VueJS教程
文档资料参考:
- 参考:https://cn.vuejs.org/
- 参考:Vue.js教程 | 菜鸟教程
- 参考:Vue.js技术揭秘
- 参考:Vue-Cli(客户端)
- 参考:创建一个Vue项目、Vue-Cli创建一个Router项目
- 参考:https://codesandbox.io
- 参考:https://codepen.io/
- API参考:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/
- Chrome浏览器安装Vue插件便于调试:Vue.js devtools
- Vue调试神器:vue-devtools
- 代码管理:代码管理
- 图标管理:iconfont
目录:
- 1、Vue介绍
- 2、计算属性和侦听器
- 3、Class 与 Style 绑定
- 4、条件渲染(v-if、v-else、v-else-if、v-show、v-for、表格)
- 5、事件处理
- 6、v-model、v-text、v-html
- 7、组件基础
- 7.1 组件的组织
- 7.2 通过 Prop 向子组件传递数据(props属性小写)
- 7.3 通过插槽分发内容(组件元素标签后增加自定义内容,slot标签内容分发,作用域插槽)
- 7.4 组件的三种使用方法
- (1)方式一:全局组件
- (2)方式二:局部注册(组件嵌套)
- (3)方式三:以一个.vue的单文件作为组件(推荐)
- 7.5 监听子组件事件(子组件把数据传回去)、自定义组件事件(事件名称小写)
- 7.6 组件上使用 v-model
- 7.7 Vue使用小技巧
8、过渡 & 动画- 8.1 Vue中CSS动画原理
- 8.2 Vue中使用Animate.css库
- 8.3 Vue中同时使用过渡和动画
- 8.4 Vue中JS动画与Velocity.js结合
- 8.5 Vue中多个元素或组件的过渡
- (1)多个元素的过渡
- (2)多个组件的过渡
- 8.6 Vue中的列表过渡
- 8.7 Vue中的动画封装(让动画复用)
- 、可复用性&组合
- 10、工具
- 11、规模化(路由)
- 12、深入响应式原理
13、Vue实例- 14、Vue CLI
15、Vue指令
1、Vue介绍
- 参考:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/index.html
- Vue.js的核心思想:数据驱动的组件,为现代化的Web界面而生
- Vue.js的特点:侵入性低;鼓励模块化;轻量、高性能
(1)MV*架构
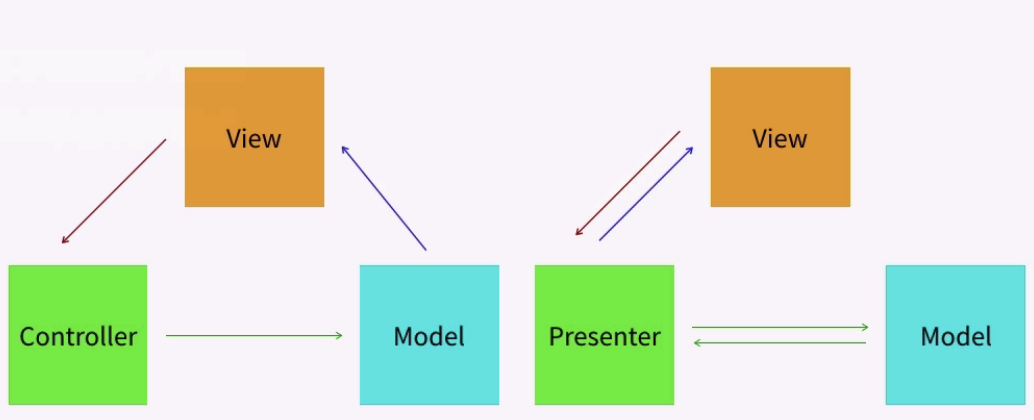
(2)MVVM架构
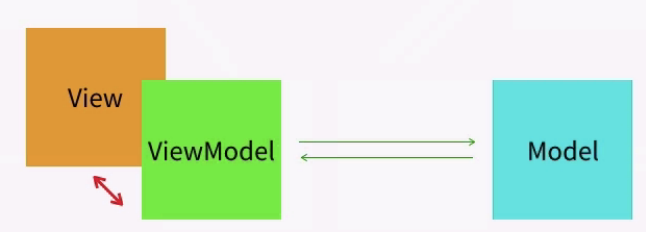
(3)Vue.js在MVVM架构中的定位
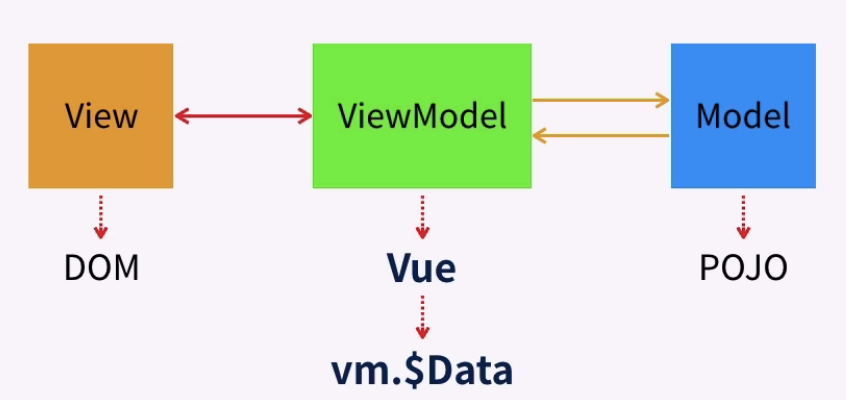
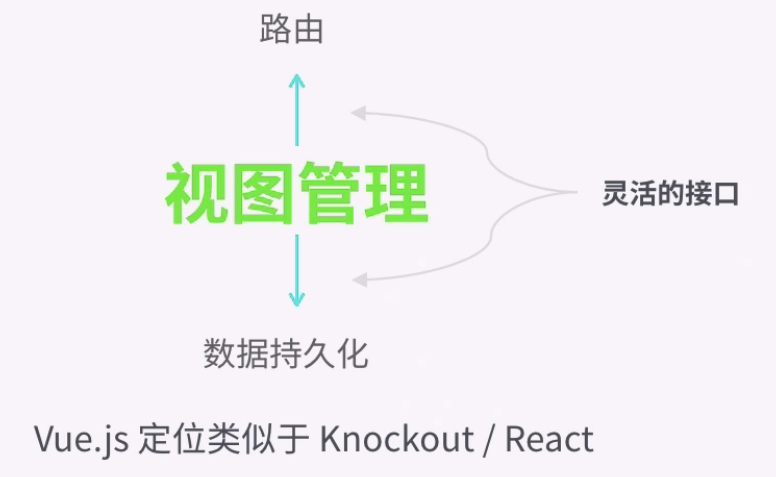
(4)Vue.js的功能定位
1.1 声明式渲染
举例(声明式渲染):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<!--<meta charset="utf-8">--> <! 选择中文字体 -->
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ message1 }}</p>
<p>{{ message2 }}</p>
</div> <script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
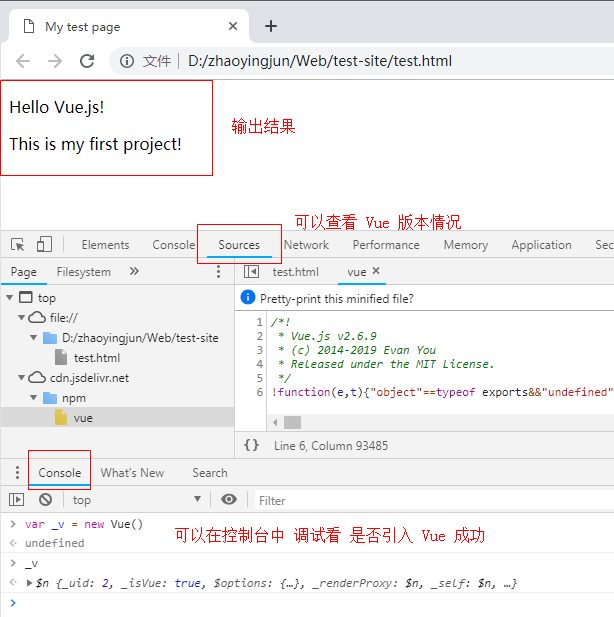
message1: 'Hello Vue.js!',
message2: 'This is my first project!',
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出结果:
1.2 声明式渲染(绑定元素特性)
