微服务组件--注册中心Spring Cloud Eureka分析
Eureka核心功能点
【1】服务注册(register):Eureka Client会通过发送REST请求的方式向Eureka Server注册自己的服务,提供自身的元数据,比如ip地址、端口、运行状况指标的url、主页地址等信息。Eureka Server接收到注册请求后,就会把这些元数据信息存储在一个双层的Map中。
【2】服务续约(renew):在服务注册后,Eureka Client会维护一个心跳来持续通知Eureka Server,说明服务一直处于可用状态,防止被剔除。Eureka Client在默认的情况下会每隔30秒(eureka.instance.leaseRenewalIntervalInSeconds)发送一次心跳来进行服务续约。
【3】服务同步(replicate):Eureka Server之间会互相进行注册,构建Eureka Server集群,不同Eureka Server之间会进行服务同步,用来保证服务信息的一致性。
【4】获取服务(get registry):服务消费者(Eureka Client)在启动的时候,会发送一个REST请求给Eureka Server,获取上面注册的服务清单,并且缓存在Eureka Client本地,默认缓存30秒(eureka.client.registryFetchIntervalSeconds)。同时,为了性能考虑,EurekaServer也会维护一份只读的服务清单缓存,该缓存每隔30秒更新一次。
【5】服务调用:服务消费者在获取到服务清单后,就可以根据清单中的服务列表信息,查找到其他服务的地址,从而进行远程调用。Eureka有Region和Zone的概念,一个Region可以包含多个Zone,在进行服务调用时,优先访问处于同一个Zone中的服务提供者。
【6】服务下线(cancel):当Eureka Client需要关闭或重启时,就不希望在这个时间段内再有请求进来,所以,就需要提前先发送REST请求给Eureka Server,告诉Eureka Server自己要下线了,Eureka Server在收到请求后,就会把该服务状态置为下线(DOWN),并把该下线事件传播出去。
【7】服务剔除(evict):有时候,服务实例可能会因为网络故障等原因导致不能提供服务,而此时该实例也没有发送请求给Eureka Server来进行服务下线,所以,还需要有服务剔除的机制。Eureka Server在启动的时候会创建一个定时任务,每隔一段时间(默认60秒),从当前服务清单中把超时没有续约(默认90秒,eureka.instance.leaseExpirationDurationInSeconds)的服务剔除。180s被剔除
【8】自我保护:既然Eureka Server会定时剔除超时没有续约的服务,那就有可能出现一种场景,网络一段时间内发生了异常,所有的服务都没能够进行续约,Eureka Server就把所有的服务都剔除了,这样显然不太合理。所以,就有了自我保护机制,当短时间内,统计续约失败的比例,如果达到一定阈值,则会触发自我保护的机制,在该机制下,Eureka Server不会剔除任何的微服务,等到正常后,再退出自我保护机制。自我保护开关(eureka.server.enable-self-preservation: false)
常见的问题
【1】当eureka服务实例有注册或下线或有实例发生故障,内存注册表虽然会及时更新数据,但是客户端不一定能及时感知到,可能会过30秒才能感知到,因为客户端拉取注册表实例这里面有一个多级缓存机制。【实现的是最终一致性】
【2】还有服务剔除的不是默认90秒没心跳的实例,剔除的是180秒没心跳的实例(eureka的bug导致,注解有说明是因为加了两次过期时间,但是很小的BUG所有不修复了【在Lease结构里说明】)
源码精髓总结
【1】服务端多级缓存设计思想:
1)在拉取注册表的时候:
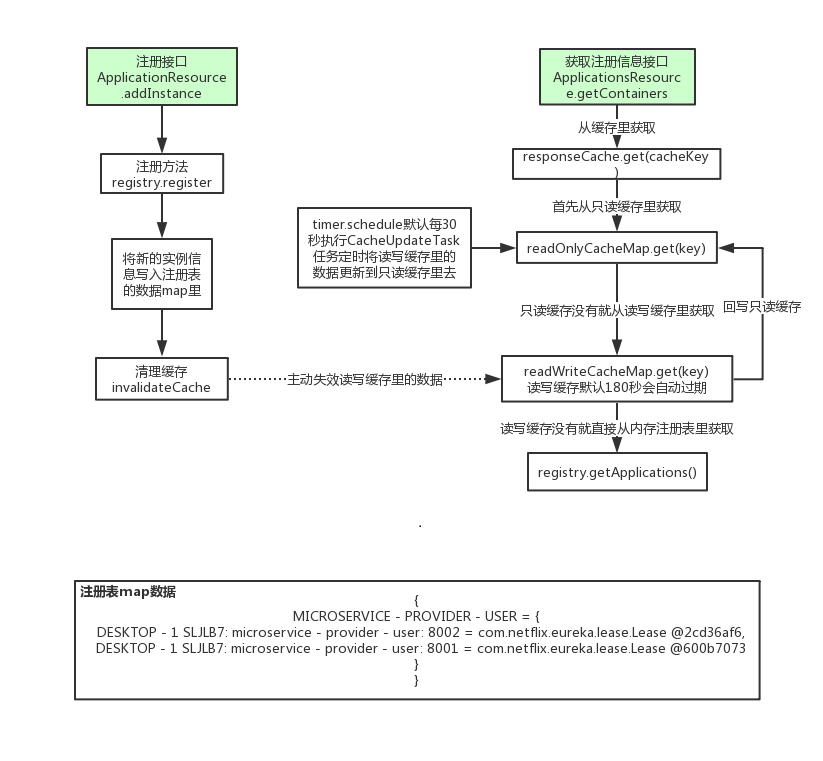
(1)首先从ReadOnlyCacheMap里查缓存的注册表。
(2)若没有,就找ReadWriteCacheMap里缓存的注册表。
(3)如果还没有,就从内存中获取实际的注册表数据。
2)在注册表发生变更的时候:
(1)会在内存中更新变更的注册表数据,同时过期掉ReadWriteCacheMap。
(2)此过程不会影响ReadOnlyCacheMap提供人家查询注册表。
(3)默认每30秒Eureka Server会将ReadWriteCacheMap更新到ReadOnlyCacheMap里
(4)默认每180秒Eureka Server会将ReadWriteCacheMap里是数据失效
(5)下次有服务拉取注册表,又会从内存中获取最新的数据了,同时填充 各级缓存
3)多级缓存机制的优点:
(1)尽可能保证了内存注册表数据不会出现频繁的读写冲突问题。
(2)并且进一步保证对Eureka Server的大量请求,都是快速从纯内存走,性能极高(可以稍微估计下对于一线互联网公司,内部上千个eureka client实例,每分钟对eureka大几千次的访问,一天就是上千万次的访问)
【2】TimedSupervisorTask定时任务的设计:
1)从整体上看,TimedSupervisorTask是固定间隔的周期性任务,一旦遇到超时就会将下一个周期的间隔时间调大,如果连续超时,那么每次间隔时间都会增大一倍,一直到达外部参数设定的上限为止,一旦新任务不再超时,间隔时间又会自动恢复为初始值,另外还有CAS来控制多线程同步。
【3】增量更新中哈希码检验的设计:
//里面的一致性哈希码,本质上就是校验数据
//如:服务器上全量块存的是【ABCDEFG】,此时它的哈希码便是全量块存的数据的哈希值,增量块存的是【FG】,
//而我们客户端是【ABCD】,增量拉下来再合并,则为【ABCDFG】,得到的哈希值便会与全量哈希值不一致,代表了缺失一部分数据
//故检验不对就会全量拉取
【4】注册表的结构说明(这个仅是记录):
实例信息存放的map,这是个两层的ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String,Lease<InstanceInfo>>>,外层map的key是appName,也就是服务名,内层map的key是instanceId,也就是实例名
注册表map数据示例如下:
{
MICROSERVICE - PROVIDER - USER = {
DESKTOP - 1 SLJLB7: microservice - provider - user: 8002 = com.netflix.eureka.lease.Lease @2cd36af6,
DESKTOP - 1 SLJLB7: microservice - provider - user: 8001 = com.netflix.eureka.lease.Lease @600b7073
},
MICROSERVICE - PROVIDER - ORDER = {
DESKTOP - 1 SLJLB7: microservice - provider - order: 8002 = com.netflix.eureka.lease.Lease @2cd36af6,
DESKTOP - 1 SLJLB7: microservice - provider - order: 8001 = com.netflix.eureka.lease.Lease @600b7073
}
}
Eureka服务端源码分析
【1】分析注解@EnableEurekaServer是如何开启eurekaServer服务注册功能
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableEurekaServer {} //注释有说:这个注解是为了激活Eureka相关的配置类EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类
//但是却是导入了EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration类
【2】分析导入的EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration类
//注释说明:采用Marker的bean去激活EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类
//但实际上并没有做什么,直接去EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类看他是怎么处理的
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration {
@Bean
public Marker eurekaServerMarkerBean() {
return new Marker();
} class Marker {}
}
【3】分析EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.class)
//当发现了这里,便明白了,这个配置类要生效是必须要有Marker类的存在
//而且EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类本身是基于SpringBoot的SPI机制,自动导入的
@ConditionalOnBean(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.Marker.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ EurekaDashboardProperties.class,InstanceRegistryProperties.class })
@PropertySource("classpath:/eureka/server.properties")
public class EurekaServerAutoConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {...}
【4】分析EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类中的方法
//初始化集群节点集合
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public PeerEurekaNodes peerEurekaNodes(PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry, ServerCodecs serverCodecs, ReplicationClientAdditionalFilters replicationClientAdditionalFilters) {
return new RefreshablePeerEurekaNodes(registry, this.eurekaServerConfig,
this.eurekaClientConfig, serverCodecs, this.applicationInfoManager,
replicationClientAdditionalFilters);
} //初始化EurekaServer的相关配置
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
protected static class EurekaServerConfigBeanConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public EurekaServerConfig eurekaServerConfig(EurekaClientConfig clientConfig) {
EurekaServerConfigBean server = new EurekaServerConfigBean();
if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
// Set a sensible default if we are supposed to replicate
server.setRegistrySyncRetries(5);
}
return server;
}
} //初始化一些接口,用于获取EurekaServer的信息
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "eureka.dashboard", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public EurekaController eurekaController() {
return new EurekaController(this.applicationInfoManager);
} //基于EurekaServer的配置,注册表,集群节点集合,以及服务实例初始化EurekaServer上下文
@Bean
public EurekaServerContext eurekaServerContext(ServerCodecs serverCodecs, PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry, PeerEurekaNodes peerEurekaNodes) {
return new DefaultEurekaServerContext(this.eurekaServerConfig, serverCodecs, registry, peerEurekaNodes, this.applicationInfoManager);
} //初始化经过包装的Eureka原生启动类
@Bean
public EurekaServerBootstrap eurekaServerBootstrap(PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry, EurekaServerContext serverContext) {
return new EurekaServerBootstrap(this.applicationInfoManager,
this.eurekaClientConfig, this.eurekaServerConfig, registry,
serverContext);
} //初始化集群注册表
@Bean
public PeerAwareInstanceRegistry peerAwareInstanceRegistry(ServerCodecs serverCodecs) {
this.eurekaClient.getApplications(); // force initialization
return new InstanceRegistry(this.eurekaServerConfig, this.eurekaClientConfig,
serverCodecs, this.eurekaClient,
this.instanceRegistryProperties.getExpectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews(),
this.instanceRegistryProperties.getDefaultOpenForTrafficCount());
}
【5】分析EurekaServerAutoConfiguration类导入的EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration类
//因为实现了SmartLifecycle接口,会在初始化完成后根据isAutoStartup()的返回值确认是否调用start()方法
//故查看EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration类#start()方法
@Override
public void start() {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
//初始化EurekaServer,同时启动Eureka Server
eurekaServerBootstrap.contextInitialized(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.servletContext);
log.info("Started Eureka Server");
//发送Eureka注册事件
publish(new EurekaRegistryAvailableEvent(getEurekaServerConfig()));
// 设置启动的状态为true
EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.running = true;
// 发送Eureka Start事件,其他还有各种事件,我们可以监听这种时间,然后做一些特定的业务需求
publish(new EurekaServerStartedEvent(getEurekaServerConfig()));
}
catch (Exception ex) {...}
}).start();
} //初始化EurekaServer的运行环境和上下文
//EurekaServerBootstrap类#contextInitialized方法
public void contextInitialized(ServletContext context) {
try {
//初始化运行环境
initEurekaEnvironment();
//初始化上下文
initEurekaServerContext(); context.setAttribute(EurekaServerContext.class.getName(), this.serverContext);
