自己动手实现STL 01:内存配置器的实现(stl_alloc.h)
一、前言
在STL中,容器是其中的重中之重,基本的STL中的算法,仿函数等都是围绕着容器实现的功能。而,内存配置器,是容器的实现的基础。所以,我第一次要去编写便是内存配置器的实现。在STL中,内存配置器的实现是在stl_alloc.h中。
二、配置器原理简要介绍
在SGI STL中配置分为两级,第一级配置器和第二级配置器。两者关系如下:
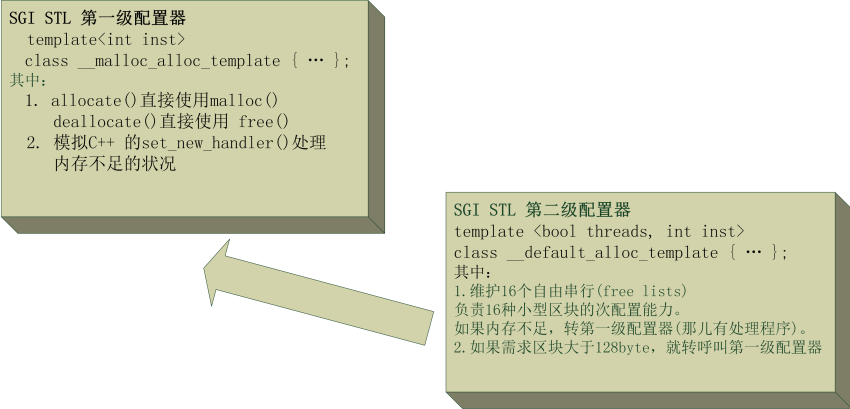
图1:第一级配置器和第二级配置器
在SGI STL中内存的配置器分为两级,第一级配置器和第二级配置器。第一级配置器就是,直接调用系统的malloc分配内存。对于小于128byte的内存分配请求,我们使用第二级内存配置器。第二级内存配置器是一个内存池,其中共有16个已分配好的区块形成的链表。这16个链表的中区块的大小依次是8,16,24....128byte,都8的倍数。每次请求小于等于128byte时,把请求的大小上调到最接近的8的倍数,比如,7就上调为8,30就上调为32,然后找到对应大小区块的链表,从中取下一个区块返回给请求。
第二级配置器使用内存池的好处就是,可以避免太多小额区块造成的内存破碎。同时,每次分配内存都需要调用malloc去分配,malloc调用的消耗的时间等资源是一定的,对于大区块的分配这样的消耗的时间等资源,是没有什么的。但是对于小额区块的,它的消耗就显得太不值的了。我们可以采用一次预分配一块连续的大区块,把它串成一个定额大小的区块链表,(8的倍数字节),下次使用的时候,从对应预分配的区块链表中找一个能够满足大小的,最接近的区块直接返回给请求,这样就可以避免对于小区块的malloc调用。同时对于小区块的释放,可以直接把它加入到内存池中对应大小的链表中即可。

图2:把连续大区块串成小额区块
在第二级配置器中维持一个free_list[16]数组,其中存储着8-128byte各种大小区块的链表的头节点地址。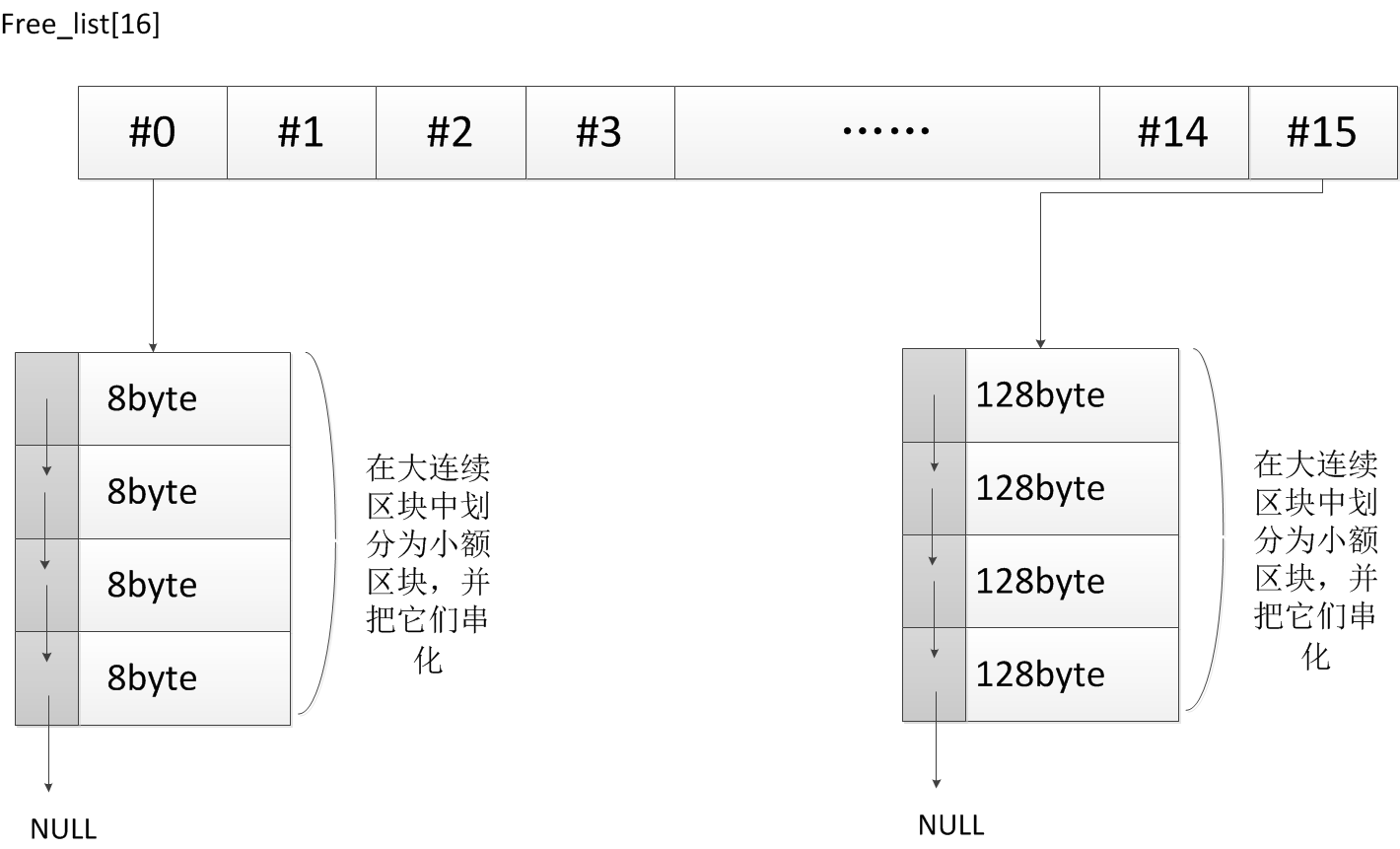
图3:free_list[16]结构
每次分配只要从适当大小的链表中取出第一个节点,返回给请求,让free_list对应的位置的保存链表的下一个节点地址。释放的时候,对于小于等于128byte的区块,只要把它插入对应大小区块链表的头,然后调整保存的链表头结点的地址就可以了。当需求大小区块的使用完了的时候,可以利用malloc一次分配适当大小的大区块,然后把它分割为对应大小的小区块,在把它们串联起来形成链表,把第一个节点地址存入对应的free_list的位置中。
三、实现源代码
上面只是配置器的简介,在源码中有详细的注释。源码如下:
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: stl_alloc_wjzh.h
> Author: wjzh
> Mail: wangjzh_1@163.com
> Created Time: 2014年10月31日 星期五 16时06分23秒
************************************************************************/ #ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALLOC_WJZH_H
#define __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALLOC_WJZH_H #ifdef __SUNPRO_CC
# define __PRIVATE public
#else
# define __PRIVATE private
#endif #ifdef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
# define __USE_MALLOC
#endif #if 0
# include <new>
# define __THROW_BAD_ALLOC throw bad_alloc
#elif !defined(__THROW_BAD_ALLOC)
//# include <iostream.h>
#include <iostream>
# define __THROW_BAD_ALLOC std::cerr << "out of memory" << std::endl; exit()
#endif #ifndef __ALLOC
# define __ALLOC alloc
#endif
#ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS
# include <windows.h>
#endif #include <stddef.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
#ifndef __RESTRICT
# define __RESTRICT
#endif #if !defined(__STL_PTHREADS) && !defined(_NOTHREADS) \
&& !defined(__STL_SGI_THREADS) && !defined(__STL_WIN32THREADS)
# define _NOTHREADS
#endif #ifdef __STL_PTHREADS
# include <pthread.h>
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK \
if (threads) pthread_mutex_lock(&__node_allocator_lock)
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK \
if (threads) pthread_mutex_unlock(&__node_allocator_lock)
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS true
# define __VOLATILE volatile
# endif
# ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK \
EnterCriticalSection(&__node_allocator_lock)
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK \
LeaveCriticalSection(&__node_allocator_lock)
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS true
# define __VOLATILE volatile
# endif # ifdef __STL_SGI_THREADS
extern "C" {
extern int __us_rsthread_malloc;
}
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK if (threads && __us_rsthread_malloc) \
{ __lock(&__node_allocator_lock); }
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK if(threads && __us_rsthread_malloc) \
{ __unlcok(&__node_allocator_lock); }
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS true
# define __VOLATILE volatile
# endif # ifdef _NOTHREADS
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK
# define __NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS false
# define __VOLATILE
# endif __STL_BEGIN_NAMESPACE #if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma set woff 1174
#endif #ifdef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
# ifdef __DECLARE_GLOBALS_HERE
void (* __malloc_alloc_oom_handler)() = ;
#else
extern void (* __malloc_alloc_oom_handler)();
# endif
#endif template <int inst>
class __malloc_alloc_template {
private:
static void *oom_malloc(size_t);
