LC 499. The Maze III 【lock,hard】
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up(u), down (d), left (l) or right (r), but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction. There is also a hole in this maze. The ball will drop into the hole if it rolls on to the hole.
Given the ball position, the hole position and the maze, find out how the ball could drop into the hole by moving the shortest distance. The distance is defined by the number of empty spaces traveled by the ball from the start position (excluded) to the hole (included). Output the moving directions by using 'u', 'd', 'l' and 'r'. Since there could be several different shortest ways, you should output the lexicographically smallest way. If the ball cannot reach the hole, output "impossible".
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The ball and the hole coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
Example 1:
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 0 Input 2: ball coordinate (rowBall, colBall) = (4, 3)
Input 3: hole coordinate (rowHole, colHole) = (0, 1) Output: "lul" Explanation: There are two shortest ways for the ball to drop into the hole.
The first way is left -> up -> left, represented by "lul".
The second way is up -> left, represented by 'ul'.
Both ways have shortest distance 6, but the first way is lexicographically smaller because 'l' < 'u'. So the output is "lul".
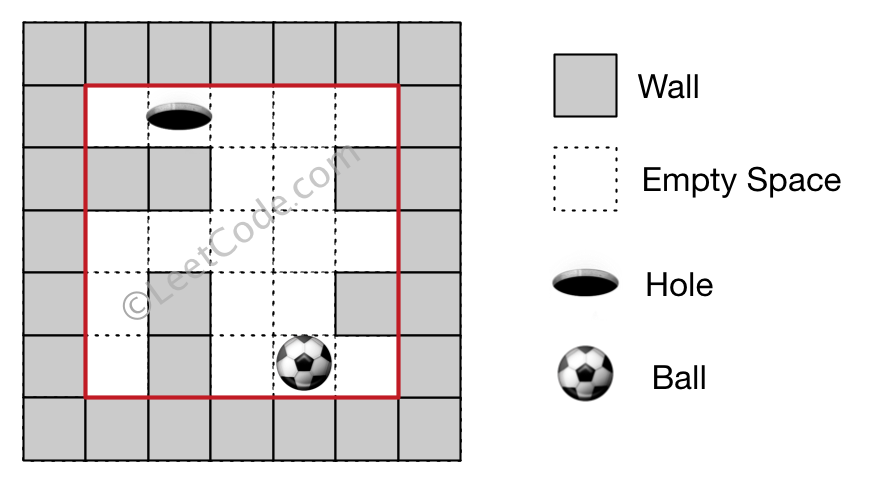
Example 2:
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 1
0 1 0 0 0 Input 2: ball coordinate (rowBall, colBall) = (4, 3)
Input 3: hole coordinate (rowHole, colHole) = (3, 0) Output: "impossible" Explanation: The ball cannot reach the hole.
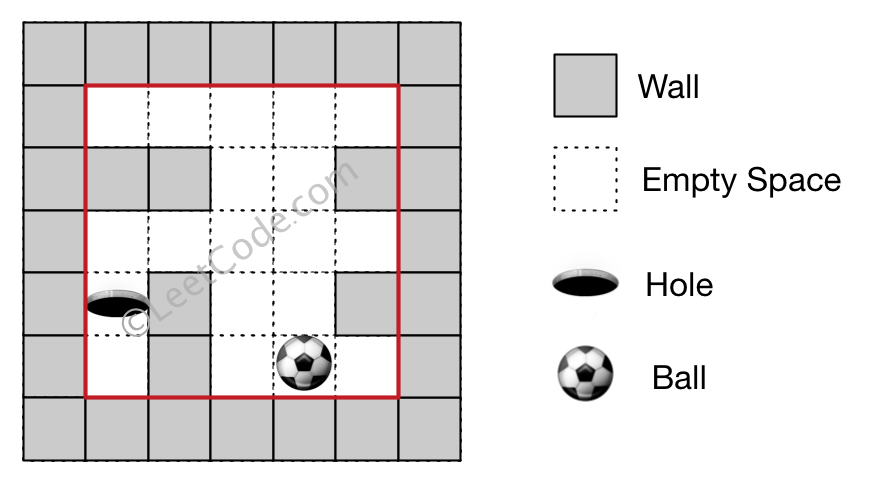
Note:
- There is only one ball and one hole in the maze.
- Both the ball and hole exist on an empty space, and they will not be at the same position initially.
- The given maze does not contain border (like the red rectangle in the example pictures), but you could assume the border of the maze are all walls.
- The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces, and the width and the height of the maze won't exceed 30.
