babylon.js 学习笔记(3)
一、理解babylon.js 坐标系
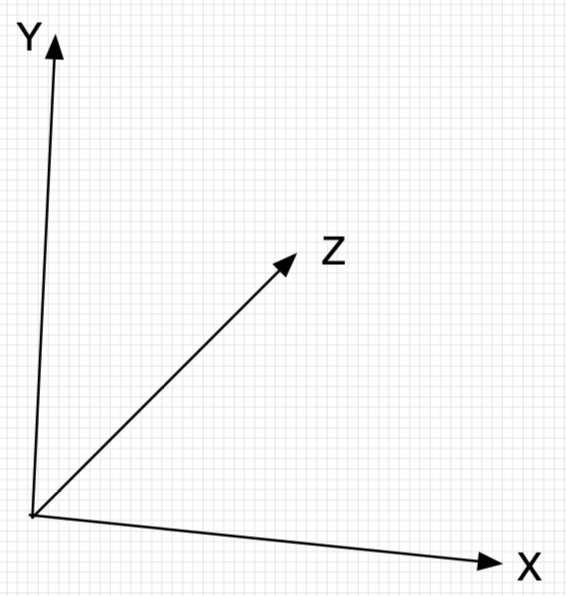
const createScene = function () {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine);
const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", -Math.PI / 2, Math.PI / 2.5, 3, new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0));
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(1, 1, 0));
//方块1(靠左,靠下,靠前)
const box1 = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("box", { size: 0.4 }, scene);
//Vector(x,y,z) 表示x,y,z三轴的坐标值
box1.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(-1, -0.199, -0.4);
//方块2(放在正中央)
const box2 = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("box", { size: 0.4 }, scene);
box2.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0);
//方块3(靠右,靠上,靠后)
const box3 = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("box", { size: 0.4 }, scene);
box3.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(1, 0.2, 0.4);
var ground = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateGround("ground", { width: 3, height: 1.5 }, scene);
let groundMaterial = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("Ground Material", scene);
ground.material = groundMaterial;
ground.material.diffuseColor = BABYLON.Color3.Black();
return scene;
};
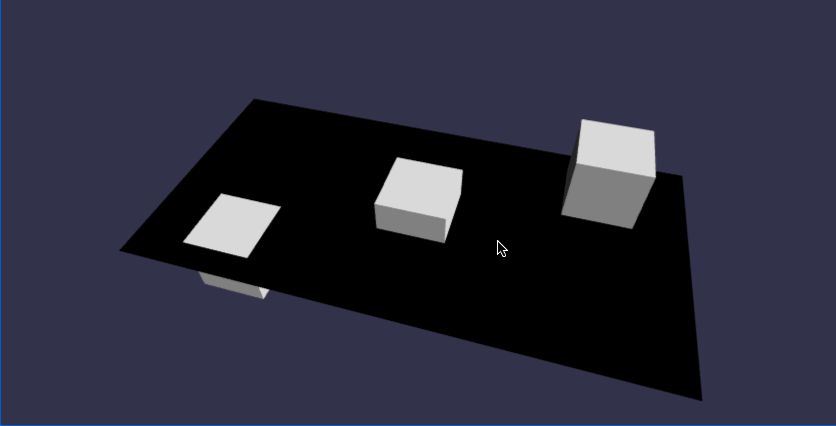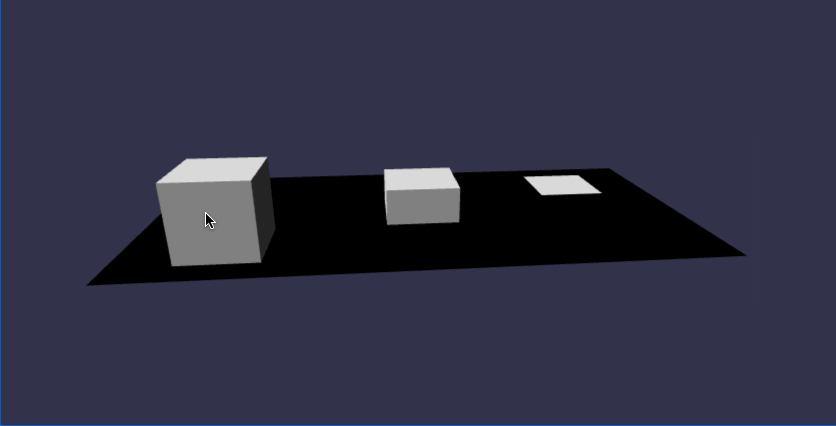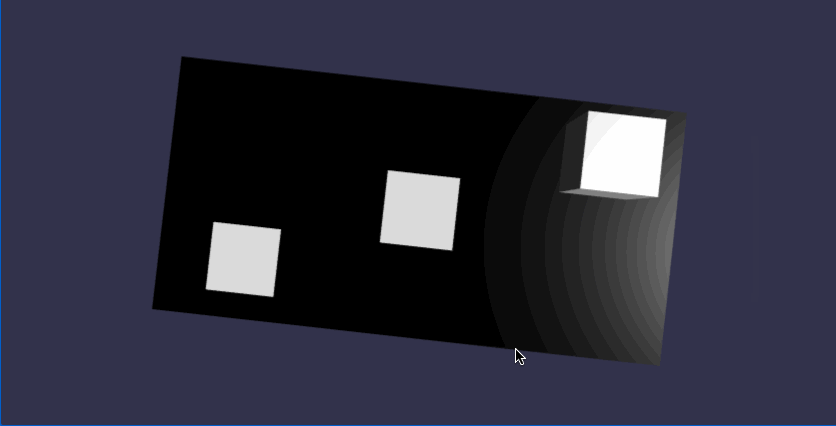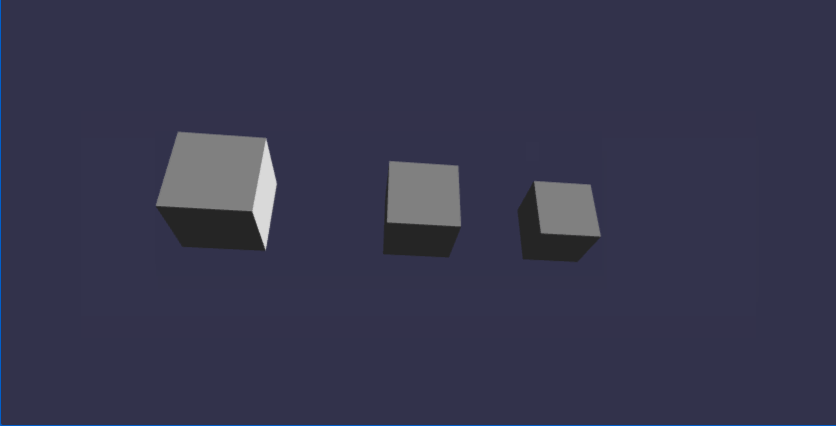
在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day03/01.html
//方块1(靠左,靠下,靠前)
