EM and GMM(Code)
In EM and GMM(Theory), I have introduced the theory of em algorithm for gmm. Now lets practice it in matlab!
1. Generate 1000 pieces of random 2-dimention data which obey 5 gaussian distribution.
function X = GenerateData
Sigma = [1, 0; 0, 1];
mu1 = [1, -1];
x1 = mvnrnd(mu1, Sigma, 200);
mu2 = [5.5, -4.5];
x2 = mvnrnd(mu2, Sigma, 200);
mu3 = [1, 4];
x3 = mvnrnd(mu3, Sigma, 200);
mu4 = [6, 4.5];
x4 = mvnrnd(mu4, Sigma, 200);
mu5 = [9, 0.0];
x5 = mvnrnd(mu5, Sigma, 200);
% obtain the 1000 data points to be clustered
X = [x1; x2; x3; x4; x5];
end
2. Complete em algorithm.
function [Mu, Sigma, Pi, r_nk] = EmForGmm(Data, classNum, initVal)
% Data : Matrix(n * d), n is the quantity of the data and d is the data
% dimention
% classNum : Scale
% initVal : Cell(3 * 1), initial value for Mu, Sigma and Pi
% cell 1: Mu
% cell 2: Sigma
% cell 3: Pi
[sampleNum, sampleDim] = size(Data);
indexPoint = zeros(sampleNum, 1);
while(1)
for n = 1 : sampleNum
x = Data(n, :);
px_nk_sumk = 0;
for k = 1 : classNum
Sigma_k = initVal{2}(:,:,k);
Mu_k = initVal{1}(k,:);
Pi_k = initVal{3}(k);
px(n,k) = (1/(2*pi^(sampleDim/2)*det(Sigma_k)^(0.5))) ...
* exp(-0.5 * (x - Mu_k)*inv(Sigma_k)*(x - Mu_k)');
px_nk_sumk = px_nk_sumk + Pi_k * px(n, k);
end
for k = 1 : classNum
Sigma_k = initVal{2}(:,:,k);
Mu_k = initVal{1}(k,:);
Pi_k = initVal{3}(k);
r(n, k) = Pi_k * px(n, k) / px_nk_sumk;
end
end
Nk = sum(r)';
newMuK = r' * Data;
Nkk = repmat(Nk,1,2);
newMuK = newMuK ./ Nkk;
for i = 1 : classNum
nk = Nk(i);
MuT = repmat(newMuK(i,:),sampleNum,1);
xT = Data - MuT;
rT = r(:,i);
rT = repmat(rT,1,2);
newSigma(:,:,i) = xT' * (xT .* rT) / nk;
end
newPiK = Nk / sampleNum;
indexPointT = indexPoint;
[aa,indexPoint] = max(r,[],2);
j1 = sum(sum(abs(newMuK - initVal{1}))) < 1e-6;
j2 = sum(sum(sum(abs(newSigma - initVal{2})))) < 1e-6;
j3 = sum(abs(newPiK - initVal{3})) < 1e-6;
clf;
if (j1 && j2 && j3)
for i = 1:sampleNum
if (indexPoint(i)==1)
plot(Data(i,1), Data(i,2), 'r.')
end
if (indexPoint(i)==2)
plot(Data(i,1), Data(i,2), 'b.')
end
if (indexPoint(i)==3)
plot(Data(i,1), Data(i,2), 'k.')
end
if (indexPoint(i)==4)
plot(Data(i,1), Data(i,2), 'g.')
end
if (indexPoint(i)==5)
plot(Data(i,1), Data(i,2), 'm.')
