mybatis源码解读(四)——事务的配置
上一篇博客我们介绍了mybatis中关于数据源的配置原理,本篇博客介绍mybatis的事务管理。
对于事务,我们是在mybatis-configuration.xml 文件中配置的:
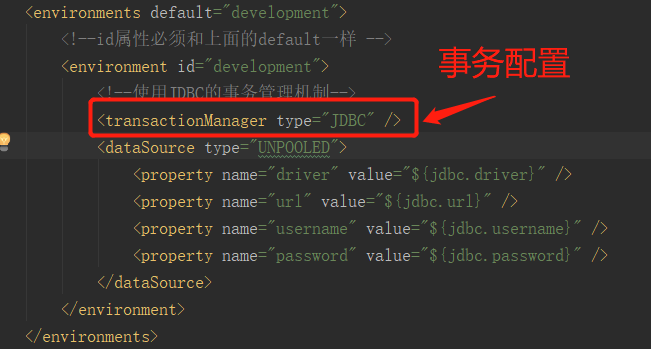
关于解析 <environments />标签在上一篇数据源的配置我们已经介绍了,不了解的可以参考上篇博客。
1、mybatis 支持的事务类图
mybatis 支持的所有事务的所有类都在如下包中:
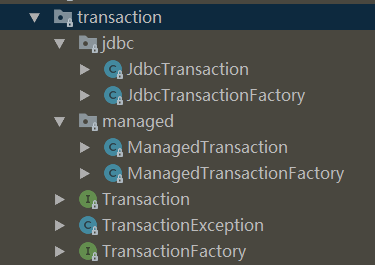
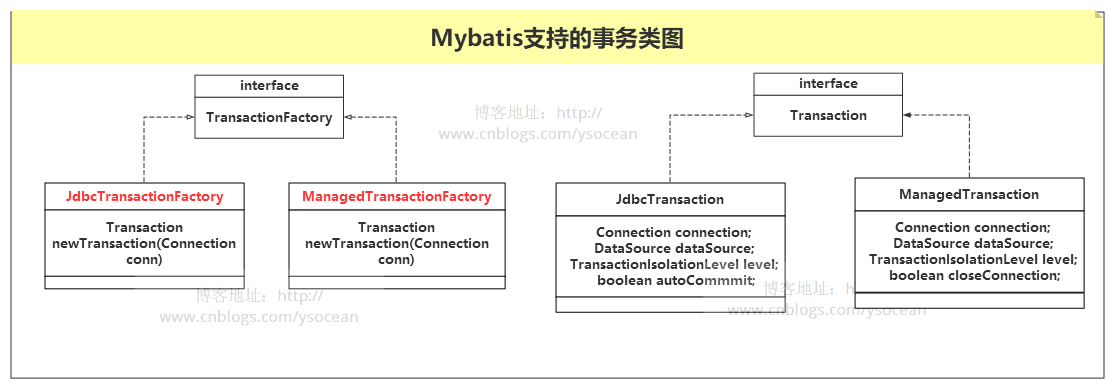
下面通过类图来理解该包中所有类的关系:
2、mybatis 支持的两种事务类型管理器
通过配置文件中的 type 属性:
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
我们可以配置不同的事务管理器来管理事务。在mybatis中支持两种事务类型管理器,分别是:
①、type = "JDBC":这个配置就是直接使用了 JDBC 的提交和回滚设置,它依赖于从数据源得到的连接来管理事务作用域。
②、type="MANAGED":这个配置几乎没做什么。它从来不提交或回滚一个连接,而是让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期(比如 JEE 应用服务器的上下文)。 默认情况下它会关闭连接,然而一些容器并不希望这样,因此需要将 closeConnection 属性设置为 false 来阻止它默认的关闭行为。例如:
<transactionManager type="MANAGED">
<property name="closeConnection" value="false"/>
</transactionManager>
注意:和数据源配置一样,通常项目中我们不会单独使用 mybatis 来管理事务。比如选择框架 Spring +mybatis,这时候没有必要配置事务管理器, 因为 Spring 模块会使用自带的管理器来覆盖前面的配置。
再回头看看在 mybatis 的 org.apache.ibatis.transaction 包下的所有类,也就是上面的类图。mybatis的事务首先会定义一个事务接口 Transaction,
3、初始化事务管理器
我们说事务(Transaction),一般是指要做的或所做的事情。在数据库中,事务具有如下四个属性:
①、原子性(atomicity):一个事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中包括的诸操作要么都做,要么都不做。
②、一致性(consistency):事务必须是使数据库从一个一致性状态变到另一个一致性状态。一致性与原子性是密切相关的。
③、隔离性(isolation):一个事务的执行不能被其他事务干扰。即一个事务内部的操作及使用的数据对并发的其他事务是隔离的,并发执行的各个事务之间不能互相干扰。
④、持久性(durability):持久性也称永久性(permanence),指一个事务一旦提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就应该是永久性的。接下来的其他操作或故障不应该对其有任何影响。
这也就是常说的事务 ACID 特性。而在程序中,对于事务的操作通常是:
1、创建事务(create)
2、提交事务(commit)
3、回滚事务(rollback)
4、关闭事务(close)
在mybatis的 org.apache.ibatis.transaction 包下的 Transaction 接口便为我们定义了这一套操作:
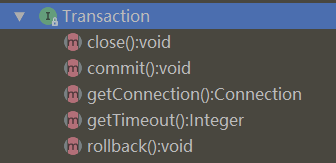
/**
* Copyright 2009-2016 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.ibatis.transaction; import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException; /**
* Wraps a database connection.
* Handles the connection lifecycle that comprises: its creation, preparation, commit/rollback and close.
*
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public interface Transaction { /**
* Retrieve inner database connection
* @return DataBase connection
* @throws SQLException
*/
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException; /**
