数据结构复习之Vector
/**
* The number of times this list has been <i>structurally modified</i>.
* Structural modifications are those that change the size of the
* list, or otherwise perturb it in such a fashion that iterations in
* progress may yield incorrect results.
*
* <p>This field is used by the iterator and list iterator implementation
* returned by the {@code iterator} and {@code listIterator} methods.
* If the value of this field changes unexpectedly, the iterator (or list
* iterator) will throw a {@code ConcurrentModificationException} in
* response to the {@code next}, {@code remove}, {@code previous},
* {@code set} or {@code add} operations. This provides
* <i>fail-fast</i> behavior, rather than non-deterministic behavior in
* the face of concurrent modification during iteration.
*
* <p><b>Use of this field by subclasses is optional.</b> If a subclass
* wishes to provide fail-fast iterators (and list iterators), then it
* merely has to increment this field in its {@code add(int, E)} and
* {@code remove(int)} methods (and any other methods that it overrides
* that result in structural modifications to the list). A single call to
* {@code add(int, E)} or {@code remove(int)} must add no more than
* one to this field, or the iterators (and list iterators) will throw
* bogus {@code ConcurrentModificationExceptions}. If an implementation
* does not wish to provide fail-fast iterators, this field may be
* ignored.
*/
protected transient int modCount = 0;
迭代器要用到modCount属性
/**
* The array buffer into which the components of the vector are
* stored. The capacity of the vector is the length of this array buffer,
* and is at least large enough to contain all the vector's elements.
*
* <p>Any array elements following the last element in the Vector are null.
*
* @serial
*/
protected Object[] elementData;
Vector的元素就存储在这个Object数组里,因而Vector的容量就是这个数组的长度,其值至少要大于Vector的要存储的元素的数量,该数组最后一个元素之后的元素都是null。
/**
* The number of valid components in this {@code Vector} object.
* Components {@code elementData[0]} through
* {@code elementData[elementCount-1]} are the actual items.
*
* @serial
*/
protected int elementCount;
这个值代表Vector内有效数据的数量,而且起始元素的下标为0。
/**
* The amount by which the capacity of the vector is automatically
* incremented when its size becomes greater than its capacity. If
* the capacity increment is less than or equal to zero, the capacity
* of the vector is doubled each time it needs to grow.
*
* @serial
*/
protected int capacityIncrement;
有了这个值后,当Vector的大小超过了它的容量的时,Vector的容量才可以实现自动增长。当capacityIncrement小于等于0时,vector的容量就会在需要增长时直接翻倍。(该值可以在初始化时和初始容量一块指定,不指定时默认为0,初始容量默认为10)
/**
* Constructs a vector containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this
* vector
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
* @since 1.2
*/
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
}
也可以通过给定的集合来初始化一个Vector,通过该集合的迭代器的顺序来赋值。(c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)不理解,待查资料)
/**
* Copies the components of this vector into the specified array.
* The item at index {@code k} in this vector is copied into
* component {@code k} of {@code anArray}.
*
* @param anArray the array into which the components get copied
* @throws NullPointerException if the given array is null
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the specified array is not
* large enough to hold all the components of this vector
* @throws ArrayStoreException if a component of this vector is not of
* a runtime type that can be stored in the specified array
* @see #toArray(Object[])
*/
public synchronized void copyInto(Object[] anArray) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, anArray, 0, elementCount);
}
将vector的内容复制给另一指定数组。
/**
* Trims the capacity of this vector to be the vector's current
* size. If the capacity of this vector is larger than its current
* size, then the capacity is changed to equal the size by replacing
* its internal data array, kept in the field {@code elementData},
* with a smaller one. An application can use this operation to
* minimize the storage of a vector.
*/
public synchronized void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (elementCount < oldCapacity) {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount);
}
}
如果vector的容量大于实际存储的元素数量,那么就将vector的容量调整为实际存储的元素数量,通过对内部数组重新赋值来实现,可以通过该操作最小化vector所占的内存。
/**
* Increases the capacity of this vector, if necessary, to ensure
* that it can hold at least the number of components specified by
* the minimum capacity argument.
*
* <p>If the current capacity of this vector is less than
* {@code minCapacity}, then its capacity is increased by replacing its
* internal data array, kept in the field {@code elementData}, with a
* larger one. The size of the new data array will be the old size plus
* {@code capacityIncrement}, unless the value of
* {@code capacityIncrement} is less than or equal to zero, in which case
* the new capacity will be twice the old capacity; but if this new size
* is still smaller than {@code minCapacity}, then the new capacity will
* be {@code minCapacity}.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
public synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > 0) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(minCapacity);
}
}
/**
* This implements the unsynchronized semantics of ensureCapacity.
