机器学习作业(八)异常检测与推荐系统——Matlab实现
题目下载【传送门】
第1题
简述:对于一组网络数据进行异常检测.
第1步:读取数据文件,使用高斯分布计算 μ 和 σ²:
% The following command loads the dataset. You should now have the
% variables X, Xval, yval in your environment
load('ex8data1.mat'); % Estimate my and sigma2
[mu sigma2] = estimateGaussian(X);
其中高斯分布计算函数estimateGaussian:
function [mu sigma2] = estimateGaussian(X) % Useful variables
[m, n] = size(X); % You should return these values correctly
mu = zeros(n, 1);
sigma2 = zeros(n, 1); mu = mean(X);
sigma2 = var(X, 1);
% mu = mu';
% sigma2 = sigma2'; end
第2步:计算概率p(x):
% Returns the density of the multivariate normal at each data point (row)
% of X
p = multivariateGaussian(X, mu, sigma2);
其中概率计算函数
function p = multivariateGaussian(X, mu, Sigma2) k = length(mu); if (size(Sigma2, 2) == 1) || (size(Sigma2, 1) == 1)
Sigma2 = diag(Sigma2);
end X = bsxfun(@minus, X, mu(:)');
p = (2 * pi) ^ (- k / 2) * det(Sigma2) ^ (-0.5) * ...
exp(-0.5 * sum(bsxfun(@times, X * pinv(Sigma2), X), 2)); end
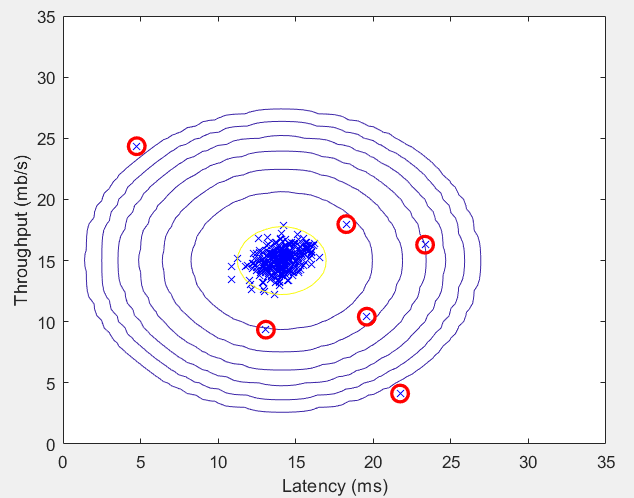
第3步:可视化数据,并绘制概率等高线:
% Visualize the fit
visualizeFit(X, mu, sigma2);
xlabel('Latency (ms)');
ylabel('Throughput (mb/s)');
其中visualizeFit函数:
function visualizeFit(X, mu, sigma2) [X1,X2] = meshgrid(0:.5:35);
Z = multivariateGaussian([X1(:) X2(:)],mu,sigma2);
Z = reshape(Z,size(X1)); plot(X(:, 1), X(:, 2),'bx');
hold on;
% Do not plot if there are infinities
if (sum(isinf(Z)) == 0)
contour(X1, X2, Z, 10.^(-20:3:0)');
end
hold off; end
运行结果:

第4步:使用交叉验证集选出最佳参数 ε:
pval = multivariateGaussian(Xval, mu, sigma2); [epsilon F1] = selectThreshold(yval, pval);
fprintf('Best epsilon found using cross-validation: %e\n', epsilon);
fprintf('Best F1 on Cross Validation Set: %f\n', F1);
其中selectThreshold函数:
function [bestEpsilon bestF1] = selectThreshold(yval, pval) bestEpsilon = 0;
bestF1 = 0;
F1 = 0; stepsize = (max(pval) - min(pval)) / 1000;
for epsilon = min(pval):stepsize:max(pval)
predictions = pval < epsilon;
tp = sum(predictions .* yval);
prec = tp / sum(predictions);
rec = tp / sum(yval);
F1 = 2 * prec * rec / (prec + rec); if F1 > bestF1
bestF1 = F1;
bestEpsilon = epsilon;
end
end end
运行结果:

第5步:找出异常点,并可视化标记:
% Find the outliers in the training set and plot the
outliers = find(p < epsilon); % Draw a red circle around those outliers
hold on
plot(X(outliers, 1), X(outliers, 2), 'ro', 'LineWidth', 2, 'MarkerSize', 10);
hold off
运行结果:
第2题
简述:实现电影推荐系统
第1步:读取数据文件(截取较少的数据):
% Load data
load ('ex8_movies.mat'); % Y is a 1682x943 matrix, containing ratings (1-5) of 1682 movies on
% 943 users
%
% R is a 1682x943 matrix, where R(i,j) = 1 if and only if user j gave a
% rating to movie i % Load pre-trained weights (X, Theta, num_users, num_movies, num_features)
load ('ex8_movieParams.mat'); % Reduce the data set size so that this runs faster
num_users = 4; num_movies = 5; num_features = 3;
X = X(1:num_movies, 1:num_features);
Theta = Theta(1:num_users, 1:num_features);
Y = Y(1:num_movies, 1:num_users);
R = R(1:num_movies, 1:num_users);
第2步:计算代价函数和梯度:
J = cofiCostFunc([X(:) ; Theta(:)], Y, R, num_users, num_movies, ...
num_features, 1.5);
其中cofiCostFunc函数:
function [J, grad] = cofiCostFunc(params, Y, R, num_users, num_movies, ...
num_features, lambda) % Unfold the U and W matrices from params
X = reshape(params(1:num_movies*num_features), num_movies, num_features);
Theta = reshape(params(num_movies*num_features+1:end), ...
num_users, num_features); % You need to return the following values correctly
J = 0;
X_grad = zeros(size(X));
Theta_grad = zeros(size(Theta)); cost = (X * Theta' - Y) .* R;
J = 1 / 2 * sum(sum(cost .^ 2));
J = J + lambda / 2 * (sum(sum(Theta .^ 2)) + sum(sum(X .^ 2))); X_grad = cost * Theta;
X_grad = X_grad + lambda * X; Theta_grad = X' * cost;
Theta_grad = Theta_grad' + lambda * Theta; grad = [X_grad(:); Theta_grad(:)]; end
第3步:进行梯度检测:
% Check gradients by running checkNNGradients
checkCostFunction(1.5);
其中checkCostFunction函数:
function checkCostFunction(lambda) % Set lambda
if ~exist('lambda', 'var') || isempty(lambda)
lambda = 0;
end %% Create small problem
X_t = rand(4, 3);
Theta_t = rand(5, 3); % Zap out most entries
Y = X_t * Theta_t';
Y(rand(size(Y)) > 0.5) = 0;
R = zeros(size(Y));
R(Y ~= 0) = 1; %% Run Gradient Checking
X = randn(size(X_t));
Theta = randn(size(Theta_t));
num_users = size(Y, 2);
num_movies = size(Y, 1);
num_features = size(Theta_t, 2); numgrad = computeNumericalGradient( ...
@(t) cofiCostFunc(t, Y, R, num_users, num_movies, ...
num_features, lambda), [X(:); Theta(:)]); [cost, grad] = cofiCostFunc([X(:); Theta(:)], Y, R, num_users, ...
num_movies, num_features, lambda); disp([numgrad grad]);
fprintf(['The above two columns you get should be very similar.\n' ...
'(Left-Your Numerical Gradient, Right-Analytical Gradient)\n\n']); diff = norm(numgrad-grad)/norm(numgrad+grad);
fprintf(['If your cost function implementation is correct, then \n' ...
'the relative difference will be small (less than 1e-9). \n' ...
'\nRelative Difference: %g\n'], diff); end
其中computeNumericalGradient函数:
function numgrad = computeNumericalGradient(J, theta) numgrad = zeros(size(theta));
perturb = zeros(size(theta));
e = 1e-4;
for p = 1:numel(theta)
% Set perturbation vector
perturb(p) = e;
loss1 = J(theta - perturb);
loss2 = J(theta + perturb);
% Compute Numerical Gradient
numgrad(p) = (loss2 - loss1) / (2*e);
perturb(p) = 0;
end end
第4步:对某一用户进行预测,初始化用户的信息:
movieList = loadMovieList(); % Initialize my ratings
my_ratings = zeros(1682, 1); my_ratings(1) = 4;
my_ratings(98) = 2;
my_ratings(7) = 3;
my_ratings(12)= 5;
my_ratings(54) = 4;
my_ratings(64)= 5;
my_ratings(66)= 3;
my_ratings(69) = 5;
my_ratings(183) = 4;
my_ratings(226) = 5;
my_ratings(355)= 5;
其中loadMovieList函数:
function movieList = loadMovieList() %% Read the fixed movieulary list
fid = fopen('movie_ids.txt'); % Store all movies in cell array movie{}
n = 1682; % Total number of movies movieList = cell(n, 1);
for i = 1:n
% Read line
line = fgets(fid);
% Word Index (can ignore since it will be = i)
[idx, movieName] = strtok(line, ' ');
% Actual Word
movieList{i} = strtrim(movieName);
end
fclose(fid); end
第5步:将新用户增加到数据集中:
% Load data
load('ex8_movies.mat'); % Y is a 1682x943 matrix, containing ratings (1-5) of 1682 movies by
% 943 users
%
% R is a 1682x943 matrix, where R(i,j) = 1 if and only if user j gave a
% rating to movie i % Add our own ratings to the data matrix
Y = [my_ratings Y];
R = [(my_ratings ~= 0) R];
第6步:均值归一化:
% Normalize Ratings
[Ynorm, Ymean] = normalizeRatings(Y, R);
其中normalizeRatings函数:
function [Ynorm, Ymean] = normalizeRatings(Y, R) [m, n] = size(Y);
Ymean = zeros(m, 1);
Ynorm = zeros(size(Y));
for i = 1:m
idx = find(R(i, :) == 1);
Ymean(i) = mean(Y(i, idx));
Ynorm(i, idx) = Y(i, idx) - Ymean(i);
end end
第7步:实现梯度下降,训练模型:
% Useful Values
num_users = size(Y, 2);
num_movies = size(Y, 1);
num_features = 10; % Set Initial Parameters (Theta, X)
X = randn(num_movies, num_features);
Theta = randn(num_users, num_features); initial_parameters = [X(:); Theta(:)]; % Set options for fmincg
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 100); % Set Regularization
lambda = 10;
theta = fmincg (@(t)(cofiCostFunc(t, Ynorm, R, num_users, num_movies, ...
num_features, lambda)), ...
initial_parameters, options); % Unfold the returned theta back into U and W
X = reshape(theta(1:num_movies*num_features), num_movies, num_features);
Theta = reshape(theta(num_movies*num_features+1:end), ...
num_users, num_features);
第8步:实现推荐功能:
p = X * Theta';
my_predictions = p(:,1) + Ymean; movieList = loadMovieList(); [r, ix] = sort(my_predictions, 'descend');
fprintf('\nTop recommendations for you:\n');
for i=1:10
j = ix(i);
fprintf('Predicting rating %.1f for movie %s\n', my_predictions(j), ...
movieList{j});
end
运行结果:

机器学习作业(八)异常检测与推荐系统——Matlab实现的更多相关文章
- 基于机器学习的web异常检测
基于机器学习的web异常检测 Web防火墙是信息安全的第一道防线.随着网络技术的快速更新,新的黑客技术也层出不穷,为传统规则防火墙带来了挑战.传统web入侵检测技术通过维护规则集对入侵访问进行拦截.一 ...
- 基于机器学习的web异常检测——基于HMM的状态序列建模,将原始数据转化为状态机表示,然后求解概率判断异常与否
基于机器学习的web异常检测 from: https://jaq.alibaba.com/community/art/show?articleid=746 Web防火墙是信息安全的第一道防线.随着网络 ...
- 机器学习作业(七)非监督学习——Matlab实现
题目下载[传送门] 第1题 简述:实现K-means聚类,并应用到图像压缩上. 第1步:实现kMeansInitCentroids函数,初始化聚类中心: function centroids = kM ...
- 机器学习作业(二)逻辑回归——Matlab实现
题目太长啦!文档下载[传送门] 第1题 简述:实现逻辑回归. 第1步:加载数据文件: data = load('ex2data1.txt'); X = data(:, [1, 2]); y = dat ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记--week9(上)(异常检测&推荐系统)
本周内容较多,故分为上下两篇文章. 一.内容概要 1. Anomaly Detection Density Estimation Problem Motivation Gaussian Distrib ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 15—Anomaly Detection异常检测
Lecture 15 Anomaly Detection 异常检测 15.1 异常检测问题的动机 Problem Motivation 异常检测(Anomaly detection)问题是机器学习算法 ...
- Stanford机器学习---第十一讲.异常检测
之前一直在看Standford公开课machine learning中Andrew老师的视频讲解https://class.coursera.org/ml/class/index 同时配合csdn知名 ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—Week 9 习题—异常检测
[1]异常检测 [2]高斯分布 [3]高斯分布 [4] 异常检测 [5]特征选择 [6] [7]多变量高斯分布 Answer: ACD B 错误.需要矩阵Σ可逆,则要求m>n 测验1 Answ ...
- 斯坦福机器学习视频笔记 Week9 异常检测和高斯混合模型 Anomaly Detection
异常检测,广泛用于欺诈检测(例如“此信用卡被盗?”). 给定大量的数据点,我们有时可能想要找出哪些与平均值有显着差异. 例如,在制造中,我们可能想要检测缺陷或异常. 我们展示了如何使用高斯分布来建模数 ...
随机推荐
- UML之三、建模元素(2)
本章继续介绍建模元素 https://blog.csdn.net/bit_kaki/article/details/78471760 1:边界 任何一个对象都有一个边界,外界只能通过这个边界来认识对象 ...
- 类加载机制与JVM调优命令
一.类加载过程 类加载:类加载器将.class字节码文件加载进Java虚拟机的内存中. 加载:在硬盘上查找并通过IO读入字节码文件 连接:执行校验.准备.解析(可选)步骤 校验:校验字节码文件的正确性 ...
- kuangbin专题 专题九 连通图 POJ 3177 Redundant Paths
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/article/371?tdsourcetag=s_pcqq_aiomsg 题目:给定一个连通图,题目说,任意两个点至少有一条路线可以相互到达, 为保证 ...
- webpack打包进行丑化压缩遇到(TypeError Cannot read property 'compilation' of undefined)问题
今天再重新配置老项目node打包环境的时候遇到了一个问题. 在打包的时候报: TypeError: Cannot read property 'compilation' of undefined 错误 ...
- SQL中的real、float、decimal、numeric数据类型区别
概述: 浮点数据类型包括real型.float型.decimal型和numeric型.浮点数据类型用于存储十进制小数. 在SQL Server 中浮点数值的数据采用上舍入(Round up)的方式进行 ...
- 树莓派搭载CentOS7系统初始配置
系统属性: 树莓派型号:3b SD:32GB 系统:CentOS-Userland-7-armv7hl-RaspberryPI-Minimal-1908-sda.raw 开机配置: 连接树莓派: 配件 ...
- CF1310D Tourism
吐槽: 为什么这场CF-不寻常,1D不应该是2F么-[悲] 题意: 给定一个完全图,路径带权且 \(dis_{i,j}\) 不一定等于 \(dis_{j,i}\),边数为\(k\)不存在奇环且起点和终 ...
- IIS在已有站点上->添加应用程序命令
已有站点:HTTP80 %systemroot%\system32\inetsrv\APPCMD ADD APP /SITE.NAME:"HTTP80" /path:/Redire ...
- mybatis+maven自动生成代码框架
说明 通过可配置化,通过数据库自动生成model,da和mapper文件,这对于可定制化开发来说是非常有用的,减少了很多重复的工作. 添加依赖 <properties> <proje ...
- TCP 协议快被淘汰了,UDP 协议才是新世代的未来?
TCP 协议可以说是今天互联网的基石,作为可靠的传输协议,在今天几乎所有的数据都会通过 TCP 协议传输,然而 TCP 在设计之初没有考虑到现今复杂的网络环境,当你在地铁上或者火车上被断断续续的网络折 ...
