spring的笔记1 关云长
1.1 实例化方式
l 3种bean实例化方式:默认构造、静态工厂、实例工厂
1.1.1 默认构造
|
<bean id="" class=""> 必须提供默认构造 |
1.1.2 静态工厂
l 常用与spring整合其他框架(工具)
l 静态工厂:用于生成实例对象,所有的方法必须是static
|
<bean id="" class="工厂全限定类名" factory-method="静态方法"> |
1.1.2.1 工厂-创建实例
|
public class MyBeanFactory { public static UserService createService(){ return new UserServiceImpl(); }} |
1.1.2.2 spring配置
|
<!-- 将静态工厂创建的实例交予spring class 确定静态工厂全限定类名 <bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.c_inject.b_static_factory.MyBeanFactory" factory-method="createService"></bean> |
1.1.3 实例工厂
l 实例工厂:必须先有工厂实例对象,通过实例对象创建对象。提供所有的方法都是“非静态”的。
1.1.3.1 工厂
|
/** 实例工厂,所有方法非静态 创建实例 */ public class MyBeanFactory { public UserService createService(){ return new UserServiceImpl(); } } |
1.1.3.2 spring配置
|
<!-- 创建工厂实例 --> <bean id="myBeanFactoryId" class="com.itheima.c_inject.c_factory.MyBeanFactory"></bean> <!-- 获得userservice * factory-bean 确定工厂实例 * factory-method 确定普通方法--> <bean id="userServiceId" factory-bean="myBeanFactoryId" factory-method="createService"></bean> |
1.2 Bean种类
l 普通bean:之前操作的都是普通bean。<beanid="" class="A"> ,spring直接创建A实例,并返回
l FactoryBean:是一个特殊的bean,具有工厂生成对象能力,只能生成特定的对象。
bean必须使用 FactoryBean接口,此接口提供方法 getObject() 用于获得特定bean。
<bean id="" class="FB"> 先创建FB实例,使用调用getObject()方法,并返回方法的返回值
FB fb = new FB();
returnfb.getObject();
l BeanFactory 和 FactoryBean 对比?
BeanFactory:工厂,用于生成任意bean。
FactoryBean:特殊bean,用于生成另一个特定的bean。例如:ProxyFactoryBean ,此工厂bean用于生产代理。<bean id=""class="....ProxyFactoryBean"> 获得代理对象实例。AOP使用
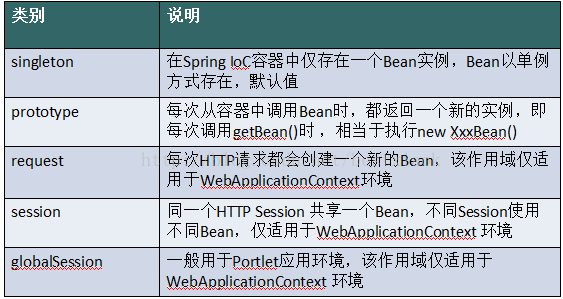
1.3 作用域
l 作用域:用于确定spring创建bean实例个数
l 取值:
singleton 单例,默认值。
prototype 多例,每执行一次getBean将获得一个实例。例如:struts整合spring,配置action多例。
l 配置信息
|
<bean id="" class="" scope=""> |
|
<bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.d_scope.UserServiceImpl" |
1.4 生命周期-11个步骤
1.4.1 初始化和销毁
l 目标方法执行前后执行后,将进行初始化或销毁。
|
<bean id="" class="" init-method="初始化方法名称" destroy-method="销毁的方法名称"> |
1.4.1.1 目标类
|
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { @Override public void addUser() { System.out.println("e_lifecycle add user"); } public void myInit(){ System.out.println("初始化"); } public void myDestroy(){ System.out.println("销毁"); } } |
1.4.1.2 spring配置
|
<!-- init-method 用于配置初始化方法,准备数据等 <bean id="userServiceId" class="com.itheima.e_lifecycle.UserServiceImpl" init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestroy" ></bean> |
1.4.1.3 测试
|
@Test public void demo02() throws Exception{ //spring 工厂 String xmlPath = "com/itheima/e_lifecycle/beans.xml"; ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userServiceId"); userService.addUser(); //要求:1.容器必须close,销毁方法执行; // applicationContext.getClass().getMethod("close").invoke(applicationContext); // * 此方法接口中没有定义,实现类提供 applicationContext.close(); } |
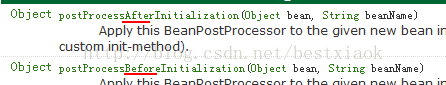
1.4.2 BeanPostProcessor 后处理Bean
l spring 提供一种机制,只要实现此接口BeanPostProcessor,并将实现类提供给spring容器,spring容器将自动执行,在初始化方法前执行before(),在初始化方法后执行after() 。 配置<bean class="">
l Factory hook(勾子) that allows for custom modification of new bean instances, e.g.checking for marker interfaces or wrapping them with proxies.