const box1 = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("box", { size: 0.4 }, scene);
//Vector(x,y,z) 表示x,y,z三轴的坐标值
box1.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(-1, -0.199, -0.4);
box1.scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.5, 1, 1); //方块2(放在正中央)
const box2 = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("box", { size: 0.4 }, scene);
box2.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0);
box2.scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(1, 0.5, 1);
//绕y轴转45度
box2.rotation = new BABYLON.Vector3(0,Math.PI/4,0); //方块3(靠右,靠上,靠后)
const box3 = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("box", { size: 0.4 }, scene);
box3.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(1, 0.2, 0.4);
box3.scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(1, 1, 0.5);
box3.rotation = new BABYLON.Vector3(-Math.PI/4,0,0);

在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day03/02.html
二、画1个简单的小房子

如上图,画1个三棱柱,以及1个立方体,组合起来即可。但babylon.js中并没有创建三棱柱的api,只能创建圆柱体,还记得前面学过的吗?任何复杂的对象(即mesh),都是一堆小三角形及各种切面的组合,三角形数越多,最终的对象越逼真。当圆柱体的边数设置为3时,即退化成三棱柱。
//Cylinder的边tessellation足够大时,即为圆柱形
const roof0 = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("roof0", {diameter: 1.3, height: 1.2, tessellation: 32},scene);
roof0.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(-1,0.26,0);
roof0.scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.25,0.25,0.25); const roof1 = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("roof1", {diameter: 1.3, height: 1.2, tessellation: 32},scene);