举例(声明式渲染,绑定元素特性):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="app-2">
<span v-bind:title="message">
鼠标悬停几秒钟查看此处动态绑定的提示信息!
</span>
</div> <script>
new Vue({
el: '#app-2',
data: {
message: '页面加载于 ' + new Date().toLocaleDateString(),
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出结果:

1.3 条件与循环
举例1:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="app-2">
<span v-if="seen">
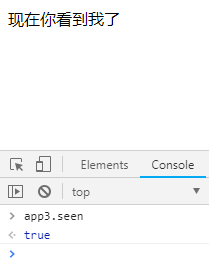
现在你看到我了
</span>
</div> <script>
var app3 = new Vue({
el: '#app-2',
data: {
seen: true
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
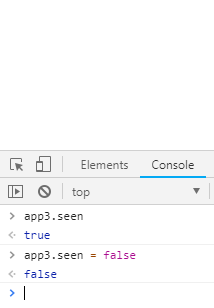
输出结果(在控制台输入 app3.seen = false,文字内容即消失了):
举例2:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="app-2">
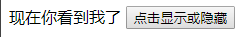
<span v-if="seen"> 现在你看到我了 </span>
<button v-on:click="switchSeen">点击显示或隐藏</button> <!-- v-on:click 可以用 @click替代 -->
</div> <script>
var app3 = new Vue({
el: '#app-2',
data: {
seen: true
},
methods: {
switchSeen: function () {
this.seen = !this.seen;
}
}
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:
举例3:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
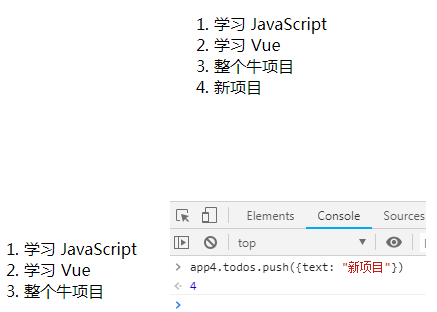
<div id="app-4">
<ol>
<li v-for="todo in todos">
{{ todo.text }}
</li>
</ol>
</div> <script>
var app4 = new Vue({
el: '#app-4',
data: {
todos: [
{ text: '学习 JavaScript' },
{ text: '学习 Vue' },
{ text: '整个牛项目' }
]
}
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果(在控制台里,输入 app4.todos.push({ text: '新项目' }),你会发现列表最后添加了一个新项目):
1.4 处理用户输入(包括双向数据绑定,v-model)
- 参考:表单输入绑定
举例1:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="app-5">
<p>{{ msg_input }}</p>
<br>
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
<button v-on:click="reverseMessage">逆转消息</button> <!-- v-on:click 可以用 @click替代 -->
</div> <script>
var app5 = new Vue({
el: '#app-5',
data: {
msg: "Hello, Vue.js!",
msg_input: "Hello, Vue!"
