django中间件介绍
在学习django中间件之前,先来认识一下django的生命周期,如下图所示:
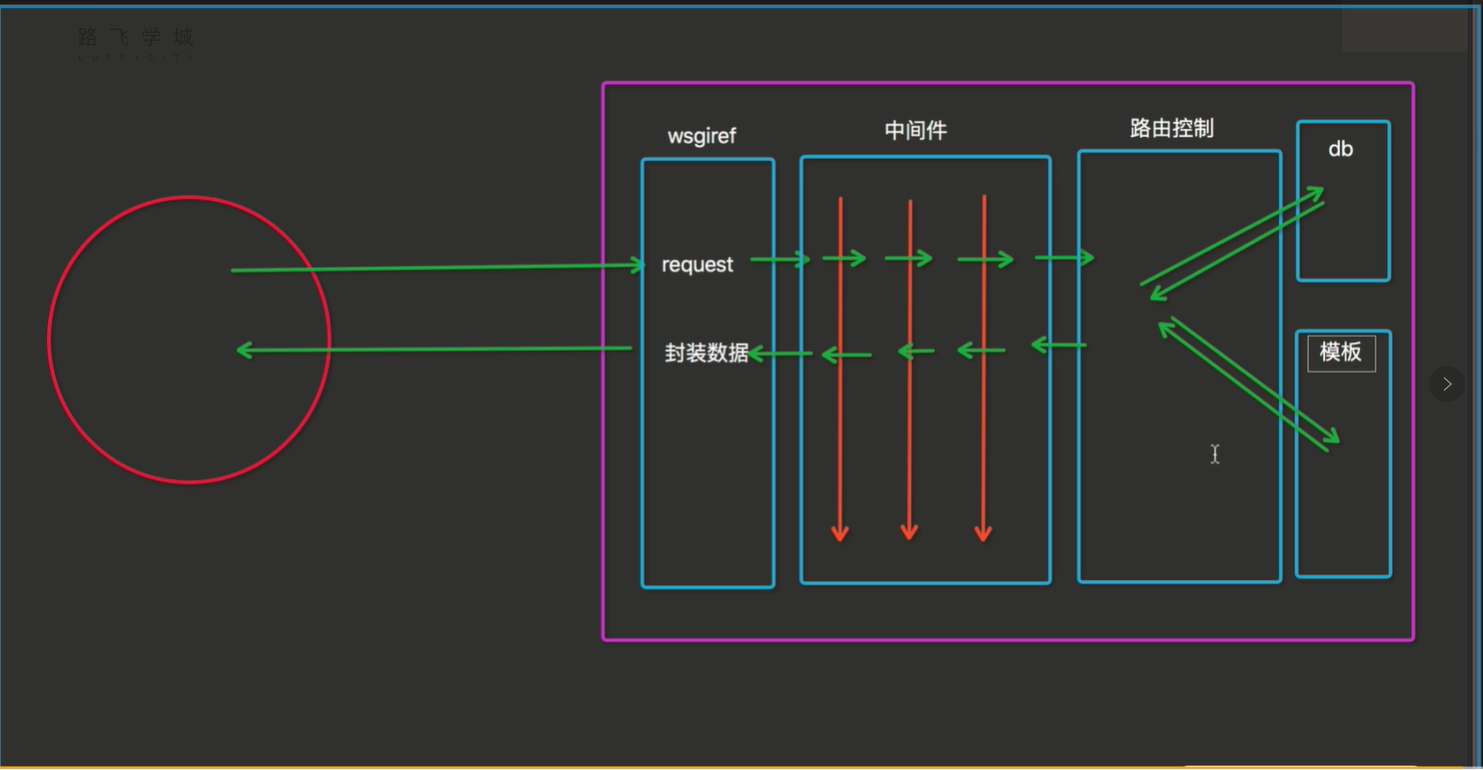
django生命周期:浏览器发送的请求会先经过wsgiref模块处理解析出request(请求数据)给到中间件,然后通过路由控制执行对应的视图函数,从而和模板,db进行交互,交互完的数据再通过视图函数返回给中间件,最后wsgiref模块将返回的数据封装成http形式的数据给到浏览器并进行展示。
了解了django的生命周期后,我们就可以开始着手写一个自己的中间件了,接下来认识几个常用的中间件方法
1.process_request
单个中间件
首先在app下创建一个py文件,定义你的中间件类名
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
from django.http import HttpResponse class MiddlewareShow(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self, request): print('MiddlewareShow1')
然后将你的py文件路径写入django主项目的settings的MIDDLEWARE中
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
'proxy_pro.middleware.MiddlewareShow' # 此条是新加的 从该项目路径开始写
]
然后执行一个视图函数即可,查看控制台打印
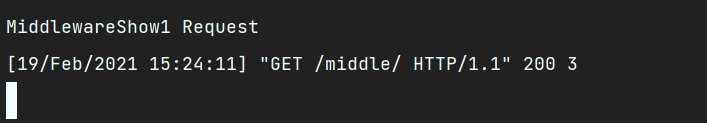
此时自己创建的process_request方法就生效了
多个中间件
此时在之前的py文件中再新建一个类
class MiddlewareShow(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Request')
class MiddlewareShowTwo(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Request')
然后将新建类的路径也放在django主项目的settings的MIDDLEWARE中
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
'proxy_pro.middleware.MiddlewareShow',
'proxy_pro.middleware.MiddlewareShowTwo'
]
执行视图函数,查看控制台打印

此时定义的两个中间件都生效了,执行顺序是先1后2
2.process_response
分别在刚才的类中添加response方法
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
from django.http import HttpResponse class MiddlewareShow(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Request') def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Response')
return response class MiddlewareShowTwo(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Request') def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Response')
return response
执行视图函数,查看控制台打印
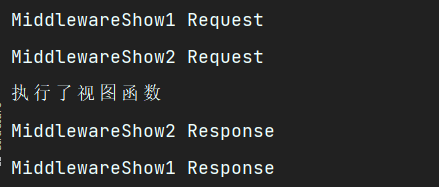
此时可以看出请求先依次执行了中间件的Request,然后再去执行视图函数,返回是先执行跟后面的中间件再依次往前
这时突然冒出一个想法,如果在request时直接返回了某个东西,还会继续去执行后面的视图函数吗?那我们就来测试一下
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
from django.http import HttpResponse class MiddlewareShow(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Request')
return HttpResponse('request1时已返回') def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Response')
return response class MiddlewareShowTwo(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Request') def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Response')
return response
执行视图函数,查看控制台
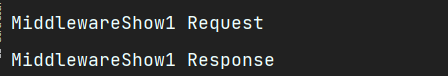
此时可以看出当request中有返回时,直接不执行后面的内容了
3.process_view
分别在刚才的py文件中添加view方法
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
from django.http import HttpResponse class MiddlewareShow(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Request') def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Response')
return response def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('MiddlewareShow1 process_view') class MiddlewareShowTwo(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Request') def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Response')
return response def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('MiddlewareShow2 process_view')
执行视图函数,查看控制台返回
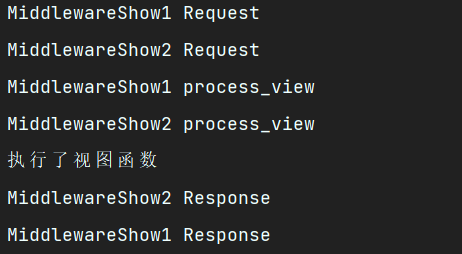
此时可以看出这个process_view方法会在执行完request后执行,执行完再去执行视图函数
这时候就有疑问了,那这个有什么用呢?我们先把它里面的参数打印一下
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
from django.http import HttpResponse class MiddlewareShow(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Request') def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Response')
return response def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('MiddlewareShow1 process_view')
print('=====>callback', callback)
print('=====>callback_args', callback_args) class MiddlewareShowTwo(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Request') def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Response')
return response def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('MiddlewareShow2 process_view')
执行视图函数打印结果
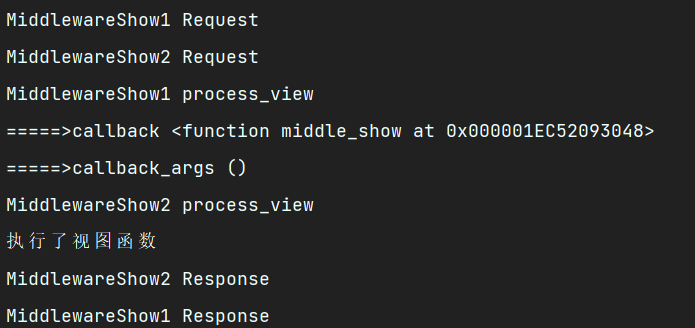
此时可以看到这个view里面的参数callback是视图方法,callback_args是请求参数,那我们试着去请求下看看
class MiddlewareShow(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Request')
def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Response')
return response
def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('MiddlewareShow1 process_view')
print('=====>callback', callback)
print('=====>callback_args', callback_args)
ret = callback(callback_args) # 请求
return ret
class MiddlewareShowTwo(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Request')
def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Response')
return response
def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('MiddlewareShow2 process_view')
查看打印结果
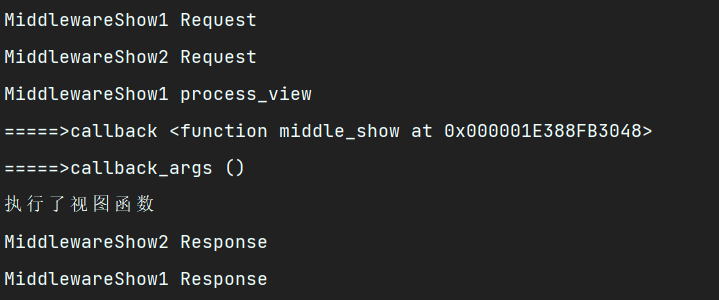
结果显然易见,请求视图函数成功了,返回了以后就没有去执行process_view2了,这边的作用就是可以拦截请求
4.process_exception
分别在刚才的py文件中添加exception方法
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
from django.http import HttpResponse class MiddlewareShow(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Request') def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Response')