roof1.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(-0.5,0.26,0);
roof1.scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.25,0.25,0.25);
//绕x轴转90度
roof1.rotation = new BABYLON.Vector3(Math.PI / 2,0,0); //Cylinder的边tessellation=3时,即为三棱柱
const roof2 = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("roof2", {diameter: 1.3, height: 1.2, tessellation: 3},scene);
roof2.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(0,0.24,0);
roof2.scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.4,0.4,0.4);
roof2.rotation = new BABYLON.Vector3(0,Math.PI / 2,Math.PI / 2); //三棱柱+方块,组合成1个简单的房子
const roof = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("roof", {diameter: 1.3, height: 1.2, tessellation: 3},scene);
roof.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.9,0.6,0);
roof.scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.4,0.4,0.4);
roof.rotation = new BABYLON.Vector3(0,Math.PI / 2,Math.PI / 2); const box = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("box", { size: 0.4 }, scene);
box.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.9, 0.24, 0);
box.scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.95, 1.2, 0.95);

在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day03/03.html
样子是有了,但是光秃秃的,比较难看,可以给它贴上壁纸,先找二张壁纸图片:


//设置屋顶及屋身的贴图材质
const roofMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("roofMat");
roofMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/roof.jpg", scene);
const boxMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("boxMat");
boxMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/floor.png"); roof.material = roofMat;
