HDU 3435 A new Graph Game(最小费用最大流)&HDU 3488
A new Graph Game
Time Limit: 8000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1849 Accepted Submission(s): 802
edge in an undirected graph as a set rather than an ordered pair.
Now given an undirected graph, you could delete any number of edges as you wish. Then you will get one or more connected sub graph from the original one (Any of them should have more than one vertex).
You goal is to make all the connected sub graphs exist the Hamiltonian circuit after the delete operation. What’s more, you want to know the minimum sum of all the weight of the edges on the “Hamiltonian circuit” of all the connected sub graphs (Only one “Hamiltonian
circuit” will be calculated in one connected sub graph! That is to say if there exist more than one “Hamiltonian circuit” in one connected sub graph, you could only choose the one in which the sum of weight of these edges is minimum).
For example, we may get two possible sums:
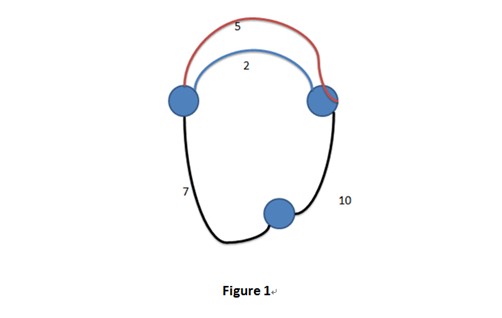
(1) 7 + 10 + 5 = 22
(2) 7 + 10 + 2 = 19
(There are two “Hamiltonian circuit” in this graph!)
In each case, the first line contains two integers n and m, indicates the number of vertices and the number of edges. (1 <= n <=1000, 0 <= m <= 10000)
Then m lines, each line contains three integers a,b,c ,indicates that there is one edge between a and b, and the weight of it is c . (1 <= a,b <= n, a is not equal to b in any way, 1 <= c <= 10000)
the minimum sum of weight you may get if you delete the edges in the optimal strategy.
3 3 4
1 2 5
2 1 2
2 3 10
3 1 7 3 2
1 2 3
1 2 4 2 2
1 2 3
1 2 4
Case 1: 19
Case 2: NO
Case 3: 6HintIn Case 1:
You could delete edge between 1 and 2 whose weight is 5. In Case 2:
It’s impossible to get some connected sub graphs that any of them exists the Hamiltonian circuit after the delete operation.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 10010;
const int MAXM = 100100;
const int INF = 1<<30;
struct EDG{
int to,next,cap,flow;
int cost; //每条边的单位价格
}edg[MAXM];
int head[MAXN],eid;
int pre[MAXN], cost[MAXN] ; //点0~(n-1) void init(){
eid=0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
}
void addEdg(int u,int v,int cap,int cst){
edg[eid].to=v; edg[eid].next=head[u]; edg[eid].cost = cst;
edg[eid].cap=cap; edg[eid].flow=0; head[u]=eid++; edg[eid].to=u; edg[eid].next=head[v]; edg[eid].cost = -cst;
edg[eid].cap=0; edg[eid].flow=0; head[v]=eid++;
} bool inq[MAXN];
bool spfa(int sNode,int eNode,int n){
queue<int>q;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
inq[i]=false; cost[i]= INF;
}
cost[sNode]=0; inq[sNode]=1; pre[sNode]=-1;
q.push(sNode);
while(!q.empty()){
int u=q.front(); q.pop();
inq[u]=0;
for(int i=head[u]; i!=-1; i=edg[i].next){
int v=edg[i].to;
if(edg[i].cap-edg[i].flow>0 && cost[v]>cost[u]+edg[i].cost){ //在满足可增流的情况下。最小花费
cost[v] = cost[u]+edg[i].cost;
pre[v]=i; //记录路径上的边
if(!inq[v])
q.push(v),inq[v]=1;
}
}
}
return cost[eNode]!=INF; //推断有没有增广路
}
//反回的是最大流,最小花费为minCost
int minCost_maxFlow(int sNode,int eNode ,int& minCost,int n){
int ans=0;
while(spfa(sNode,eNode,n)){
ans++;
for(int i=pre[eNode]; i!=-1; i=pre[edg[i^1].to]){
edg[i].flow+=1; edg[i^1].flow-=1;
minCost+=edg[i].cost;
}
}
return ans;
}
void scanf(int &ans){
char ch;
while(ch=getchar()){
if(ch>='0'&&ch<='9')
break;
}
ans=ch-'0';
while(ch=getchar()){
if(ch<'0'||ch>'9')
break;
ans=ans*10+ch-'0';
}
}
int mapt[1005][1005];
int main(){
int T,_case=0,n,m , u, v, d ;
scanf(T);
while(T--){
scanf(n); scanf(m);
init();
int s=0, t=2*n+1; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
addEdg(s , i , 1 , 0);
addEdg(i+n , t , 1 , 0);
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++)
mapt[i][j]=INF;
}
while(m--){
scanf(u); scanf(v); scanf(d);
if(mapt[u][v]>d)
mapt[u][v]=mapt[v][u]=d;
}
for( u=1; u<=n; u++)
for(v=1; v<=n; v++)
if(mapt[u][v]!=INF)
addEdg(u,v+n,1,mapt[u][v]); int mincost=0;
n-= minCost_maxFlow(s , t , mincost , t+1);
printf("Case %d: ",++_case);
if(n==0)
printf("%d\n",mincost);
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
HDU 3435 A new Graph Game(最小费用最大流)&HDU 3488的更多相关文章
- 【进阶——最小费用最大流】hdu 1533 Going Home (费用流)Pacific Northwest 2004
题意: 给一个n*m的矩阵,其中由k个人和k个房子,给每个人匹配一个不同的房子,要求所有人走过的曼哈顿距离之和最短. 输入: 多组输入数据. 每组输入数据第一行是两个整型n, m,表示矩阵的长和宽. ...