l spring提供工厂勾子,用于修改实例对象,可以生成代理对象,是AOP底层。
模拟
A a =new A();
a = B.before(a) --> 将a的实例对象传递给后处理bean,可以生成代理对象并返回。
a.init();
a = B.after(a);
a.addUser(); //生成代理对象,目的在目标方法前后执行(例如:开启事务、提交事务)
a.destroy()
1.4.2.1 编写实现类
|
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("前方法: " + beanName); return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException System.out.println("后方法: " + beanName); // bean 目标对象 // 生成 jdk 代理 return Proxy.newProxyInstance( MyBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler(){ @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("------开启事务"); //执行目标方法 Object obj = method.invoke(bean, args); System.out.println("------提交事务"); return obj; }}); } } |
1.4.2.2 配置
|
<!-- 将后处理的实现类注册给spring --> <bean class="com.itheima.e_lifecycle.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean> |
l 问题1:后处理bean作用某一个目标类,还是所有目标类?
所有
l 问题2:如何只作用一个?
通过“参数2”beanName进行控制
1.5 属性依赖注入
l 依赖注入方式:手动装配 和 自动装配
l 手动装配:一般进行配置信息都采用手动
基于xml装配:构造方法、setter方法
基于注解装配:
l 自动装配:struts和spring 整合可以自动装配
byType:按类型装配
byName:按名称装配
constructor构造装配,
auto: 不确定装配。
1.5.1 构造方法
1.5.1.1 目标类
|
public class User { private Integer uid; private String username; private Integer age; public User(Integer uid, String username) { super(); this.uid = uid; this.username = username; } public User(String username, Integer age) { super(); this.username = username; this.age = age; } |
1.5.1.2 spring配置
|
<!-- 构造方法注入 * <constructor-arg> 用于配置构造方法一个参数argument name :参数的名称 value:设置普通数据 ref:引用数据,一般是另一个bean id值 开始。如果只有索引,匹配到了多个构造方法时,默认使用第一个。 type :确定参数类型 --> <bean id="userId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.a_constructor.User" > <constructor-arg index="0" type="java.lang.String" value="1"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="1" type="java.lang.Integer" value="2"></constructor-arg> </bean> |
1.5.2 setter方法
|
<!-- setter方法注入 * 普通数据 <property name="" value="值"> 等效 <property name=""> <value>值 * 引用数据 <property name="" ref="另一个bean"> 等效 <property name=""> <ref bean="另一个bean"/> --> <bean id="personId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.b_setter.Person"> <property name="pname" value="阳志"></property> <property name="age"> <value>1234</value> </property> <property name="homeAddr" ref="homeAddrId"></property> <property name="companyAddr"> <ref bean="companyAddrId"/> </property> </bean> <bean id="homeAddrId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.b_setter.Address"> <property name="addr" value="阜南"></property> <property name="tel" value="911"></property> </bean> <bean id="companyAddrId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.b_setter.Address"> <property name="addr" value="北京八宝山"></property> <property name="tel" value="120"></property> </bean> |
1.5.3 P命令空间[了解]
l 对“setter方法注入”进行简化,替换<property name="属性名">,而是在
<beanp:属性名="普通值" p:属性名-ref="引用值">
l p命名空间使用前提,必须添加命名空间
|
<bean id="personId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.c_p.Person" p:pname="禹太璞" p:age="22" p:homeAddr-ref="homeAddrId" p:companyAddr-ref="companyAddrId"> </bean> <bean id="homeAddrId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.c_p.Address" p:addr="DG" p:tel="东莞"> </bean> <bean id="companyAddrId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.c_p.Address" p:addr="DG" p:tel="岛国"> </bean> |
1.5.4 SpEL[了解]
l 对<property>进行统一编程,所有的内容都使用value
<propertyname="" value="#{表达式}">
#{123}、#{'jack'} : 数字、字符串
#{beanId} :另一个bean引用
#{beanId.propName} :操作数据
#{beanId.toString()} :执行方法
#{T(类).字段|方法} :静态方法或字段
|
<!-- <property name="cname" value="#{'jack'}"></property> <property name="cname" value="#{customerId.cname.toUpperCase()}"></property> 通过另一个bean,获得属性,调用的方法 <property name="cname" value="#{customerId.cname?.toUpperCase()}"></property> ?. 如果对象不为null,将调用方法 --> <bean id="customerId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.d_spel.Customer" > <property name="cname" value="#{customerId.cname?.toUpperCase()}"></property> <property name="pi" value="#{T(java.lang.Math).PI}"></property> </bean> |
1.5.5 集合注入
|
<!-- 集合的注入都是给<property>添加子标签 数组:<array> List:<list> Set:<set> Map:<map> ,map存放k/v 键值对,使用<entry>描述 Properties:<props> <prop key=""></prop> 【】 普通数据:<value> 引用数据:<ref> --> <bean id="collDataId" class="com.itheima.f_xml.e_coll.CollData" > <property name="arrayData"> <array> <value>DS</value> <value>DZD</value> <value>屌丝</value> <value>屌中屌</value> </array> </property> <property name="listData"> <list> <value>于嵩楠</value> <value>曾卫</value> <value>杨煜</value> <value>曾小贤</value> </list> </property> <property name="setData"> <set> <value>停封</value> <value>薄纸</value> <value>关系</value> </set> </property> <property name="mapData"> <map> <entry key="jack" value="杰克"></entry> <entry> <key><value>rose</value></key> <value>肉丝</value> </entry> </map> </property> <property name="propsData"> <props> <prop key="高富帅">嫐</prop> <prop key="白富美">嬲</prop> <prop key="男屌丝">挊</prop> </props> </property> </bean> |
spring的笔记1 关云长的更多相关文章
- Spring Security笔记:HTTP Basic 认证
在第一节 Spring Security笔记:Hello World 的基础上,只要把Spring-Security.xml里改一个位置 <http auto-config="true ...