end
hold on;
end
break;
else
initVal{1} = newMuK;
initVal{2} = newSigma;
initVal{3} = newPiK;
end
end
Mu = newMuK;
Sigma = newSigma;
Pi = newPiK;
r_nk = r;
end
3. Complete main function.
clear,clc,clf
Data = GenerateData;
classNum = 5;
[sampleNum, sampleDia] = size(Data); %% Initial value
% indexNum = floor(1 + (sampleNum - 1) * rand(1,classNum));
indexNum = [50,300,500,700,900];
initMu = Data(indexNum,:); initSigmaT = [1 0.2;0.2 1];
initSigma = zeros(2,2,classNum);
for i = 1 : classNum
initSigma(:,:,i) = initSigmaT;
initPi(i,1) = 1 / classNum;
end
initVal = cell(3,1);
initVal{1} = initMu;
initVal{2} = initSigma;
initVal{3} = initPi; %% EM algorithm
[Mu, Sigma, Pi, r_nk] = EmForGmm(Data, classNum, initVal);
4. Result.
The cluster result can be show as figure 3.
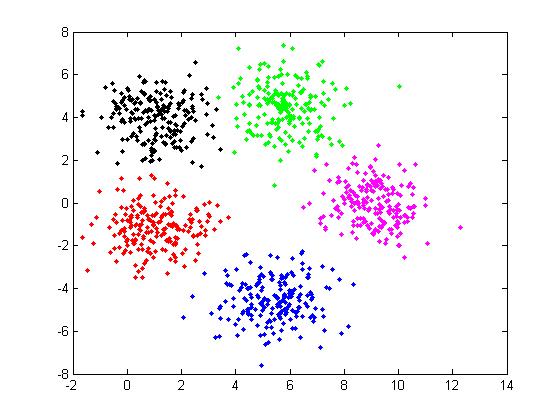
Figure 3
The probality distribution function can be writen as:
\[ p(\mathbf{x}) = \sum_{k=1}^{K}\pi_kp(\mathbf{x}|\mu_k\Sigma_k) \]
where,
$\mu_1 = (1.028, -1.158) $, $\mu_2 = (5.423, -4.538) $, $\mu_3 = (1.036, 3.975) $, $\mu_4 = (5.835, 4.474) $, $\mu_5 = (9.074, -0.063) $
Notice that, when generate the data:
$\mu_1 = (1, -1) $, $\mu_2 = (5.5, -4.5) $, $\mu_3 = (1, 4) $, $\mu_4 = (6, 4.5) $, $\mu_5 = (9, 0) $)
\[
\Sigma_1 = \left(
\begin{array}{cc}
1.0873& 0.0376\\
0.0376& 0.8850
\end{array}
\right),
\Sigma_2 = \left(
\begin{array}{cc}
1.1426& 0.0509\\
0.0509& 0.9192
\end{array}
\right),
\Sigma_3 = \left(
\begin{array}{cc}
0.9752& -0.0712\\
-0.0712& 0.9871
\end{array}
\right),
\Sigma_4 = \left(
\begin{array}{cc}
1.0111& -0.0782\\
-0.0782& 1.2034
\end{array}
\right),
\Sigma_5 = \left(
\begin{array}{cc}
0.8665& -0.1527\\
-0.1527& 0.9352
\end{array}
\right)
\]
Notice that, when generate the data:
\[\Sigma = \left(
\begin{array}{cc}
1& 0\\
0& 1
\end{array}
\right)
\]
$\pi_1 = 0.1986$, $\pi_2 = 0.2004 $, $\pi_3 = 0.1992$, $\pi_4 = 0.2015 $, $\pi_5 = 0.2002$
Notice that, when generate the data: each guassian components occupy 20% of all data. (1000 data point, 200 for each guassian components)
EM and GMM(Code)的更多相关文章
- EM and GMM(Theory)
Part 1: Theory 目录: What's GMM? How to solve GMM? What's EM? Explanation of the result What's GMM? GM ...
- 微信小程序API登录凭证(code),获得的用户登录态拥有一定的时效性
调用接口获取登录凭证(code)进而换取用户登录态信息,包括用户的唯一标识(openid) 及本次登录的 会话密钥(session_key).用户数据的加解密通讯需要依赖会话密钥完成. OBJECT参 ...