static void *oom_realloc(void *, size_t);
#ifndef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
static void (* __malloc_alloc_oom_handler)();
#endif
public:
static void* allocate(size_t n)
{
void *result = malloc(n);
if ( == result) result = oom_malloc(n);
return result;
} static void deallocate(void *p, size_t)
{
free(p);
} static void * reallocate(void *p, size_t , size_t new_sz)
{
void *result = realloc(p, new_sz);
if ( == result) result = oom_realloc(p, new_sz);
return result;
} static void (* set_malloc_handler(void (*f)()))()
{
void (* old)() = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
__malloc_alloc_oom_handler = f;
return(old);
} }; // malloc_alloc out-of-memory handling
// 分配内存时,没有内存时的处理 #ifndef __STL_STATIC_TEMPLATE_MEMBER_BUG
template <int inst>
void (* __malloc_alloc_template<inst>::__malloc_alloc_oom_handler)() = ;
#endif template <int inst>
void * __malloc_alloc_template<inst>::oom_malloc(size_t n)
{
void (* my_malloc_handler)();
void *result;
for (;;)
{
my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
if ( == my_malloc_handler) { __THROW_BAD_ALLOC; }
(*my_malloc_handler)();
result = malloc(n);
if (result) return (result);
}
} template <int inst>
void * __malloc_alloc_template<inst>::oom_realloc(void *p, size_t n)
{
void (* my_malloc_handler)();
void *result; for (;;)
{
my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
if ( == my_malloc_handler) { __THROW_BAD_ALLOC; }
(*my_malloc_handler)();
result = realloc(p, n);
if (result) return (result);
}
} typedef __malloc_alloc_template<> malloc_alloc; template<class T, class Alloc>
class simple_alloc
{
public:
static T *allocate(size_t n)
{
return == n ? : (T*) Alloc::allocate(n * sizeof(T));
}
static T *allocate(void)
{
return (T*) Alloc::allocate(sizeof(T));
}
static void deallocate(T *p, size_t n)
{
if ( != n) Alloc::deallocate(p, n * sizeof(T));
}
static void deallocate(T *p)
{
Alloc::deallocate(p, sizeof(T));
}
}; // Allocator adaptor to check size arguments for debugging.