},
methods: {
reverseMessage: function () {
this.msg = this.msg.split('').reverse().join('')
}
}
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:
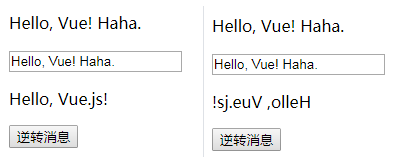
举例2(双向数据绑定):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
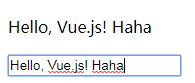
<div id="app-5">
<p>{{ msg }}</p>
<!-- <input type="text" v-bind:value="msg"> -->
<input type="text" v-model="msg">
</div> <script>
var app5 = new Vue({
el: '#app-5',
data: {
msg: "Hello, Vue.js!",
},
methods: {
}
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:(双向绑定之前和双向绑定之后效果)

1.5 组件化应用构建
举例1:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body> <ol id="app">
<!-- 创建一个 todo-item 组件的实例 -->
<todo-item></todo-item>
<li>内容补充</li>
</ol> <script>
// 定义一个名为 todo-item 的新组件
Vue.component("todo-item", {
template: '<li>这是个待办项</li>'
}); var app = new Vue({
el: '#app'
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:

举例2:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body> <div id="app-7">
<ol>
<!-- 创建一个 todo-item 组件的实例 -->
<!-- 现在我们为每个 todo-item 提供 todo 对象,todo 对象是变量,即其内容可以是动态的。我们也需要为每个组件提供一个“key”。 -->
<todo-item v-for="item in groceryList" v-bind:todo="item" v-bind:key="item.id">
</todo-item>
</ol>
</div> <script>
// 定义一个名为 todo-item 的新组件
Vue.component("todo-item", {
props: ['todo'],
template: '<li>{{ todo.text }}</li>'
}); var app = new Vue({
el: '#app-7',
data: {
groceryList: [
{ id: 0, text: '蔬菜' },
{ id: 1, text: '奶酪' },
{ id: 2, text: '随便其它什么人吃的东西' }
]
}
})
</script>
</body> </html>
注释:应用分割成了两个更小的单元。子单元通过 prop 接口与父单元进行了良好的解耦。我们现在可以进一步改进 <todo-item> 组件,提供更为复杂的模板和逻辑,而不会影响到父单元。
输出结果:

1.6 实例生命周期钩子
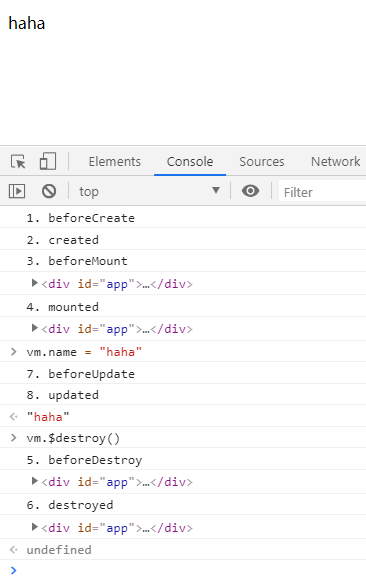
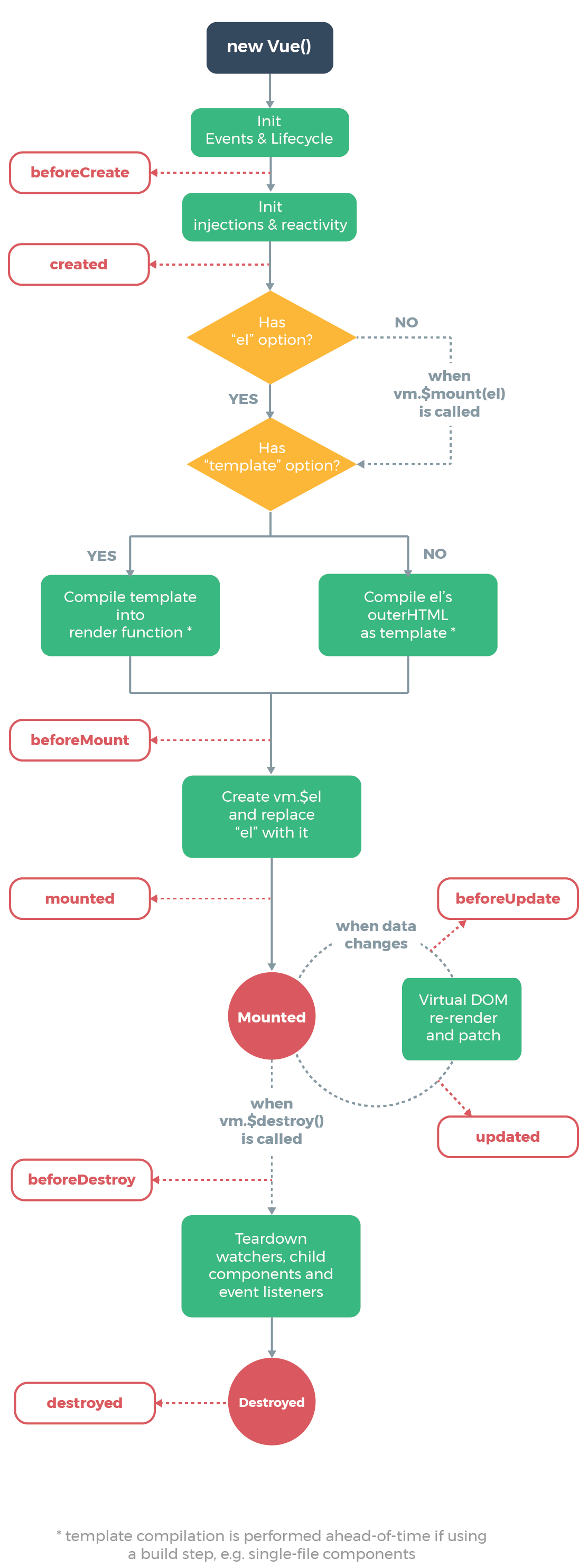
每个 Vue 实例在被创建时都要经过一系列的初始化过程——例如,需要设置数据监听、编译模板、将实例挂载到 DOM 并在数据变化时更新 DOM 等。同时在这个过程中也会运行一些叫做生命周期钩子的函数,这给了用户在不同阶段添加自己的代码的机会。
举例1:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Vue实例生命周期函数</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="app">
<blog-post :title="name"></blog-post>
</div> <script>
Vue.component("blog-post", {
props: ['title'],
template: `
<div>
<p>{{ title }}</p>
</div>
`
}); // 生命周期函数就是 Vue实例 在某一个时间点会自动执行的函数
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
name: 'Vue.js',
},
beforeCreate() { // Vue实例 部分初始化(事件和生命周期初始化完成)
console.log("1. beforeCreate");
},
created() { // Vue实例 初始化基本完成
console.log("2. created");
},
// 查询 Vue实例 中是否存在 el 选项
// 查询 Vue实例 中是否存在 template 选项
beforeMount() { // 页面渲染之前,模板和数据相结合,即将挂载在页面上一瞬间之前
console.log("3. beforeMount");
console.log(this.$el);
},
mounted() { // 模板和数据相结合,即将挂载在页面上之后
console.log("4. mounted");
console.log(this.$el);
},
beforeDestroy() {
console.log("5. beforeDestroy");
},
destroyed() {
console.log("6. destroyed");
},
beforeUpdate() { // 数据改变,重新渲染之前
console.log("7. beforeUpdate");
},
updated() { // 数据改变,重新渲染之后
console.log("8. updated");
}, computed: { },
methods: { }
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:
举例2(比如 created 钩子可以用来在一个实例被创建之后执行代码):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body> <div id="app-7">
<ol>
<!-- 创建一个 todo-item 组件的实例 -->
<!-- 现在我们为每个 todo-item 提供 todo 对象,todo 对象是变量,即其内容可以是动态的。我们也需要为每个组件提供一个“key”。 -->
<todo-item v-for="item in groceryList" v-bind:todo="item" v-bind:key="item.id">
</todo-item>
</ol>
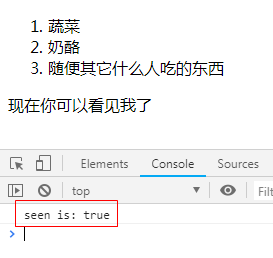
<div v-if="seen">
<p>现在你可以看见我了</p>
</div>
</div> <script>
// 定义一个名为 todo-item 的新组件
Vue.component("todo-item", {
props: ['todo'],
template: '<li>{{ todo.text }}</li>'
}); var app = new Vue({
el: '#app-7',
data: {
groceryList: [
{ id: 0, text: '蔬菜' },
{ id: 1, text: '奶酪' },
{ id: 2, text: '随便其它什么人吃的东西' }
],
seen: true
},
created: function () {
// this 指向 vm 实例
console.log("seen is: " + this.seen);
}
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:
1.7 生命周期图示
2、计算属性和侦听器
2.1 计算属性
对于任何复杂逻辑,你都应当使用计算属性。计算属性比调用方法性能会更好。
计算属性,依赖于数据属性发生变化时候,其才会重新调用一次该计算属性(比如 return new Date();)。
举例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body> <div id="example">
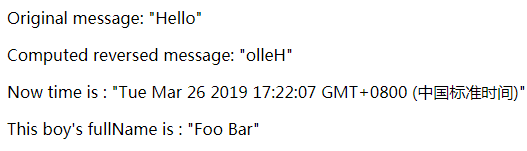
<p>Original message: "{{ message }}"</p>
<p>Computed reversed message: "{{ reversedMessage }}"</p>
<p>Now time is : "{{ now }}"</p>
<p>This boy's fullName is : "{{ fullName }}"</p>
</div> <script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#example',
data: {
message: 'Hello',
firstName: "Foo",
lastName: "Bar"
},
// 计算属性是基于它们的依赖进行缓存的,只在相关依赖发生改变时它们才会重新求值
computed: {
// 计算属性的 getter
reversedMessage: function () {
// `this` 指向 vm 实例
return this.message.split('').reverse().join('');
},
now: function () {
return new Date();
},
// 计算属性的 setter,计算属性默认只有getter,不过在需要时,也可以提供一个setter
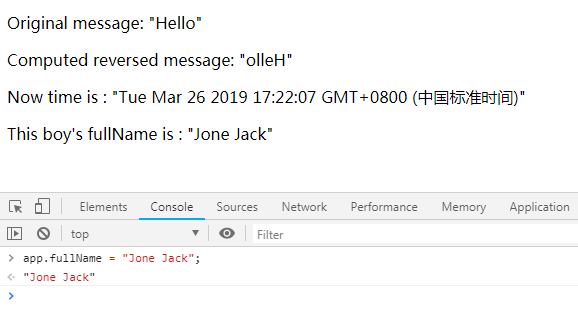
fullName: {
// getter
get: function () {
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName;
},
set: function (newValue) {
var names = newValue.split(" ");
this.firstName = names[0];
this.lastName = names[names.length - 1];
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:
2.2 侦听器
虽然计算属性在大多数情况下更合适,但有时也需要一个自定义的侦听器。这就是为什么 Vue 通过 watch 选项提供了一个更通用的方法,来响应数据的变化。当需要在数据变化时执行异步或开销较大的操作时,这个方式是最有用的。
举例1(侦听器,方式一):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="app">
{{ fullName }}
</div> <script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
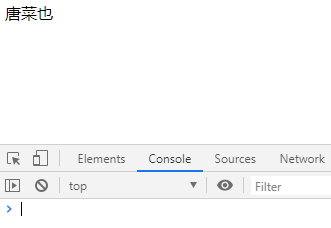
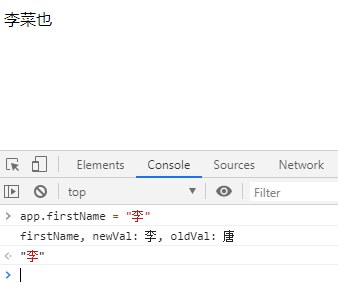
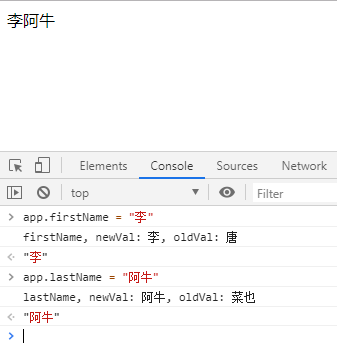
firstName: "唐",
lastName: "菜也",
fullName: "唐菜也"
},
watch: {
firstName(newVal, oldVal){
console.log("firstName, newVal: " + newVal + ", oldVal: " + oldVal);
this.fullName = newVal + this.lastName;
},
lastName(newVal, oldVal){
console.log("lastName, newVal: " + newVal + ", oldVal: " + oldVal);
this.fullName = this.firstName + newVal;
}
}
}) </script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:
举例2(侦听器,方式二):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="app">
{{ fullName }}
</div> <script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
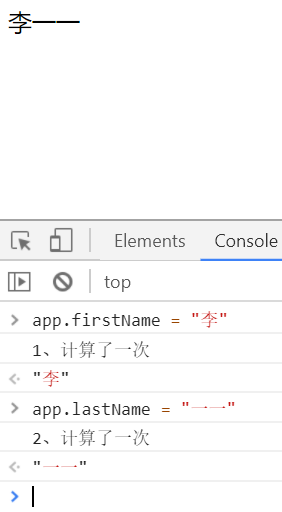
firstName: "唐",
lastName: "菜也",
fullName: "唐菜也",
age: 28,
},
watch: {
firstName: function () { // 监听 firstName 属性的变化
console.log("1、计算了一次");
this.fullName = this.firstName + this.lastName;
},
lastName: function () { // 监听 lastName 属性的变化
console.log("2、计算了一次");
this.fullName = this.firstName + this.lastName;
}
}
}) </script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:

举例3(侦听器,方式三):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="app">
{{ fullName }}
</div> <script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: "唐",
lastName: "菜也",
fullName: "唐菜也",
age: 28,
},
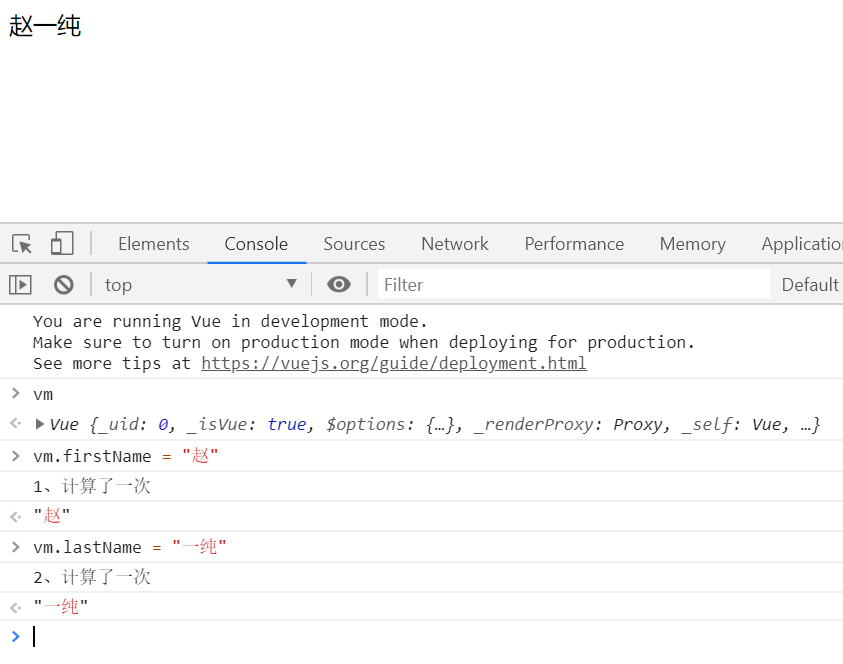
}) vm.$watch("firstName", function (val) {
console.log("1、计算了一次");
this.fullName = val + this.lastName;
}); vm.$watch("lastName", function (val) {
console.log("2、计算了一次");
this.fullName = this.firstName + val;
}); </script>
</body> </html>
举例4(计算属性方式实现):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="app">
