strings[0]), Double.parseDouble(strings[1]), 1.0);
}
}); JavaRDD<Tuple3<Double, Double, Double>>[] split = parsedData.randomSplit(new double[]{0.7, 0.3}, 1234L);
JavaRDD<Tuple3<Double, Double, Double>> train = split[0];
JavaRDD<Tuple3<Double, Double, Double>> test = split[1]; final IsotonicRegressionModel model = new IsotonicRegression().setIsotonic(true).run(train); JavaRDD<Tuple2<Double, Double>> preditionAndLabel = test.map(new Function<Tuple3<Double, Double, Double>, Tuple2<Double, Double>>() {
public Tuple2<Double, Double> call(Tuple3<Double, Double, Double> doubleDoubleDoubleTuple3) throws Exception {
double predict = model.predict(doubleDoubleDoubleTuple3._1());
return new Tuple2<Double, Double>(predict, doubleDoubleDoubleTuple3._2());
}
}); Double MSE = new JavaDoubleRDD(preditionAndLabel.map(new Function<Tuple2<Double, Double>, Object>() {
public Object call(Tuple2<Double, Double> doubleDoubleTuple2) throws Exception { return Math.pow(doubleDoubleTuple2._1() - doubleDoubleTuple2._2(), 2.0);
}
}).rdd()).mean(); System.out.println("Mean Squared Error = " + MSE);
}
}
isotonic regression
spark MLlib Classification and regression 学习的更多相关文章
- Spark MLlib Deep Learning Convolution Neural Network (深度学习-卷积神经网络)3.1
3.Spark MLlib Deep Learning Convolution Neural Network (深度学习-卷积神经网络)3.1 http://blog.csdn.net/sunbow0 ...
- Spark MLlib Deep Learning Deep Belief Network (深度学习-深度信念网络)2.1
Spark MLlib Deep Learning Deep Belief Network (深度学习-深度信念网络)2.1 http://blog.csdn.net/sunbow0 Spark ML ...
- Spark入门实战系列--8.Spark MLlib(上)--机器学习及SparkMLlib简介
[注]该系列文章以及使用到安装包/测试数据 可以在<倾情大奉送--Spark入门实战系列>获取 .机器学习概念 1.1 机器学习的定义 在维基百科上对机器学习提出以下几种定义: l“机器学 ...
- Spark MLlib 机器学习
本章导读 机器学习(machine learning, ML)是一门涉及概率论.统计学.逼近论.凸分析.算法复杂度理论等多领域的交叉学科.ML专注于研究计算机模拟或实现人类的学习行为,以获取新知识.新 ...
- Spark MLlib架构解析(含分类算法、回归算法、聚类算法和协同过滤)
Spark MLlib架构解析 MLlib的底层基础解析 MLlib的算法库分析 分类算法 回归算法 聚类算法 协同过滤 MLlib的实用程序分析 从架构图可以看出MLlib主要包含三个部分: 底层基 ...
- spark Mllib基本功系列编程入门之 SVM实现分类
话不多说.直接上代码咯.欢迎交流. /** * Created by whuscalaman on 1/7/16. */import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, Spar ...
- spark Mllib SVM实例
Mllib SVM实例 1.数据 数据格式为:标签, 特征1 特征2 特征3…… 0 128:51 129:159 130:253 131:159 132:50 155:48 156:238 157: ...
- spark MLlib实现的基于朴素贝叶斯(NaiveBayes)的中文文本自动分类
1.自动文本分类是对大量的非结构化的文字信息(文本文档.网页等)按照给定的分类体系,根据文字信息内容分到指定的类别中去,是一种有指导的学习过程. 分类过程采用基于统计的方法和向量空间模型可以对常见的文 ...
- 在Java Web中使用Spark MLlib训练的模型
PMML是一种通用的配置文件,只要遵循标准的配置文件,就可以在Spark中训练机器学习模型,然后再web接口端去使用.目前应用最广的就是基于Jpmml来加载模型在javaweb中应用,这样就可以实现跨 ...
随机推荐
- Django JSON,AJAX
JSON 概念 JSON 指的是 JavaScript 对象表示法(JavaScript Object Notation) JSON 是轻量级的文本数据交换格式 JSON 独立于语言 * JSON 具 ...
- Git服务器Gogs简易安装-Windows环境
1.下载git for windows https://github.com/git-for-windows/git/releases/download/v2.15.0.windows.1/Git-2 ...
- 将服务器文件上传到ftp shell操作
date cd /home/data today_now=`date +%Y%m%d` #当前日期 cur_date=${today_now::} #echo ${cur_date} #判断是否文件生 ...
- Docker:跨主机容器间通信之overlay [十五]
一.配置overlay类型网络准备工作 1.在luoahong3主机上 docker run -d -p 8500:8500 -h consul --name consul progrium/cons ...
- js深拷贝
// 判断是否为对象 function isObject(o) { return (typeof o === 'object' || typeof o === 'function') &&am ...
- EF CodeFirst系列(5)---FluentApi
FluentApi总结 1.FluentApi简介 EF中的FluentApi作用是通过配置领域类来覆盖默认的约定.在EF中,我们通过DbModelBuilder类来使用FluentApi,它的功能比 ...
- git 重命名本地分支,并提交到远程
1.重命名 git branch -m oldBranchName newBranchName 2.删除远程分支:git push origin :oldBranchName 3.将重命名过的分支提交 ...
- 深入浅出mybatis之启动详解
深入浅出mybatis之启动详解 MyBatis功能丰富,但使用起来非常简单明了,今天我们来追踪一下它的启动过程. 目录 如何启动MyBatis 如何使用MyBatis MyBatis启动过程 如何启 ...
- SQL Server 常用的系统函数
Ø 简介 本文主要列举 SQL Server 中常用的一些系统函数,帮助我们在编写 SQL 时忘了某个函数的用法方便查阅.主要分为以下几类函数,更多函数可参考官网. 1. 字符串函数 2. ...
- ansible入门及组件介绍
Ansible简介 Ansible是自动化运维的工具,基于Python开发,实现了批量系统配置.批量程序部署.批量运行命令等功能.Ansible是基于模块工作的,ansible提供一个框架,通过模块实 ...
