Elasticsearch 模块 - Shard Allocation 机制
1. 背景
shard allocation 意思是分片分配, 是一个将分片分配到节点的过程; 可能发生该操作的过程包括:
- 初始恢复(
initial recovery) - 副本分配(
replica allocation) - 重新平衡(
rebalance) - 节点的新增和删除
分片的分配操作, 是由 master 角色的节点来决定什么时候移动分片, 以及移动到哪个节点上, 以达到集群的均衡;
说明
本文基于 Elasticsearch 7.4.0 版本
2. 机制分析
2.1. Allocation 触发条件
- 新增或删除
index索引 node节点的新增或删除- 执行
reroute命令 - 修改
replica副本数量 - 集群重启
具体对应源码解释:来源
| 序号 | 调用函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AllocationService.applyStartedShards | Shard 启动状态修改 |
| 2 | AllocationService.applyFailedShards | Shard 失效状态修改 |
| 3 | AllocationService.deassociateDeadNodes | Node 节点离开集群 |
| 4 | AllocationService.reroute(AllocationCommands) | 执行 relocation 命令 |
| 5 | TransportClusterUpdateSettingsAction.masterOperation | 集群配置修改操作 |
| 6 | MetaDataCreateIndexService.onlyCreateIndex | 创建新索引 index 请求 |
| 7 | MetaDataDeleteIndexService.deleteIndexs | 删除索引 index 操作 |
| 8 | MetaDataIndexStateService.closeIndex | 关闭 index 操作 |
| 9 | MetaDataIndexStateService.openIndex | 打开 index操作 |
| 10 | NodeJoinController.JoinTaskExecutor | 通过集群发现的节点加入集群 |
| 11 | GatewayService.GatewayRecoveryListener | 通过 GatewayRecovery 恢复的节点加入集群 |
| 12 | LocalAllocateDangledIndices.submitStateUpdateTask | 恢复磁盘内存而在 MateDate 内不存在的 index |
| 13 | RestoreService.restoreSnapshot | 从 snapshot 中恢复的 index |
2.2. Rebalance 的触发条件
在 rebalance 之前会经过 2.3.2 中介绍的所有策略里实现的 canRebalance 方法, 全部通过后才会执行下面的 Rebalance 过程;
Rebalance 过程是通过调用 balanceByWeights() 方法, 计算 shard 所在的每个 node 的 weight 值,
weightIndex = node.numShards(index) + numAdditionalShards - balancer.avgShardsPerNode(index) \\
weight = theta0 * weightShard + theta1 * weightIndex \\
\]
其中:
numAdditionalShards一般为 0, 调用weightShardAdded,weightShardRemoved方法时分别取值为1和-1;- theta0 =
cluster.routing.allocation.balance.shard系统动态配置项, 默认值为0.45f; - theta1 =
cluster.routing.allocation.balance.index系统动态配置项, 默认值为0.55f;

源码如下:
private static class WeightFunction {
private final float indexBalance;
private final float shardBalance;
private final float theta0;
private final float theta1;
WeightFunction(float indexBalance, float shardBalance) {
float sum = indexBalance + shardBalance;
if (sum <= 0.0f) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Balance factors must sum to a value > 0 but was: " + sum);
}
theta0 = shardBalance / sum;
theta1 = indexBalance / sum;
this.indexBalance = indexBalance;
this.shardBalance = shardBalance;
}
float weight(Balancer balancer, ModelNode node, String index) {
final float weightShard = node.numShards() - balancer.avgShardsPerNode();
final float weightIndex = node.numShards(index) - balancer.avgShardsPerNode(index);
