jdk1.8-Vector
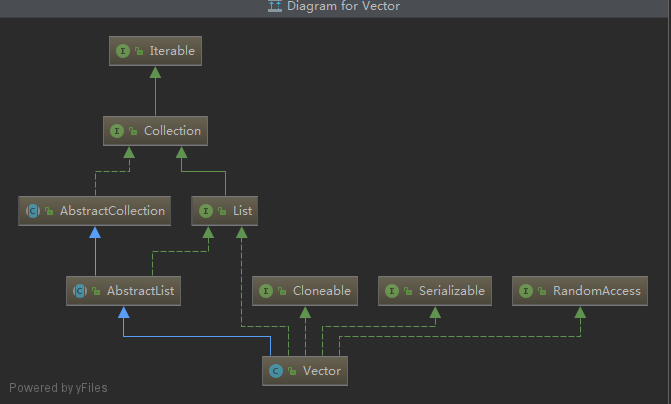
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
RandmoAccess快速随机访问接口
/**
* The array buffer into which the components of the vector are
* stored. The capacity of the vector is the length of this array buffer,
* and is at least large enough to contain all the vector's elements.
*
* <p>Any array elements following the last element in the Vector are null.
*
* @serial
*/
protected Object[] elementData;
分析:该数组缓冲区是存储vector元素,并且至少足够大到包含vector的所有元素
/**
* The number of valid components in this {@code Vector} object.
* Components {@code elementData[0]} through
* {@code elementData[elementCount-1]} are the actual items.
*
* @serial
*/
protected int elementCount;
分析:vector中实际元素的数量
/**
* The amount by which the capacity of the vector is automatically
* incremented when its size becomes greater than its capacity. If
* the capacity increment is less than or equal to zero, the capacity
* of the vector is doubled each time it needs to grow.
*
* @serial
*/
protected int capacityIncrement;
分析:vector增加的容量capacityIncrement,如果vector实际元素数量大于当前容量,vector将自动扩容,扩容的容量为当前容量加上capacityIncrement。如果没有指定增加的容量,那么vector在扩容时成倍的增长。
/** use serialVersionUID from JDK 1.0.2 for interoperability */
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2767605614048989439L;
分析:版本号
/**
* Constructs an empty vector so that its internal data array
* has size {@code 10} and its standard capacity increment is
* zero.
*/
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
分析:无参构造函数vector会初始化一个长度为10的空数组,它的标准容量增量为0(ps:也就是上面提到的capacityIncrement = 0)
/**
* Constructs an empty vector with the specified initial capacity and
* with its capacity increment equal to zero.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the vector
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
分析:指定vector初始化长度,构造一个指定的长度空数组,它的标准容量增量为0。
/**
* Constructs an empty vector with the specified initial capacity and
* capacity increment.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the vector
* @param capacityIncrement the amount by which the capacity is
* increased when the vector overflows
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
//初始化长度为传进来长度的空数组
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
//容量增加值为传进来的capacityIncrement值
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
分析:指定初始化长度和容量增量值
/**
* Constructs a vector containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this
* vector
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
* @since 1.2
*/
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
//将集合转为数组,赋值给Object数组elementData
elementData = c.toArray();
//vector长度等于集合长度
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
//c.toArray方法返回的数据错误,重新拷贝
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
}
分析:传入指定的集合,将集合元素赋值给vector
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this Vector.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this Vector
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
//抽象父类AbstractList的成员变量,修改次数记录
modCount++;
//保证容量足够大
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
//elementCount是当前元素个数,数组下标是从0开始的,所以elementData[elementCount]是当前需要添加元素的位置
//elementCount++
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
分析:方法参数为当前vector实际个数 + 1
/**
* This implements the unsynchronized semantics of ensureCapacity.
* Synchronized methods in this class can internally call this
* method for ensuring capacity without incurring the cost of an
* extra synchronization.
*
* @see #ensureCapacity(int)
*/
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
//如果传进来的值大于当前vector容量数组长度,调用grow方法
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
分析:这里没有加锁操作,因为调用这个方法的外部方法都是加了锁保证了同步,这里就没必要再进行加锁产生额外的性能消耗。
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
//旧的数组容量(长度大小)
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//如果指定了增加容量值capacityIncrement的值大于0,那么新的容量为原来容量加上capacityIncrement值大小
//否则新的容量扩大为原来容量的两倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
//判断扩容后的容量是否小于传进来的vector最小容量,那么新的容量等于需要的最小容量
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
//如果扩容后的容量大于规定的最大值Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
//根据当前能容纳所有数据最小容量值minCapacity进行判断newCapacity的容量大小
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
//将旧数组数据拷贝到新数组
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
分析:grow方法也就是真正进行vector扩容逻辑判断方法。这里我们需要掌握两点
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this Vector.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices). Returns the element that was removed from the Vector.