{{ fullNameFun }}
</div> <script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: "唐",
lastName: "菜也",
fullName: "唐菜也"
},
watch: {/*
firstName(newVal, oldVal){
console.log("firstName, newVal: " + newVal + ", oldVal: " + oldVal);
this.fullName = newVal + this.lastName;
},
lastName(newVal, oldVal){
console.log("lastName, newVal: " + newVal + ", oldVal: " + oldVal);
this.fullName = this.firstName + newVal;
} */
},
computed: {
fullNameFun(){
return this.firstName + this.lastName;
}
}
}) </script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:同上。
3、Class 与 Style 绑定
3.1 绑定class
三种方式:
- 直接绑定方式
- 绑定数组方式
- 绑定对象方式
举例1(方式一:直接绑定方式):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <style>
.class-active {
color: red;
}
.class-font-size {
font-size: 75px;
}
</style>
</head> <body>
<div id="app">
<div v-bind:class="{'class-active':isActive, 'class-font-size':isFontSet}">
我是一些文字的内容
</div>
</div> <script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
isActive: true,
isFontSet: true
}
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:
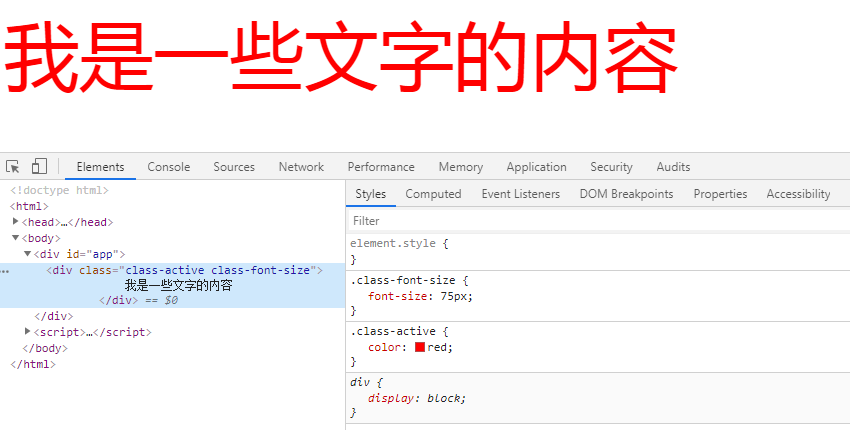
举例2-1(方式二:数组绑定方式):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <style>
.class-active {
color: red;
} .class-font-size {
font-size: 75px;
}
</style>
</head> <body>
<div id="app">
<div v-bind:class="className">
我是一些文字的内容
</div>
</div> <script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
className: ["class-active", "class-font-size"]
}
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:同上。
举例2-2(方式二:数组方式):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <style>
.class-active {
color: red;
} .class-font-size {
font-size: 75px;
}
</style>
</head> <body>
<div id="app">
<div v-bind:class="[classActive, classFontSize]"> 我是一些文字的内容 </div> <!-- classActive 和 classFontSize 都是变量 -->
</div> <script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
classActive: "class-active",
classFontSize: "class-font-size",
}
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:略。
举例3(方式三:对象绑定方式):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script> <style>
.class-active {
color: red;
} .class-font-size {
font-size: 75px;
}
</style>
</head> <body>
<div id="app">
<div v-bind:class="classObject">
我是一些文字的内容
</div>
</div> <script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
classObject: {
'class-active': true,
'class-font-size': true
} }
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:略。
3.2 绑定内联样式
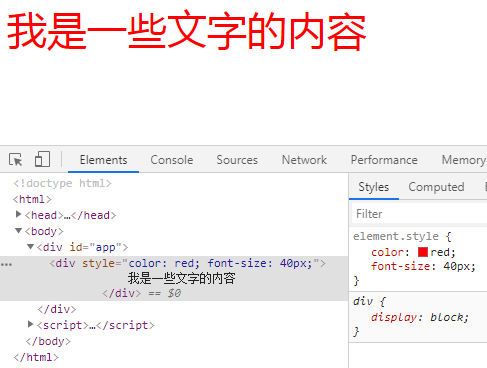
举例1(方式一:对象方式):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="app">
<div v-bind:style="{color: theColor, 'font-size': fontSize + 'px'}">
我是一些文字的内容
</div>
</div> <script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
'theColor': 'red',
'fontSize': 40
}
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:
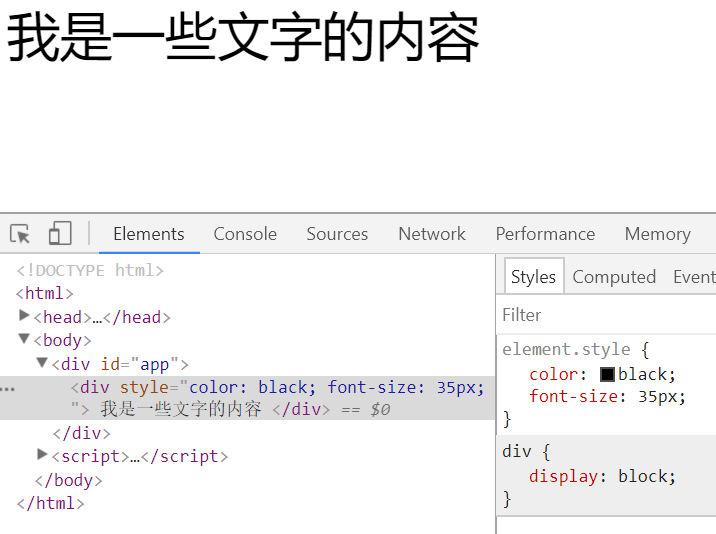
举例2(方式一:对象方式):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="app">
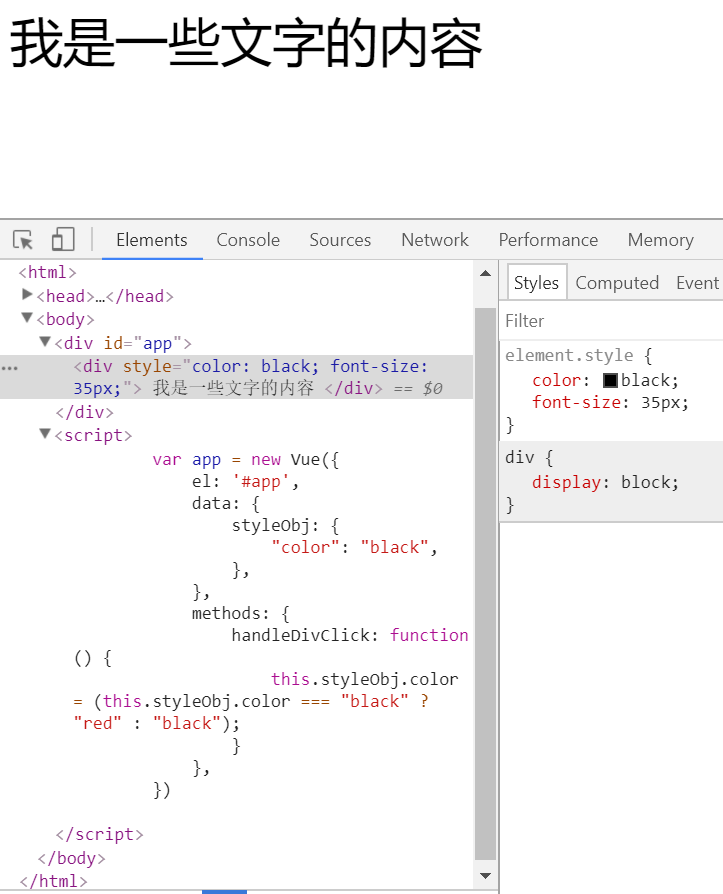
<div :style="styleObj" @click="handleDivClick"> 我是一些文字的内容 </div>
</div> <script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
styleObj: {
"color": "black",
"font-size": "35px",
},
},
methods: {
handleDivClick: function () {
this.styleObj.color = (this.styleObj.color === "black" ? "red" : "black");
}
},
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:
举例3(方式二:数组方式):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<div id="app">
<div :style="[styleObj, {'font-size': '35px'}]" @click="handleDivClick"> 我是一些文字的内容 </div>
</div> <script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
styleObj: {
"color": "black",
},
},
methods: {
handleDivClick: function () {
this.styleObj.color = (this.styleObj.color === "black" ? "red" : "black");
}
},
})
</script>
</body> </html>
输出结果:
4、条件渲染(v-if、v-else、v-else-if、v-show、v-for、表格)
v-if 是“真正”的条件渲染,因为它会确保在切换过程中条件块内的事件监听器和子组件适当地被销毁和重建。
v-if 也是惰性的:如果在初始渲染时条件为假,则什么也不做——直到条件第一次变为真时,才会开始渲染条件块。
相比之下,v-show 就简单得多——不管初始条件是什么,元素总是会被渲染,并且只是简单地基于 CSS 进行切换。
一般来说,v-if 有更高的切换开销,而 v-show 有更高的初始渲染开销。因此,如果需要非常频繁地切换,则使用 v-show 较好;如果在运行时条件很少改变,则使用 v-if 较好。
4.1 v-if、v-else、v-else-if
举例1:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html> <head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=gb2312" />
<meta http-equiv="Content-Language" content="zh-cn" />
<title>My test page</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head> <body> <div id="example">
<p v-if="awesome">Vue is awesome!</p>
<p v-else>Oh noVueJS教程的更多相关文章
- Vue入门手册整理
目录 第一章.环境搭建 第二章.目录结构 第三章.Vue调试 第四章.定义页面 附录资料 第一章.环境搭建 1.1.准备: npm: 6.9.0 (npm > 3.0) node: v10.15 ...
- web前端技术合集
视频课程包含: 微服务精品课程包含:Ajax和Jquery基础入门视频.ajax教程.css视频教程.JQuery视频教程.MUI快速混合APP开发-视频.vuejs教程.极客学院HTML5全套教程. ...
- 完全解析Array.apply(null, { length: 1000 })
Array.apply(null, { length: 1000 }) 点击打开视频讲解更加详细 在阅读VueJS教程时有这么段demo code: render: function (createE ...
- 中文代码示例之Vuejs入门教程(一)
原址: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/30917346 为了检验中文命名在主流框架中的支持程度, 在vuejs官方入门教程第一部分的示例代码中尽量使用了中文命名. 所有演示 ...
- 2017-11-09 中文代码示例之Vuejs入门教程(一)
"中文编程"知乎专栏原链 为了检验中文命名在主流框架中的支持程度, 在vuejs官方入门教程第一部分的示例代码中尽量使用了中文命名. 所有演示都在本地测试通过, 源码在这里. 下面 ...
- 2017-11-20 中文代码示例之Vuejs入门教程(一)问题后续
"中文编程"知乎专栏原文 第一个issue: Error compiling template if using unicode naming as v-for alias · I ...
- VueJS简明教程(一)之基本使用方法
简介:这是一篇超级简单的入门文章 如果说是JQuery是手工作坊,那么Vue.js就像是一座工厂,虽然Vue.js做的任何事情JQuery都可以做,但无论是代码量还是流程规范性都是前者较优. Vue. ...
- Vuejs 基础学习教程
(四)构建基础进阶-env文件与环境设置 我们在实际开发中,我们一般会经历项目的开发阶段,测试阶段,和最终上线阶段,每个阶段对于项目代码的需要可能都有所不同,那我们怎么让它在不同阶段呈现不同的效果呢? ...
- webpack vuejs项目学习心得
最近在做移动端的项目,最近webpack和vuejs很火,就想到了用vuejs webpack来构建我的项目 先了解了一些webpack的入门基础 http://webpack.github.io/d ...
随机推荐
- Web从入门到放弃<3>
UI简单的美化全部来源于Bootstrap 知识来自<javascript dom编程艺术第二版> <1> 点击列表 页面不跳转图片刷新: 主要点: href如何点击完如何不 ...
- 在visual studio 2013中编译Lua5.3.1
注:以下是基于 别人的教程或笔记来操作并按照自己的操作记录的纯文字版编译和hello lua过程. 原图文版链接: 原文链接 1.创建空的解决方案: 文件->新建->项目->其他项目 ...
- jenkins中slave节点连接的两种常用方式
我们在使用jenkins的时候,一般来说肯定是有slave节点的,本来网上也有好多关于jenkins节点配置的教程,我也就不写了.简单说明一下:任务一般是在slave上面运行的.当然不是讲master ...
- 微信小程序+java后台
博主是大四学生,毕业设计做的是微信小程序+java后台.陆陆续续经历了三个月(因为白天要实习又碰上过年玩了一阵子),从对微信小程序一无所知到完成毕设,碰到许多问题,在跟大家分享一下自己的经历和一个小程 ...
- RGB与HSB之间转换
先来了解一些概念: 1.RGB是一种加色模型,就是将不同比例的Red/Green/Blue混合在一起得到新颜色.通常RGB颜色模型表示为: 2.HSB(HSV) 通过色相/饱和度/亮度三要素来表达颜色 ...
- echarts4.0折线图让某个点闪烁
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title> ...
- Eigen::Matrix与array数据转换
1. 数组转化为Eigen::Matrix ]; cout << "colMajor matrix = \n" << Map<Matrix3i> ...
- 527D.Clique Problem
题解: 水题 两种做法: 1.我的 我们假设$xi>xj$ 那么拆开绝对值 $$xi-w[i]>x[j]+w[j]$$ 由于$w[i]>0$,所以$x[i]+w[i]>x[j] ...
- 多线程下载图片,同步下载http://www.importnew.com/15731.html
package mutiDownload; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.RandomA ...
- php代理
有些网上接口请求需要用代理 php代码 <?php header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin:*'); $url=$_POST['urlString']; $res ...