return theta0 * weightShard + theta1 * weightIndex;
}
}
2.3. 源码分析
分片分配就是把一个分片分配到集群中某个节点的过程, 其中分配决策包含了两个方面:
- 哪些分片应该分配到哪些节点上
- 哪个分片作为主分片, 哪个作为副本分片
Elasticsearch 主要通过两个基础组件来完成分片分配这个过程的: allocator 和 deciders;
allocator寻找最优的节点来分配分片;deciders负责判断并决定是否要进行分配;
- 新建的索引
allocator 负责找出拥有分片数量最少的节点列表, 按分片数量递增排序, 分片数量较少的会被优先选择; 对于新建索引, allocator 的目标是以更为均衡的方式把新索引的分片分配到集群的节点中;
deciders 依次遍历 allocator 给出的节点列表, 判断是否要把分片分配给该节点, 比如是否满足分配过滤规则, 分片是否将超出节点磁盘容量阈值等等;
- 已有的索引
allocator 对于主分片, 只允许把主分片指定在已经拥有该分片完整数据的节点上; 对于副本分片, 则是先判断其他节点上是否已有该分片的数据的拷贝, 如果有这样的节点, allocator 则优先把分片分配到这其中一个节点上;
2.3.1. Allocator
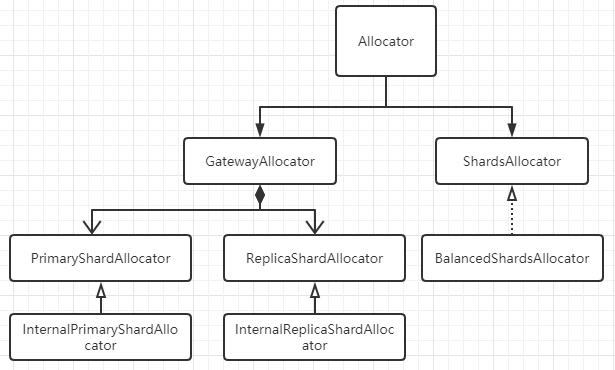
PrimaryShardAllocator找到拥有某Shard最新数据(主分片)的节点;ReplicaShardAllocator找到磁盘上拥有这个Shard数据(副本分片)的节点;BalancedShardsAllocator找到拥有最少Shard个数的节点;
public class BalancedShardsAllocator implements ShardsAllocator {
public static final Setting<Float> INDEX_BALANCE_FACTOR_SETTING = Setting.floatSetting("cluster.routing.allocation.balance.index", 0.55f, 0.0f, Property.Dynamic, Property.NodeScope);
public static final Setting<Float> SHARD_BALANCE_FACTOR_SETTING = Setting.floatSetting("cluster.routing.allocation.balance.shard", 0.45f, 0.0f, Property.Dynamic, Property.NodeScope);
public static final Setting<Float> THRESHOLD_SETTING = Setting.floatSetting("cluster.routing.allocation.balance.threshold", 1.0f, 0.0f, Property.Dynamic, Property.NodeScope);
private volatile WeightFunction weightFunction;
private volatile float threshold;
}
2.3.2. Deciders
Deciders 决策期基础组件的抽象类为 AllocationDecider:
public abstract class AllocationDecider {
public Decision canRebalance(ShardRouting shardRouting, RoutingAllocation allocation) {
return Decision.ALWAYS;
}
public Decision canAllocate(ShardRouting shardRouting, RoutingNode node, RoutingAllocation allocation) {
return Decision.ALWAYS;
}
public Decision canRemain(ShardRouting shardRouting, RoutingNode node, RoutingAllocation allocation) {
return Decision.ALWAYS;
}
public Decision canAllocate(ShardRouting shardRouting, RoutingAllocation allocation) {
return Decision.ALWAYS;
}
public Decision canAllocate(IndexMetadata indexMetadata, RoutingNode node, RoutingAllocation allocation) {
return Decision.ALWAYS;
}
public Decision canAllocate(RoutingNode node, RoutingAllocation allocation) {
return Decision.ALWAYS;
}
public Decision shouldAutoExpandToNode(IndexMetadata indexMetadata, DiscoveryNode node, RoutingAllocation allocation) {
return Decision.ALWAYS;
}
public Decision canRebalance(RoutingAllocation allocation) {
return Decision.ALWAYS;
}
}