template <class Alloc>
class debug_alloc
{
private:
enum { extra = }; // Size of space used to store size. Note
// that this must be large enough to preserve
// alignment. public:
static void * allocate(size_t n)
{
char *result = (char *)Alloc::allocate(n + extra);
*(size_t *)result = n; //前size_t大小用来记录result的大小,实际预分配了extra个字节,用来存储大小,
//但是只用size_t字节,因为不同系统size_t大小不同,8个字节足够满足所有系统了
return result + extra;
} static void deallocate(void *p, size_t n)
{
char * real_p = (char *)p - extra;
assert(*(size_t *)real_p == n);
Alloc::deallocate(real_p, n + extra);
} static void * reallocate(void *p, size_t old_sz, size_t new_sz)
{
char * real_p = (char *)p - extra;
assert(*(size_t *)real_p == old_sz);
char * result = (char *)
Alloc::reallocate(real_p, old_sz + extra, new_sz+ extra);
*(size_t *)result = new_sz;
return result + extra;
} }; #ifdef __USE_MALLOC typedef malloc_alloc alloc;
typedef malloc_alloc single_client_alloc; #else //下面是第二级配置器
//主要是维护一个内存池,用来小于128byte的小型区块内存的分配
//其中,有多个链表,各链表中的node大小从8-128byte,都是8的倍数
//分配时,不是8的倍数,上调至最近的8的倍数,
//然后从相应链表中取下一个对应大小的node分配给请求
#ifdef __SUNPRO_CC
enum {__ALIGN = }; //小型区块的上调边界
enum {__MAX_BYTES = }; //小型区块的上限
enum {__NFREELISTS = __MAX_BYTES/__ALIGN};
#endif //第二级配置器
template <bool threads, int inst>
class __default_alloc_template
{
private:
# ifndef __SUNPRO_CC
enum {__ALIGN = }; //小型区块的上调边界
enum {__MAX_BYTES = }; //小型区块的上限
enum {__NFREELISTS = __MAX_BYTES/__ALIGN};
# endif
//大小上调至8的倍数
static size_t ROUND_UP(size_t bytes)
{
return (((bytes) + __ALIGN-) & ~(__ALIGN - ));
}
__PRIVATE:
union obj
{
union obj * free_list_link; //用于在链表中指向下一个节点
char client_data[]; //用于存储实际区块的内存地址,由于这是一个union,很好的节约了这个数据的内存
};
private:
# ifdef __SUNPRO_CC
static obj * __VOLATILE free_list[];
# else
static obj * __VOLATILE free_list[__NFREELISTS];
# endif
static size_t FREELIST_INDEX(size_t bytes)
{
return (((bytes) + __ALIGN-)/__ALIGN - );
} //返回大小为n的对象,并可能加入大小为n的其他区块到free list
static void *refill(size_t n);
//配置一块空间,可容纳nobjs个大小为"size"的区块
//如果配置nobjs个区块有所不便,nobjs可能会降低
static char *chunk_alloc(size_t size, int &nobjs); //chunk 分配、配置的状态
static char *start_free; //内存池起始位置。只在chunk_alloc()中变化
static char *end_free; //内存池结束位置。只在chunk_alloc()中变化
static size_t heap_size;
/*
# ifdef __STL_SGI_THREADS
static volatile unsigned long __node_allocator_lock;
static void __lock(volatile unsigned long *);
static inline void __unlock(volatile unsigned long *);
# endif
*/ # ifdef __STL_PTHREADS
static pthread_mutex_t __node_allocator_lock;
# endif # ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS
static CRITICAL_SECTION __node_allocator_lock;
static bool __node_allocator_lock_initialized; public:
__default_alloc_template()
{
//假定第一个构造函数的调用在线程启动起
if (!__node_allocator_lock_initialized)
{
InitializedCriticalSection(&__node_allocator_lock);
__node_allocator_lock_initialized = true;
}
}
private:
# endif class lock
{
public:
lock() { __NODE_ALLOCATOR_LOCK; }
~lock() { __NODE_ALLOCATOR_UNLOCK; }
};
friend class lock;
public:
//n必须大于0
static void * allocate(size_t n)
{
obj * __VOLATILE * my_free_list;
obj * __RESTRICT result; //需要分配的大小大于二级配置器的__MAX_BYTES,直接使用第一级配置器
if (n > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES)
{
return(malloc_alloc::allocate(n));
}
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n); //找到比需要分配的大小大,且最接近的大小块所在的链表所在free_list数组中的位置 //如果支持线程,定义lock
# ifndef _NOTHREADS
lock lock_instance;
# endif
result = *my_free_list; //取出找的对应链表的指向第一个节点的指针
if (result == ) //对应的链表中没有剩余未分配的节点区块
{
void *r = refill(ROUND_UP(n)); //再从内存池中分配一批,需求大小的区块(实际大小是请求大小上调至8的倍数后的数值),
//然后,放入对应链表,待分配给请求
return r;
}
//如果对应大小区块的链表中不为空,还有待分配的区块,取出第一个节点
*my_free_list = result -> free_list_link;
return (result);
}; //p不可以是0
static void deallocate(void *p, size_t n)
{
obj *q = (obj *)p;
obj * __VOLATILE * my_free_list; //大于区块大小上限的,直接调用第一级配置器释放
if (n > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES)
{
malloc_alloc::deallocate(p, n);
return;
}
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);
//需要修改my_free_list,如果支持线程,那么需要加上互斥锁
# ifndef _NOTHREADS
lock lock_instance;
# endif //头插法,插入对应大小的区块链表
q -> free_list_link = *my_free_list;
*my_free_list = q;
//lock是静态对象,到此,将自动析构销毁,在其析构函数中,会释放锁
} static void *reallocate(void *p, size_t old_sz, size_t new_sz); }; typedef __default_alloc_template<__NODE_ALLOCATOR_THREADS, > alloc;
typedef __default_alloc_template<false, > single_client_alloc; // 我们从大的chunks中分配内存,是为了避免使用malloc太频繁了
// 假设size已经适当上调至8的倍数
// 我持有allocation lock
// 注意参数objs 是pass by reference
template <bool threads, int inst>
char *
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::chunk_alloc(size_t size, int& nobjs)
{
char * result;
size_t total_bytes = size * nobjs;
size_t bytes_left = end_free - start_free; //内存池剩余空间 if (bytes_left >= total_bytes)
{
//内存池中剩余的空间足够满足需求量
result = start_free;
start_free += total_bytes;
return(result);
}
else if (bytes_left >= size)
{
//内存池剩余空间不能完全满足需求量,但足够供应一个及以上的区块
nobjs = bytes_left/size;
total_bytes = size * nobjs;
result = start_free;
start_free += total_bytes;
return (result);
}
else
{
//内存池连一个区块的大小都无法满足
size_t bytes_to_get = * total_bytes + ROUND_UP(heap_size >> );
//以下试着让内存池中的残余零头还有利用价值
if (bytes_left > )
{
//内存池中内还有一些零头,先配给适当的free list
//首先寻找适当的free list
obj * __VOLATILE * my_free_list =
free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(bytes_left); //调整free list,将内存池中残余的空间编入
((obj *)start_free) -> free_list_link = *my_free_list;
*my_free_list = (obj *)start_free;
} //配置heap空间,用来补充内存池
start_free = (char *)malloc(bytes_to_get);
if ( == start_free)
{
//如果heap空间不足,malloc()失败
int i;
obj * __VOLATILE *my_free_list, *p;
//试着检视我们手上的东西。这不会造成伤害。我们不打算尝试配置
//较小的区块,因为那在多线程机器上容易导致灾难
//以下搜索适当的free list
//所谓适当是指“尚有未用区块,且区块够大”之free list
for (i = size; i <= __MAX_BYTES; i += __ALIGN)
{
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(i);
p = *my_free_list;
if ( != p)
{
//free list内尚有未用区块
//调整free list以释放出未用的区块到内存池
*my_free_list = p -> free_list_link;
start_free = (char *)p;
end_free = start_free + i;
// 此时内存池已经有内存了
// 递归调用自己,为了修正objs
return chunk_alloc(size, nobjs);
//注意,任何残余的零头终将被编入适当的free list中备用 }
}
end_free = ; //如果出现意外(山穷水尽,到处都没有内存可用了)
//调用第一级配置器,看看out-of-memory机制能否尽点力
start_free = (char *)malloc_alloc::allocate(bytes_to_get);
//这会导致抛出异常,或内存不足的情况获得改善
}
heap_size += bytes_to_get;
end_free = start_free + bytes_to_get;
//递归调用自己,为了修正objs
return chunk_alloc(size, nobjs);
}
} // 返回一个大小为n的对象,并且有时候会为适当的free list 增加节点
// 假设n已经适当上调至8的倍数
// 我们持有allocation lock
template <bool threads, int inst>
void* __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::refill(size_t n)
{
int nobjs = ; //默认一次分配20个需求大小的区块
char * chunk = chunk_alloc(n, nobjs); //chunk是分配的空间的开始地址,令其类型为char *,主要是因为一个char的大小正好是一个byte
obj * __VOLATILE *my_free_list;
obj * result;
obj * current_obj, * next_obj;
int i; //如果只获得一个区块,这个区块就分配给调用者,free list 无新节点
if ( == nobjs) return chunk;
//否则准备调整free list,纳入新节点
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n); //以下在chunk空间内建立free list
result = (obj *)chunk; //这一块准备返回给客端
// 以下导引free list 指向新配置的空间(取自内存池) //由于chunk是char*,所以加上n,就表示走过n个char,
//一个char正好是一个byte,所以chunk+n现在指向第二个区块
*my_free_list = next_obj = (obj *)(chunk + n);
for (i = ; ; ++i)
{
// 从1开始,因为第0个将返回给客端
current_obj = next_obj;
// 每次移动n个char,正好是n个byte,所以正好指向下个区块
next_obj = (obj *)((char *)next_obj + n);
if (nobjs - == i)
{
// 已经遍历完,此时next_obj指向的内存已经超出我们分配的大小了
// 不属于我们的内存
current_obj -> free_list_link = ;
break;
}
else
{
current_obj -> free_list_link = next_obj;
}
}
return result;
} template<bool threads, int inst>
void*
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::reallocate(void *p,
size_t old_sz,
size_t new_sz)
{
void * result;
size_t copy_sz; if (old_sz > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES && new_sz > (size_t) __MAX_BYTES)
{
return realloc(p, new_sz);
}
if (ROUND_UP(old_sz) == ROUND_UP(new_sz)) return p;
result = allocate(new_sz);
copy_sz = new_sz > old_sz ? old_sz : new_sz;
memcpy(result, p, copy_sz);
deallocate(p, old_sz);
return result; } #ifdef __STL_PTHREADS
template <bool threads,int inst>
pthread_mutex_t
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__node_allocator_lock
= PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
#endif #ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS
template <bool threads, int inst> CRITICAL_SECTION
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__node_allocator_lock; template <bool threads, int inst> bool
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__node_allocator_lock_initialized
= false;
#endif //省略了通用lock的实现(即不使用pthread,也没有win32thread) template <bool threads, int inst>
char *__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::start_free = ; //设置初始值 template <bool threads, int inst>
char *__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::end_free = ; //设置初始值 template <bool threads, int inst>
size_t __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::heap_size = ; //设置初始值 //初始化16种大小的区块链表为空
template <bool threads, int inst>
typename __default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::obj * __VOLATILE
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::free_list[
# ifdef __SUNPRO_CC
__NFREELISTS
# else
__default_alloc_template<threads, inst>::__NFREELISTS
# endif
] = {, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , }; # ifdef __STL_WIN32THREADS
// Create one to get critical section initialized.
// We do this onece per file, but only the first constructor
// does anything.
static alloc __node_allocator_dummy_instance;
# endif # endif /* ! __USE_MALLOC */ #if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma reset woff 1174
#endif __STL_END_NAMESPACE #undef __PRIVATE #endif /* __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_ALLOC_WJZH_H */ //End
自己动手实现STL 01:内存配置器的实现(stl_alloc.h)的更多相关文章
- SGI STL内存配置器存在内存泄漏吗?
阅读了SGI的源码后对STL很是膜拜,很高质量的源码,从中学到了很多.温故而知新!下文中所有STL如无特殊说明均指SGI版本实现. STL 内存配置器 STL对内存管理最核心部分我觉得是其将C++对象 ...
- STL内存配置器
一.STL内存配置器的总体设计结构 1.两级内存配置器:SGI-STL中设计了两级的内存配置器,主要用于不同大小的内存分配需求,当需要分配的内存大小大于128bytes时, 使用第一级配置器,否则使用 ...
- STL的空间配置器std_alloc 笔记
STL的空间配置器std_alloc 笔记 C++的内存分配基本操作是 ::operator new(),内存释放是 ::operator delete(),这里个全局函数相当于C的malloc和fr ...