- 【Spring学习笔记-MVC-3.1】SpringMVC返回Json数据-方式1-扩展
<Spring学习笔记-MVC>系列文章,讲解返回json数据的文章共有3篇,分别为: [Spring学习笔记-MVC-3]SpringMVC返回Json数据-方式1:http://www ...
- (转) Spring读书笔记-----Spring的Bean之配置依赖
前一篇博客介绍了Spring中的Bean的基本概念和作用域(Spring读书笔记-----Spring的Bean之Bean的基本概念),现在介绍Spring Bean的基本配置. 从开始我们知道Jav ...
- spring 入门笔记(一)
最近学习spring 通过笔记形式加深自己对spring的理解,也希望能跟各位入门者分享和讨论. 一.下载spring 下载spring也费了不少功夫,目前还没从spring官网找到下载入口,我从下面 ...
- struts2,hibernate,spring整合笔记(3)
struts2,hibernate,spring整合笔记(1) struts2,hibernate,spring整合笔记(2) 配好struts和hibernate就要开始spring了 老规矩,还是 ...
- struts2,hibernate,spring整合笔记(2)
上一话struts2,hibernate,spring整合笔记(1) 接下来继续 配置完struts之后就要开始hibernate的配置 hibernate的环境并不依赖web开发环境,在我第一次配置 ...
- Spring读书笔记——bean解析
前情回顾 上篇<Spring读书笔记--bean加载>我们从代码角度介绍了有哪些类负责解析XML文件,又是如何一步步从XML格式脱变成我们熟悉的bean的,直到DefaultBeanDef ...
- Spring读书笔记——bean创建(上)
通过<Spring读书笔记--bean加载>和<Spring读书笔记--bean解析>,我们明白了两件事. Spring如何加载消化一个xml配置文件 Spring如何将xml ...
- Spring读书笔记——bean创建(下)
有关Spring加载bean系列,今天这是最后一篇了,主要接上篇对于从Spring容器中获取Bean的一些细节实现的补充. <Spring读书笔记--bean加载>--Spring如何加载 ...
随机推荐
- 【Python】常用内建模块(卒)
内容来自廖雪峰的官方网站 笔记性质 1.datetime 2.collections 3.base64 4.struct 5.hashlib 6.itertools 7.contextlib 8.XM ...
- ASP.NET CORE MVC 2.0 发布到IIS 配置问题
装完.NET CORE 2.0和IIS , 配置好网站, 报500.19 配置文件错误. 解决方法: 1) 安装.NET Core Windows Server Hosting : https:/ ...
- OwinStartup not firing
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20203982/owinstartup-not-firing 缺少依赖 Make sure you have installe ...
- ubuntu 14.04 建立wifi热点
昨天突然想起来我可以用笔记本搞一个热点这样我的手机就不用上流量了,但是手机死活搜不到建好的信号,目前的解决方案如下: 直接用ubuntu自带的创建wifi网络功能是不好使的,因为android系统不支 ...
- 腾讯开源手游热更新方案,Unity3D下的Lua编程
原文:http://www.sohu.com/a/123334175_355140 作者|车雄生 编辑|木环 腾讯最近在开源方面的动作不断:先是微信跨平台基础组件Mars宣布开源,腾讯手游又于近期开源 ...
- GitLab使用总结[转]
http://blog.csdn.net/huaishu/article/details/50475175 GitLab使用总结
- 【Python】内置函数清单
Python内置(built-in)函数随着python解释器的运行而创建.在Python的程序中,你可以随时调用这些函数,不需要定义.最常见的内置函数是: print("Hello Wor ...
- Angular路由的定义和使用
一.什么是routing(路由) Almost all non-trivial, non-demo Single Page App (SPA) require multiple pages. A se ...
- com.itnba.maya.domel.Diaoyantimu_$$_javassist_1 cannot be cast to javassist.util.proxy.Proxy错误问题解决方法
控制台报错显示: com.itnba.maya.domel.Diaoyantimu_$$_javassist_1 cannot be cast to javassist.util.proxy.Prox ...
- Elasticsearch 文档专用
ES安装等操作 http://blog.csdn.net/cnweike/article/details/33736429 https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasti ...