特征向量-Eigenvalues_and_eigenvectors#Graphs 线性变换
总结:
1、线性变换运算封闭,加法和乘法
2、特征向量经过线性变换后方向不变
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_map
Examples of linear transformation matrices
In two-dimensional space R2 linear maps are described by 2 × 2 real matrices. These are some examples:
- rotation
- by 90 degrees counterclockwise:
- by an angle θ counterclockwise:
- by 90 degrees counterclockwise:
- reflection
- about the x axis:
- about the y axis:
- about the x axis:
- scaling by 2 in all directions:
- horizontal shear mapping:
- squeeze mapping:
- projection onto the y axis:
In mathematics, a linear map (also called a linear mapping, linear transformation or, in some contexts, linear function) is a mapping V → W between two modules (including vector spaces) that preserves (in the sense defined below) the operations of addition and scalar multiplication.
An important special case is when V = W, in which case the map is called a linear operator,[1] or an endomorphism of V. Sometimes the term linear function has the same meaning as linear map, while in analytic geometry it does not.
A linear map always maps linear subspaces onto linear subspaces (possibly of a lower dimension);[2] for instance it maps a plane through the origin to a plane, straight line or point. Linear maps can often be represented as matrices, and simple examples include rotation and reflection linear transformations.
In the language of abstract algebra, a linear map is a module homomorphism. In the language of category theory it is a morphism in the category of modules over a given ring.
Definition and first consequences
Let 





 |
additivity / operation of addition |
 |
homogeneity of degree 1 / operation of scalar multiplication |
Thus, a linear map is said to be operation preserving. In other words, it does not matter whether you apply the linear map before or after the operations of addition and scalar multiplication.
This is equivalent to requiring the same for any linear combination of vectors, i.e. that for any vectors 

Denoting the zero elements of the vector spaces 






Occasionally, 








A linear map 

These statements generalize to any left-module 

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eigenvalues_and_eigenvectors#Graphs
A {\displaystyle A} 


A {\displaystyle A} 


In linear algebra, an eigenvector or characteristic vector of a linear transformation is a non-zero vector that does not change its direction when that linear transformation is applied to it. More formally, if T is a linear transformation from a vector space V over a field F into itself and v is a vector in V that is not the zero vector, then v is an eigenvector of T if T(v) is a scalar multiple of v. This condition can be written as the equation
- T ( v ) = λ v , {\displaystyle T(\mathbf {v} )=\lambda \mathbf {v} ,}
where λ is a scalar in the field F, known as the eigenvalue, characteristic value, or characteristic root associated with the eigenvector v.
If the vector space V is finite-dimensional, then the linear transformation T can be represented as a square matrix A, and the vector v by a column vector, rendering the above mapping as a matrix multiplication on the left hand side and a scaling of the column vector on the right hand side in the equation
- A v = λ v . {\displaystyle A\mathbf {v} =\lambda \mathbf {v} .}
There is a correspondence between n by n square matrices and linear transformations from an n-dimensional vector space to itself. For this reason, it is equivalent to define eigenvalues and eigenvectors using either the language of matrices or the language of linear transformations.[1][2]
Geometrically an eigenvector, corresponding to a real nonzero eigenvalue, points in a direction that is stretched by the transformation and the eigenvalue is the factor by which it is stretched. If the eigenvalue is negative, the direction is reversed.[3]
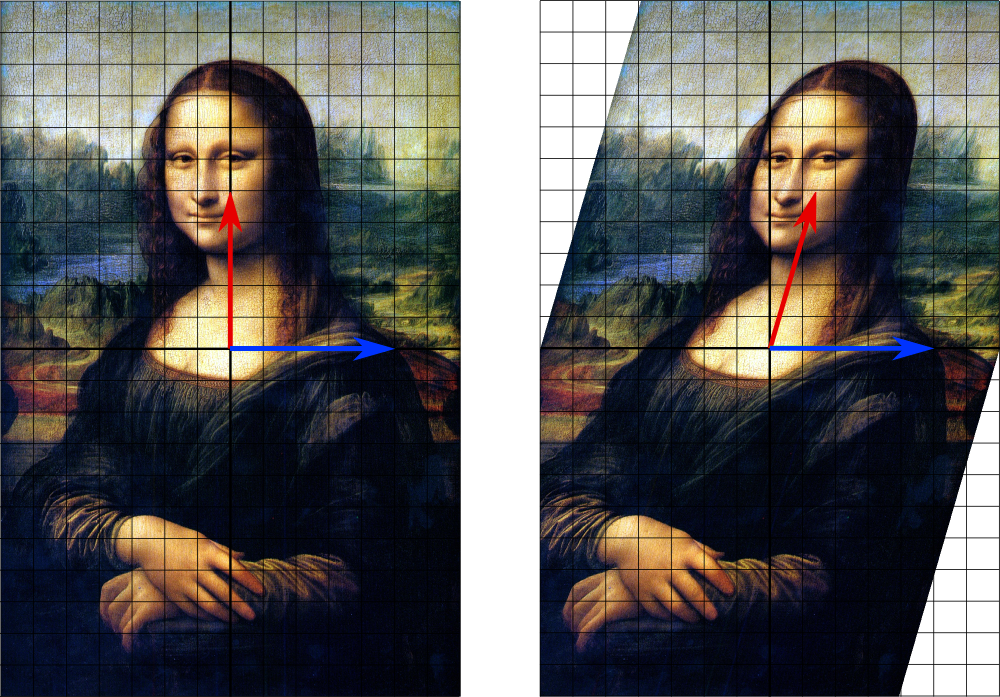