- 带你深入理解STL之空间配置器(思维导图+源码)
前不久把STL细看了一遍,由于看得太"认真",忘了做笔记,归纳和总结这步漏掉了.于是为了加深印象,打算重看一遍,并记录下来里面的一些实现细节.方便以后能较好的复习它. 以前在项目中 ...
- STL之空间配置器allocator
摘要 C++STL的空间配置器将内存的分配.释放,对象的构造.析构都分开执行,内存分配由alloc::allocate()负责,内存的释放由alloc::deallocate()负责:对象的构造由:: ...
- STL库的内存配置器(allocator)
正在学习中,如果有错,还请多多指教,根据不断的理解,会进行更改,更改之前的样子都会保留下来,记录错误是最大的进步,嗯嗯! 具有次配置力的SGI空间配置器(SGI是STL的一种版本,也有其他的版本) 这 ...
- [STL]双层级配置器
考虑到过多“小型区块”可能造成的内存碎片问题,SGI设计了双层级配置器: 第一级配置器直接调用malloc()和free(): 第二级配置器分两种情况:当配置区块大于128字节时,调用第一级配置器:当 ...
- STL 之 空间配置器(allocator)
一.SGI 标准的空间配置器,std::allocator SGI也定义了一个符合部分标准,名为allocator的配置器,但是它自己不使用,也不建议我们使用,主要原因是效率不佳. 它只是把C++的操 ...
- STL之空间配置器
在前面很多随笔里都有提到new对象是先分配内存然后初始化对象,主要是对operator new和placement new的使用 在SGI STL中内存的分配和初始化是分开的,分配内存是使用类模板,模 ...
随机推荐
- php Tp5下mysql的增删改查
// 增 public function insert(){ $data = array( "username"=>"user121", "pa ...
- .net core UseHttpsRedirection() 正式环境无效
莫名其妙遇到这样的问题.这样的配置在本地可以,正式环境就不行了. ··· public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, Microsoft.AspNet ...
- springcloud微服务总结五 服务熔断
一:雪崩效应 如下图所示:A作为服务提供者,B为A的服务消费者,C和D是B的服务消费者.A不可用引起了B的不可用,并将不可用像滚雪球一样放大到C和D时,导致整个系统瘫痪,雪崩效应就形成了. 雪崩过程: ...
- Qt 学习之路 2(64):使用 QJsonDocument 处理 JSON
Home / Qt 学习之路 2 / Qt 学习之路 2(64):使用 QJsonDocument 处理 JSON Qt 学习之路 2(64):使用 QJsonDocument 处理 JSON 豆子 ...
- P4219 [BJOI2014]大融合
传送门 动态维护森林 显然考虑 $LCT$ 但是发现询问求的是子树大小,比较不好搞 维护 $sum[x]$ 表示节点 $x$ 的子树大小,$si[x]$ 表示 $x$ 的子树中虚儿子的子树大小和 那么 ...
- 关于webpack 以及 webpack配置和常用插件的学习记录 (2) ------ devServer
DevServer: devserver会启动一个http服务器用于服务网页请求,接收webpack发出的文件变化的信号.通过websocket协议自动刷新网页,实现实时预览. 安装: npm i w ...
- 【研究】Joomla二阶注入
受影响Joomla版本:3.7.0 到 3.8.3 1.下载安装Joomla3.8.3,登录后台管理系统:http://127.0.0.1/joomla/administrator/index.php ...
- python 函数的递归
递归:简单来说就是自己调用自己 这里我们又要举个例子来说明递归能做的事情. 例一: 现在你们问我,alex老师多大了?我说我不告诉你,但alex比 egon 大两岁. 你想知道alex多大,你是不是还 ...
- PIE SDK波段合成
1.算法功能简介 波段合成功能主要用于将多幅图像合并为一个新的多波段图像(即波段的叠加打包,构建一个新的多波段文件),从而可根据不同的用途选择不同波长范围内的波段合成 RGB 彩色图像. PIE支持算 ...
- android上最多有多少个http连接?
1.使用HttpUrlConnection能有几个 测试机器版本是5.1.1 个数 网络连接是否报错 写文件是否报错 1024 A/art: art/runtime/indirect_refere ...