- hdu 2485 Destroying the bus stations 最小费用最大流
题意: 最少需要几个点才能使得有向图中1->n的距离大于k. 分析: 删除某一点的以后,与它相连的所有边都不存在了,相当于点的容量为1.但是在网络流中我们只能直接限制边的容量.所以需要拆点来完成 ...
- hdu 2686&&hdu 3376(拆点+构图+最小费用最大流)
Matrix Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Subm ...
- hdu 3488(KM算法||最小费用最大流)
Tour Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/65535 K (Java/Others)Total Submis ...
- hdu 2686 Matrix 最小费用最大流
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2686 Yifenfei very like play a number game in the n*n ...
- hdu 1533 Going Home 最小费用最大流
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1533 On a grid map there are n little men and n house ...
- hdu 4494 Teamwork 最小费用最大流
Teamwork Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4494 ...
- HDU 5988.Coding Contest 最小费用最大流
Coding Contest Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)To ...
- hdu 3667(拆边+最小费用最大流)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3667 思路:由于花费的计算方法是a*x*x,因此必须拆边,使得最小费用流模板可用,即变成a*x的形式. ...
- hdu 3395(KM算法||最小费用最大流(第二种超级巧妙))
Special Fish Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Tota ...
随机推荐
- iOS UIApplication的代理方法总结
1.简单介绍 1> 整个应用程序的象征,一个应用程序就一个UIApplication对象.使用了单例设计模式 2> 通过[UIApplication sharedApplication]訪 ...
- Ejb in action(一)——开篇介绍
从今天開始.我们共同来学习JavaEE中一个很重要的规范:Ejb. 既然您已经找到了这篇文章.就说明您至少已经对分布式开发有个大体上的概念了,之前没了解过也没关系,正好通过咱们的共同学习,一起来了解它 ...
- struts2訪问servlet的API
1.struts作为控制器,正常非常多时候要訪问到servlet的API.经常使用功能: (1).获取请求參数,控制界面跳转 (2).把共享数据存储于request,session,servl ...
- Discuz常见小问题-如何修改网站标题title
在全局-SEO设置中,找到论坛的title修改即可
- Java8新特性 - Lambda表达式 - 基本知识
A lambda expression is an unnamed block of code (or an unnamed function) with a list of formal param ...
- php之快速入门学习-6(字符串变量)
PHP 字符串变量 字符串变量用于存储并处理文本. PHP 中的字符串变量 字符串变量用于包含有字符的值. 在创建字符串之后,我们就可以对它进行操作了.您可以直接在函数中使用字符串,或者把它存储在变量 ...
- 算法笔记_168:历届试题 矩阵翻硬币(Java)
目录 1 问题描述 2 解决方案 1 问题描述 问题描述 小明先把硬币摆成了一个 n 行 m 列的矩阵. 随后,小明对每一个硬币分别进行一次 Q 操作. 对第x行第y列的硬币进行 Q 操作的定义: ...
- exception Access restriction: The type 'BASE64Encoder' is not API
Created by Marydon on 1.情景展示 在eclipse中切换jdk版本后,报错信息为:exception Access restriction: The type 'BASE6 ...
- EXCEPTION-STRUTS2
CreateTime--2016年8月29日17:05:50Author:Marydon 声明:异常类文章主要是记录了我遇到的异常信息及解决方案,解决方案大部分都是百度解决的,(这里只是针对我遇到 ...
- 稀疏矩阵的加法(用十字链表实现A=A+B)
描写叙述: 输入两个稀疏矩阵A和B,用十字链表实现A=A+B,输出它们相加的结果. 输入: 第一行输入四个正整数,各自是两个矩阵的行m.列n.第一个矩阵的非零元素的个数t1和第二个矩阵的非零元素的个数 ...