* Synchronized methods in this class can internally call this
* method for ensuring capacity without incurring the cost of an
* extra synchronization.
*
* @see #ensureCapacity(int)
*/
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
增加vector的容量,如果有必要,要保证增加后的容量由minCapacity给出的最小容量。如果vector当前的容量小于minCapacity,就通过对内部数组重新赋值一个更大的数组的方式来扩容。当capacityIncrement小于等于0时,新数组的大小是之前的2倍,大于0时新数组的大小等于旧数组的大小与capacityIncrement只和。如果增加后的数组容量仍然小于minCapacity,那么新数组的大小为minCapacity。(ensureCapacityHelper方法不加synchronized是因为ensureCapacity方法加了synchronized,而且ensureCapacityHelper方法是在ensureCapacity内部调用的,因而没必要增加额外的synchronized)
而设置MAX_ARRAY_SIZE是因为,vector内部元素的数量elementCount和容量都是int型因而不能超出int的范围,而减8是因为某些VM里设有头结点,所以要留出这部分的空间。
hugeCapacity方法中判断minCapacity是否小于零则是因为负数减MAX_ARRAY_SIZE也可能大于0,例如
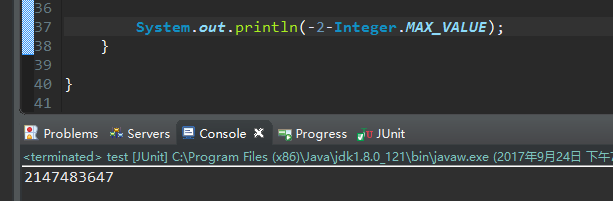
但是这里又为什么返回了Integer.MAX_VALUE呢(待解决)
/**
* Sets the size of this vector. If the new size is greater than the
* current size, new {@code null} items are added to the end of
* the vector. If the new size is less than the current size, all
* components at index {@code newSize} and greater are discarded.
*
* @param newSize the new size of this vector
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the new size is negative
*/
public synchronized void setSize(int newSize) {
modCount++;
if (newSize > elementCount) {
ensureCapacityHelper(newSize);
} else {
for (int i = newSize ; i < elementCount ; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
}
elementCount = newSize;
}
setSize方法用来修改当前vector的大小,如果newSize大于当前元素数量elementCount那么调用ensureCapacityHelper方法进行扩容(此时没有经过ensureCapacity方法),当newSize小于elementCount时,将数组下标大于等于newSize的元素的值设为null,两种情况最后都要将elementCount大小改为newSize。
/**
* Returns the current capacity of this vector.
*
* @return the current capacity (the length of its internal
* data array, kept in the field {@code elementData}
* of this vector)
*/
public synchronized int capacity() {
return elementData.length;
}
/**
* Returns the number of components in this vector.
*
* @return the number of components in this vector
*/
public synchronized int size() {
return elementCount;
}
/**
* Tests if this vector has no components.
*
* @return {@code true} if and only if this vector has
* no components, that is, its size is zero;
* {@code false} otherwise.
*/
public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {
return elementCount == 0;
}
以上三个方法分别返回vector容量、元素数量elementCount以及判断vector是否为空。
/**
* Returns an enumeration of the components of this vector. The
* returned {@code Enumeration} object will generate all items in
* this vector. The first item generated is the item at index {@code 0},
* then the item at index {@code 1}, and so on.
*
* @return an enumeration of the components of this vector
* @see Iterator
*/
public Enumeration<E> elements() {
return new Enumeration<E>() {
int count = 0;
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
return count < elementCount;
}
public E nextElement() {
synchronized (Vector.this) {
if (count < elementCount) {
return elementData(count++);
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException("Vector Enumeration");
}
};
}
该方法返回vector内部元素按下标顺序的Enumeration(类似枚举类型)
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in
* this vector, searching forwards from {@code index}, or returns -1 if
* the element is not found.
* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that
* <tt>(i >= index && (o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i))))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @param index index to start searching from
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the element in
* this vector at position {@code index} or later in the vector;
* {@code -1} if the element is not found.
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the specified index is negative
* @see Object#equals(Object)
*/
public synchronized int indexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
indexOf方法从给定index开始查找vector内是否存有Object o(可以为空),如果有则返回第一次出现的下标,如果不存在返回-1。
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this vector contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this vector
* contains at least one element {@code e} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>.
*
* @param o element whose presence in this vector is to be tested
* @return {@code true} if this vector contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0) >= 0;
}
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this vector, or -1 if this vector does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in
* this vector, or -1 if this vector does not contain the element
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
return indexOf(o, 0);
}
这两个方法都调用上边的indexOf方法,contains判断是否包含Object o,如果存在,返回true,否则返回false,indexOf也判断是否包含Object o,如果包含则返回第一次出现的下标,不存在返回-1。
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in
* this vector, searching backwards from {@code index}, or returns -1 if
* the element is not found.
* More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that
* <tt>(i <= index && (o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i))))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @param index index to start searching backwards from
* @return the index of the last occurrence of the element at position
* less than or equal to {@code index} in this vector;
* -1 if the element is not found.
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the specified index is greater
* than or equal to the current size of this vector
*/
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= "+ elementCount);
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index; i >= 0; i--)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
lastIndexOf方法类似indexOf方法,区别在于lastIndexOf方法从后向前查找,因而返回的是最后一次出现的下标,不存在仍然返回-1。
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this vector, or -1 if this vector does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index {@code i} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in
* this vector, or -1 if this vector does not contain the element
*/
public synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
return lastIndexOf(o, elementCount-1);
}
该方法调用lastIndexOf发法,返回Object o最后一次出现的下标,不存在仍然返回-1。
/**
* Returns the component at the specified index.
*
* <p>This method is identical in functionality to the {@link #get(int)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface).
*
* @param index an index into this vector
* @return the component at the specified index
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
return elementData(index);
}
/**
* Returns the first component (the item at index {@code 0}) of
* this vector.
*
* @return the first component of this vector
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this vector has no components
*/
public synchronized E firstElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return elementData(0);
}
/**
* Returns the last component of the vector.
*
* @return the last component of the vector, i.e., the component at index
* <code>size() - 1</code>.
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this vector is empty
*/
public synchronized E lastElement() {
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return elementData(elementCount - 1);
}
elementAt返回指定下标的元素,firstElement返回第一个元素,lastElement返回最后一个元素。
/**
* Sets the component at the specified {@code index} of this
* vector to be the specified object. The previous component at that
* position is discarded.
*
* <p>The index must be a value greater than or equal to {@code 0}
* and less than the current size of the vector.
*
* <p>This method is identical in functionality to the
* {@link #set(int, Object) set(int, E)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface). Note that the
* {@code set} method reverses the order of the parameters, to more closely
* match array usage. Note also that the {@code set} method returns the
* old value that was stored at the specified position.
*
* @param obj what the component is to be set to
* @param index the specified index
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
public synchronized void setElementAt(E obj, int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
elementData[index] = obj;
}
该方法用来修改指定index的值(注意,不能添加index >= elementCount时会抛出异常),该方法与List接口中的set方法功能一样,区别在于set方法参数顺序更接近数组的用法,此外set还会返回旧元素的值。
/**
* Deletes the component at the specified index. Each component in
* this vector with an index greater or equal to the specified
* {@code index} is shifted downward to have an index one
* smaller than the value it had previously. The size of this vector
* is decreased by {@code 1}.
*
* <p>The index must be a value greater than or equal to {@code 0}
* and less than the current size of the vector.
*
* <p>This method is identical in functionality to the {@link #remove(int)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface). Note that the
* {@code remove} method returns the old value that was stored at the
* specified position.
*
* @param index the index of the object to remove
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
该方法通过将给定index(不包括index)后的所有有效元素前移的方式达到删除下标为index的元素的目的。
/**
* Inserts the specified object as a component in this vector at the
* specified {@code index}. Each component in this vector with
* an index greater or equal to the specified {@code index} is
* shifted upward to have an index one greater than the value it had
* previously.
*
* <p>The index must be a value greater than or equal to {@code 0}
* and less than or equal to the current size of the vector. (If the
* index is equal to the current size of the vector, the new element
* is appended to the Vector.)
*
* <p>This method is identical in functionality to the
* {@link #add(int, Object) add(int, E)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface). Note that the
* {@code add} method reverses the order of the parameters, to more closely
* match array usage.
*
* @param obj the component to insert
* @param index where to insert the new component
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index > size()})
*/
public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {
modCount++;
if (index > elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index
+ " > " + elementCount);
}
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);
elementData[index] = obj;
elementCount++;
}
该方法将index及其后的所有有效元素后移一位,然后将obj对象赋值给下标为index元素,从而实现插入元素(当index=elementCount效果等同于在最后添加一个元素)
数据结构复习之Vector的更多相关文章
- 数据结构逆向分析-Vector
数据结构逆向分析-Vector 这个应该是家喻户晓了的东西把,如果说C/C++程序员Vector都不用的话,可能就是一个不太好的程序员. Vector就是一个STL封装的动态数组,数组大家都知道是通过 ...
- Java 常用数据结构深入分析(Vector、ArrayList、List、Map)
线性表,链表,哈希表是常用的数据结构,在进行Java开发时,JDK已经为我们提供了一系列相应的类来实现基本的数据结构.这些类均在java.util包中.本文试图通过简单的描述,向读者阐述各个类的作用以 ...
- 数据结构复习:交换排序原理及C++实现
1. 交换排序的基本思想 两两比较key值,如果发生逆序(排列的顺序与期望的顺序相反)就交换,知道所有对象都排序完毕!常见的3种交换排序算法:冒泡排序,shaker排序和快速排序. 2. 冒泡排序 设 ...
- 数据结构复习:希尔排序的C++实现
1.原理介绍 希尔排序又称为缩小增量排序,由D.L.Shell在1959年提出而得名. 该算法先取一个小于数据表中元素个数 n 的整数gap, 并以此作为第一个间隔,将数据分为gap个子序列,所有距离 ...
- 数据结构复习:直接插入排序与二分插入排序的C++实现
1.直接插入排序 直接插入排序的过程可以理解为一个固定长度的数组被分为两个集合,即已排序集合和未排序. 开始时已排序集合为空,而未排序集合即为整个数组.当排序开始后插入一个对象,已排序集合元素数目加1 ...
- 数据结构复习之C语言指针与结构体
数据结构指针复习: #include <stdio.h> void main() { ] = {, , , , }; // a[3] == *(3+a) printf(+a)); // a ...
- 从零开始学习R语言(一)——数据结构之“向量”(Vector)
本文首发于知乎专栏:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/59688569 也同步更新于我的个人博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/nickwu/p/125370 ...
- c语言数据结构复习
1)线性表 //顺序存储下线性表的操作实现 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> typedef int ElemType; /*线性表 ...
- NOIP 考前 数据结构复习
BZOJ 1455 左偏树即可 #include <cstdio> #define LL long long ; struct Info{LL l,r,v,Dis;}Tree[Maxn]; ...
随机推荐
- LINQ更新提示找不到行或行已更改的解决一例
LINQ对一行数据进行更改,怎么都无法提交,所有字段值都不是空值,后来看了实体,我发现更改的数据是主键,去数据库看这个字段却不是主键,原来是数据库取消主键了,实体代码没取消,因为更改了主键,所以无法更 ...
- 运行python “没有那个文件或目录3” 或 “/usr/local/bin/python3^M: bad interpreter: 没有那个文件或目录” 错误
原因 如果使用的是#!/usr/local/bin/python3这种方式,就会出现 “/usr/local/bin/python3^M: bad interpreter: 没有那个文件或目录” 错误 ...
- python cookbook 小结
最近一直在看python cookbook.这本书主要讲的是python 语言的一些编程素材.正如它的名字一样,烹饪书.就好像再讲如何处理食材(各种类型的数据),然后再煮菜(算法).打个比方,煮菜随便 ...
- 代码生成器——实现生成pojo,sql,mapper接口
代码生成器(记录一次兴趣代码,多多指教.转载请标明作者) 在我们开始实现代码生成器之前我们先来对代码生成器有一个简单的了解. 1.什么是代码生成器? 故名思义,也就是生成代码的一个程序.那它是一个什么 ...
- cron表达式总结
cron表达式用于配置cronTrigger的实例,在定时任务中会用到cron表达式.cron表达式实际上是由七个子表达式组成.这些表达式之间用空格分隔. 可通过工具校验:http://cron.qq ...
- Mybatis映射文件中#取值时指定参数相关规则
Mybatis映射文件中#取值时指定参数相关规则 在#{}中,除了需要的数值外,还可以规定参数的一些其他规则. 例如:javaType,jdbcType,mode(存储过程),numericScale ...
- Mybatis日志
[DEBUG] 2018-05-20 09:56:36,404(19404) --> [main] org.slf4j.impl.JCLLoggerAdapter.trace(JCLLogger ...
- Linux(例如CentOS 7)打开TCP 22端口,基于SSH协议
SSH 为 Secure Shell 的缩写,由 IETF 的网络工作小组(Network Working Group)所制定:SSH 为建立在应用层和传输层基础上的安全协议.SSH 是目前较可靠,专 ...
- (6)tcp-socket
(1)client端口: import socket# 产生一个socket对象sk = socket.socket()# 建立连接sk.connect( ("127.0.0.1" ...
- setting.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><settings xmlns="http://mave ...