}
catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RuntimeException(...);
}
}
【6】分析初始化上下文initEurekaServerContext方法做了什么【进行了服务同步,服务剔除的启动】
protected void initEurekaServerContext() throws Exception {
// For backward compatibility
JsonXStream.getInstance().registerConverter(new V1AwareInstanceInfoConverter(),
XStream.PRIORITY_VERY_HIGH);
XmlXStream.getInstance().registerConverter(new V1AwareInstanceInfoConverter(),
XStream.PRIORITY_VERY_HIGH);
if (isAws(this.applicationInfoManager.getInfo())) {
this.awsBinder = new AwsBinderDelegate(this.eurekaServerConfig,
this.eurekaClientConfig, this.registry, this.applicationInfoManager);
this.awsBinder.start();
}
//初始化eureka server上下文
EurekaServerContextHolder.initialize(this.serverContext);
log.info("Initialized server context");
// Copy registry from neighboring eureka node
// 从相邻的eureka节点复制注册表
int registryCount = this.registry.syncUp();
// 默认每30秒发送心跳,1分钟就是2次
// 修改eureka状态为up
// 同时,这里面会开启一个定时任务,用于清理60秒没有心跳的客户端。自动下线
// 根据属性值可知是PeerAwareInstanceRegistry类
this.registry.openForTraffic(this.applicationInfoManager, registryCount);
// Register all monitoring statistics.
EurekaMonitors.registerAllStats();
}
//返回了一个EurekaServerContextHolder【其实就是将serverContext设置进入到里面当做属性值】
public static synchronized void initialize(EurekaServerContext serverContext) {
holder = new EurekaServerContextHolder(serverContext);
}
【7】服务同步的逻辑
//进行服务同步
@Override
public int syncUp() {
// Copy entire entry from neighboring DS node
int count = 0;
//从配置文件中拿到注册的节点
for (int i = 0; ((i < serverConfig.getRegistrySyncRetries()) && (count == 0)); i++) {
if (i > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(serverConfig.getRegistrySyncRetryWaitMs());
} catch (InterruptedException e) { break; }
}
//调用节点的http请求获取所有的服务实例
Applications apps = eurekaClient.getApplications();
for (Application app : apps.getRegisteredApplications()) {
for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) {
try {
if (isRegisterable(instance)) {
//将其他节点的实例注册到本节点
register(instance, instance.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs(), true);
count++;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {...}
}
}
}
return count;
}
【8】服务剔除的逻辑
//进行服务剔除
@Override
public void openForTraffic(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, int count) {
// Renewals happen every 30 seconds and for a minute it should be a factor of 2.
// 计算每分钟最大续约数
this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = count;
// 每分钟最小续约数
updateRenewsPerMinThreshold(); this.startupTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (count > 0) {
this.peerInstancesTransferEmptyOnStartup = false;
}
DataCenterInfo.Name selfName = applicationInfoManager.getInfo().getDataCenterInfo().getName();
boolean isAws = Name.Amazon == selfName;
if (isAws && serverConfig.shouldPrimeAwsReplicaConnections()) {
primeAwsReplicas(applicationInfoManager);
}
logger.info("Changing status to UP");
// 设置实例的状态为UP
applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceStatus.UP);
// 开启定时任务,默认60秒执行一次,用于清理60秒之内没有续约的实例
super.postInit();
} protected void updateRenewsPerMinThreshold() {
this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold = (int) (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews
* (60.0 / serverConfig.getExpectedClientRenewalIntervalSeconds())
* serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());
} protected void postInit() {
renewsLastMin.start();
if (evictionTaskRef.get() != null) {
evictionTaskRef.get().cancel();
}
evictionTaskRef.set(new EvictionTask());
//服务剔除任务
//evictionIntervalTimerInMs = 60 * 1000,即每60s执行一次,且延迟60s
evictionTimer.schedule(evictionTaskRef.get(),
serverConfig.getEvictionIntervalTimerInMs(),
serverConfig.getEvictionIntervalTimerInMs());
}
//EvictionTask类#run方法
@Override
public void run() {
try {
long compensationTimeMs = getCompensationTimeMs();
logger.info("Running the evict task with compensationTime {}ms", compensationTimeMs);
evict(compensationTimeMs);
} catch (Throwable e) {...}
} //剔除逻辑
public void evict(long additionalLeaseMs) {
logger.debug("Running the evict task"); if (!isLeaseExpirationEnabled()) {
logger.debug("DS: lease expiration is currently disabled.");
return;
} // We collect first all expired items, to evict them in random order. For large eviction sets,
// if we do not that, we might wipe out whole apps before self preservation kicks in. By randomizing it,
// the impact should be evenly distributed across all applications.
List<Lease<InstanceInfo>> expiredLeases = new ArrayList<>();
for (Entry<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> groupEntry : registry.entrySet()) {
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseMap = groupEntry.getValue();
if (leaseMap != null) {
for (Entry<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> leaseEntry : leaseMap.entrySet()) {
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = leaseEntry.getValue();
if (lease.isExpired(additionalLeaseMs) && lease.getHolder() != null) {
expiredLeases.add(lease);
}
}
}
} // To compensate for GC pauses or drifting local time, we need to use current registry size as a base for
// triggering self-preservation. Without that we would wipe out full registry.
int registrySize = (int) getLocalRegistrySize();
int registrySizeThreshold = (int) (registrySize * serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());
int evictionLimit = registrySize - registrySizeThreshold; int toEvict = Math.min(expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit);
if (toEvict > 0) {
logger.info("Evicting {} items (expired={}, evictionLimit={})", toEvict, expiredLeases.size(), evictionLimit); Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
for (int i = 0; i < toEvict; i++) {
// Pick a random item (Knuth shuffle algorithm)
int next = i + random.nextInt(expiredLeases.size() - i);
Collections.swap(expiredLeases, i, next);
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = expiredLeases.get(i); String appName = lease.getHolder().getAppName();
String id = lease.getHolder().getId();
EXPIRED.increment();
logger.warn("DS: Registry: expired lease for {}/{}", appName, id);
internalCancel(appName, id, false);
}
}
}
Eureka客户端源码分析
【1】根据SpringBoot自动装配先找出所有会调用的类
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaClientConfigServerAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.eureka.RibbonEurekaAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.reactive.EurekaReactiveDiscoveryClientConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerEurekaAutoConfiguration org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.config.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration
【2】找到对应的自动装配类EurekaClientAutoConfiguration类
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties
@ConditionalOnClass(EurekaClientConfig.class)
@Import(DiscoveryClientOptionalArgsConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "eureka.client.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@ConditionalOnDiscoveryEnabled
@AutoConfigureBefore({ NoopDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration.class,
CommonsClientAutoConfiguration.class, ServiceRegistryAutoConfiguration.class })
@AutoConfigureAfter(name = {
"org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.RefreshAutoConfiguration",
"org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration",
"org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AutoServiceRegistrationAutoConfiguration" })
public class EurekaClientAutoConfiguration {
//初始化EurekaClient的相关配置
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EurekaClientConfig.class,
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public EurekaClientConfigBean eurekaClientConfigBean(ConfigurableEnvironment env) {
EurekaClientConfigBean client = new EurekaClientConfigBean();
if ("bootstrap".equals(this.env.getProperty("spring.config.name"))) {
// We don't register during bootstrap by default, but there will be another
// chance later.