* Commit inner database connection.
* @throws SQLException
*/
void commit() throws SQLException; /**
* Rollback inner database connection.
* @throws SQLException
*/
void rollback() throws SQLException; /**
* Close inner database connection.
* @throws SQLException
*/
void close() throws SQLException; /**
* Get transaction timeout if set
* @throws SQLException
*/
Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException; }
同时,mybatis为了获取事务采用了工厂模式,定义了一个工厂接口:TransactionFactory
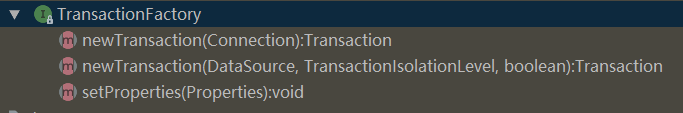
通过实现该工厂接口,mybatis提供了两种不同的事务管理器:
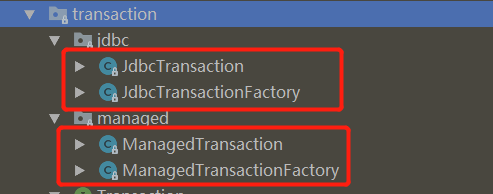
这两种事务管理器的获取也是采用了工厂模式。下面我们来分别看看这两种事务管理器。
4、JdbcTransaction
当在配置文件中配置:type = "JDBC"时,就是用 JdbcTransaction 来管理事务。使用了 JDBC 的提交和回滚设置,它依赖于从数据源得到的连接来管理事务作用域。
代码如下:
public class JdbcTransaction implements Transaction {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(JdbcTransaction.class);
//数据库连接
protected Connection connection;
//数据源
protected DataSource dataSource;
//隔离级别
protected TransactionIsolationLevel level;
//是否自动提交
protected boolean autoCommmit;
public JdbcTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel desiredLevel, boolean desiredAutoCommit) {
dataSource = ds;
level = desiredLevel;
autoCommmit = desiredAutoCommit;
}
public JdbcTransaction(Connection connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return connection;
}
//调用connection.commit()来实现
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.commit();
}
}
//调用connection.rollback()来实现
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Rolling back JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.rollback();
}
}
//调用connection.close()来实现
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null) {
resetAutoCommit();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.close();
}
}
protected void setDesiredAutoCommit(boolean desiredAutoCommit) {
try {
//事务提交状态不一致
if (connection.getAutoCommit() != desiredAutoCommit) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Setting autocommit to " + desiredAutoCommit + " on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.setAutoCommit(desiredAutoCommit);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// Only a very poorly implemented driver would fail here,
// and there's not much we can do about that.