box.material = boxMat;
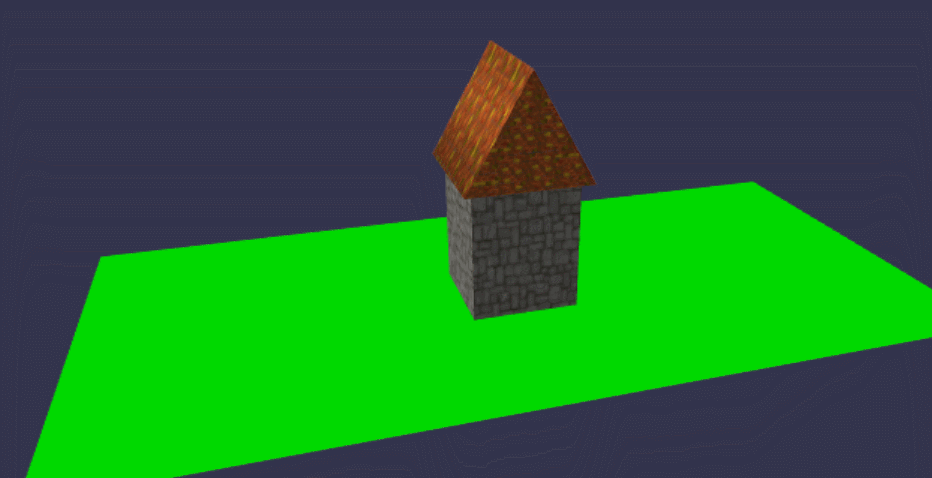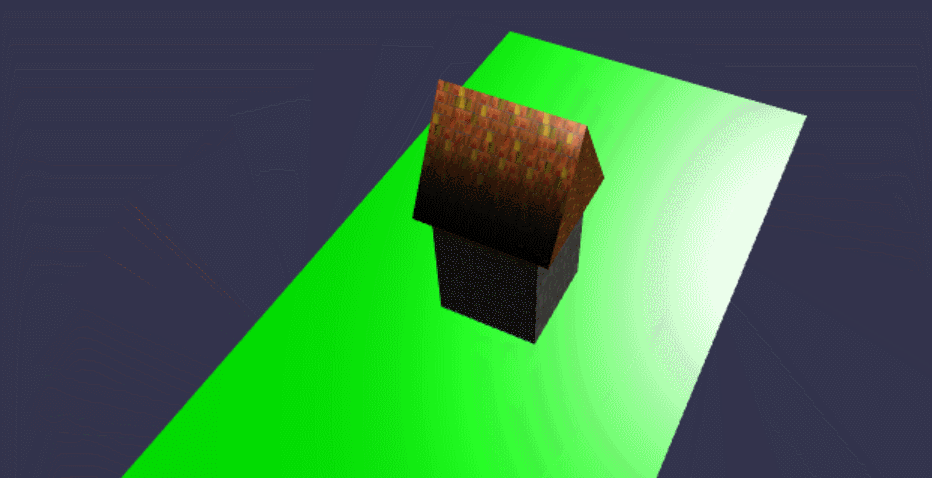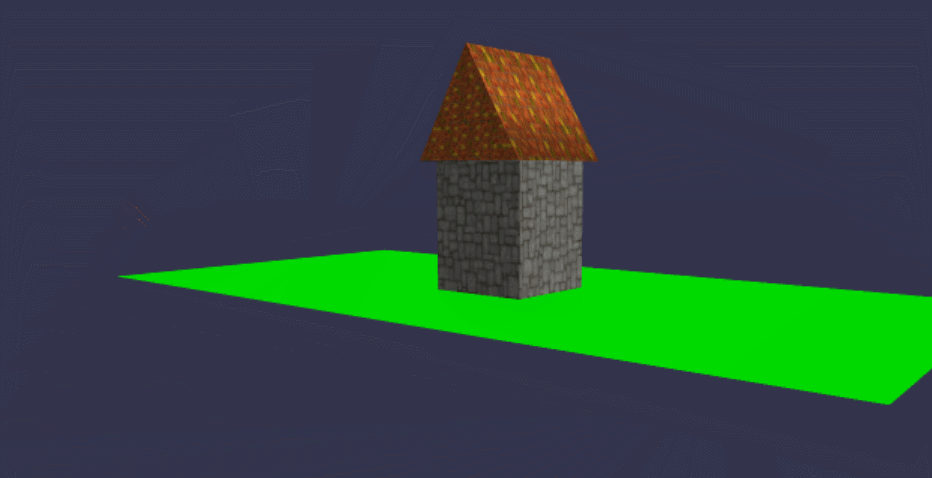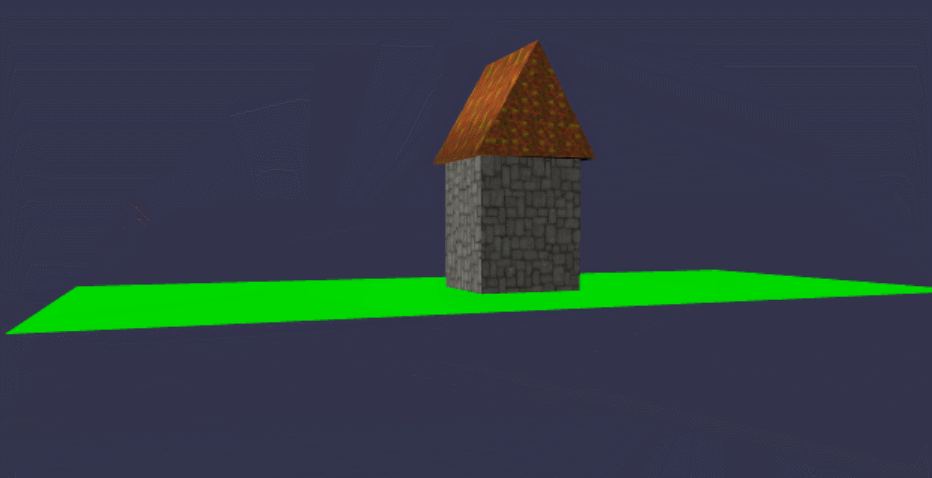
在线地址: https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day03/04.html
房子是有窗户的,再来看看如何解决窗户的问题,答案仍然是在贴图上做文章,比如将下面这张带窗户的贴纸,在整个屋身上贴一圈即可
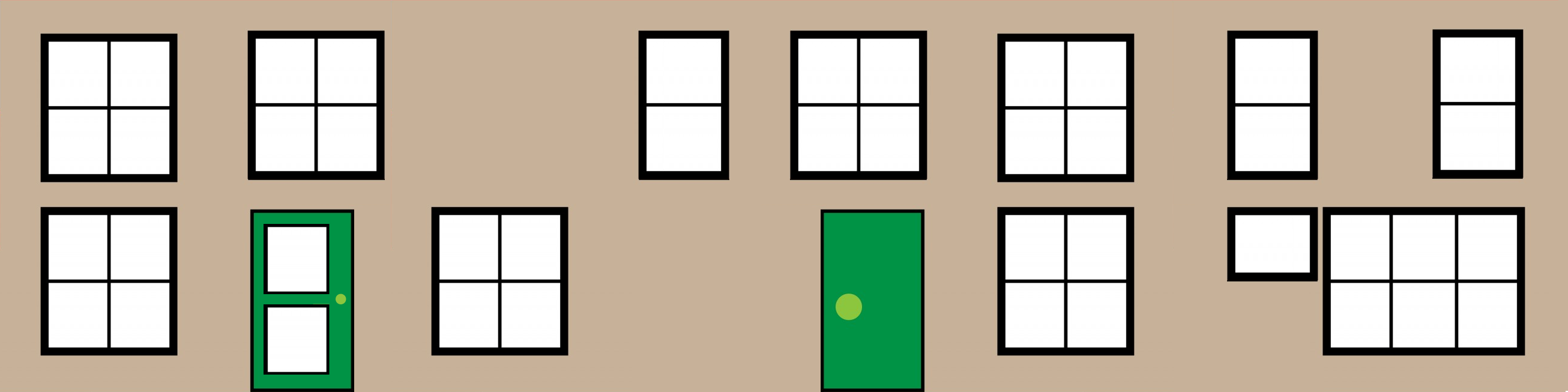
象不象某些地方的形象工程,哈

尝试用这个新贴图试一下:
//对比,画1个方块,用cubehouse贴图
const box2 = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("box", { size: 0.4 }, scene);
box2.position = new BABYLON.Vector3(1, 0.24, 0);
box2.scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.95, 1.2, 0.95);
const boxMat2 = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("boxMat2");
boxMat2.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/cubehouse.png");
box2.material = boxMat2;

在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day03/05.html
好象有哪里不对,这看上去,象个快递包裹^_~,让我们想一想:
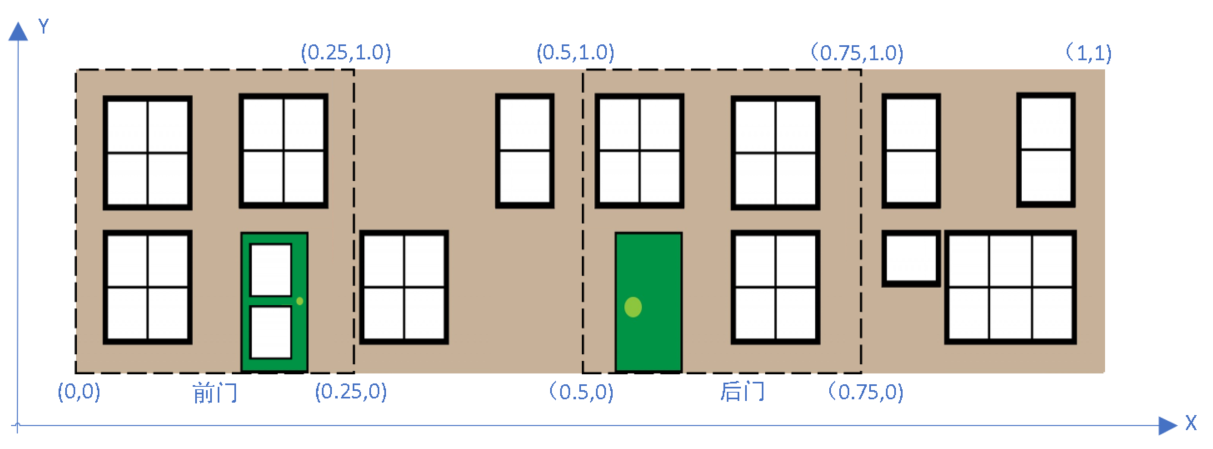
一般情况下,不用看屋身的底部和顶部(注:底部是绿色的大地,顶部被屋顶挡住了),所以可以将这张贴图切为4份,分别贴在屋身的前后左右。从CreateBox的API文档知,有1个参数faceUV可以指定box每个面的贴图:
faceUV可以使用Vector4对象做为参数:
vector (lower left x, lower left y, upper right x, upper right y)
//屋身四面的贴图坐标
const faceUV = [];
faceUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.5, 0.0, 0.75, 1.0); //后面
faceUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.0, 0.0, 0.25, 1.0); //前面
faceUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.25, 0, 0.5, 1.0); //右面
faceUV[3] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.75, 0, 1.0, 1.0); //左面 ...