ES 7.4.0 中的 Decider 决策器包括以下所示, 他们均实现上面的 AllocationDecider 抽象类, 并重写 canRebalance, canAllocate, canRemain, canForceAllocatePrimary 等方法;
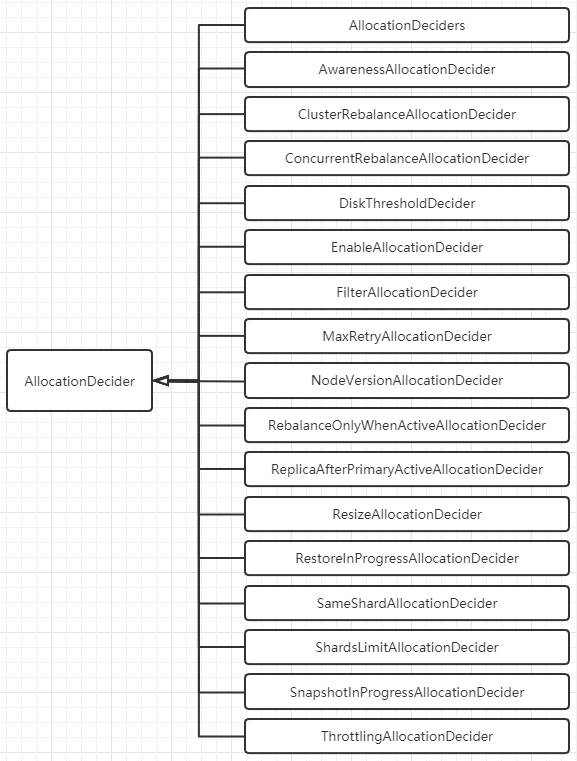
决策器比较多, 大致分类如下, 并列举决策器对应的配置项:
2.3.2.1. 负载均衡类
SameShardAllocationDecider: 避免主副分片分配到同一个节点;AwarenessAllocationDecider: 感知分配器, 感知服务器, 机架等, 尽量分散存储 Shard;对应的配置参数有:
cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.attributes: rack_idcluster.routing.allocation.awareness.attributes: zoneShardsLimitAllocationDecider: 同一个节点上允许存在同一个index的shard数目;index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node: 表示该索引每个节点上允许最多的shard数量; 默认值=-1, 表示无限制;cluster.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node:cluster级别, 表示集群范围内每个节点上允许最多的shard数量, 默认值=-1, 表示无限制;index级别会覆盖cluster级别;
2.3.2.2. 并发控制类
ThrottlingAllocationDecider:recovery阶段的限速配置, 避免过多的recovering allocation导致该节点的负载过高;cluster.routing.allocation.node_initial_primaries_recoveries: 当前节点在进行主分片恢复时的数量, 默认值=4;cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_incoming_recoveries: 默认值=2, 通常是其他节点上的副本 shard 恢复到该节点上;cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_outgoing_recoveries: 默认值=2, 通常是当前节点上的主分片 shard 恢复副本分片到其他节点上;cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_recoveries: 统一配置上面两个配置项;ConcurrentRebalanceAllocationDecider:rebalace并发控制, 表示集群同时允许进行rebalance操作的并发数量;cluster.routing.allocation.cluster_concurrent_rebalance, 默认值=2通过检查
RoutingNodes类中维护的reloadingShard计数器, 看是否超过配置的并发数;DiskThresholdDecider: 根据节点的磁盘剩余量来决定是否分配到该节点上;cluster.routing.allocation.disk.threshold_enabled, 默认值=true;cluster.routing.allocation.disk.watermark.low: 默认值=85%, 达到这个值后, 新索引的分片不会分配到该节点上;cluster.routing.allocation.disk.watermark.high: 默认值=90%, 达到这个值后, 会触发已分配到该节点上的Shard会rebalance到其他节点上去;
2.3.2.3. 条件限制类
RebalanceOnlyWhenActiveAllocationDecider: 所有Shard都处于active状态下才可以执行rebalance操作;FilterAllocationDecider: 通过接口动态设置的过滤器;cluster级别会覆盖index级别;index.routing.allocation.require.{attribute}
index.routing.allocation.include.{attribute}
index.routing.allocation.exclude.{attribute}
cluster.routing.allocation.require.{attribute}
cluster.routing.allocation.include.{attribute}
cluster.routing.allocation.exclude.{attribute}- require 表示必须满足, include 表示可以分配到指定节点, exclude 表示不允许分配到指定节点;
- {attribute} 还有 ES 内置的几个选择, _name, _ip, _host;
ReplicaAfterPrimaryActiveAllocationDecider: 保证只在主分片分配完成后(active状态)才开始分配副本分片;ClusterRebalanceAllocationDecider: 通过集群中active的shard状态来决定是否可以执行rebalance;cluster.routing.allocation.allow_rebalanceindices_all_active(默认): 当集群所有的节点分配完成, 才可以执行rebalance操作;
indices_primaries_active: 只要所有主分片分配完成, 才可以执行rebalance操作;