client.setRegisterWithEureka(false);
}
return client;
} //Client启动时的自动注册Bean
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(AutoServiceRegistrationProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public EurekaAutoServiceRegistration eurekaAutoServiceRegistration(
ApplicationContext context, EurekaServiceRegistry registry,
EurekaRegistration registration) {
return new EurekaAutoServiceRegistration(context, registry, registration);
} //EurekaClient配置类
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnMissingRefreshScope
protected static class EurekaClientConfiguration { @Autowired
private ApplicationContext context; @Autowired
private AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs<?> optionalArgs; @Bean(destroyMethod = "shutdown")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EurekaClient.class,search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public EurekaClient eurekaClient(ApplicationInfoManager manager, EurekaClientConfig config) {
return new CloudEurekaClient(manager, config, this.optionalArgs, this.context);
} @Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ApplicationInfoManager.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public ApplicationInfoManager eurekaApplicationInfoManager(EurekaInstanceConfig config) {
InstanceInfo instanceInfo = new InstanceInfoFactory().create(config);
return new ApplicationInfoManager(config, instanceInfo);
} @Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(AutoServiceRegistrationProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public EurekaRegistration eurekaRegistration(EurekaClient eurekaClient, CloudEurekaInstanceConfig instanceConfig, ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, @Autowired( required = false) ObjectProvider<HealthCheckHandler> healthCheckHandler) {
return EurekaRegistration.builder(instanceConfig).with(applicationInfoManager)
.with(eurekaClient).with(healthCheckHandler).build();
} }
....
}
【2.1】分析注解@AutoConfigureAfter导入的EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration类做了什么
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties
@ConditionalOnClass(EurekaClientConfig.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "eureka.client.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@ConditionalOnDiscoveryEnabled
@ConditionalOnBlockingDiscoveryEnabled
public class EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration { //基于EurekaClientAutoConfiguration的启动标志
@Deprecated
@Bean
public Marker eurekaDiscoverClientMarker() {
return new Marker();
} //将EurekaClient包装成EurekaDiscoveryClient
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public EurekaDiscoveryClient discoveryClient(EurekaClient client,
EurekaClientConfig clientConfig) {
return new EurekaDiscoveryClient(client, clientConfig);
} //心跳检测的处理配置
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "eureka.client.healthcheck.enabled",matchIfMissing = false)
protected static class EurekaHealthCheckHandlerConfiguration { @Autowired(required = false)
private StatusAggregator statusAggregator = new SimpleStatusAggregator(); @Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HealthCheckHandler.class)
public EurekaHealthCheckHandler eurekaHealthCheckHandler() {
return new EurekaHealthCheckHandler(this.statusAggregator);
} } @Deprecated
class Marker { } //定义了Client配置重刷的监听器
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass(RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent.class)
protected static class EurekaClientConfigurationRefresher implements ApplicationListener<RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent> {
....
} } //看得出来包装也只是将配置和客户端放在了一起
public EurekaDiscoveryClient(EurekaClient eurekaClient,
EurekaClientConfig clientConfig) {
this.clientConfig = clientConfig;
this.eurekaClient = eurekaClient;
}
【3】分析EurekaClient的相关配置EurekaClientConfigBean类
//仅列举了部分
@ConfigurationProperties(EurekaClientConfigBean.PREFIX)
public class EurekaClientConfigBean implements EurekaClientConfig, Ordered {
//客户端配置前缀
public static final String PREFIX = "eureka.client";
//public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "/eureka";
//默认的注册地址
public static final String DEFAULT_URL = "http://localhost:8761" + DEFAULT_PREFIX + "/";
//默认域
public static final String DEFAULT_ZONE = "defaultZone"; private static final int MINUTES = 60; //多长时间从注册中心服务端拉取一次服务信息,单位秒;这个就是主动拉取注册中心上所有服务的实例信息
private int registryFetchIntervalSeconds = 30;
//多长时间复制实例变化到eureka服务端,单位秒;这个配置是复制实例信息到注册中心
private int instanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds = 30;
//实例初始化复制信息到eureka服务端的间隔时间,所以可以看到,其实实例的初始化阶段不是立即复制实例信息到注册中心的,单位秒
private int initialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds = 40;
//eureka服务端的变化,多长时间,客户端会获取一次eureka服务的信息
private int eurekaServiceUrlPollIntervalSeconds = 5 * MINUTES;
//eureka server的代理端口
private String proxyPort;
//eureka server的代理host name
private String proxyHost;
//账号
private String proxyUserName;
//密码
private String proxyPassword;
//从server读取所需的超时时间
private int eurekaServerReadTimeoutSeconds = 8;
//连接server的超时时间
private int eurekaServerConnectTimeoutSeconds = 5;
//被允许连接到所有server host的总连接数
private int eurekaServerTotalConnections = 200;
// 被允许连接到每一个server host的总连接数
private int eurekaServerTotalConnectionsPerHost = 50;
//连接到server的http连接的空闲超时时间,超时会被清理掉
private int eurekaConnectionIdleTimeoutSeconds = 30;
//heartbeatExecutor 心跳的线程数
private int heartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize = 2;
//客户端初始化阶段强制注册,默认关闭
private boolean shouldEnforceRegistrationAtInit = false; ...
}
【4】分析EurekaClientConfiguration配置类里面生成的EurekaClient的Bean
//CloudEurekaClient类【继承DiscoveryClient类】#构造方法
public CloudEurekaClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs<?> args, ApplicationEventPublisher publisher) {
super(applicationInfoManager, config, args);
this.applicationInfoManager = applicationInfoManager;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.eurekaTransportField = ReflectionUtils.findField(DiscoveryClient.class,
"eurekaTransport");
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.eurekaTransportField);
} //DiscoveryClient类【继承EurekaClient(原生的EurekaClient)】#构造方法
public DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, final EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args) {
this(applicationInfoManager, config, args, ResolverUtils::randomize);
} public DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, final EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args, EndpointRandomizer randomizer) {
//主要是这个this指向,毕竟里面的都是方法传参
this(applicationInfoManager, config, args, new Provider<BackupRegistry>() {
private volatile BackupRegistry backupRegistryInstance; @Override
public synchronized BackupRegistry get() {
if (backupRegistryInstance == null) {
String backupRegistryClassName = config.getBackupRegistryImpl();
if (null != backupRegistryClassName) {
try {
backupRegistryInstance = (BackupRegistry) Class.forName(backupRegistryClassName).newInstance();
logger.info("Enabled backup registry of type {}", backupRegistryInstance.getClass());
} catch (InstantiationException e) {..} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {..} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {...}
} if (backupRegistryInstance == null) {
logger.warn("Using default backup registry implementation which does not do anything.");
backupRegistryInstance = new NotImplementedRegistryImpl();
}
} return backupRegistryInstance;
}
}, randomizer);
}
【5】分析DiscoveryClient的构造方法
@Inject
DiscoveryClient(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, EurekaClientConfig config, AbstractDiscoveryClientOptionalArgs args, Provider<BackupRegistry> backupRegistryProvider, EndpointRandomizer endpointRandomizer) {
if (args != null) {
this.healthCheckHandlerProvider = args.healthCheckHandlerProvider;
this.healthCheckCallbackProvider = args.healthCheckCallbackProvider;
this.eventListeners.addAll(args.getEventListeners());