const box2 = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("box", { size: 0.4,faceUV:faceUV }, scene);
...

在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day03/06.html
为了方便后面代码复用,我们把创建地面、屋顶、屋身 这些基本逻辑,封装一下:
//调整地面/屋顶/屋身的大小及位置
const adjust = (ground, roof, box) => {
const scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.5, 0.5, 0.5);
ground.scaling = scaling;
roof.scaling = scaling;
box.scaling = scaling;
box.position.y = ground.position.y + 0.25;
roof.position.y = box.position.y + 0.4; box.position.x = -1;
roof.position.x = box.position.x;
} //创建地面
const buildGround = () => {
const groundMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("groundMat");
groundMat.diffuseColor = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 1, 0);
const ground = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateGround("ground", { width: 6, height: 3 });
ground.material = groundMat;
return ground;
} //创建屋顶
const buildRoof = () => {
const roofMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("roofMat");
roofMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/roof.jpg"); const roof = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("roof", { diameter: 1.3, height: 1.2, tessellation: 3 });
roof.material = roofMat;
roof.scaling.x = 0.75;
roof.rotation.z = Math.PI / 2;
roof.position.y = 1.22; return roof;
} //创建屋身
const buildBox = () => {
const boxMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("boxMat");
boxMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/cubehouse.png") const faceUV = [];
faceUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.5, 0.0, 0.75, 1.0); //后面
faceUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.0, 0.0, 0.25, 1.0); //前面
faceUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.25, 0, 0.5, 1.0); //右面
faceUV[3] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.75, 0, 1.0, 1.0); //左面 const box = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("box", { faceUV: faceUV, wrap: true });
box.material = boxMat;
box.position.y = 0.5; return box;
} //在这里添加自己的核心代码
const createScene = function () {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine); const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", -Math.PI / 2, Math.PI / 2.5, 3, new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0));
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0.5, 0.5, 0)); const ground = buildGround();
const roof = buildRoof();
const box = buildBox(); adjust(ground, roof, box); return scene;
};
最后,再添加1种风格的房屋做为本篇收场:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" />