always: 任何情况下都允许 rebalance 操作;MaxRetryAllocationDecider: 防止 shard 在失败次数达到上限后继续分配;index.allocation.max_retries: 设置分配的最大失败重试次数, 默认值=5;
2.3.2.4. 其他决策类
EnableAllocationDecider: 设置允许分配的分片类型;index级别配置会覆盖cluster级别配置;all(默认): 允许所有类型的分片;primaries: 仅允许主分片;new_primaries: 仅允许新建索引的主分片;none: 禁止分片分配操作;NodeVersionAllocationDecider: 检查分片所在 Node 的版本是否高于目标 Node 的 ES 版本;SnapshotInProgressAllocationDecider: 决定snapshot期间是否允许allocation, 因为snapshot只会发生在主分片上, 所以该配置只会限制主分片的allocation;cluster.routing.allocation.snapshot.relocation_enabled
接下来介绍一下在 Elasticsearch 中涉及到 Allocation 和 Rebalance 的相关配置项;
3. cluster-level 配置
3.1. Shard allocation 配置
控制分片的分配和恢复;
| 配置 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| cluster.routing.allocation.enable | all | 启用或禁用针对特定类型分片的分配; 1. all: 允许分配所有类型的分片; 2. primaries: 只允许分配主分片(primary shard); 3. new_primaries: 只允许分配新索引的主分片(primary shard);4. none: 禁用分片分配;该设置不会影响重启节点时本地主分片的恢复; |
| cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_incoming_recoveries | 2 | 一个节点允许并发的传入分片(incoming shard)数量 |
| cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_outgoing_recoveries | 2 | 一个节点允许并发的传出分片(incoming shard)数量 |
| cluster.routing.allocation.node_concurrent_recoveries | 上面两者的合并配置 | |
| cluster.routing.allocation.node_initial_primaries_recoveries | 4 | 单个节点上同时初始化的主分片数量 |
| cluster.routing.allocation.same_shard.host | false | 是否执行检查, 以防止基于host name和host address, 在单个主机上分配同一分片的多个实例; 该设置仅用于在同一台计算机上启动多个节点的情况; |
3.2. Shard rebalancing 配置
控制集群之间的分片平衡;
| 配置 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| cluster.routing.rebalance.enable | all | 启用或禁用针对特定类型分片的rebalancing;1. all: 允许rebalancing所有类型的分片;2. primaries: 只允许rebalancing主分片;3. replicas: 只允许rebalancing副本分片;4. none: 禁用rebalancing; |
| cluster.routing.allocation.allow_rebalance | indices_all_active | 指定何时允许执行rebalancing;1. always: 总是允许;2. indices_primaries_active: 当集群中所有主分片已分配时才允许rebalancing;3. indices_all_active: 当集群中所有分片(包括主分片和副本分片)都已分配时才允许rebalancing; |
| cluster.routing.allocation.cluster_concurrent_rebalance | 2 | 指定整个集群中允许同时在节点间移动的分片数量; 该配置仅控制由于集群不平衡引起的并发分片分配数量, 对分配过滤(allocation filtering)或强制感知(forced awareness)的分片分配不做限制; |
3.3. 分片平衡启发式
以下配置用于决定每个分片的存放位置; 当rebalancing操作不再使任何节点的权重超过balance.threshold时, 集群即达到平衡;
| 配置 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| cluster.routing.allocation.balance.shard | 0.45f | 定义节点上分配的分片总数的权重因子; 提升该值会导致集群中所有节点趋向于分片数量相等; |
| cluster.routing.allocation.balance.index | 0.55f | 定义节点上分配的每个索引的分片数量的权重因子; 提升该值会导致集群中所有节点上每个索引的分片数量趋向于相等; |
| cluster.routing.allocation.balance.threshold | 1.0f | 定义应当执行操作的最小优化值(非负浮点数); 提升该值会导致集群在优化分片平衡方面不太积极; |
4. Index-level 配置