return response def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('MiddlewareShow1 process_view')
# print('=====>callback', callback)
# print('=====>callback_args', callback_args)
# ret = callback(callback_args)
# return ret def process_exception(self, request, exception):
print('MiddlewareShow1 process_exception')
return HttpResponse(exception) class MiddlewareShowTwo(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Request') def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Response')
return response def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('MiddlewareShow2 process_view') def process_exception(self, request, exception):
print('MiddlewareShow2 process_exception')
return HttpResponse(exception)
执行视图函数,查看控制台

问题来了,为啥没有走这个中间件方法呢?别慌,我们在视图函数中加个错
def middle_show(request):
leo print('执行了视图函数') return HttpResponse('hhh')
此时在执行下看看

此时可以看到当process_exception2获取到报错后,就返回了没有执行process_exception1
那如果我们在process_exception1处理呢,我们来测试下
from django.utils.deprecation import MiddlewareMixin
from django.http import HttpResponse class MiddlewareShow(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Request') def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow1 Response')
return response def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('MiddlewareShow1 process_view')
# print('=====>callback', callback)
# print('=====>callback_args', callback_args)
# ret = callback(callback_args)
# return ret def process_exception(self, request, exception):
print('MiddlewareShow1 process_exception')
return HttpResponse(exception) class MiddlewareShowTwo(MiddlewareMixin): def process_request(self, request):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Request') def process_response(self, request, response):
print('MiddlewareShow2 Response')
return response def process_view(self, request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs):
print('MiddlewareShow2 process_view') def process_exception(self, request, exception):
print('MiddlewareShow2 process_exception')
执行视图函数,打印看下
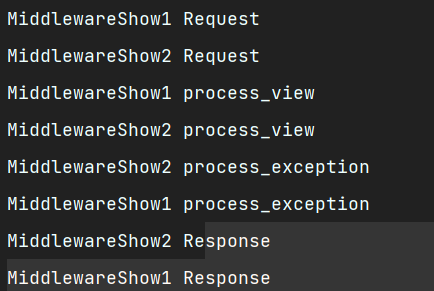
此时还会走到process_exception1哦,然后把错误返回给页面。
以上就是django中间件的介绍,希望和大家多多学习!转载请说明出处,尊重劳动成果!!!
django中间件介绍的更多相关文章
- python Django 中间件介绍
我们一直都在使用中间件,只是没有注意到而已,打开Django项目的Settings.py文件,看到下面的MIDDLEWARE配置项,django默认自带的一些中间件: MIDDLEWARE = [ ' ...
- {Django基础九之中间件} 一 前戏 二 中间件介绍 三 自定义中间件 四 中间件的执行流程 五 中间件版登陆认证
Django基础九之中间件 本节目录 一 前戏 二 中间件介绍 三 自定义中间件 四 中间件的执行流程 五 中间件版登陆认证 六 xxx 七 xxx 八 xxx 一 前戏 我们在前面的课程中已经学会了 ...