this.preRegistrationHandler = args.preRegistrationHandler;
} else {
this.healthCheckCallbackProvider = null;
this.healthCheckHandlerProvider = null;
this.preRegistrationHandler = null;
} this.applicationInfoManager = applicationInfoManager;
InstanceInfo myInfo = applicationInfoManager.getInfo(); clientConfig = config;
staticClientConfig = clientConfig;
transportConfig = config.getTransportConfig();
instanceInfo = myInfo;
if (myInfo != null) {
appPathIdentifier = instanceInfo.getAppName() + "/" + instanceInfo.getId();
} else {...} this.backupRegistryProvider = backupRegistryProvider;
this.endpointRandomizer = endpointRandomizer;
this.urlRandomizer = new EndpointUtils.InstanceInfoBasedUrlRandomizer(instanceInfo);
localRegionApps.set(new Applications()); fetchRegistryGeneration = new AtomicLong(0); remoteRegionsToFetch = new AtomicReference<String>(clientConfig.fetchRegistryForRemoteRegions());
remoteRegionsRef = new AtomicReference<>(remoteRegionsToFetch.get() == null ? null : remoteRegionsToFetch.get().split(",")); if (config.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
this.registryStalenessMonitor = new ThresholdLevelsMetric(this, METRIC_REGISTRY_PREFIX + "lastUpdateSec_", new long[]{15L, 30L, 60L, 120L, 240L, 480L});
} else {
this.registryStalenessMonitor = ThresholdLevelsMetric.NO_OP_METRIC;
} if (config.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
this.heartbeatStalenessMonitor = new ThresholdLevelsMetric(this, METRIC_REGISTRATION_PREFIX + "lastHeartbeatSec_", new long[]{15L, 30L, 60L, 120L, 240L, 480L});
} else {
this.heartbeatStalenessMonitor = ThresholdLevelsMetric.NO_OP_METRIC;
} //从这里开始初始化Eureka Client
if (!config.shouldRegisterWithEureka() && !config.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
logger.info("Client configured to neither register nor query for data.");
scheduler = null;
heartbeatExecutor = null;
cacheRefreshExecutor = null;
eurekaTransport = null;
instanceRegionChecker = new InstanceRegionChecker(new PropertyBasedAzToRegionMapper(config), clientConfig.getRegion()); // This is a bit of hack to allow for existing code using DiscoveryManager.getInstance()
// to work with DI'd DiscoveryClient
DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setDiscoveryClient(this);
DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setEurekaClientConfig(config); initTimestampMs = System.currentTimeMillis();
logger.info("Discovery Client initialized at timestamp {} with initial instances count: {}",
initTimestampMs, this.getApplications().size()); return; // no need to setup up an network tasks and we are done
} try {
// default size of 2 - 1 each for heartbeat and cacheRefresh
scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2,
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build());
//心跳的线程池
heartbeatExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-HeartbeatExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff
//缓存重刷的线程池
cacheRefreshExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
1, clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize(), 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("DiscoveryClient-CacheRefreshExecutor-%d")
.setDaemon(true)
.build()
); // use direct handoff eurekaTransport = new EurekaTransport();
scheduleServerEndpointTask(eurekaTransport, args); AzToRegionMapper azToRegionMapper;
if (clientConfig.shouldUseDnsForFetchingServiceUrls()) {
azToRegionMapper = new DNSBasedAzToRegionMapper(clientConfig);
} else {
azToRegionMapper = new PropertyBasedAzToRegionMapper(clientConfig);
}
if (null != remoteRegionsToFetch.get()) {
azToRegionMapper.setRegionsToFetch(remoteRegionsToFetch.get().split(","));
}
instanceRegionChecker = new InstanceRegionChecker(azToRegionMapper, clientConfig.getRegion());
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to initialize DiscoveryClient!", e);
} if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry() && !fetchRegistry(false)) {
fetchRegistryFromBackup();
} // call and execute the pre registration handler before all background tasks (inc registration) is started
if (this.preRegistrationHandler != null) {
this.preRegistrationHandler.beforeRegistration();
} if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka() && clientConfig.shouldEnforceRegistrationAtInit()) {
try {
if (!register() ) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Registration error at startup. Invalid server response.");
}
} catch (Throwable th) {...}
} // finally, init the schedule tasks (e.g. cluster resolvers, heartbeat, instanceInfo replicator, fetch
//最核心代码,初始化定时任务
initScheduledTasks(); try {
Monitors.registerObject(this);
} catch (Throwable e) {...} DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setDiscoveryClient(this);
DiscoveryManager.getInstance().setEurekaClientConfig(config); initTimestampMs = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
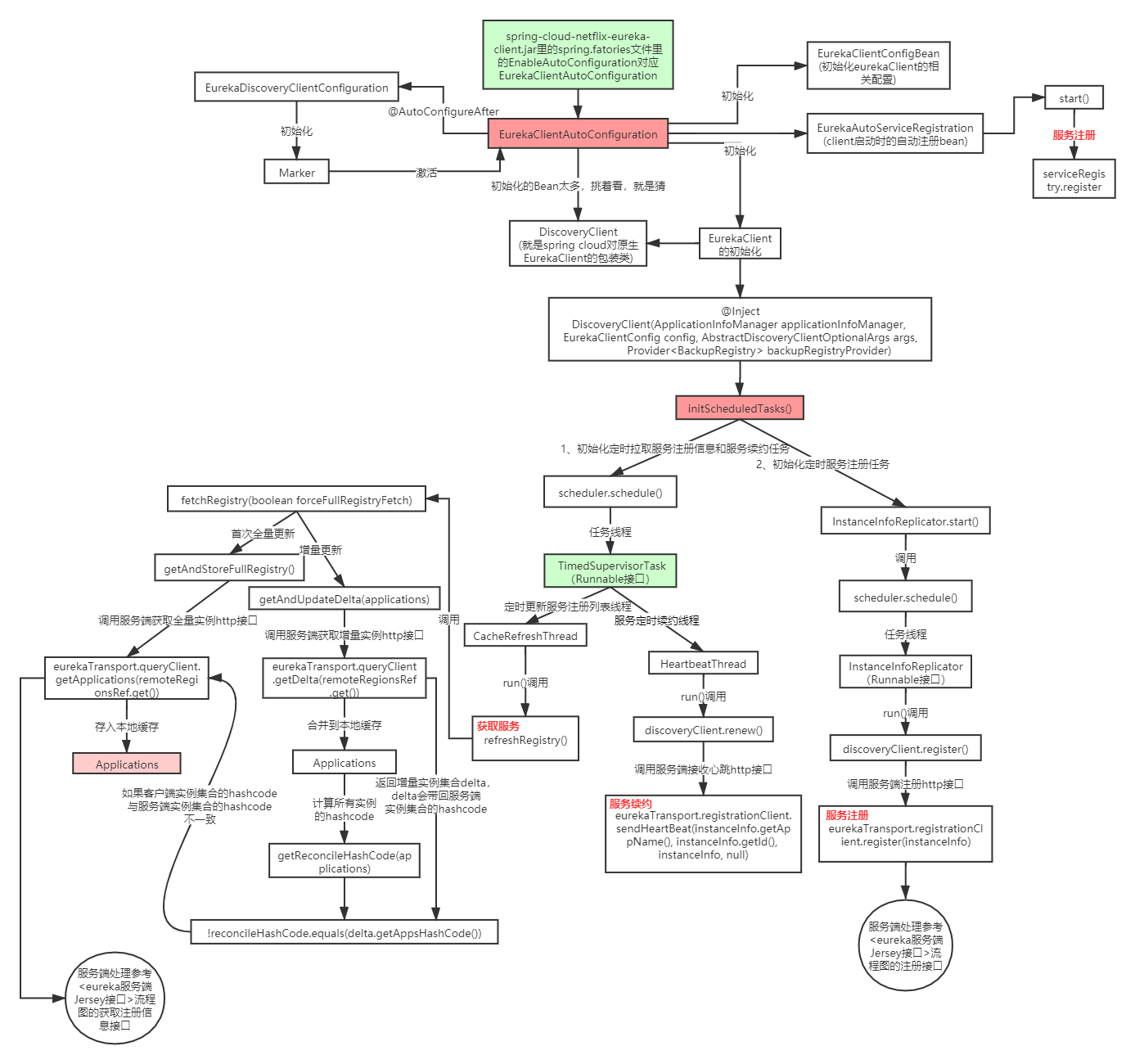
【6】核心逻辑initScheduledTasks初始化定时任务,是做了什么
/**
* Initializes all scheduled tasks.
*/
private void initScheduledTasks() {
//获取服务注册列表信息
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
//服务注册列表更新的周期时间
//默认是30
int registryFetchIntervalSeconds = clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds();
int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
//定时更新服务注册列表
//这里的延时任务明显是只调用一次,具体在分析他的任务的run方法
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"cacheRefresh",
scheduler,
cacheRefreshExecutor,
registryFetchIntervalSeconds,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new CacheRefreshThread() //该线程执行更新的具体逻辑
),
registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
//服务续约的周期时间
int renewalIntervalInSecs = instanceInfo.getLeaseInfo().getRenewalIntervalInSecs();
int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
//应用启动可见此日志,内容是:Starting heartbeat executor: renew interval is: 30
logger.info("Starting heartbeat executor: " + "renew interval is: {}", renewalIntervalInSecs); // Heartbeat timer
// 服务定时续约
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"heartbeat",
scheduler,
heartbeatExecutor,
renewalIntervalInSecs,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new HeartbeatThread() //该线程执行续约的具体逻辑
),
renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS); //这个Runable中含有服务注册的逻辑
instanceInfoReplicator = new InstanceInfoReplicator(
this,
instanceInfo,
clientConfig.getInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds(),
2); // burstSize statusChangeListener = new ApplicationInfoManager.StatusChangeListener() {
@Override
public String getId() {
return "statusChangeListener";
} @Override
public void notify(StatusChangeEvent statusChangeEvent) {
if (InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getStatus() || InstanceStatus.DOWN == statusChangeEvent.getPreviousStatus()) {
// log at warn level if DOWN was involved
logger.warn("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);
} else {
logger.info("Saw local status change event {}", statusChangeEvent);
}
instanceInfoReplicator.onDemandUpdate();
}
}; if (clientConfig.shouldOnDemandUpdateStatusChange()) {
applicationInfoManager.registerStatusChangeListener(statusChangeListener);
}
//服务注册
instanceInfoReplicator.start(clientConfig.getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds());
} else {
logger.info("Not registering with Eureka server per configuration");
}
}
【6.1】定时任务TimedSupervisorTask类的设计
//TimedSupervisorTask类#run方法
//这里存在一个设计的亮点
public class TimedSupervisorTask extends TimerTask {
... public TimedSupervisorTask(String name, ScheduledExecutorService scheduler, ThreadPoolExecutor executor,
int timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit, int expBackOffBound, Runnable task) {
this.scheduler = scheduler;
this.executor = executor;
this.timeoutMillis = timeUnit.toMillis(timeout);
this.task = task; //可以看出任务还是需要根据传入来的
this.delay = new AtomicLong(timeoutMillis);
this.maxDelay = timeoutMillis * expBackOffBound;
// Initialize the counters and register.
successCounter = Monitors.newCounter("success");
timeoutCounter = Monitors.newCounter("timeouts");
rejectedCounter = Monitors.newCounter("rejectedExecutions");
throwableCounter = Monitors.newCounter("throwables");
threadPoolLevelGauge = new LongGauge(MonitorConfig.builder("threadPoolUsed").build());
Monitors.registerObject(name, this);
} @Override
public void run() {
Future<?> future = null;
try {
future = executor.submit(task);
threadPoolLevelGauge.set((long) executor.getActiveCount());
//设置了超时时间
future.get(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // block until done or timeout
//出现任务不超时的情况又会将延迟时间重置(这里主要是配合下面捕捉异常的超时翻倍情况)
delay.set(timeoutMillis);
threadPoolLevelGauge.set((long) executor.getActiveCount());
successCounter.increment();
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
logger.warn("task supervisor timed out", e);
//出现超时的记录
timeoutCounter.increment();
//将超时时间翻倍(在最大的任务时间内),主动延迟
long currentDelay = delay.get();
long newDelay = Math.min(maxDelay, currentDelay * 2);
//设置为最新的值,考虑到多线程,所以用了CAS
delay.compareAndSet(currentDelay, newDelay); } catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
//一旦线程池的阻塞队列中放满了待处理任务,触发了拒绝策略,就会将调度器停掉
if (executor.isShutdown() || scheduler.isShutdown()) {
logger.warn("task supervisor shutting down, reject the task", e);
} else {
logger.warn("task supervisor rejected the task", e);
}
//被拒绝的次数
rejectedCounter.increment();
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (executor.isShutdown() || scheduler.isShutdown()) {
logger.warn("task supervisor shutting down, can't accept the task");
} else {
logger.warn("task supervisor threw an exception", e);
} throwableCounter.increment();
} finally {
if (future != null) {
//这里任务要么执行完毕,要么发生异常,都用cancel方法来清理任务;
future.cancel(true);
}
//只要调度器没有停止,就再指定等待时间之后在执行一次同样的任务
//任务里面又塞入这个任务
if (!scheduler.isShutdown()) {
//假设外部调用时传入的超时时间为30秒(构造方法的入参timeout),最大间隔时间为50秒(构造方法的入参expBackOffBound)
//如果最近一次任务没有超时,那么就在30秒后开始新任务,
//如果最近一次任务超时了,那么就在50秒后开始新任务(异常处理中有个乘以二的操作,乘以二后的60秒超过了最大间隔50秒)
scheduler.schedule(this, delay.get(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
}
}
【6.2】分析更新服务注册列表任务 CacheRefreshThread【获取服务逻辑】
//DiscoveryClient类的内置类
class CacheRefreshThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
refreshRegistry();
}
} //DiscoveryClient类#refreshRegistry方法
@VisibleForTesting
void refreshRegistry() {
try {
boolean isFetchingRemoteRegionRegistries = isFetchingRemoteRegionRegistries(); boolean remoteRegionsModified = false;
// This makes sure that a dynamic change to remote regions to fetch is honored.
String latestRemoteRegions = clientConfig.fetchRegistryForRemoteRegions();
//不做aws环境的配置这个if逻辑不会执行
if (null != latestRemoteRegions) {
String currentRemoteRegions = remoteRegionsToFetch.get();
if (!latestRemoteRegions.equals(currentRemoteRegions)) {
// Both remoteRegionsToFetch and AzToRegionMapper.regionsToFetch need to be in sync
synchronized (instanceRegionChecker.getAzToRegionMapper()) {
if (remoteRegionsToFetch.compareAndSet(currentRemoteRegions, latestRemoteRegions)) {
String[] remoteRegions = latestRemoteRegions.split(",");
remoteRegionsRef.set(remoteRegions);
instanceRegionChecker.getAzToRegionMapper().setRegionsToFetch(remoteRegions);
remoteRegionsModified = true;
} else {....}
}
} else {
// Just refresh mapping to reflect any DNS/Property change
instanceRegionChecker.getAzToRegionMapper().refreshMapping();
}
}
//获取注册信息方法
boolean success = fetchRegistry(remoteRegionsModified);
if (success) {
registrySize = localRegionApps.get().size();
lastSuccessfulRegistryFetchTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
} if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {...省略日志内容...}
} catch (Throwable e) {...}
} private boolean fetchRegistry(boolean forceFullRegistryFetch) {
Stopwatch tracer = FETCH_REGISTRY_TIMER.start(); try {
// 如果增量被禁用,或者是第一次,那么获取所有应用程序
// 取出本地缓存之前获取的服务列表信息
Applications applications = getApplications();
//是否禁用增量更新
if (clientConfig.shouldDisableDelta()
|| (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress()))
|| forceFullRegistryFetch
//是否第一次拉取
|| (applications == null)
|| (applications.getRegisteredApplications().size() == 0)
|| (applications.getVersion() == -1)) //Client application does not have latest library supporting delta
{
//全量获取
getAndStoreFullRegistry();
} else {
//增量获取
getAndUpdateDelta(applications);
}
//更新本地缓存
applications.setAppsHashCode(applications.getReconcileHashCode());
logTotalInstances();
} catch (Throwable e) {
return false;
} finally {
if (tracer != null) {
tracer.stop();
}
} // Notify about cache refresh before updating the instance remote status
//将本地缓存更新的事件广播给所有已注册的监听器,注意该方法已被CloudEurekaClient类重写
onCacheRefreshed();
// Update remote status based on refreshed data held in the cache
//检查刚刚更新的缓存中,有来自Eureka server的服务列表,其中包含了当前应用的状态,
//当前实例的成员变量lastRemoteInstanceStatus,记录的是最后一次更新的当前应用状态,
//上述两种状态在updateInstanceRemoteStatus方法中作比较 ,如果不一致,就更新lastRemoteInstanceStatus,并且广播对应的事件
updateInstanceRemoteStatus();
// registry was fetched successfully, so return true
return true;
} @Override
public Applications getApplications() {
return localRegionApps.get();
}
【6.2.1】分析全量更新
private void getAndStoreFullRegistry() throws Throwable {
long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get();
Applications apps = null;
//由于并没有配置特别关注的region信息,因此会调用eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications方法从服务端获取服务列表
EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress() == null
? eurekaTransport.queryClient.getApplications(remoteRegionsRef.get())
: eurekaTransport.queryClient.getVip(clientConfig.getRegistryRefreshSingleVipAddress(), remoteRegionsRef.get());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {
//返回对象就是服务列表
apps = httpResponse.getEntity();
}
logger.info("The response status is {}", httpResponse.getStatusCode());
if (apps == null) {...}
else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {
//考虑到多线程同步,只有CAS成功的线程,才会把自己从Eureka server获取的数据来替换本地缓存
localRegionApps.set(this.filterAndShuffle(apps));
} else {...}
}
//EurekaHttpClientDecorator类#getApplications方法
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> getApplications(final String... regions) {
//这里面涉及到配置是否重试
return execute(new RequestExecutor<Applications>() {
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> execute(EurekaHttpClient delegate) {
//调用AbstractJerseyEurekaHttpClient类
return delegate.getApplications(regions);
}
@Override
public RequestType getRequestType() {
return RequestType.GetApplications;
}
});
}
@Override
public EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> getApplications(String... regions) {
//取增量数据的path是"apps/delta"
return getApplicationsInternal("apps/", regions);
}
//具体的请求响应处理都在此方法中
private EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> getApplicationsInternal(String urlPath, String[] regions) {
ClientResponse response = null;
String regionsParamValue = null;
try {
//jersey、resource这些关键词都预示着这是个restful请求
WebResource webResource = jerseyClient.resource(serviceUrl).path(urlPath);
if (regions != null && regions.length > 0) {
regionsParamValue = StringUtil.join(regions);
webResource = webResource.queryParam("regions", regionsParamValue);
}
Builder requestBuilder = webResource.getRequestBuilder();
addExtraHeaders(requestBuilder);
//发起网络请求,将响应封装成ClientResponse实例
response = requestBuilder.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_TYPE).get(ClientResponse.class);
Applications applications = null;
if (response.getStatus() == Status.OK.getStatusCode() && response.hasEntity()) {
//取得全部应用信息
applications = response.getEntity(Applications.class);
}
return anEurekaHttpResponse(response.getStatus(), Applications.class)
.headers(headersOf(response))
.entity(applications)
.build();
} finally {
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
}
}
//总结:获取全量数据,是通过jersey-client库的API向Eureka server发起restful请求http://localhost:8761/eureka/apps实现的,并将响应的服务列表数据放在一个成员变量中作为本地缓存
【6.2.2】分析增量更新
//分析增量更新
//里面的一致性哈希码,本质上就是校验数据
//如:服务器上全量块存的是【ABCDEFG】,此时它的哈希码便是全量块存的数据的哈希值,增量块存的是【FG】,
//而我们客户端是【ABCD】,增量拉下来再合并,则为【ABCDFG】,得到的哈希值便会与全量哈希值不一致,代表了缺失一部分数据
//故检验不对就会全量拉取
private void getAndUpdateDelta(Applications applications) throws Throwable {
long currentUpdateGeneration = fetchRegistryGeneration.get(); Applications delta = null;
//增量信息是通过eurekaTransport.queryClient.getDelta方法完成的
EurekaHttpResponse<Applications> httpResponse = eurekaTransport.queryClient.getDelta(remoteRegionsRef.get());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode()) {
//delta中保存了Eureka server返回的增量更新
delta = httpResponse.getEntity();
}
//如果没有
if (delta == null) {
//如果增量信息为空,就直接发起一次全量更新
getAndStoreFullRegistry();
}
//考虑到多线程同步问题,这里通过CAS来确保请求发起到现在是线程安全的,
//如果这期间fetchRegistryGeneration变了,就表示其他线程也做了类似操作,因此放弃本次响应的数据
else if (fetchRegistryGeneration.compareAndSet(currentUpdateGeneration, currentUpdateGeneration + 1)) {
logger.debug("Got delta update with apps hashcode {}", delta.getAppsHashCode());
String reconcileHashCode = "";
if (fetchRegistryUpdateLock.tryLock()) {
try {
//用Eureka返回的增量数据和本地数据做合并操作
updateDelta(delta);
//用合并了增量数据之后的本地数据来生成一致性哈希码
reconcileHashCode = getReconcileHashCode(applications);
} finally {
fetchRegistryUpdateLock.unlock();
}
} else {...}
//Eureka server在返回增量更新数据时,也会返回服务端的一致性哈希码,
//理论上每次本地缓存数据经历了多次增量更新后,计算出的一致性哈希码应该是和服务端一致的,
//如果发现不一致,就证明本地缓存的服务列表信息和Eureka server不一致了,需要做一次全量更新
if (!reconcileHashCode.equals(delta.getAppsHashCode()) || clientConfig.shouldLogDeltaDiff()) {
//一致性哈希码不同,就在reconcileAndLogDifference方法中做全量更新
reconcileAndLogDifference(delta, reconcileHashCode); // this makes a remoteCall
}
} else {...}
} //updateDelta方法将增量更新数据和本地数据做合并
private void updateDelta(Applications delta) {
int deltaCount = 0;
//遍历所有服务
for (Application app : delta.getRegisteredApplications()) {
//遍历当前服务的所有实例
for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) {
//取出缓存的所有服务列表,用于合并
Applications applications = getApplications();
String instanceRegion = instanceRegionChecker.getInstanceRegion(instance);
//判断正在处理的实例和当前应用是否在同一个region
if (!instanceRegionChecker.isLocalRegion(instanceRegion)) {
//如果不是同一个region,接下来合并的数据就换成专门为其他region准备的缓存
Applications remoteApps = remoteRegionVsApps.get(instanceRegion);
if (null == remoteApps) {
remoteApps = new Applications();
remoteRegionVsApps.put(instanceRegion, remoteApps);
}
applications = remoteApps;
} ++deltaCount;
//对新增的实例的处理
if (ActionType.ADDED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {
Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());
if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);
}
logger.debug("Added instance {} to the existing apps in region {}", instance.getId(), instanceRegion);
applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance);
}
//对修改实例的处理
else if (ActionType.MODIFIED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {
Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());
if (existingApp == null) {
applications.addApplication(app);
}
logger.debug("Modified instance {} to the existing apps ", instance.getId()); applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName()).addInstance(instance); }
//对删除实例的处理
else if (ActionType.DELETED.equals(instance.getActionType())) {
Application existingApp = applications.getRegisteredApplications(instance.getAppName());
if (existingApp != null) {
logger.debug("Deleted instance {} to the existing apps ", instance.getId());
existingApp.removeInstance(instance);
/*
* We find all instance list from application(The status of instance status is not only the status is UP but also other status)
* if instance list is empty, we remove the application.