- 三维卷积:全景图像Spherical CNNs(Code)
卷积神经网络(CNN)可以很好的处理二维平面图像的问题.然而,对球面图像进行处理需求日益增加.例如,对无人机.机器人.自动驾驶汽车.分子回归问题.全球天气和气候模型的全方位视觉处理问题. 将球形信号的 ...
- css里px em rem特点(转)
1.px特点: 1.IE无法调整px作为单位的字体大小: 2.Firefox能够调整px.em和rem. px是像素,是相对长度单位,是相对于显示器屏幕分辨率而言的. 2.em特点: 1.em的值并不 ...
- PCL:描述三维离散点的ROPS特征(Code)
前言: 三维点云为三维欧式空间点的集合.对点云的形状描述若使用局部特征,则可分为两种:固定世界坐标系的局部描述和寻找局部主方向的局部描述,ROPS特征为寻找局部主方向的特征描述. 1.寻找主方向(对X ...
- Python:Matplotlib 画曲线和柱状图(Code)
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/ikerpeng/article/details/20523679 参考资料:http://matplotlib.org/gallery.html ...
- Qt:&OpenCV—Q图像处理基本操作(Code)
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/emouse/archive/2013/03/31/2991333.html 作者写作一系列:http://www.cnblogs.com/em ...
- 编码(Code)
很遗憾,直接搜索Code或者编码是很难得找到这本书的,我也是无意中才接触到本书. 第一次读本书,对各方面的知识都不算很懂,觉得很多地方都写的太多浅显,好像本该就是这样子,一个编码系统说的那么麻烦干嘛, ...
- px和em的区别(转)
在国内网站中,包括三大门户,以及“引领”中国网站设计潮流的蓝色理想,ChinaUI等都是使用了px作为字体单位.只有百度好歹做了个可调的表率.而 在大洋彼岸,几乎所有的主流站点都使用em作为字体单位, ...
随机推荐
- iOS常用的第三方库GitHub地址
MJRefresh https://github.com/CoderMJLee/MJRefresh#期待 Facebook-POP https://github.com/facebook/pop /* ...
- Xcode各版本官方下载
官方下载, 用开发者账户登录,建议用Safari浏览器下载. 官方下载地址: https://developer.apple.com/xcode/downloads/ Xcode 66.4: http ...
- css(四)-- 盒子模型和定位
盒子模型: 盒子模型就是把一个html边框比作成了一个盒子的边框,盒子模型要做用于操作数据与边框之间的距离或者 是边框与边框之间的距离. 盒子模型主要是用于操作内边距(padding)与外边距(mar ...
- Android与JNI(二) ---- Java调用C++ 动态调用
目录: 1. 简介 2. JNI 组件的入口函数 3. 使用 registerNativeMethods 方法 4. 测试 5. JNI 帮助方法 6. 参考资料 1. 简介 Android与JNI( ...
- [repost]Xcode因为证书问题经常报的那些错
[reference]http://www.jianshu.com/p/b10680a32d3 1. 确认下证书是不是开发证书,如果是发布证书就会出现这样的提示. 2. 证书失效了,去开发者中 ...
- iOS 导航栏不可点击
self.navigationController.navigationBar.userInteractionEnabled = NO;
- hibernate-Maven
1.创建Maven 2.创建Maven工程 3.然后一直下一步 4.创建成功后Maven 5.下载jra包 //hibernate <dependencies> <dependenc ...
- xdebug.var_display_max_data
Xdebug Display Full Details on var_dump() Xdebug is an excellent addition to a PHP developers arsena ...
- YII 1.0 发表文章用到的小物件
<?php $form = $this->beginWidget('CActiveForm',array('htmlOptions'=>array('enctype'=>'mu ...
- php中cookie实现二级域名可访问操作的方法
本文实例讲述了php中cookie实现二级域名可访问操作的方法.分享给大家供大家参考.具体方法如下: cookie在一些应用中很常用,假设我有一个多级域名要求可以同时访问主域名绑定的cookie,下面 ...