以下配置控制每个索引中的分片分配;
4.1. index-level 分片分配过滤(来源)
配置需要分两步:
- 在每个 Elasticsearch 节点的
elasticsearch.yml配置文件中添加自定义节点属性, 比如以small,medium,big区分节点类型, 则配置文件中可添加:
node.attr.size: medium
或者在启动 Elasticsearch 服务时, 在命令行里添加 ./bin/elasticsearch -Enode.attr.size=medium;
- 在新建索引的
mapping时, 添加index.routing.allocation.include/exclude/require.size: medium的过滤配置即可;
PUT <index_name>/_settings
{
"index.routing.allocation.include.size": "medium"
}
可以配置多个自定义节点属性, 并且必须同时满足索引里配置的多个过滤条件;
- index.routing.allocation.include.{attribute}: {values}
- index.routing.allocation.require.{attribute}: {values}
- index.routing.allocation.exclude.{attribute}: {values}
其中 {attribute} 可以是上面提到的自定义节点属性, ES 自己也有一些内置的节点属性:
| attribute | 说明 |
|---|---|
| _name | 通过节点名称进行匹配 |
| _host_ip | 通过节点 IP 地址进行匹配 |
| _publish_ip | 通过节点的发布 IP 地址进行匹配 |
| _ip | 通过 _host_ip 或 _publish_ip 进行匹配 |
| _host | 通过节点的hostname进行匹配 |
| _id | 通过节点的 id 进行匹配 |
其中 {values} 可以是单个值, 也可以是逗号分隔的多个值, 也可以使用通配符 * 进行模糊匹配;
4.2. 设置延迟分配, 当节点离开时(来源)
当某个节点由于突发原因, 比如网络中断, 人为操作重启等, 需要暂时离开集群时, 集群会立刻新建副本分片以替换丢失的副本, 然后在剩余的所有节点之间进行rebalancing, 这样导致在短时间内该突发节点又恢复过来后, 原先的副本就无法再使用, 集群会将刚才新建的副本分片再拷贝回到该节点上; 这样就会造成不必要的资源浪费, 以及节点分片rebalancing带来的波动;
可以使用 index.unassigned.node_left.delayed_timeout 动态设置来延迟由于节点离开而导致未分配的副本分片的分配问题; 该配置默认值 1m;
PUT _all/_settings
{
"settings": {
"index.unassigned.node_left.delayed_timeout": "5m"
}
}
修改成以上配置后, 如果在 5m 内, 该节点可以恢复重新加入集群, 则集群会自动恢复该节点的副本分片分配, 恢复速度很快;
注意
- 此设置不影响将副本分片升级为主分片;
- 此设置不影响之前未分配的副本分片;
- 在整个集群重新启动后, 该延迟分配不会生效;
4.3. 索引恢复的优先级(来源)
索引分片恢复的优先级按照:
- 可选的
index.priority配置, 值越大优先级越高; index索引的创建日期, 越新的索引优先级越高;index索引的名称;
4.4. 每个节点的分片总数(来源)
| 配置 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node | unbounded(-1) | 指定单个节点上最多分配的分片数量, 包括主分片和副本分片;(具体某个索引) |
| cluster.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node | unbounded(-1) | 指定单个节点上最多分配的分片数量, 包括主分片和副本分片;(与索引无关, 全局设置) |
这些配置是硬性配置, 可能会导致一些分片无法分配, 需要慎重配置;
5. 阅读来源
- Shard allocation and cluster-level routing
- Elasticsearch底层系列之 Shard Allocation 机制
- ELASTICSEARCH ALLOCATION 分析
- Elasticsearch Shard Allocation 机制
- Elasticsearch Allocation&Rebalance
Elasticsearch 模块 - Shard Allocation 机制的更多相关文章
- Elasticsearch技术解析与实战(四)shard&replica机制
序言 shard&replica机制 1.index包含多个shard 2.每个shard都是一个最小工作单元,承载部分数据,lucene实例,完整的建立索引和处理请求的能力 3.增减节点时, ...
- Elasticsearch技术解析与实战--shard&replica机制
序言 1.shard&replica机制 (1)index包含多个shard (2)每个shard都是一个最小工作单元,承载部分数据,lucene实例,完整的建立索引和处理请求的能力 (3)增 ...
- ES跨版本升级?——难道升级集群发生shard allocation是因为要分配replica节点???
Full cluster restart upgrade Elasticsearch requires a full cluster restart when upgrading across maj ...
