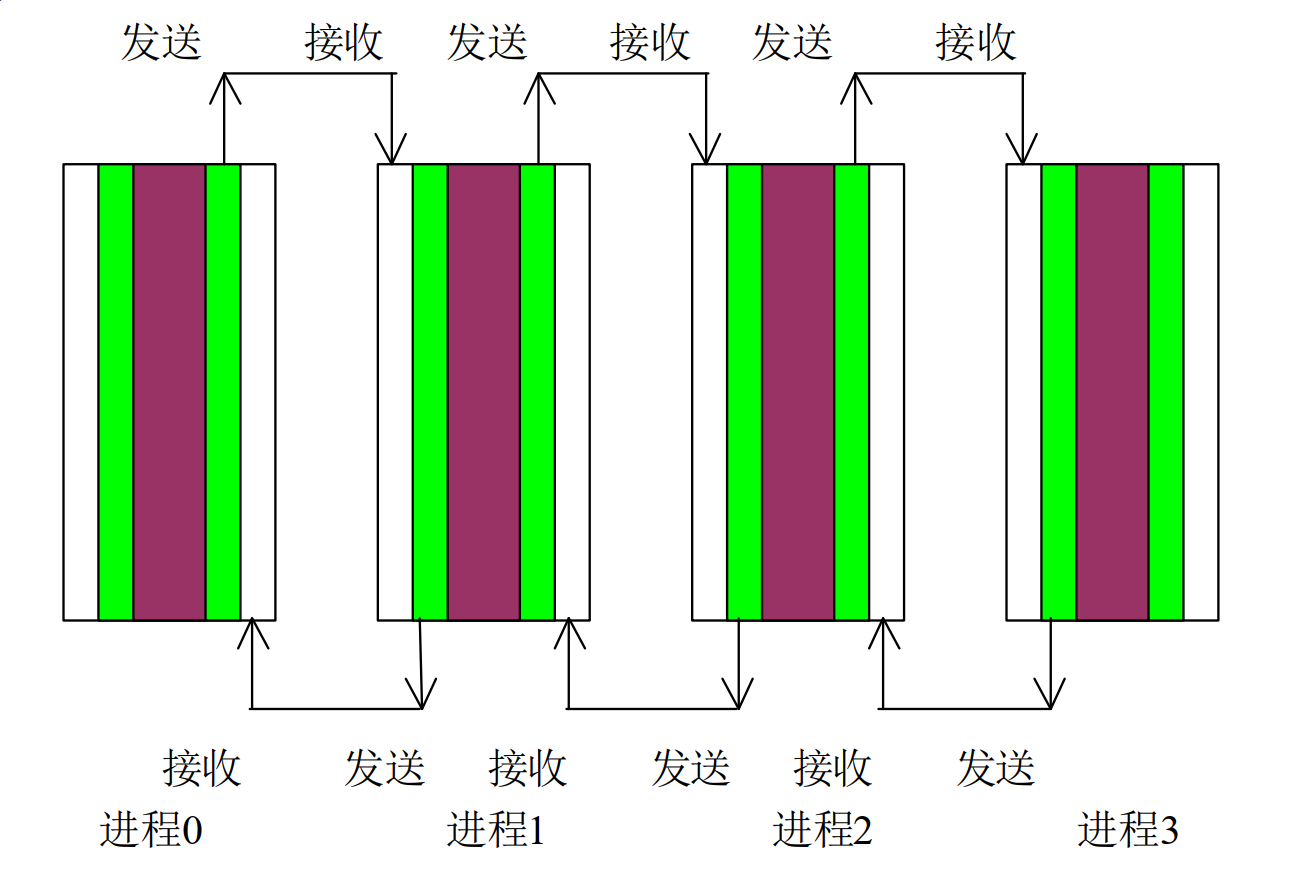
MPI实现Jacobi
一、Jacobi迭代
#include<stdio.h>
#include<mpi.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define totalsize 16
#define mysize totalsize / 4
#define steps 10
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int rank, size, i, j, begin_col, end_col;
//除分块大小外,还包括左右两边各一列
float a[totalsize][mysize + 2], b[totalsize][mysize + 2];
float temp[totalsize];//临时数组
MPI_Status status;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &size);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
printf("Process %d of %d is alive\n", rank, size);
//数组初始化
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
for (j = 0; j < mysize + 2; j++)
a[i][j] = 0;
if (rank == 0)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][1] = 8.0;
}
if (rank == 3)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][mysize] = 8.0;
}
for (i = 1; i < mysize + 1; i++)
{
a[0][i] = 8.0;
a[totalsize - 1][i] = 8.0;
}
//Jacobi 迭代
for (int n = 1; n <= steps; n++)
{
//从右边的邻居得到数据
if (rank < 3)
{
MPI_Recv(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank + 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][mysize + 1] = temp[i];
}
//向左侧的邻居发送数据
if (rank > 0)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
temp[i] = a[i][1];
MPI_Send(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank - 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
//向右侧的邻居发送数据
if (rank < 3)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
temp[i] = a[i][mysize];
MPI_Send(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank + 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
//从左侧的邻居得到数据
if (rank > 0)
{
MPI_Recv(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank - 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][0] = temp[i];
}
begin_col = 1;
end_col = mysize;
if (rank == 0) begin_col = 2;
if (rank == 3) end_col = mysize - 1;
for (i = 1; i < totalsize - 1; i++)
for (j = begin_col; j <= end_col; j++)