throw new TransactionException("Error configuring AutoCommit. "
+ "Your driver may not support getAutoCommit() or setAutoCommit(). "
+ "Requested setting: " + desiredAutoCommit + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
protected void resetAutoCommit() {
try {
if (!connection.getAutoCommit()) {
// MyBatis does not call commit/rollback on a connection if just selects were performed.
// Some databases start transactions with select statements
// and they mandate a commit/rollback before closing the connection.
// A workaround is setting the autocommit to true before closing the connection.
// Sybase throws an exception here.
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.setAutoCommit(true);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Error resetting autocommit to true "
+ "before closing the connection. Cause: " + e);
}
}
}
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
if (level != null) {
connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());
}
setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommmit);
}
@Override
public Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
}
5、ManagedTransaction
ManagedTransaction的代码实现几乎都是一个空的方法,它选择让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期(比如 JEE 应用服务器的上下文)。
/**
* Copyright 2009-2016 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.ibatis.transaction.managed; import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import javax.sql.DataSource; import org.apache.ibatis.logging.Log;
import org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.TransactionIsolationLevel;
import org.apache.ibatis.transaction.Transaction; /**
* {@link Transaction} that lets the container manage the full lifecycle of the transaction.
* Delays connection retrieval until getConnection() is called.
* Ignores all commit or rollback requests.
* By default, it closes the connection but can be configured not to do it.
*
* @author Clinton Begin
*
* @see ManagedTransactionFactory
*/
public class ManagedTransaction implements Transaction { private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(ManagedTransaction.class); private DataSource dataSource;
private TransactionIsolationLevel level;
private Connection connection;
private boolean closeConnection; public ManagedTransaction(Connection connection, boolean closeConnection) {
this.connection = connection;
this.closeConnection = closeConnection;
} public ManagedTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean closeConnection) {
this.dataSource = ds;
this.level = level;
this.closeConnection = closeConnection;
} @Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (this.connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return this.connection;
} @Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
// Does nothing
} @Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
// Does nothing
} @Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (this.closeConnection && this.connection != null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "]");
}
this.connection.close();
}
} protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
this.connection = this.dataSource.getConnection();
if (this.level != null) {
this.connection.setTransactionIsolation(this.level.getLevel());
}
} @Override
public Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException {
return null;
} }
mybatis源码解读(四)——事务的配置的更多相关文章
- mybatis源码解读(三)——数据源的配置
在mybatis-configuration.xml 文件中,我们进行了如下的配置: <!-- 可以配置多个运行环境,但是每个 SqlSessionFactory 实例只能选择一个运行环境常用: ...
- spring IOC DI AOP MVC 事务, mybatis 源码解读
demo https://gitee.com/easybao/aop.git spring DI运行时序 AbstractApplicationContext类的 refresh()方法 1: pre ...
- Mybatis源码解读-SpringBoot中配置加载和Mapper的生成
本文mybatis-spring-boot探讨在springboot工程中mybatis相关对象的注册与加载. 建议先了解mybatis在spring中的使用和springboot自动装载机制,再看此 ...
- MyBatis源码解读(3)——MapperMethod
在前面两篇的MyBatis源码解读中,我们一路跟踪到了MapperProxy,知道了尽管是使用了动态代理技术使得我们能直接使用接口方法.为巩固加深动态代理,我们不妨再来回忆一遍何为动态代理. 我相信在 ...
