Summary: Lowest Common Ancestor in a Binary Tree & Shortest Path In a Binary Tree
转自:Pavel's Blog
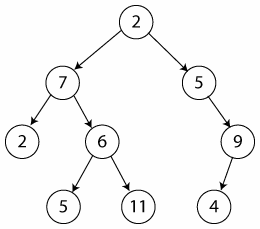 |
public static Node lowestCommonAncestor(Node root, Node a, Node b) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.equals(a) || root.equals(b)) {
// if at least one matched, no need to continue
// this is the LCA for this root
return root;
}
Node l = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, a, b);
Node r = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, a, b);
if (l != null && r != null) {
return root; // nodes are each on a seaparate branch
}
// either one node is on one branch,
// or none was found in any of the branches
return l != null ? l : r;
}
For the node used we will use the following class:
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node right;
public Node left;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
这个问题再follow up一下,就是要找到shortest path in a binary tree between two nodes
public class Solution {
public static List<Node> shortestPath(Node root, Node a, Node b) {
ArrayList<Node> path1 = new ArrayList<Node>();
ArrayList<Node> path2 = new ArrayList<Node>();
Node LCA = lowestCommonAncestor(root, a, b);
helper(LCA.left, a, b, path1, new ArrayList<Node>());
helper(LCA.right, a, b, path2, new ArrayList<Node>());
Collections.reverse(path1);
path1.add(LCA);
path1.addAll(new ArrayList<Node>(path2));
return path1;
}
public void helper(Node root, Node a, Node b, ArrayList<Node> outpath, ArrayList<Node> temp) {
if (root == null) return;
temp.add(root);
if (root == a || root == b) {
outpath = new ArrayList<Node>(temp);
return;
}
helper(root.left, a, b, outpath, temp);
helper(root.right, a, b, outpath, temp);
temp.remove(temp.size()-1);
}
}
别人的Stack做法,未深究 他说First stack is not really needed, a simple list would do - I just like symmetry.
public static <V> void shortestpath(
Node<V> root, Node<V> a, Node<V> b,
Stack<Node<V>> outputPath) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.data.equals(a.data) || root.data.equals(b.data)) {
outputPath.push(root);
return;
} shortestpath(root.left, a, b, outputPath);
shortestpath(root.right, a, b, outputPath); outputPath.push(root);
} public static List<Node> shortestPath(Node root, Node a, Node b) {
Stack<Node> path1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Node> path2 = new Stack<>(); Node lca = lowestCommonAncestor(root, a, b); // This is to handle the case where one of the nodes IS the LCA
Node r = lca.equals(a) ? a : (lca.equals(b) ? b : lca); shortestpath(r.left, a, b, path1);
shortestpath(r.right, a, b, path2); path1.push(r);
// invert the second path
while (!path2.isEmpty()) {
path1.push(path2.pop());
}
return path1;
}
Summary: Lowest Common Ancestor in a Binary Tree & Shortest Path In a Binary Tree的更多相关文章
- Range Minimum Query and Lowest Common Ancestor
作者:danielp 出处:http://community.topcoder.com/tc?module=Static&d1=tutorials&d2=lowestCommonAnc ...
- A1143. Lowest Common Ancestor
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is the deepest node that has both U ...
- PAT A1143 Lowest Common Ancestor (30 分)——二叉搜索树,lca
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is the deepest node that has both U ...
- 1143 Lowest Common Ancestor
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is the deepest node that has both U ...
- PAT 甲级 1143 Lowest Common Ancestor
https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805343727501312 The lowest common ance ...
- PAT 1143 Lowest Common Ancestor[难][BST性质]
1143 Lowest Common Ancestor(30 分) The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is ...
- [PAT] 1143 Lowest Common Ancestor(30 分)
1143 Lowest Common Ancestor(30 分)The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is ...
- 1143. Lowest Common Ancestor (30)
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is the deepest node that has both U ...
- PAT 1143 Lowest Common Ancestor
The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is the deepest node that has both U ...
随机推荐
- UITableView 如何设置背景颜色
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_6734cee201011kya.html 原因:1.backgroundView 属性不为nil,所有设置backgroundColor ...
- 浏览器 User Agent字符串列表
http://www.73207.com/useragent/ http://www.73207.com/useragent/pages/internet-2520explorer/index.htm ...
- win8/win7中使用Git Extensions PuTTy模式提交时 git-credential-winstore.exe": No such file or directory 错误解决方案
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/hlizard/p/3627792.html 报错类似以下错误 \"F:/GitExtensions/GitCredentialWinSt ...
- 单例模式全面学习(C++版)
单例模式:用来创建独一无二的,只能够有一个实例的对象. 单例模式的结构是设计模式中最简单的,但是想要完全实现一个线程安全的单例模式还是有很多陷阱的,所以面试的时候属于一个常见的考点~ 单例模式的应用场 ...
- 严版数据结构题集2.13 & 2.14
1.试写一算法在带头结点的单链表结构上实现线性表操作Locate(L,x) 2.试写一算法在带头结点的单链表结构上实现线性表操作Length(L) #include<stdio.h> #i ...
- http后台json解析实例
localhost:8080/hbinterface/orderInterface/sIReverseAccept.do?bizType=4&&bnetAccount=ESBTEST2 ...
- zookeeper 安装的三种模式
Zookeeper安装 zookeeper的安装分为三种模式:单机模式.集群模式和伪集群模式. 单机模式 首先,从Apache官网下载一个Zookeeper稳定版本,本次教程采用的是zookeeper ...
- PHP生成页面二维码解决办法?详解
随着科技的进步,二维码应用领域越来越广泛,今天我给大家分享下如何使用PHP生成二维码,以及如何生成中间带LOGO图像的二维码. 具体工具: phpqrcode.php内库:这个文件可以到网上下载,如果 ...
- [EF]vs15+ef6+mysql code first方式
写在前面 前面有篇文章,尝试了db first方式,但不知道是什么原因一直没有成功,到最后也没解决,今天就尝试下code first的方式. [EF]vs15+ef6+mysql这个问题,你遇到过么? ...
- Mybatis批量insert报错的解决办法【the right syntax to use near '' at line...】
Java中使用Mybatis批量插入数据时Mapper.xml中的sql如下: <insert id="batchSave"> into t_emp(emp_name, ...