b[i][j] = 0.25 * (a[i][j + 1] + a[i][j - 1] + a[i + 1][j] + a[i - 1][j]);
for (i = 1; i < totalsize - 1; i++)
for (j = begin_col; j <= end_col; j++)
a[i][j] = b[i][j];
}
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
printf("Process %d:\n", rank);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= mysize; j++)
printf("%.2fP%d\t", a[i][j], rank);
printf("\n");
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
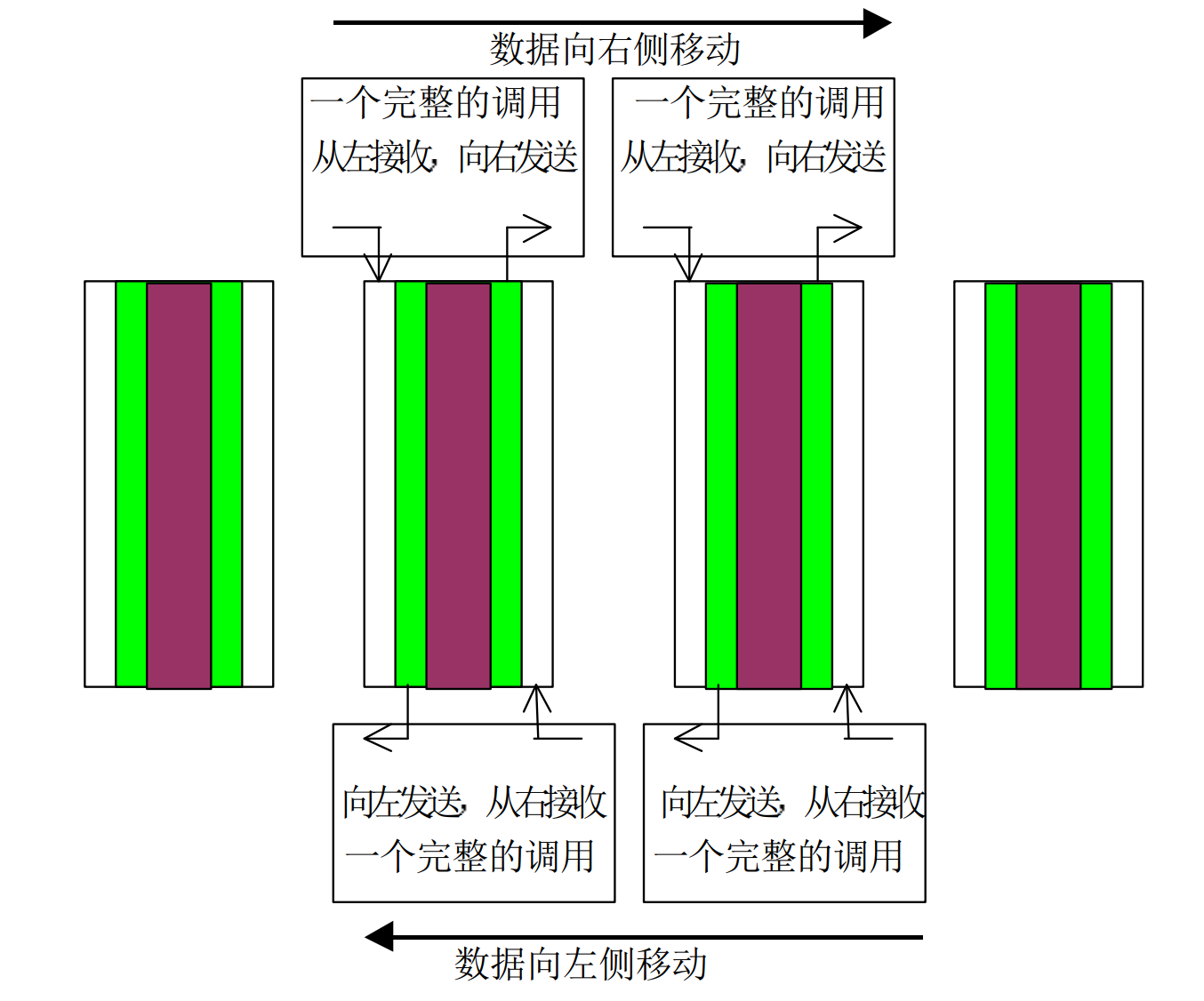
二、用捆绑发送接收实现Jacobi 迭代
#include<stdio.h>
#include<mpi.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define totalsize 16
#define mysize totalsize / 4
#define steps 10
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int rank, size, i, j, begin_col, end_col;
//除分块大小外,还包括左右两边各一列
float a[totalsize][mysize + 2], b[totalsize][mysize + 2];
float temp[totalsize],temp1[totalsize];//临时数组
MPI_Status status;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &size);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
printf("Process %d of %d is alive\n", rank, size);
//数组初始化
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
for (j = 0; j < mysize + 2; j++)
a[i][j] = 0;
if (rank == 0)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][1] = 8.0;
}
if (rank == 3)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][mysize] = 8.0;
}
for (i = 1; i < mysize + 1; i++)
{
a[0][i] = 8.0;
a[totalsize - 1][i] = 8.0;
}
//Jacobi 迭代
for (int n = 1; n <= steps; n++)
{
//从左向右平移数据
if (rank == 0)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
temp[i] = a[i][mysize];
MPI_Send(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank + 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
else if (rank == 3)
{
MPI_Recv(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank - 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][1] = temp[i];
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
temp[i] = a[i][1];
MPI_Sendrecv(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank - 1, 10, &temp1[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, \
rank + 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][1] = temp1[i];
}
//从右向左平移数据
if (rank == 0)
{
MPI_Recv(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank + 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][mysize] = temp[i];
}
else if (rank == 3)
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
temp[i] = a[i][1];
MPI_Send(&temp, totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank - 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
temp[i] = a[i][1];
MPI_Sendrecv(&temp[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, rank + 1, 10, &temp1[0], totalsize, MPI_FLOAT, \
rank - 1, 10, MPI_COMM_WORLD, &status);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
a[i][mysize] = temp1[i];
}
begin_col = 1;
end_col = mysize;
if (rank == 0) begin_col = 2;
if (rank == 3) end_col = mysize - 1;
for (i = 1; i < totalsize - 1; i++)
for (j = begin_col; j <= end_col; j++)
b[i][j] = 0.25 * (a[i][j + 1] + a[i][j - 1] + a[i + 1][j] + a[i - 1][j]);
for (i = 1; i < totalsize - 1; i++)
for (j = begin_col; j <= end_col; j++)
a[i][j] = b[i][j];
}
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
printf("Process %d:\n", rank);
for (i = 0; i < totalsize; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= mysize; j++)
printf("%.2fP%d\t", a[i][j], rank);
printf("\n");
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
矩阵乘
#include <stdio.h>
#include "mpi.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
#define SIZE 5
//生成随机矩阵
int** generate_matrix(int size)
{
int num = 0, m;
int** matrix;
matrix = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * size);
for (m = 0; m < size; m++)
matrix[m] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
int i, j;
srand(time(NULL) + rand());
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
matrix[i][j] = rand() % 20;
}
}
return matrix;
}
//输出矩阵
void print_matrx(int** a, int size)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < size; j++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
//矩阵相乘([参考](https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35614920/article/details/80570839))
int* Multiplication(int** a, int b[], int size)
{
int* result;
result = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
int i, m, n, sum = 0;
for (m = 0; m < size; m++)
{
for (n = 0; n < size; n++)
{
sum += a[n][m] * b[n];
}
result[m] = sum;
sum = 0;
}
return result;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int size, rank, dest;
MPI_Comm comm = MPI_COMM_WORLD;
MPI_Status status;
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_size(comm, &size);
MPI_Comm_rank(comm, &rank);
int** matrix1;
int** matrix2;
int send_buff[SIZE* SIZE];
matrix1 = generate_matrix(size);
matrix2 = generate_matrix(size);
if (rank == 0)
{
printf("matrix1 is :\n");
print_matrx((int**)matrix1, size);
printf("matrix2 is :\n");
print_matrx((int**)matrix2, size);
int j, k, tmp = 0;
for (j = 0; j < size; j++)
for (k = 0; k < size; k++)
{
send_buff[tmp] = matrix1[j][k];
tmp++;
}
}
int rbuf[SIZE];
int* result;
result = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
//分发列
MPI_Scatter(send_buff, size, MPI_INT, rbuf, size, MPI_INT, 0, comm);
result = Multiplication((int**)matrix2, rbuf, size);
MPI_Barrier(comm);//等待所有进程计算结束
int* recv_buff;
recv_buff = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size * size);
MPI_Barrier(comm);
MPI_Gather(result, size, MPI_INT, recv_buff, size, MPI_INT, 0, comm);//收集各列数据
//根进程进行输出
if (rank == 0)
{
printf("\nresult is :\n");
int m, n, tmp = 0;
for (m = 0; m < size; m++)
{
for (n = 0; n < size; n++)
{
printf("%d ", recv_buff[tmp]);
tmp++;
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
MPI实现Jacobi的更多相关文章
- 雅克比迭代算法(Jacobi Iterative Methods) -- [ mpi , c++]
雅克比迭代,一般用来对线性方程组,进行求解.形如: \(a_{11}*x_{1} + a_{12}*x_{2} + a_{13}*x_{3} = b_{1}\) \(a_{21}*x_{1} + a_ ...
- 【MPI学习4】MPI并行程序设计模式:非阻塞通信MPI程序设计
这一章讲了MPI非阻塞通信的原理和一些函数接口,最后再用非阻塞通信方式实现Jacobi迭代,记录学习中的一些知识. (1)阻塞通信与非阻塞通信 阻塞通信调用时,整个程序只能执行通信相关的内容,而无法执 ...
- 【MPI学习2】MPI并行程序设计模式:对等模式 & 主从模式
这里的内容主要是都志辉老师<高性能计算之并行编程技术——MPI并行程序设计> 书上有一些代码是FORTAN的,我在学习的过程中,将其都转换成C的代码,便于统一记录. 这章内容分为两个部分: ...
- 查找素数Eratosthenes筛法的mpi程序
思路: 只保留奇数 (1)由输入的整数n确定存储奇数(不包括1)的数组大小: n=(n%2==0)?(n/2-1):((n-1)/2);//n为存储奇数的数组大小,不包括基数1 (2)由数组大小n.进 ...
- kmeans算法并行化的mpi程序
用c语言写了kmeans算法的串行程序,再用mpi来写并行版的,貌似参照着串行版来写并行版,效果不是很赏心悦目~ 并行化思路: 使用主从模式.由一个节点充当主节点负责数据的划分与分配,其他节点完成本地 ...
- MPI Maelstrom - POJ1502最短路
Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Description BIT has recently taken delivery of their new sup ...
- MPI之求和
// MPI1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点. // #include "stdafx.h" #include "mpi.h" #include &l ...
- VS2012下配置MPI
并行处理结课实验,要用到MPI编程,我的电脑和VS2012都是64位的,以为MPICH也得是64位才行,结果饶了很大的弯——配置正确,添加引用之后,仍然无法识别MPI函数. 后来换了个32位的MPIC ...
- MPI+WIN10并行试运行
系统:2015 win10专业版 x64 MPI安装包:mpich2-1.4.1p1-win-x86-64.man 将后缀改为.msi 以管理员身份安装 安装过程一路默认,注意<behappy为 ...
随机推荐
- Apache Tomcat/8.5.51 secretRequired="true"
1.报错IllegalArgumentException: The AJP Connector is configured with secretRequired="true" b ...
- SUM and COUNT -- SQLZOO
SUM and COUNT 注意:where语句中对表示条件的需要用单引号, 下面的译文使用的是有道翻译如有不正确,请直接投诉有道 01.Show the total population of th ...
- PHP is_writable() 函数
定义和用法 is_writable() 函数检查指定的文件是否可写. 如果文件可写,该函数返回 TRUE. 语法 is_writable(file) 参数 描述 file 必需.规定要检查的文件. 提 ...
- PHP 获取图像宽度与高度
PHP 获取图像宽度函数:imagesx() imagesx() 函数用于获取图像的宽度,单位为像素,返回值为整型.高佣联盟 www.cgewang.com 语法: int imagesx( reso ...
- PHP imagecolorclosestalpha - 取得与指定的颜色加透明度最接近的颜色的索引
imagecolorclosestalpha — 取得与指定的颜色加透明度最接近的颜色的索引.高佣联盟 www.cgewang.com 语法 int imagecolorclosestalpha ( ...
- “随手记”开发记录day09
今天完成了关于我们页面和更新查找页面 效果
- Axios源码分析
Axios是一个基于promise的HTTP库,可以用在浏览器和node.js中. 文档地址:https://github.com/axios/axios axios理解和使用 1.请求配置 { // ...
- 微信公众号里放XLS链接
微信公众号里放XLS链接 我们都知道创建一个微信公众号在公众号中发布一些文章是非常简单的,但公众号添加附件下载的功能却被限制,如今可以使用小程序“微附件”进行在公众号中添加附件,如:xls,word等 ...
- Linux探测工具BCC(可观测性)
BCC(可观测性) 目录 BCC(可观测性) 简介 动机 版本要求 安装 安装依赖 安装和编译LLVM 安装和编译BCC windows源码查看 BCC的基本使用 工具讲解 execsnoop ope ...
- 2020-05-21:es底层读写原理?倒排索引原理?
福哥答案2020-05-21: es不熟悉,答案仅供参考:es写数据过程1.客户端选择一个node发送请求过去,这个node就是coordinating node(协调节点)2.coordinatin ...