- MyBatis源码解读之延迟加载
1. 目的 本文主要解读MyBatis 延迟加载实现原理 2. 延迟加载如何使用 Setting 参数配置 设置参数 描述 有效值 默认值 lazyLoadingEnabled 延迟加载的全局开关.当 ...
- Mybatis源码解析(四) —— SqlSession是如何实现数据库操作的?
Mybatis源码解析(四) -- SqlSession是如何实现数据库操作的? 如果拿一次数据库请求操作做比喻,那么前面3篇文章就是在做请求准备,真正执行操作的是本篇文章要讲述的内容.正如标题一 ...
- Mybatis源码解读-插件
插件允许对Mybatis的四大对象(Executor.ParameterHandler.ResultSetHandler.StatementHandler)进行拦截 问题 Mybatis插件的注册顺序 ...
- 使用react全家桶制作博客后台管理系统 网站PWA升级 移动端常见问题处理 循序渐进学.Net Core Web Api开发系列【4】:前端访问WebApi [Abp 源码分析]四、模块配置 [Abp 源码分析]三、依赖注入
使用react全家桶制作博客后台管理系统 前面的话 笔者在做一个完整的博客上线项目,包括前台.后台.后端接口和服务器配置.本文将详细介绍使用react全家桶制作的博客后台管理系统 概述 该项目是基 ...
- MyBatis源码解读(1)——SqlSessionFactory
在前面对MyBatis稍微有点了解过后,现在来对MyBatis的源码试着解读一下,并不是解析,暂时定为解读.所有对MyBatis解读均是基于MyBatis-3.4.1,官网中文文档:http://ww ...
随机推荐
- java线程池ThreadPoolExecutor 如何与 AsyncTask() 组合使用
简单说下Executors类,提供的一系列创建线程池的方法: 他们都有两个构造方法 1. --------newFixedThreadPool (创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会 ...
- 简述Java内存泄露
翻译人员: 铁锚翻译时间: 2013年11月4日原文链接: The Introduction of Memory Leaks内存管理一直是Java 所鼓吹的强大优点.开发者只需要简单地创建对象,而Ja ...
- 比较ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector
翻译人员: 铁锚 翻译时间: 2013年12月2日 原文链接: ArrayList vs. LinkedList vs. Vector 1. List概述 List,就如图名字所示一样,是元素的有序列 ...
- 彻底搞清楚 RxJava 是什么东西
其实从rxjava14年出现到现在,我是去年从一个朋友那里听到的,特别是随着现在app项目越来越大,分层越来越不明确的情况下,rxjava出现了,以至于出现了rxandroid.其实如果你了解观察者模 ...
- Python学习笔记 - 迭代器Iterator
我们已经知道,可以直接作用于for循环的数据类型有以下几种: 一类是集合数据类型,如list.tuple.dict.set.str等: 一类是generator,包括生成器和带yield的genera ...
- Android SDK下载失败的解决方法
Android SDK下载失败的解决方法 图1 在下载过程中,Android SDK Manager Log中出现下面出错信息: Preparing toinstall archives Downlo ...
- Linux下xargs命令详解
http://www.cnblogs.com/perfy/archive/2012/07/24/2606101.html xargs是给命令传递参数的一个过滤器,也是组合多个命令的一个工具.它把一个数 ...
- Git与远程reposiory的相关命令
问题1:Git如何同步远程repository的分支(branch) 某天,小C同学问我,为啥VV.git仓库里面本来已经删除了branchA这个分支,但是我的mirror中还是有这个分支呢? 分析: ...
- win32 线程通信初步
// 线程通信机制.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点. // #include "stdafx.h" #define NUM_THREADS 10 #include < ...
- 链路层 - SLIP,PPP,
最常使用的封装格式是RFC 894定义的格式.图2 - 1显示了两种不同形式的封装格式.图中每个方框下面的数字是它们的字节长度. 两种帧格式都采用48 bit(6字节)的目的地址和源地址( 8 0 2 ...
