python爬虫数据解析之BeautifulSoup
BeautifulSoup是一个可以从HTML或者XML文件中提取数据的python库。它能够通过你喜欢的转换器实现惯用的文档导航,查找,修改文档的方式。
BeautfulSoup是python爬虫三大解析方法之一。
首先来看个例子:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'lxml')
print(soup.prettify())
这个beautiful对象可以按照标准的缩进结构输出。
<html>
<head>
<title>
The Dormouse's story
</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="title">
<b>
The Dormouse's story
</b>
</p>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
Elsie
</a>
,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">
Lacie
</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">
Tillie
</a>
;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">
...
</p>
</body>
</html>
接下来用以上例子来使用beautifulsoup
# soup.title 找到第一个title标签,其他也一样
print(soup.title)

# soup.title.name 找到title标签的名字
print(soup.title.name)
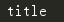
# 找到第一个p标签的class属性
print(soup.p['class'])
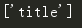
# 找到第一个p标签的属性和属性值,以字典形式呈现
print(soup.p.attrs)
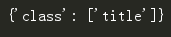
其属性可以修改和删除,操作方法和字典一样.
# 找到title标签的内容,3中方式
print(soup.title.string)

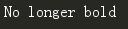
# 找到title标签的内容,并替换
soup.title.string.replace_with("No longer bold")
print(soup.title.string)
# 输出head的子标签
print(soup.head.contents)

# 输出head的第一个子标签
print(soup.head.contents[0])

# 输出head的子标签
print(soup.head.children)

返回一个列表对象,用来做迭代.
# 输出head的所有子孙节点
print(soup.head.descendants)

如果tag包含了多个子节点,tag就无法确定 .string 方法应该调用哪个子节点的内容, .string 的输出结果是 None
如果tag中包含多个字符串 ,可以使用 .strings 来循环获取:
输出的字符串中可能包含了很多空格或空行,使用 .stripped_strings 可以去除多余空白内容:
# 找到title标签的父标签
print(soup.title.parent)

# 找到第一个a标签
link = soup.a
# 找打a节点的所有父节点
for parent in link.parents:
print(parent.name)
在文档树中,使用 .next_sibling 和 .previous_sibling 属性来查询兄弟节点:
find()
find(name, attrs, recursive, text, **wargs) # recursive 递归的,循环的
# 找到第一个a节点
print(soup.find('a'))

# 找文本为Elsie的第一个a节点
print(soup.find('a', text='Elsie'))
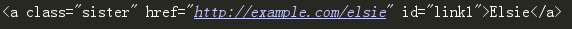
# 通过正则表达式查找第一个包含字符a的标签
print(soup.find(re.compile('a')))

# 找到一个包含id='link3'标签
print(soup.find(id="link3"))

# 找到一个包含id='link3'标签
print(soup.find(attrs={'id':'link3'}))

class是python的保留关键字,所以无法使用class这个关键字。
有2种方法:
第一种:soup.find(attrs={'class':'haha'})
第二种:soup.find(class_='haha')
# 定义函数查找
def search_one(tag):
return tag.has_attr('id') and tag.get('id')=='link3'
oder = soup.find(search_one)
print(oder)

find_all()
find_all(name, attrs, recursive, text, limit, **kwargs)
调用tag的 find_all() 方法时,Beautiful Soup会检索当前tag的所有子孙节点,如果只想搜索tag的直接子节点,可以使用参数 recursive=False .
# 找到所有的a标签,返回的是列表
print(soup.find_all('a'))
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
# 找到所有的a标签中的第一个
print(soup.find_all('a', limit=1))

# 找到所有包含a字符的标签,返回一个列表
print(soup.find_all(re.compile('a')))
[<head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
# 找到所有的a标签和b标签
print(soup.find_all(['a', 'b']))
[<b>The Dormouse's story</b>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
# 找到所有的有属性值为sister的a标签
print(soup.find_all("a", "sister"))
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
# 找到所有的有id属性值为link1的a标签
print(soup.find_all(id='link1'))

class是python的保留关键字,所以无法使用class这个关键字。
有2种方法:
第一种:soup.find_all(attrs={'class':'haha'})
第二种:soup.find_all(class_='haha')
# 找到所有的内容为Elsie的内容
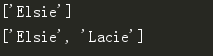
print(soup.find_all(text='Elsie'))
print(soup.find_all(text=['Elsie', 'Lacie']))
CSS选择器
Beautiful Soup支持大部分的CSS选择器 [6] ,在 Tag 或 BeautifulSoup 对象的 .select() 方法中传入字符串参数,即可使用CSS选择器的语法找到tag
常见的选择器:标签选择器(a)、类选择器(.)、id选择器(#)、层级选择器
div .dudu #lala .meme .xixi 下面好多级
div > p > a > .lala 只能是下面一级
# 找到select标签
print(soup.select('title'))