*
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return element that was removed
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
//修改次数加1
modCount++;
//校验下标是否越界
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
//根据索引取出旧的值
E oldValue = elementData(index);
//需要移动的元素个数
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
//elementData数组从index+1位置的元素开始读取元素,拷贝到elementData数组下标从index开始,长度为mumMoved
//相当于从index + 1位置往后的元素都往左移动一个下标
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
//数组末尾置为null,索引减1
elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work
return oldValue;
}
分析:删除操作也添加了synchronized锁,因此也是线程安全的,其它操作比较简单,直接看注释。
jdk1.8-Vector的更多相关文章
- Java容器解析系列(4) ArrayList Vector Stack 详解
ArrayList 这里关于ArrayList本来都读了一遍源码,并且写了一些了,突然在原来的笔记里面发现了收藏的有相关博客,大致看了一下,这些就是我要写的(╹▽╹),而且估计我还写不到博主的水平,这 ...
- LinkedList、ArrayList、Vector三者的关系与区别?
LinkedList.ArrayList.Vector三者的关系与区别? 区分ArrayList,Vector,LinkedList的区别 ArrayList,Vector的区别: 1.出现版本:Ar ...
- 【原】Java学习笔记026 - 集合
package cn.temptation; public class Sample01 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 需求:从三国演义中 ...
- Java基础——集合(持续更新中)
集合框架 Java.util.Collection Collection接口中的共性功能 1,添加 booblean add(Object obj); 往该集合中添加元素,一次添加一个 boolea ...
- 超详细的java集合讲解
1 集合 1.1 为什么会出现集合框架 [1] 之前的数组作为容器时,不能自动拓容 [2] 数值在进行添加和删除操作时,需要开发者自己实现添加和删除. 1.2 Collection接口 1.2.1 C ...
- java集合详解(附栈,队列)
1 集合 1.1 为什么会出现集合框架 [1] 之前的数组作为容器时,不能自动拓容 [2] 数值在进行添加和删除操作时,需要开发者自己实现添加和删除. 1.2 Collection接口 1.2.1 C ...
- 给jdk写注释系列之jdk1.6容器(10)-Stack&Vector源码解析
前面我们已经接触过几种数据结构了,有数组.链表.Hash表.红黑树(二叉查询树),今天再来看另外一种数据结构:栈. 什么是栈呢,我就不找它具体的定义了,直接举个例子,栈就相当于一个很窄的木桶 ...
- JDK1.8源码阅读系列之三:Vector
本篇随笔主要描述的是我阅读 Vector 源码期间的对于 Vector 的一些实现上的个人理解,用于个人备忘,有不对的地方,请指出- 先来看一下 Vector 的继承图: 可以看出,Vector 的直 ...
- 学习JDK1.8集合源码之--Vector
1. Vector简介 Vector是JDK1.0版本就推出的一个类,和ArrayList一样,继承自AbstractList,实现了List.RandomAccess.Cloneable.java. ...
- Stack&Vector源码分析 jdk1.6
参照:http://www.cnblogs.com/tstd/p/5104099.html Stack(Fitst In Last Out) 1.定义 public class Stack<E& ...
随机推荐
- Linux系统用户权限管理
Linux系统中三种基本权限 用户属主.用户属组及其它人权限 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 762 11-11 20:34 a.out 文件类型 ls命令中的缩写 应用 一般文件 - ...
- Java方法调用机制
最近在编程时,修改方法传入对象的对象引用,并没有将修改反映到调用方法中.奇怪为什么结果没有变化,原因是遗忘了Java对象引用和内存分配机制.本文介绍3个点: ① 该问题举例说明 ② 简要阐述Java内 ...
- yii 创建模块module
yii安装完成后的使用: yii也是单入口脚本, 入口文件为 http://hostname/web/index.php 使用模块: 在根目录下创建modules目录 在modules目录下创建模块 ...
- 通过远程 HTTP GET 请求载入信息
jQuery.get(url, [data], [callback], [type]) 概述 通过远程 HTTP GET 请求载入信息. 这是一个简单的 GET 请求功能以取代复杂 $.ajax .请 ...
- CF1033D Divisors Pollard-rho
好像卡常,第10个点一直TLE~ Code: #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long #define ull unsigned long ...
- docker命令集锦
sudo docker image ls 查看有哪些image镜像sudo docker run hello 运行image 删除全部containerdocker rm $(docker conta ...
- sh_21_遍历字典的列表
sh_21_遍历字典的列表 students = [ {"name": "阿土"}, {"name": "小美"} ] ...
- vue中render: h => h(App)的详细解释
2018年06月20日 10:54:32 H-L 阅读数 5369 render: h => h(App) 是下面内容的缩写: render: function (createEleme ...
- triplet
询问次数<=min(2*n,n+35) 一种类似hash的交互题 部分分n=5,限制10次 发现都问出来可以通过次数和大小确定所有的值和对应位置! n比较大 发现(X1,X2,i)能确定一些情况 ...
- postgres的数据库备份和恢复
备份和恢复 一条命令就可以解决很简单: 这是备份的命令: pg_dump -h 127/0.0.1 -U postgres databasename > databasename.bak 指令解 ...