- Elasticsearch系列---分布式架构机制讲解
概要 本篇主要介绍Elasticsearch的数据索引时的分片机制,集群发现机制,primary shard与replica shard是如何分工合作的,如何对集群扩容,以及集群的容错机制. 分片机制 ...
- Skywalking-13:Skywalking模块加载机制
模块加载机制 基本概述 Module 是 Skywalking 在 OAP 提供的一种管理功能特性的机制.通过 Module 机制,可以方便的定义模块,并且可以提供多种实现,在配置文件中任意选择实现. ...
- ElasticSearch 分布式及容错机制
1 ElasticSearch分布式基础 1.1 ES分布式机制 分布式机制:Elasticsearch是一套分布式的系统,分布式是为了应对大数据量.它的特性就是对复杂的分布式机制隐藏掉. 分片机制: ...
- 【前端】CommonJS的模块加载机制
CommonJS的模块加载机制 CommonJS模块的加载机制是,输入的是被输出的值的拷贝.也就是说,一旦输出一个值,模块内部的变化就影响不到这个值. 例如: // lib.js var counte ...
- Dojo初探之1:AMD规范,编写符合AMD规范(异步模块加载机制)的模块化JS(其中dojo采用1.11.2版本)
一.AMD规范探索 1.AMD规范(即异步模块加载机制) 我们在接触js的时候,一般都是通过各种function来定义一些方法,让它们帮我们做一些事情,一个js可以包含很多个js,而这些functio ...
- Django的日志中关闭elasticsearch模块的日志
今天用python的日志模块,为Django项目配置了日志,运行的时候发现日志在疯狂的涨,检查后发现竟然是elasticsearch的日志,但是我没有打这个日志啊,根据日志提供的文件位置,我在elas ...
随机推荐
- Educational Codeforces Round 95 (Rated for Div. 2) C. Mortal Kombat Tower (DP)
题意:你和基友两人从左往右轮流打怪兽,强怪用\(1\)表示,垃圾用\(0\)表示,但基友比较弱,打不过强怪,碰到强怪需要用一次魔法,而你很强,无论什么怪都能乱杀,基友先打,每人每次至少杀一个怪兽,最多 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 94 (Rated for Div. 2) A. String Similarity (构造水题)
题意:给你一个长度为\(2*n-1\)的字符串\(s\),让你构造一个长度为\(n\)的字符串,使得构造的字符串中有相同位置的字符等于\(s[1..n],s[2..n+1],...,s[n,2n-1] ...
- 三、Jmeter 定时器
首先需要清楚Jmeter中各个元件的执行顺序: 元件的执行顺序 了解了元件有作用域之后,来看看元件的执行顺序,元件执行顺序的规则很简单,在同一作用域名范围内,测试计划中的元件按照如下顺序执行. (1) ...
- PPT 倒计时时钟,用 GIF 动画实现,可直接使用 -- 附 Python 实现代码
在上课时,有时需要显示一个倒计时时钟,让学生做题. PPT 没有简单有效的方法实现倒计时时钟,参考了多个方案,最终决定采用 GIF 动画来实现. 这样使用起来很简单,只要把事先做好的各个时长的倒计时动 ...
- 在kubernetes集群里集成Apollo配置中心(6)之实战使用apollo分环境管理dubbo服务
生产实践 1.迭代新需求/修复BUG(编码--->提git) 2.测试环境发版,测试(应用通过编译打包发布至test命名空间) 3.测试通过,上线(应用镜像直接发布至prod命名空间) 系统架构 ...
- CentOS 7 架设LNMP动态网站
1.安装Nginx 1)使用Nginx官方的yum源 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo [nginx] name=nginx re ...
- 国内centos/windows10安装minikube
centos/windows10安装minikube 目录 centos/windows10安装minikube A win10安装minikube 1 下载安装kubectl.exe 1.1 准备目 ...
- Leetcode(15)-三数之和
给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组. 注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组. ...
- Gym 101480F Frightful Formula(待定系数)题解
#include<cmath> #include<set> #include<map> #include<queue> #include<cstd ...
- how to input special keyboard symbol in macOS(⌘⇧⌃⌥)
how to input special keyboard symbol in macOS(⌘⇧⌃⌥) emoji ctrl + command + space / ⌘⇧⌃ ⌘⇧⌃ Character ...