# 找到body下的a
print(soup.select('body a'))
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
找到某个tag标签下的直接子标签
# 找到head下的title
print(soup.select('head > title'))

# 找到p下的a
print(soup.select('p > a'))
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
# 找到p下的id选择器link1
print(soup.select('p > #link1'))
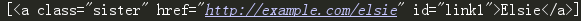
找到第一个有id选择器link1第二个有类选择器sister
print(soup.select('#link1 ~ .sister'))

# 找到有id选择器link1和类选择器sister
print(soup.select('#link1 + .sister'))

# 通过类名查找
print(soup.select('.sister'))
print(soup.select("[class~=sister]"))
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
# 通过id查找
print(soup.select('a#link1'))
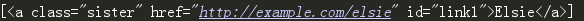
# 通过属性查找
print(soup.select('a[id]'))
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
# 通过属性查找
print(soup.select('a[href="http://example.com/elsie"]'))
# 只要包含一部分属性就行
print(soup.select('a[href*="m/el"]'))
# 属性的结尾
print(soup.select('a[href$="elsie"]'))
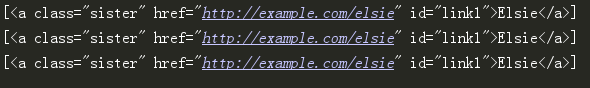
例子
1 爬取诗词名句网 的水浒传并保存到本地 网址:http://www.shicimingju.com/book/shuihuzhuan.html
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import os #解析出所有的目录
def main(url, headers):
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers).text
soup = BeautifulSoup(response, 'lxml')
titles = soup.find_all(attrs=['class', 'book-mulu'])
for one_title in titles:
# 得到一个一个a标签的列表
mulu_lst = one_title.find_all('a')
write_in(mulu_lst) # 写入文件
def write_in(mulu):
# 创建文件夹
if not os.path.exists('shuihu'):
os.mkdir('shuihu')
# 解析每一章节
for one_mulu in mulu:
# 拿到新的页面
text = requests.get(url='http://www.shicimingju.com'+one_mulu['href'], headers=ua_headers).text
soup1 = BeautifulSoup(text, 'lxml')
content = soup1.find_all(attrs=['class', 'chapter_content'])
# 解析这个div
for one_content in content:
# 去出2遍空格
con = one_content.get_text().strip()
# 将每段空格换为换行符
con1 = con.replace(' ', '\n')
# 以章节为名写入文件夹
with open('shuihu/'+ one_mulu.string + '.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(con1) if __name__ == '__main__':
url = 'http://www.shicimingju.com/book/shuihuzhuan.html'
ua_headers = {"User-Agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, like Gecko) "
"Version/5.1 Safari/534.50"}
main(url, ua_headers)
得到本地书籍:可以拖到手机上去看

其实上段代码的beautifulsoup可以简化的,但是我为了练习find_all就写了以上代码,可以用其他方式简化的.
2 爬取抽屉网首页的新闻标题和连接 https://dig.chouti.com/
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup def main():
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=ua_headers).text
soup = BeautifulSoup(response, 'lxml')
titles = soup.find_all('a', class_="show-content color-chag")
for one_title in titles:
print('标题' + one_title.text.strip() + '的链接为:' + one_title['href']) if __name__ == '__main__':
url = 'https://dig.chouti.com/'
ua_headers = { "User-Agent":'Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 6.0; Trident/4.0)'}
main()
得到输出:

3 爬取58同城的房源信息 深圳二手房,并保存到xls文件
https://sz.58.com/ershoufang/?utm_source=market&spm=u-2d2yxv86y3v43nkddh1.BDPCPZ_BT&PGTID=0d30000c-0000-4591-0324-370565eccba8&ClickID=1
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import xlwt # 得到soup对象
def main(url,headers):
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers).text
soup = BeautifulSoup(response, 'lxml')
parse(soup) # 解析出数据,写入xls
def parse(soup):
# 找到带有类选择器house-list-wrap下面的所有li标签
li_list = soup.select('ul.house-list-wrap > li')
# 创建xls文件
wookbook = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8')
sheet = wookbook.add_sheet('58 sheet')
title_lst = ['name', 'total_price', 'one_price', 'huxing', 'area', 'direction', 'height']
hang, lie = 0, 0
# 把第零行的标题写进去
for one in title_lst:
sheet.write(0, lie, one)
lie += 1
# 写入每一行
hang += 1
for one_li in li_list:
sheet.write(hang, 0, one_li.select('h2 > a')[0].text.strip())
sheet.write(hang, 1, one_li.select('div.price > p.sum')[0].text)
sheet.write(hang, 2, one_li.select('div.price > p.unit')[0].text)
sheet.write(hang, 3, one_li.select('div.list-info > p.baseinfo > span')[0].text)
sheet.write(hang, 4, one_li.select('div.list-info > p.baseinfo > span')[1].text.strip())
sheet.write(hang, 5, one_li.select('div.list-info > p.baseinfo > span')[2].text)
sheet.write(hang, 6, one_li.select('div.list-info > p.baseinfo > span')[3].text)
hang += 1
wookbook.save('58深圳二手房子.xls') if __name__ == '__main__':
url = 'https://sz.58.com/ershoufang/?utm_source=market&spm=u-2d2yxv86y3v43nkddh1.' \
'BDPCPZ_BT&PGTID=0d30000c-0000-4591-0324-370565eccba8&ClickID=1'
ua_headers = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 (KHTML, "
"like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50"}
main(url, ua_headers)
得到xls文件.
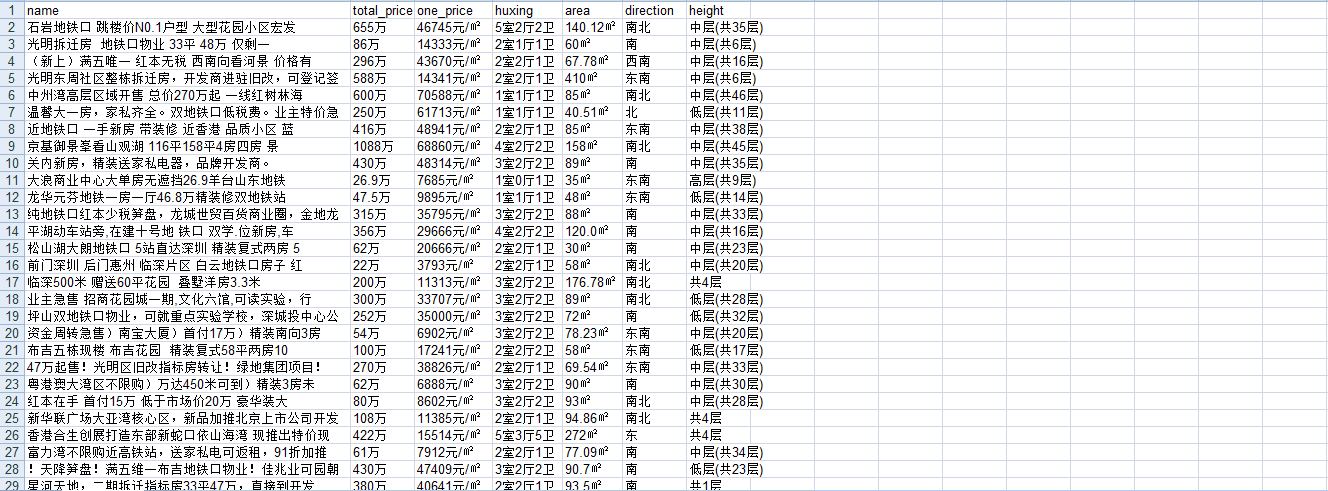
python爬虫数据解析之BeautifulSoup的更多相关文章
- python爬虫--数据解析
数据解析 什么是数据解析及作用 概念:就是将一组数据中的局部数据进行提取 作用:来实现聚焦爬虫 数据解析的通用原理 标签定位 取文本或者属性 正则解析 正则回顾 单字符: . : 除换行以外所有字符 ...
- python爬虫数据解析之正则表达式
爬虫的一般分为四步,第二个步骤就是对爬取的数据进行解析. python爬虫一般使用三种解析方式,一正则表达式,二xpath,三BeautifulSoup. 这篇博客主要记录下正则表达式的使用. 正则表 ...
- python爬虫数据解析的四种不同选择器Xpath,Beautiful Soup,pyquery,re
这里主要是做一个关于数据爬取以后的数据解析功能的整合,方便查阅,以防混淆 主要讲到的技术有Xpath,BeautifulSoup,PyQuery,re(正则) 首先举出两个作示例的代码,方便后面举例 ...
- python爬虫数据解析之xpath
xpath是一门在xml文档中查找信息的语言.xpath可以用来在xml文档中对元素和属性进行遍历. 在xpath中,有7中类型的节点,元素,属性,文本,命名空间,处理指令,注释及根节点. 节点 首先 ...
- Python爬虫html解析工具beautifulSoup在pycharm中安装及失败的解决办法
1.安装步骤: 首先,你要先进入pycharm的Project Interpreter界面,进入方法是:setting(ctrl+alt+s) ->Project Interpreter,Pro ...
- [转]Python爬虫html解析工具beautifulSoup在pycharm中安装及失败的解决办法
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yysbolg/p/9040649.html 刚开始学习一门技术最麻烦的问题就是搞定IDE环境,直接在PyCharm里安装BeautifulS ...
- 070.Python聚焦爬虫数据解析
一 聚焦爬虫数据解析 1.1 基本介绍 聚焦爬虫的编码流程 指定url 基于requests模块发起请求 获取响应对象中的数据 数据解析 进行持久化存储 如何实现数据解析 三种数据解析方式 正则表达式 ...
- python爬虫+数据可视化项目(关注、持续更新)
python爬虫+数据可视化项目(一) 爬取目标:中国天气网(起始url:http://www.weather.com.cn/textFC/hb.shtml#) 爬取内容:全国实时温度最低的十个城市气 ...
- 爬虫-数据解析-bs4
1.数据解析 解析: 根据指定的规则对数据进行提取 作用: 实现聚焦爬虫 数据解析方式: - 正则表达式 - bs4 - xpath 数据解析的通用原理: 数据解析需要作用在页面源码中(一组html标 ...
随机推荐
- spring-boot-starter-druid
i have found from the document, and seems that spring-boot only support tomcat-jdbc,HikariCP and DBC ...
- SQL—对数据表内容的基本操作
数据表 students id name sex age address 101 张汉 男 14 杭州 102 欧阳钦 男 13 杭州 103 吴昊 男 14 北京 104 钱进进 男 1 ...
- 借助HTML中的特殊符号在markdown中打印出来
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/html5_/article/details/21639475 HTML中的特殊符号 原创 2014年03月20日 18:35:23 标签: HTML ...
- Oracle 重建控制文件一例
环境:OEL 5.7 + Oracle 10.2.0.5 背景:在Oracle的运维过程中,时常会遇到一些场景是需要重建控制文件才可以解决的.本文的场景可以通过复制控制文件到新路径,运行一段时间后,再 ...
- java 四舍五入保留两位小数
// 保留两位小数 System.out.println(Double.parseDouble(String.format("%.2f", 55.5454545454))); // ...
- 带logo图片或不带logo图片的二维码生成与解析,亲测成功
最近公司需要实现二维码功能,本人经过一顿百度,终于实现了,因有3个功能:不带logo图片.带logo图片.解析二维码,篇幅较长,请耐心读之,直接复制粘贴即可. 前提:myeclipse10:jar包: ...
- ASP.NET Core的实时库: SignalR简介及使用
大纲 本系列会分为2-3篇文章. 第一篇介绍了SignalR的预备知识和原理 本文介绍SignalR以及ASP.NET Core里使用SignalR. 本文的内容: 介绍SignalR 在ASP.NE ...
- 【数学基础篇】---详解极限与微分学与Jensen 不等式
一.前述 数学基础知识对机器学习还有深度学习的知识点理解尤为重要,本节主要讲解极限等相关知识. 二.极限 1.例子 当 x 趋于 0 的时候,sin(x) 与 tan(x) 都趋于 0. 但是哪一个趋 ...
- 分布式系统关注点(15)——「水平&垂直切分」详解
如果第二次看到我的文章,欢迎右侧扫码订阅我哟~
- 小程序 textarea、input 层级过高,导致填写内容穿透,z-index无效问题解决方案。
小程序的textare.input输入框层级是最高的 那么我们在textare.input输入的内容就会总是显示在最上一层. 这是时为什么呢?官方文档有说明,因为textare.input这些是原生组 ...