*/
if (existingApp.getInstancesAsIsFromEureka().isEmpty()) {
applications.removeApplication(existingApp);
}
}
}
}
}
logger.debug("The total number of instances fetched by the delta processor : {}", deltaCount); getApplications().setVersion(delta.getVersion());
//整理数据,使得后续使用过程中,这些应用的实例总是以相同顺序返回
getApplications().shuffleInstances(clientConfig.shouldFilterOnlyUpInstances());
//和当前应用不在同一个region的应用,其实例数据也要整理
for (Applications applications : remoteRegionVsApps.values()) {
applications.setVersion(delta.getVersion());
applications.shuffleInstances(clientConfig.shouldFilterOnlyUpInstances());
}
}
【6.3】分析服务定时续约任务 HeartbeatThread(也就是心跳机制)
private class HeartbeatThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
if (renew()) {
lastSuccessfulHeartbeatTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
}
boolean renew() {
EurekaHttpResponse<InstanceInfo> httpResponse;
try {
//发送心跳请求
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.sendHeartBeat(instanceInfo.getAppName(), instanceInfo.getId(), instanceInfo, null);
logger.debug(PREFIX + "{} - Heartbeat status: {}", appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.NOT_FOUND.getStatusCode()) {
REREGISTER_COUNTER.increment();
logger.info(PREFIX + "{} - Re-registering apps/{}", appPathIdentifier, instanceInfo.getAppName());
long timestamp = instanceInfo.setIsDirtyWithTime();
boolean success = register();
if (success) {
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(timestamp);
}
return success;
}
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode();
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + "{} - was unable to send heartbeat!", appPathIdentifier, e);
return false;
}
}
【7】分析服务注册的instanceInfoReplicator.start方法
public void start(int initialDelayMs) {
if (started.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
instanceInfo.setIsDirty(); // for initial register
Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, initialDelayMs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next);
}
}
//InstanceInfoReplicator类#run方法
public void run() {
try {
discoveryClient.refreshInstanceInfo();
Long dirtyTimestamp = instanceInfo.isDirtyWithTime();
if (dirtyTimestamp != null) {
//服务注册
discoveryClient.register();
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(dirtyTimestamp);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("There was a problem with the instance info replicator", t);
} finally {
Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next);
}
}
boolean register() throws Throwable {
logger.info(PREFIX + "{}: registering service...", appPathIdentifier);
EurekaHttpResponse<Void> httpResponse;
try {
//发起注册请求
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register(instanceInfo);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn(PREFIX + "{} - registration failed {}", appPathIdentifier, e.getMessage(), e);
throw e;
}
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.NO_CONTENT.getStatusCode();
}
【8】Eureka Server服务端Jersey接口部分分析
【8.1】服务端Jersey接口处理类ApplicationResource
@Produces({"application/xml", "application/json"})
public class ApplicationResource {
...
//注册一个实例的信息
@POST
@Consumes({"application/json", "application/xml"})
public Response addInstance(InstanceInfo info,
@HeaderParam(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION) String isReplication) {
logger.debug("Registering instance {} (replication={})", info.getId(), isReplication);
// validate that the instanceinfo contains all the necessary required fields
// 参数校验,不符合验证规则的,返回400状态码,
if (isBlank(info.getId())) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Missing instanceId").build();
} else if (isBlank(info.getHostName())) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Missing hostname").build();
} else if (isBlank(info.getIPAddr())) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Missing ip address").build();
} else if (isBlank(info.getAppName())) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Missing appName").build();
} else if (!appName.equals(info.getAppName())) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Mismatched appName, expecting " + appName + " but was " + info.getAppName()).build();
} else if (info.getDataCenterInfo() == null) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Missing dataCenterInfo").build();
} else if (info.getDataCenterInfo().getName() == null) {
return Response.status(400).entity("Missing dataCenterInfo Name").build();
}
// handle cases where clients may be registering with bad DataCenterInfo with missing data
DataCenterInfo dataCenterInfo = info.getDataCenterInfo();
if (dataCenterInfo instanceof UniqueIdentifier) {
String dataCenterInfoId = ((UniqueIdentifier) dataCenterInfo).getId();
if (isBlank(dataCenterInfoId)) {
boolean experimental = "true".equalsIgnoreCase(serverConfig.getExperimental("registration.validation.dataCenterInfoId"));
if (experimental) {
String entity = "DataCenterInfo of type " + dataCenterInfo.getClass() + " must contain a valid id";
return Response.status(400).entity(entity).build();
} else if (dataCenterInfo instanceof AmazonInfo) {
AmazonInfo amazonInfo = (AmazonInfo) dataCenterInfo;
String effectiveId = amazonInfo.get(AmazonInfo.MetaDataKey.instanceId);
if (effectiveId == null) {
amazonInfo.getMetadata().put(AmazonInfo.MetaDataKey.instanceId.getName(), info.getId());
}
} else {
logger.warn("Registering DataCenterInfo of type {} without an appropriate id", dataCenterInfo.getClass());
}
}
}
// 重点在这里,进行注册
registry.register(info, "true".equals(isReplication));
return Response.status(204).build(); // 204 to be backwards compatible
}
}
【8.1.1】注册方法分析
@Override
public void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {
int leaseDuration = Lease.DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS;
if (info.getLeaseInfo() != null && info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs() > 0) {
leaseDuration = info.getLeaseInfo().getDurationInSecs();
}
super.register(info, leaseDuration, isReplication);
replicateToPeers(Action.Register, info.getAppName(), info.getId(), info, null, isReplication);
} //AbstractInstanceRegistry类#register方法
public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) {
try {
// 上只读锁
read.lock();
// 从本地MAP里面获取当前实例的信息
//注册表的结构
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(registrant.getAppName());
// 增加注册次数到监控信息里面去。
REGISTER.increment(isReplication);
if (gMap == null) {
// 如果第一次进来,那么gMap为空,则创建一个ConcurrentHashMap放入到registry里面去
final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gNewMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>();
// putIfAbsent方法主要是在向ConcurrentHashMap中添加键—值对的时候,它会先判断该键值对是否已经存在。
// 如果不存在(新的entry),那么会向map中添加该键值对,并返回null。
// 如果已经存在,那么不会覆盖已有的值,直接返回已经存在的值。
gMap = registry.putIfAbsent(registrant.getAppName(), gNewMap);
if (gMap == null) {
// 表明map中确实不存在,则设置gMap为最新创建的那个
gMap = gNewMap;
}
}
// 从MAP中查询已经存在的Lease信息 (比如第二次来)
Lease<InstanceInfo> existingLease = gMap.get(registrant.getId());
// 当Lease的对象不为空时。
if (existingLease != null && (existingLease.getHolder() != null)) {
// 当instance已经存在是,和客户端的instance的信息做比较,时间最新的那个,为有效instance信息
Long existingLastDirtyTimestamp = existingLease.getHolder().getLastDirtyTimestamp();
Long registrationLastDirtyTimestamp = registrant.getLastDirtyTimestamp(); if (existingLastDirtyTimestamp > registrationLastDirtyTimestamp) {
registrant = existingLease.getHolder();
}
} else {
// 这里只有当existinglease不存在时,才会进来。 像那种恢复心跳,信息过期的,都不会进入这里。
// Eureka‐Server的自我保护机制做的操作,为每分钟最大续约数+2 ,同时重新计算每分钟最小续约数
synchronized (lock) {
if (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews > 0) {
// Since the client wants to register it, increase the number of clients sending renews
this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews + 1;
updateRenewsPerMinThreshold();
}
}
}
// 构建一个最新的Lease信息
Lease<InstanceInfo> lease = new Lease<InstanceInfo>(registrant, leaseDuration);
if (existingLease != null) {
// 当原来存在Lease的信息时,设置他的serviceUpTimestamp, 保证服务开启的时间一直是第一次的那个
lease.setServiceUpTimestamp(existingLease.getServiceUpTimestamp());
}
// 放入本地Map中
gMap.put(registrant.getId(), lease);
// 添加到最近的注册队列里面去,以时间戳作为Key, 名称作为value,主要是为了运维界面的统计数据。
synchronized (recentRegisteredQueue) {
recentRegisteredQueue.add(new Pair<Long, String>(
System.currentTimeMillis(),
registrant.getAppName() + "(" + registrant.getId() + ")"));
}
// 分析instanceStatus
if (!InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.equals(registrant.getOverriddenStatus())) {
logger.debug("Found overridden status {} for instance {}. Checking to see if needs to be add to the "
+ "overrides", registrant.getOverriddenStatus(), registrant.getId());
if (!overriddenInstanceStatusMap.containsKey(registrant.getId())) {
logger.info("Not found overridden id {} and hence adding it", registrant.getId());
overriddenInstanceStatusMap.put(registrant.getId(), registrant.getOverriddenStatus());
}
}