- 【12】Django 中间件
前戏 我们在前面的课程中已经学会了给视图函数加装饰器来判断是用户是否登录,把没有登录的用户请求跳转到登录页面.我们通过给几个特定视图函数加装饰器实现了这个需求.但是以后添加的视图函数可能也需要加上装 ...
- Django中间件2
前戏 我们在前面的课程中已经学会了给视图函数加装饰器来判断是用户是否登录,把没有登录的用户请求跳转到登录页面.我们通过给几个特定视图函数加装饰器实现了这个需求.但是以后添加的视图函数可能也需要加上装饰 ...
- 自定义Django中间件(登录验证中间件实例)
前戏 我们在前面的课程中已经学会了给视图函数加装饰器来判断是用户是否登录,把没有登录的用户请求跳转到登录页面.我们通过给几个特定视图函数加装饰器实现了这个需求.但是以后添加的视图函数可能也需要加上装饰 ...
- Django 2.0 学习(20):Django 中间件详解
Django 中间件详解 Django中间件 在Django中,中间件(middleware)其实就是一个类,在请求到来和结束后,Django会根据自己的规则在合适的时机执行中间件中相应的方法. 1. ...
- Django中间件的5种自定义方法
阅读目录(Content) Django中间件 自定义中间件 中间件(类)中5种方法 中间件应用场景 回到顶部(go to top) Django中间件 在http请求 到达视图函数之前 和视图函 ...
- Django 中间件使用
前戏 我们在前面的课程中已经学会了给视图函数加装饰器来判断是用户是否登录,把没有登录的用户请求跳转到登录页面.我们通过给几个特定视图函数加装饰器实现了这个需求.但是以后添加的视图函数可能也需要加上装 ...
- Django中间件如何处理请求
Django中间件 在http请求 到达视图函数之前 和视图函数return之后,django会根据自己的规则在合适的时机执行中间件中相应的方法. Django1.9版本以后中间件的执行流程 1. ...
随机推荐
- JDBC连接数据库,数据库访问层
为什么需要JDBC JDBC API DriverManager JDBC驱动 JDBC的功能 JDBC步骤 数据访问层DAO DAO模式的组成 DAO模式的实际应用 为什么需要JDBC? JDBC是 ...
- HBase,以及GeoMesa设计基于HBase的设计分析,从数据模型到典型查询场景,最后进行RowKey设计
GeoMesa设计基于HBase的设计分析,从数据模型到典型查询场景,最后进行RowKey设计 一.HBase 基本概念 理解KeyValue KeyValue多版本 列定义(1) 列定义(2) Co ...
- H3C交换机端口聚合配置
1.接入交换机: interface Ten-GigabitEthernet1/0/21 port link-mode bridge port link-type trunk port trunk p ...
- dedecms织梦后台栏目显示文档数不为0,但点进去之后什么都没有
曾经通过sql语句直接删除过dede_addonarticle或者dede_archives或者dede_arctiny中的记录,这三个表是有关联的,如果要通过sql语句删除内容,一定要同时将这三个表 ...
- 在线工具生成接入信息mqtt.fx快速接入阿里云
在线工具生成接入信息mqtt.fx快速接入阿里云 在使用阿里云获取的三元组信息进行接入的时候,往往需要加密生成接入信息之后才能进行接入,因此我根据阿里云提供的加密工具实现了一个阿里云物联网平台mqtt ...
- 记angular和asp.net使用grpc进行通信
AspNetCore配置grpc服务端 新建一个Demo项目: GrpcStartup, 目录结构如下图: GrpcStartup.GrpcServices需要安装下面的依赖 <PackageR ...
- Luogu T9376 区间GCD
题目背景 无 题目描述 给定一长度为n的动态序列,请编写一种数据结构,要求支持m次操作,包括查询序列中一闭区间中所有数的GCD,与对一闭区间中所有数加上或减去一个值. 输入输出格式 输入格式: 第1行 ...
- KMP——POJ-3461 Oulipo && POJ-2752 Seek the Name, Seek the Fame && POJ-2406 Power Strings && POJ—1961 Period
首先先讲一下KMP算法作用: KMP就是来求在给出的一串字符(我们把它放在str字符数组里面)中求另外一个比str数组短的字符数组(我们叫它为ptr)在str中的出现位置或者是次数 这个出现的次数是可 ...
- hdu517 Triple
Time Limit: 12000/6000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others) Total Submissio ...
- hdu4528 小明系列故事——捉迷藏
Time Limit: 500/200 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submission(s ...