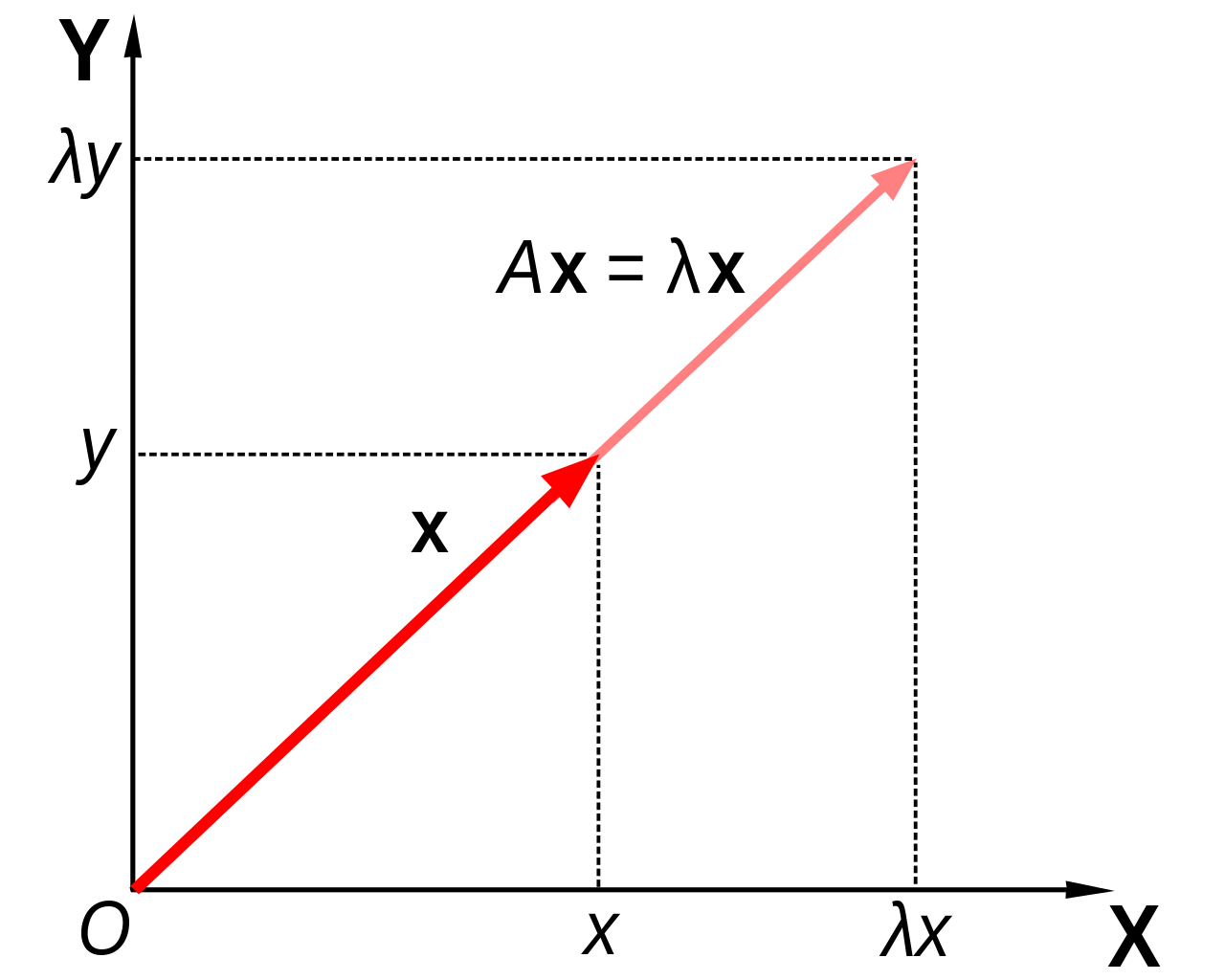
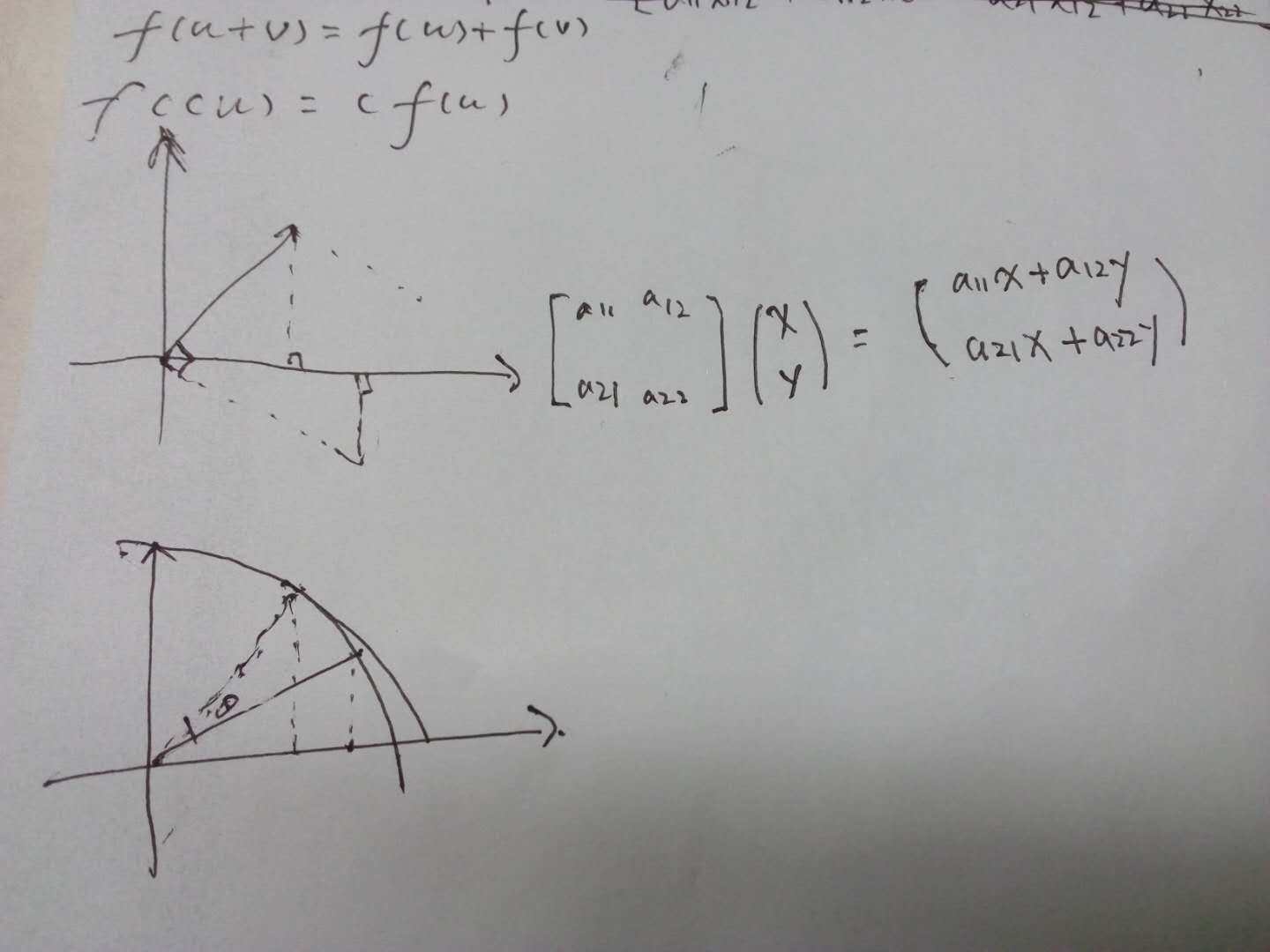
math.mit.edu/~gs/linearalgebra/ila0601.pdf
A100 was found by using the eigenvalues of A, not by multiplying 100 matrices.
- A v = λ v {\displaystyle Av=\lambda v}
,
λ {\displaystyle \lambda } 


- A v = λ v {\displaystyle Av=\lambda v}
,
λ {\displaystyle \lambda } 


特征向量-Eigenvalues_and_eigenvectors#Graphs 线性变换的更多相关文章
- 特征向量-Eigenvalues_and_eigenvectors#Graphs
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eigenvalues_and_eigenvectors#Graphs A {\displaystyle A} ...
- 知识图谱顶刊综述 - (2021年4月) A Survey on Knowledge Graphs: Representation, Acquisition, and Applications
知识图谱综述(2021.4) 论文地址:A Survey on Knowledge Graphs: Representation, Acquisition, and Applications 目录 知 ...
- paper 128:奇异值分解(SVD) --- 线性变换几何意义[转]
PS:一直以来对SVD分解似懂非懂,此文为译文,原文以细致的分析+大量的可视化图形演示了SVD的几何意义.能在有限的篇幅把这个问题讲解的如此清晰,实属不易.原文举了一个简单的图像处理问题,简单形象,真 ...
- 转载:奇异值分解(SVD) --- 线性变换几何意义(下)
本文转载自他人: PS:一直以来对SVD分解似懂非懂,此文为译文,原文以细致的分析+大量的可视化图形演示了SVD的几何意义.能在有限的篇幅把这个问题讲解的如此清晰,实属不易.原文举了一个简单的图像处理 ...
- 转载:奇异值分解(SVD) --- 线性变换几何意义(上)
本文转载自他人: PS:一直以来对SVD分解似懂非懂,此文为译文,原文以细致的分析+大量的可视化图形演示了SVD的几何意义.能在有限的篇幅把这个问题讲解的如此清晰,实属不易.原文举了一个简单的图像处理 ...
- Convolutional Neural Networks on Graphs with Fast Localized Spectral Filtering
Defferrard, Michaël, Xavier Bresson, and Pierre Vandergheynst. "Convolutional neural networks o ...
- 论文阅读:Learning Attention-based Embeddings for Relation Prediction in Knowledge Graphs(2019 ACL)
基于Attention的知识图谱关系预测 论文地址 Abstract 关于知识库完成的研究(也称为关系预测)的任务越来越受关注.多项最新研究表明,基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的模型会生成更丰富,更具表达 ...
- 论文解读二代GCN《Convolutional Neural Networks on Graphs with Fast Localized Spectral Filtering》
Paper Information Title:Convolutional Neural Networks on Graphs with Fast Localized Spectral Filteri ...
- 论文解读《The Emerging Field of Signal Processing on Graphs》
感悟 看完图卷积一代.二代,深感图卷积的强大,刚开始接触图卷积的时候完全不懂为什么要使用拉普拉斯矩阵( $L=D-W$),主要是其背后的物理意义.通过借鉴前辈们的论文.博客.评论逐渐对图卷积有了一定的 ...
随机推荐
- cocos2d-x 3.0 在C++中调用lua函数
代码用的是<cocos2d-x 3.0 在lua中调用自定义类>中的代码. 在上篇的基础上进行扩充. 写lua函数 local function process_packet(user_d ...
- VS无法导航到插入点F12失败
关闭VS 开启控制台并导航到Visual安装文件夹,例如C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2017\Community\Common7\ID ...
- [Ubuntu] arp-scan - 扫描网络设备
使用arp-scan扫描所有网络设备信息. 1. 安装arp-scan ifantastic@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get install arp-scan 2. 扫描网络所有设备 i ...
- wireshark----linux
1.[root@lc~]# tshark Running as user "root" and group "root". This could be da ...
- c语言学习笔记---符号
专题2.符号的技巧: 1) 注释符与转义符 vC语言中的接续符(\)是指示编译器行为的利器: 接续符的使用:编译器会将反斜杠剔除,嗯在反斜杠后面的字符自动解到前面的一行. 在接续单词时,反斜杠之后不能 ...
- linux mutex
#include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <cstdlib> #include <unistd.h> ...
- Excel 2010 得到当天的日期/得到一年中的第几周/得到当前一周中的星期几
=TODAY() ="第"&WEEKNUM(TODAY())&"周" =TEXT(TODAY(),"aaaa") Ctrl ...
- Telnet IMAP Commands Note
http://busylog.net/telnet-imap-commands-note/ Telnet IMAP Commands Note https://www.cnblogs.com/qiu ...
- Elasticsearch 学习之提升性能小贴士
小贴士1:规划索引.分片 以及集群增长情况 ES使得创建大量索引和超大量分片非常地容易,但更重要的是理解每个索引和分片都是一笔开销.如果拥有太多的索引或分片,单单是管理负荷就会影响到ES集群的性能,潜 ...
- Linux上的ftp服务器vsftpd之配置满天飞--设置匿名用户访问(不弹出用户名密码框)以及其他用户可正常上传
一.问题背景 没事谁折腾这鬼玩意哦...还不是因为bug. 我们的应用,用户头像是存在ftp上的.之前的ftp服务器是一台windows,我们后台服务器程序收到用户上传头像的请求时,会用一个ROOT/ ...