InstanceStatus overriddenStatusFromMap = overriddenInstanceStatusMap.get(registrant.getId());
if (overriddenStatusFromMap != null) {
logger.info("Storing overridden status {} from map", overriddenStatusFromMap);
registrant.setOverriddenStatus(overriddenStatusFromMap);
} // Set the status based on the overridden status rules
InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = getOverriddenInstanceStatus(registrant, existingLease, isReplication);
registrant.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus); // 得到instanceStatus,判断是否是UP状态,
if (InstanceStatus.UP.equals(registrant.getStatus())) {
lease.serviceUp();
}
// 设置注册类型为添加
registrant.setActionType(ActionType.ADDED);
// 租约变更记录队列,记录了实例的每次变化, 用于注册信息的增量获取、
recentlyChangedQueue.add(new RecentlyChangedItem(lease));
registrant.setLastUpdatedTimestamp();
// 清理缓存 ,传入的参数为key
invalidateCache(registrant.getAppName(), registrant.getVIPAddress(), registrant.getSecureVipAddress());
} finally {
read.unlock();
}
}
【8.1.1】分析Lease结构
public class Lease<T> {
enum Action {
Register, Cancel, Renew
};
//租约过期的时间常量,默认90秒,也就说90秒没有心跳过来,那么这边将会自动剔除该节点
public static final int DEFAULT_DURATION_IN_SECS = 90;
这个租约是属于谁的, 目前占用这个属性的是
private T holder;
//租约是啥时候过期的,当服务下线的时候,会过来更新这个时间戳registrationTimestamp : 租约的注册时间
private long evictionTimestamp;
private long registrationTimestamp;
//服务启动时间 ,当客户端在注册的时候,instanceInfo的status 为UP的时候,则更新这个时间戳
private long serviceUpTimestamp;
//最后更新时间,每次续约的时候,都会更新这个时间戳,在判断实例是否过期时,需要用到这个属性。
private volatile long lastUpdateTimestamp;
//过期时间,毫秒单位
private long duration;
public Lease(T r, int durationInSecs) {
holder = r;
registrationTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
lastUpdateTimestamp = registrationTimestamp;
duration = (durationInSecs * 1000);
}
//更新的时候设置过期时间为当前时间+90S
public void renew() {
lastUpdateTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis() + duration;
}
public void cancel() {
if (evictionTimestamp <= 0) {
evictionTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
public void serviceUp() {
if (serviceUpTimestamp == 0) {
serviceUpTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
public void setServiceUpTimestamp(long serviceUpTimestamp) {
this.serviceUpTimestamp = serviceUpTimestamp;
}
public boolean isExpired() {
return isExpired(0l);
}
//这里面存在的问题是过期时间+90S
//实际上也就是在更新时候的180s之后才算过期
public boolean isExpired(long additionalLeaseMs) {
return (evictionTimestamp > 0 || System.currentTimeMillis() > (lastUpdateTimestamp + duration + additionalLeaseMs));
}
public long getRegistrationTimestamp() {
return registrationTimestamp;
}
public long getLastRenewalTimestamp() {
return lastUpdateTimestamp;
}
public long getEvictionTimestamp() {
return evictionTimestamp;
}
public long getServiceUpTimestamp() {
return serviceUpTimestamp;
}
public T getHolder() {
return holder;
}
}
【8.2】客户端Jersey接口处理类ApplicationsResource
@Path("/{version}/apps")
@Produces({"application/xml", "application/json"})
public class ApplicationsResource {
...
private final EurekaServerConfig serverConfig;
private final PeerAwareInstanceRegistry registry;
private final ResponseCache responseCache;
@Inject
ApplicationsResource(EurekaServerContext eurekaServer) {
this.serverConfig = eurekaServer.getServerConfig();
this.registry = eurekaServer.getRegistry();
this.responseCache = registry.getResponseCache();
}
public ApplicationsResource() {
this(EurekaServerContextHolder.getInstance().getServerContext());
}
//获取关于特定{@link com.netflix.discovery.shared.Application}的信息。
@Path("{appId}")
public ApplicationResource getApplicationResource(
@PathParam("version") String version,
@PathParam("appId") String appId) {
CurrentRequestVersion.set(Version.toEnum(version));
return new ApplicationResource(appId, serverConfig, registry);
}
//获取关于所有{@link com.netflix.discovery.shared.Applications}的信息。
@GET
public Response getContainers(@PathParam("version") String version,
@HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT) String acceptHeader,
@HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT_ENCODING) String acceptEncoding,
@HeaderParam(EurekaAccept.HTTP_X_EUREKA_ACCEPT) String eurekaAccept,
@Context UriInfo uriInfo,
@Nullable @QueryParam("regions") String regionsStr) {
boolean isRemoteRegionRequested = null != regionsStr && !regionsStr.isEmpty();
String[] regions = null;
if (!isRemoteRegionRequested) {
EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL.increment();
} else {
regions = regionsStr.toLowerCase().split(",");
Arrays.sort(regions); // So we don't have different caches for same regions queried in different order.
EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL_WITH_REMOTE_REGIONS.increment();
}
// Check if the server allows the access to the registry. The server can
// restrict access if it is not
// ready to serve traffic depending on various reasons.
if (!registry.shouldAllowAccess(isRemoteRegionRequested)) {
return Response.status(Status.FORBIDDEN).build();
}
CurrentRequestVersion.set(Version.toEnum(version));
KeyType keyType = Key.KeyType.JSON;
String returnMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON;
if (acceptHeader == null || !acceptHeader.contains(HEADER_JSON_VALUE)) {
keyType = Key.KeyType.XML;
returnMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_XML;
}
//获取服务实例对应的缓存key
Key cacheKey = new Key(Key.EntityType.Application,
ResponseCacheImpl.ALL_APPS,
keyType, CurrentRequestVersion.get(), EurekaAccept.fromString(eurekaAccept), regions
);
Response response;
//是否压缩
if (acceptEncoding != null && acceptEncoding.contains(HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)) {
response = Response.ok(responseCache.getGZIP(cacheKey))
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_ENCODING, HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_TYPE, returnMediaType)
.build();
} else {
//从缓存里获取服务实例注册信息
response = Response.ok(responseCache.get(cacheKey))
.build();
}
return response;
}
//在{@link com.netflix.discovery.shared.Applications}中获取关于所有增量更改的信息。
@Path("delta")
@GET
public Response getContainerDifferential(
@PathParam("version") String version,
@HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT) String acceptHeader,
@HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT_ENCODING) String acceptEncoding,
@HeaderParam(EurekaAccept.HTTP_X_EUREKA_ACCEPT) String eurekaAccept,
@Context UriInfo uriInfo, @Nullable @QueryParam("regions") String regionsStr) {
boolean isRemoteRegionRequested = null != regionsStr && !regionsStr.isEmpty();
// If the delta flag is disabled in discovery or if the lease expiration
// has been disabled, redirect clients to get all instances
if ((serverConfig.shouldDisableDelta()) || (!registry.shouldAllowAccess(isRemoteRegionRequested))) {
return Response.status(Status.FORBIDDEN).build();
}
String[] regions = null;
if (!isRemoteRegionRequested) {
EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL_DELTA.increment();
} else {
regions = regionsStr.toLowerCase().split(",");
Arrays.sort(regions); // So we don't have different caches for same regions queried in different order.
EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL_DELTA_WITH_REMOTE_REGIONS.increment();
}
CurrentRequestVersion.set(Version.toEnum(version));
KeyType keyType = Key.KeyType.JSON;
String returnMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON;
if (acceptHeader == null || !acceptHeader.contains(HEADER_JSON_VALUE)) {
keyType = Key.KeyType.XML;
returnMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_XML;
}
Key cacheKey = new Key(Key.EntityType.Application,
ResponseCacheImpl.ALL_APPS_DELTA,
keyType, CurrentRequestVersion.get(), EurekaAccept.fromString(eurekaAccept), regions
);
if (acceptEncoding != null
&& acceptEncoding.contains(HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)) {
return Response.ok(responseCache.getGZIP(cacheKey))
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_ENCODING, HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_TYPE, returnMediaType)
.build();
} else {
return Response.ok(responseCache.get(cacheKey))
.build();
}
}
}
【8.2.1】ApplicationsResource类的getContainers方法分析
//获取关于所有{@link com.netflix.discovery.shared.Applications}的信息。
@GET
public Response getContainers(@PathParam("version") String version, @HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT) String acceptHeader,
@HeaderParam(HEADER_ACCEPT_ENCODING) String acceptEncoding, @HeaderParam(EurekaAccept.HTTP_X_EUREKA_ACCEPT) String eurekaAccept,
@Context UriInfo uriInfo, @Nullable @QueryParam("regions") String regionsStr) {
boolean isRemoteRegionRequested = null != regionsStr && !regionsStr.isEmpty();
String[] regions = null;
if (!isRemoteRegionRequested) {
EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL.increment();
} else {
regions = regionsStr.toLowerCase().split(",");
Arrays.sort(regions); // So we don't have different caches for same regions queried in different order.