<title>A Basic House</title> <style>
html,
body {
overflow: hidden;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
} #renderCanvas {
width: 50%;
height: 50%;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
margin: auto;
touch-action: none;
} #canvasZone {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style> <!-- 导入babylon核心功能 -->
<script src="../js/babylon.js"></script>
<!-- 允许scene中导入model -->
<script src="../js/babylonjs.loaders.min.js"></script>
<!-- 允许使用触屏 -->
<script src="../js/pep.js"></script>
</head> <body>
<canvas id="renderCanvas" touch-action="none"></canvas> <script>
const canvas = document.getElementById("renderCanvas");
const engine = new BABYLON.Engine(canvas, true); //调整地面/屋顶/屋身的大小及位置
const adjust = (ground, roof, box) => {
const scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.5, 0.5, 0.5);
ground.scaling = scaling;
roof.scaling = scaling;
box.scaling = scaling;
box.position.y = ground.position.y + 0.25;
roof.position.y = box.position.y + 0.4; box.position.x = -0.8;
roof.position.x = box.position.x;
} //调整-联体别墅-地面/屋顶/屋身的大小及位置
const adjustSemiHouse = (ground, roof, box) => {
const scaling = new BABYLON.Vector3(0.5, 0.5, 0.5);
roof.scaling = scaling;
box.scaling = scaling;
box.position.y = ground.position.y + 0.25;
roof.position.y = box.position.y + 0.4;
box.position.x = 0.5;
roof.position.x = box.position.x;
} //创建地面
const buildGround = () => {
const groundMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("groundMat");
groundMat.diffuseColor = new BABYLON.Color3(0, 1, 0);
const ground = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateGround("ground", { width: 6, height: 3 });
ground.material = groundMat;
return ground;
} //创建屋顶
const buildRoof = () => {
const roofMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("roofMat");
roofMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/roof.jpg"); const roof = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("roof", { diameter: 1.3, height: 1.2, tessellation: 3 });
roof.material = roofMat;
roof.scaling.x = 0.75;
roof.rotation.z = Math.PI / 2;
roof.position.y = 1.22; return roof;
} //创建-联体别墅-屋顶
const buildSemiHouseRoof = () => { const roof = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateCylinder("roof", { diameter: 1.3, height: 2.2, tessellation: 3 }); roof.scaling.y = 0.75;
roof.rotation.z = Math.PI / 2;
roof.position.y = 1.22; const roofMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("roofMat");
roofMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/roof.jpg");
roof.material = roofMat; return roof;
} //创建屋身
const buildBox = () => {
const boxMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("boxMat");
boxMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/cubehouse.png") const faceUV = [];
faceUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.5, 0.0, 0.75, 1.0); //后面
faceUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.0, 0.0, 0.25, 1.0); //前面
faceUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.25, 0, 0.5, 1.0); //右面
faceUV[3] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.75, 0, 1.0, 1.0); //左面 const box = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("box", { faceUV: faceUV, wrap: true });
box.material = boxMat;
box.position.y = 0.5; return box;
} //创建-联体别墅-屋身
const buildSemiHouseBox = () => {
const boxMat = new BABYLON.StandardMaterial("boxMat");
boxMat.diffuseTexture = new BABYLON.Texture("../assets/img/semihouse.png") const faceUV = [];
faceUV[0] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.6, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0); //rear face
faceUV[1] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.0, 0.0, 0.4, 1.0); //front face
faceUV[2] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.4, 0, 0.6, 1.0); //right side
faceUV[3] = new BABYLON.Vector4(0.4, 0, 0.6, 1.0); //left side const box = BABYLON.MeshBuilder.CreateBox("box", { width: 2, height: 1, faceUV: faceUV, wrap: true });
box.material = boxMat;
box.position.y = 0.5; return box;
} //在这里添加自己的核心代码
const createScene = function () {
const scene = new BABYLON.Scene(engine); const camera = new BABYLON.ArcRotateCamera("camera", -Math.PI / 2, Math.PI / 2.5, 3, new BABYLON.Vector3(0, 0, 0));
camera.attachControl(canvas, true);
const light = new BABYLON.HemisphericLight("light", new BABYLON.Vector3(0.5, 0.5, 0)); const ground = buildGround(); const roof = buildRoof();
const box = buildBox();
adjust(ground, roof, box); const roof2 = buildSemiHouseRoof();
const box2 = buildSemiHouseBox();
adjustSemiHouse(ground, roof2, box2); return scene;
}; const scene = createScene(); engine.runRenderLoop(function () {
scene.render();
}); window.addEventListener("resize", function () {
engine.resize();
});
</script>
</body> </html>
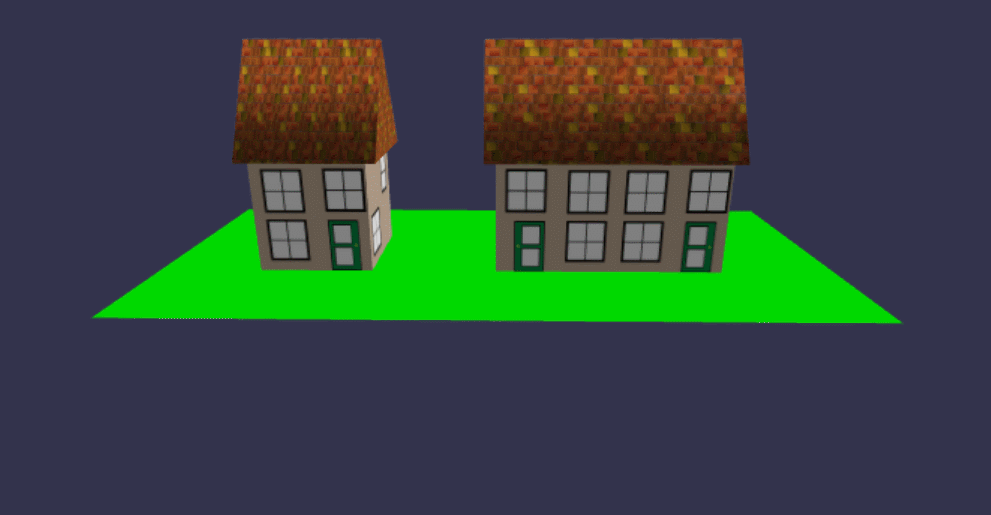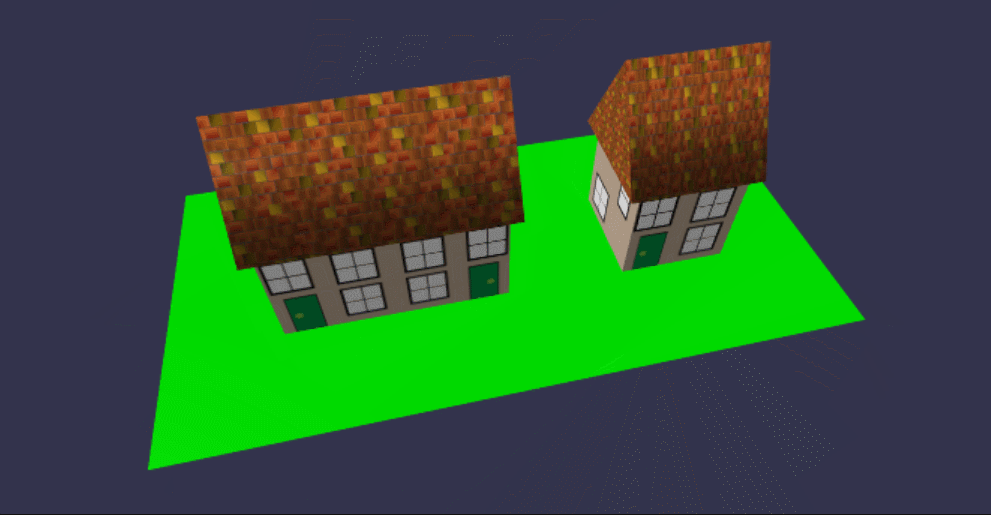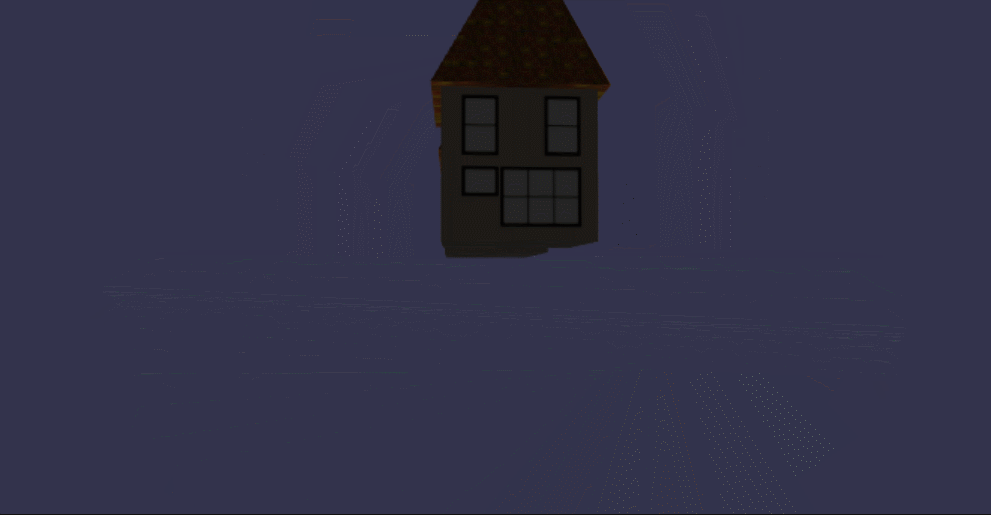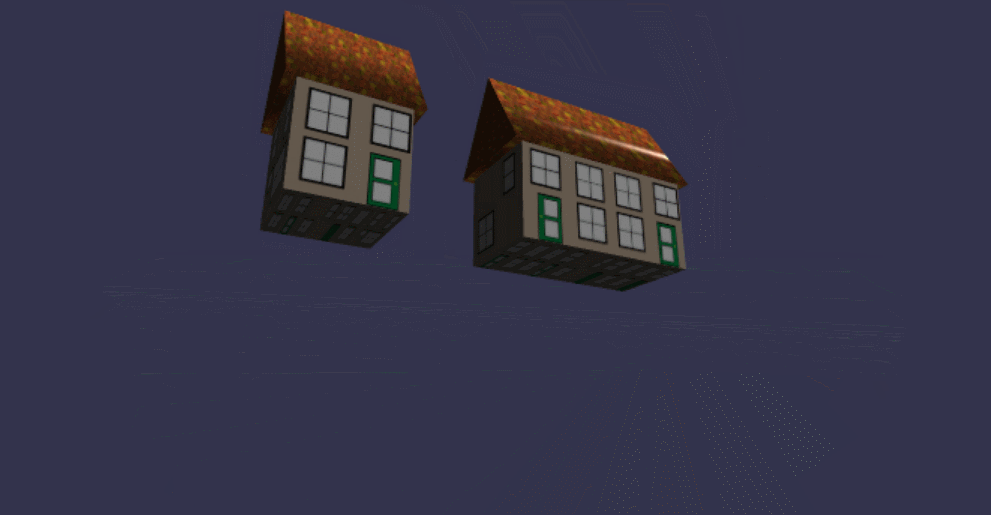
在线地址:https://yjmyzz.github.io/babylon_js_study/day03/07.html
参考文档:
https://doc.babylonjs.com/features/introductionToFeatures/chap2/variation
babylon.js 学习笔记(3)的更多相关文章
- js学习笔记:webpack基础入门(一)
之前听说过webpack,今天想正式的接触一下,先跟着webpack的官方用户指南走: 在这里有: 如何安装webpack 如何使用webpack 如何使用loader 如何使用webpack的开发者 ...