EurekaMonitors.GET_ALL_WITH_REMOTE_REGIONS.increment();
}
// Check if the server allows the access to the registry. The server can
// restrict access if it is not
// ready to serve traffic depending on various reasons.
if (!registry.shouldAllowAccess(isRemoteRegionRequested)) {
return Response.status(Status.FORBIDDEN).build();
}
CurrentRequestVersion.set(Version.toEnum(version));
KeyType keyType = Key.KeyType.JSON;
String returnMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON;
if (acceptHeader == null || !acceptHeader.contains(HEADER_JSON_VALUE)) {
keyType = Key.KeyType.XML;
returnMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_XML;
}
//获取服务实例对应的缓存key
Key cacheKey = new Key(Key.EntityType.Application,
ResponseCacheImpl.ALL_APPS,
keyType, CurrentRequestVersion.get(), EurekaAccept.fromString(eurekaAccept), regions
);
Response response;
//是否压缩
if (acceptEncoding != null && acceptEncoding.contains(HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)) {
response = Response.ok(responseCache.getGZIP(cacheKey))
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_ENCODING, HEADER_GZIP_VALUE)
.header(HEADER_CONTENT_TYPE, returnMediaType)
.build();
} else {
//从缓存里获取服务实例注册信息,从ResponseCacheImpl类中获取
response = Response.ok(responseCache.get(cacheKey))
.build();
}
return response;
}
//分析responseCache.get方法
//ResponseCacheImpl类#get方法
public String get(final Key key) {
return get(key, shouldUseReadOnlyResponseCache);
}
@VisibleForTesting
String get(final Key key, boolean useReadOnlyCache) {
Value payload = getValue(key, useReadOnlyCache);
if (payload == null || payload.getPayload().equals(EMPTY_PAYLOAD)) {
return null;
} else {
return payload.getPayload();
}
}
//精髓设计的点,利用了读写分离,有种CopyOnWrite的思维
//private final ConcurrentMap<Key, Value> readOnlyCacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<Key, Value>();
//private final LoadingCache<Key, Value> readWriteCacheMap;
@VisibleForTesting
Value getValue(final Key key, boolean useReadOnlyCache) {
Value payload = null;
try {
//只读缓存的开启
if (useReadOnlyCache) {
final Value currentPayload = readOnlyCacheMap.get(key);
//只读缓存拿不到才去读写缓存里面拿
if (currentPayload != null) {
payload = currentPayload;
} else {
payload = readWriteCacheMap.get(key);
readOnlyCacheMap.put(key, payload);
}
} else {
payload = readWriteCacheMap.get(key);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {...}
return payload;
}
//ResponseCacheImpl类#构造方法
ResponseCacheImpl(EurekaServerConfig serverConfig, ServerCodecs serverCodecs, AbstractInstanceRegistry registry) {
this.serverConfig = serverConfig;
this.serverCodecs = serverCodecs;
this.shouldUseReadOnlyResponseCache = serverConfig.shouldUseReadOnlyResponseCache();
this.registry = registry;
long responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs = serverConfig.getResponseCacheUpdateIntervalMs();
this.readWriteCacheMap =
CacheBuilder.newBuilder().initialCapacity(serverConfig.getInitialCapacityOfResponseCache())
//读写缓存默认180秒会自动定时过期
.expireAfterWrite(serverConfig.getResponseCacheAutoExpirationInSeconds(), TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.removalListener(new RemovalListener<Key, Value>() {
@Override
public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<Key, Value> notification) {
Key removedKey = notification.getKey();
if (removedKey.hasRegions()) {
Key cloneWithNoRegions = removedKey.cloneWithoutRegions();
regionSpecificKeys.remove(cloneWithNoRegions, removedKey);
}
}
})
.build(new CacheLoader<Key, Value>() {
@Override
public Value load(Key key) throws Exception {
if (key.hasRegions()) {
Key cloneWithNoRegions = key.cloneWithoutRegions();
regionSpecificKeys.put(cloneWithNoRegions, key);
}
//从内存注册表中获取
Value value = generatePayload(key);
return value;
}
});
if (shouldUseReadOnlyResponseCache) {
//默认30秒用读写缓存的数据更新只读缓存的数据
timer.schedule(getCacheUpdateTask(),
new Date(((System.currentTimeMillis() / responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs) * responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs)
+ responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs),
responseCacheUpdateIntervalMs);
}
try {
Monitors.registerObject(this);
} catch (Throwable e) {...}
}
Eureka服务端源码分析图

Eureka服务端Jersey接口分析图
Eureka客户端源码分析图
微服务组件--注册中心Spring Cloud Eureka分析的更多相关文章
- spring cloud深入学习(二)-----服务注册中心spring cloud eureka
服务治理 主要用来实现各个微服务实例的自动化注册与发现,为啥需要这玩意呢?在一开始比如A系统调用B服务,可能通过手工维护B服务的实例,并且还得采用负载均衡等方式,这些全部都得需要手工维护,等后面系统越 ...
- 高可用注册中心 ->Spring Cloud Eureka
在微服务架构这样的分布式环境中,我们需要充分考虑发生故障的情况, 所以在生产 环境中必须对各个组件进行高可用部署, 对于微服务如此, 对于服务注册中心也一样. 但 是到本节为止,我们一直都在使用单节点 ...
- 【微服务】之二:从零开始,轻松搞定SpringCloud微服务系列--注册中心(一)
微服务体系,有效解决项目庞大.互相依赖的问题.目前SpringCloud体系有强大的一整套针对微服务的解决方案.本文中,重点对微服务体系中的服务发现注册中心进行详细说明.本篇中的注册中心,采用Netf ...
- Spring Cloud 微服务四:熔断器Spring cloud hystrix
前言:在微服务架构中,一般都是进程间通信,有可能调用链都比较长,当有底层某服务出现问题时,比如宕机,会导致调用方的服务失败,这样就会发生一连串的反映,造成系统资源被阻塞,最终可能造成雪崩.在sprin ...
- 第二个视频作品《[SpringCloudAlibaba]微服务之注册中心nacos》上线了
1.场景描述 第二个视频作品出炉了,<[SpringCloudAlibaba]微服务之注册中心nacos>上线了,有需要的朋友可以直接点击链接观看.(如需购买,请通过本文链接购买) 2. ...
- 小D课堂 - 新版本微服务springcloud+Docker教程_3-01 什么是微服务的注册中心
笔记 第三章 SpringCloud核心组件注册中心 1.什么是微服务的注册中心 简介:讲解什么是注册中心,常用的注册中心有哪些 (画图) 理解注册中心:服务 ...
- 服务治理框架:Spring Cloud Eureka
最近在学习Spring Cloud的知识,现将服务治理框架 Spring Cloud Eureka 的相关知识笔记整理如下.[采用 oneNote格式排版]
- 搭建高可用服务注册中心-Spring Cloud学习第一天(非原创)
文章大纲 一.Spring Cloud基础知识介绍二.创建单一的服务注册中心三.创建一个服务提供者四.搭建高可用服务注册中心五.项目源码与参考资料下载六.参考文章 一.Spring Cloud基础 ...
- 服务发现与消费 --> Spring Cloud Eureka
在上两篇文章中,我们已经搭建起微服务架构中的核心组件 服务注册 中心(包括单节点模式和高可用模式).同时, 还对上一章中实现的Spring Boot入门程序 做了改造. 通过简单的配置,使该程序注册到 ...
随机推荐
- 花一分钟体验 Apache DolphinScheduler 第一个官方 Docker 镜像
先前Apache DolphinScheduler 社区一直是发布 Dockerfile 和 K8s Chart.yaml 文件,由用户自行 build 镜像.随着越来越多的用户伙伴们的呼声高涨,社区 ...
- Pycharm5个非常有用的技巧
PyCharm 是一款非常强大的编写 python 代码的工具.掌握一些小技巧能成倍的提升写代码的效率,本篇介绍几个经常使用的小技巧. 一.分屏展示 当你想同时看到多个文件的时候: 右击标签页: 选择 ...
- 经典设计原则 - SOLID
SOLID 设计原则包含以下 5 种原则: 单一职责原则(Single Responsibility Principle, SRP) 开闭原则(Open Closed Principle, OCP) ...
- CSS 子节点继承父节点(祖先节点)的样式
CSS 有些属性可以让子节点从父节点或祖先节点继承,文本.字体.列表属性等样式都可以被子节点继承.子节点没有自身的样式,子节点将继承父节点或祖先节点的样式. <ul class="co ...
- 内网渗透之vlunstack靶场
前言:vlunstack靶场是由三台虚拟机构成,一台是有外网ip的windows7系统(nat模式),另外两台是纯内网机器(外网ping不通),分别是域控win2008和内网主机win2003,这里就 ...
- 给网站添加pjax无刷新,换页音乐不中断
自从博客加了悬浮音乐播放器后就一直在折腾换页音乐不中断的功能 在网上查找后发现想要实现换页音乐不中断的功能必须要为博客加pjax,于是又苦苦寻找并尝试了一番 最后发现网上实现pjax功能基本上是两种方 ...
- 【BZOJ2658】[Zjoi2012]小蓝的好友(mrx) (扫描线,平衡树,模拟)
题面 终于到达了这次选拔赛的最后一题,想必你已经厌倦了小蓝和小白的故事,为了回馈各位比赛选手,此题的主角是贯穿这次比赛的关键人物--小蓝的好友. 在帮小蓝确定了旅游路线后,小蓝的好友也不会浪费这个难得 ...
- identity4 系列————纯js客户端案例篇[四]
前言 前面已经解释了两个案例了,通信原理其实已经很清楚了,那么纯js客户端是怎么处理的呢? 正文 直接贴例子哈. https://github.com/IdentityServer/IdentityS ...
- 【ASP.NET Core】在Blazor中获取 HTTP 上下文信息
今天咱们来扯一下 Blazor 应用程序怎么访问 HttpContext.其实这句话有坑,为了避免大伙伴们掉茅坑,老周直接说明:Blazor 是不能访问 HttpContext 的.哪怕你在服务容器中 ...
- CURL 用法记录
CURL 用法记录 在工作中经常需要用到curl 命令,记录一下常用的场景 Send a POST Request with JSON Data curl -d '{"login" ...