- Vue.js学习笔记(2)vue-router
vue中vue-router的使用:
- JS 学习笔记--9---变量-作用域-内存相关
JS 中变量和其它语言中变量最大的区别就是,JS 是松散型语言,决定了它只是在某一个特定时间保存某一特定的值的一个名字而已.由于在定义变量的时候不需要显示规定必须保存某种类型的值,故变量的值以及保存的 ...
- WebGL three.js学习笔记 使用粒子系统模拟时空隧道(虫洞)
WebGL three.js学习笔记 使用粒子系统模拟时空隧道 本例的运行结果如图: 时空隧道demo演示 Demo地址:https://nsytsqdtn.github.io/demo/sprite ...
- WebGL three.js学习笔记 法向量网格材质MeshNormalMaterial的介绍和创建360度全景天空盒的方法
WebGL学习----Three.js学习笔记(5) 点击查看demo演示 Demo地址:https://nsytsqdtn.github.io/demo/360/360 简单网格材质 MeshNor ...
- WebGL three.js学习笔记 创建three.js代码的基本框架
WebGL学习----Three.js学习笔记(1) webgl介绍 WebGL是一种3D绘图协议,它把JavaScript和OpenGL ES 2.0结合在一起,通过增加OpenGL ES 2.0的 ...
- vue.js 学习笔记3——TypeScript
目录 vue.js 学习笔记3--TypeScript 工具 基础类型 数组 元组 枚举 字面量 接口 类类型 类类型要素 函数 函数参数 this对象和类型 重载 迭代器 Symbol.iterat ...
- 2019-4-29 js学习笔记
js学习笔记一:js数据类型 1:基本数据类型 number类型(整数,小数) String类型 boolean类型 NaN类型其实是一个nu ...
- 一点感悟:《Node.js学习笔记》star数突破1000+
写作背景 笔者前年开始撰写的<Node.js学习笔记> github star 数突破了1000,算是个里程碑吧. 从第一次提交(2016.11.03)到现在,1年半过去了.突然有些感慨, ...
- JS学习笔记5_DOM
1.DOM节点的常用属性(所有节点都支持) nodeType:元素1,属性2,文本3 nodeName:元素标签名的大写形式 nodeValue:元素节点为null,文本节点为文本内容,属性节点为属性 ...
随机推荐
- s2-061(CVE-2020-17530)漏洞复现+利用+getshell工具。
声明 本文仅用于技术交流,请勿用于非法用途 由于传播.利用此文所提供的信息而造成的任何直接或者间接的后果及损失,均由使用者本人负责,文章作者不为此承担任何责任. 文章作者拥有对此文章的修改和解释权.如 ...
- mysql 5.7等保2.0安全配置
一.安装密码校验插件validate_password 在使用服务器插件之前,必须将它们加载到服务器中.MySQL支持在服务器启动和运行时加载插件.还可以在启动时控制加载插件的激活状态,并在运行时卸载 ...
- python打包exe自定义图标
1.生成.ico图标 https://www.aconvert.com/cn/icon/jpg-to-ico/ 2.打包 pyinstaller -F -w -i 666.ico pdfToword. ...
- WO Mic - 免费麦克风
WO Mic可以将您的手机变成电脑麦克风.您无需支付一分钱购买任何设备.如果您选择无线传输,它也是便携的.数百万用户已经安装并每天都在使用它进行通话.录音.语音遥控等活动. 三大组件协同工作以实现这一 ...
- Java8 新特性-Lambda表达式
目录 1.Lambda表达式介绍 2.Lambda表达式语法细讲 3. Lambda表达式语法精简 4. Lambda方法引用 5. 综合实例 6. @FunctionalInterface注解 7. ...
- 设计模式之“原型模式(ProtoType)”
一.原型模式(ProtoType) 作用:用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原创新的对象 白话解释:用于创建重复的对象,同时有能保证性能(这种类型的设计模式属于创建型设计模式,他提供了一种 ...
- Django内置filter总结
内置过滤器 目的是对绝大多数的内置过滤器进行测试总结学习,现设置如下: urls.py中设置: urlpatterns=[ url(r'^method',views.method,name='meth ...
- minikube dashboard ImagePullBackOff 失败问题的解决方法
问题 通过minikube启动k8s集群后,我们想安装启动k8s的dashboard插件,执行minikube dashboard后,一直卡住直到提示验证失败. 查看pod状态,我们看到kuberne ...
- sass中@use 的用法
前言在上一篇中,我们深入探讨了 Sass 中 @import 语法的局限性,正是因为这些问题,Sass 在 1.80 版本 后逐步弃用 @import,推出了更现代化的 @use 语法作为替代.在本文 ...
- PostGIS栅格数据类型解析【raster】
PostGIS 栅格数据类型解析:结构.转换与应用 一.栅格数据类型概述 在 PostGIS 中,raster 是用于存储和处理栅格数据的核心类型,支持从多种格式(如 JPEG.GeoTIFF.PNG ...