这道题DEBUG,DE了半天,用了朴素的DFS,但还是超时在大case上了。果然已经超出了我的能力范围。
class Solution {
private:
int arr[][] = { { , },{ ,- },{ , },{ -, } };
vector<string> directions = { "r","l","d","u" };
public:
string findShortestWay(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& ball, vector<int>& hole) {
vector<string> ret;
set<int> visited;
helper(maze, ball[], ball[], hole, ret, visited, "");
sort(ret.begin(), ret.end());
string tmpstr = "";
if (ret.empty()) return "impossible";
//for(auto str : ret)cout << str << endl;
for (int i = ; i < ret[].size(); i++) {
if (tmpstr.empty()) {
tmpstr += ret[][i];
}
else {
if (tmpstr.back() != ret[][i]) {
tmpstr += ret[][i];
}
}
}
return tmpstr;
}
void helper(vector<vector<int>>& maze, int x, int y, vector<int>& hole, vector<string>& ret, set<int>& visited, string path) {
int m = maze.size();
int n = maze[].size();
if (visited.count(x * n + y)) return;
if (!ret.empty() && path.size() > ret[].size()) return;
visited.insert(x*n + y);
for (int i = ; i<; i++) {
int dx = arr[i][];
int dy = arr[i][];
int tmpx, tmpy;
tmpx = x + dx;
tmpy = y + dy;
string tmppath = path;
while (tmpx < m && tmpx >= && tmpy<n && tmpy >= && maze[tmpx][tmpy] != ) {
tmppath += directions[i];
if (tmpx == hole[] && tmpy == hole[]) {
// cout << tmppath << endl;
if(ret.empty() || tmppath.size() < ret[].size()){
ret.clear();
ret.push_back(tmppath);
}
else if(tmppath.size() == ret[].size()){
ret.push_back(tmppath);
}
//ret.push_back(tmppath);
//visited.erase(x*n + y);
//return;
}
tmpx += dx; tmpy += dy;
}
tmpx -= dx; tmpy -= dy;
if (tmpx == x && tmpy == y) continue;
//cout << "tmp location " << tmpx << " and " << tmpy << endl;
//cout << path << endl;
helper(maze, tmpx, tmpy, hole, ret, visited, tmppath);
}
visited.erase(x*n + y);
}
};
下面是我的解法的改进版,调了两个小时...
核心在于初始化一个最大值数组,记录每一个小球能滞留的点,如果这个点的值被更新且小于当前的cost直接返回,因为之前经过这个点的时候,就已经是比现在小的cost,再搜索下去没有意义。
然后在找到终点之后,更新结果,AC的结果依旧惨不忍睹。
Runtime: 160 ms, faster than 8.20% of C++ online submissions for The Maze III.
class Solution {
private:
int arr[][] = { { , },{ ,- },{ , },{ -, } };
vector<string> directions = { "r","l","d","u" };
public:
string findShortestWay(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& ball, vector<int>& hole) {
string ret = "";
vector<vector<int>> visited(maze.size(), vector<int>(maze[].size(), INT_MAX));
helper(maze, ball[], ball[], hole, ret, visited, "", );
if (ret.empty()) return "impossible";
return ret;
}
void helper(vector<vector<int>>& maze, int x, int y, vector<int>& hole, string& ret, vector<vector<int>>& visited, string path, int cost) {
int m = maze.size();
int n = maze[].size();
if (visited[x][y] >= cost) {
visited[x][y] = cost;
}
else {
return;
}
for (int i = ; i<; i++) {
int dx = arr[i][];
int dy = arr[i][];
int tmpx, tmpy, tmpcost = cost;
bool check = false, found = false, inloop = false;
tmpx = x;
tmpy = y;
string tmppath = path;
while (tmpx < m && tmpx >= && tmpy<n && tmpy >= && maze[tmpx][tmpy] != ) {
if (!check) {
tmppath += directions[i];
check = true;
}
if (tmpx == hole[] && tmpy == hole[]) {
if (visited[tmpx][tmpy] > tmpcost) {
visited[tmpx][tmpy] = tmpcost;
ret = tmppath;
}
else if(visited[tmpx][tmpy] == tmpcost && ret > tmppath){
ret = tmppath;
}
found = true;
}
tmpx += dx; tmpy += dy;
tmpcost++;
inloop = true;
}
if (inloop) {
tmpx -= dx;
tmpy -= dy;
tmpcost--;
}
if (tmpx == x && tmpy == y) continue;
//if (found) continue;
//cout << "tmp location " << tmpx << " and " << tmpy << endl;
//cout << path << endl;
helper(maze, tmpx, tmpy, hole, ret, visited, tmppath, tmpcost);
}
}
};
下面是网上的解法,用的是BFD。要求图上某一个点到已知点距离最近的方法就是BFS。但我觉得能存在更好的办法(Dijkstra)。
Runtime: 4 ms, faster than 100.00% of C++ online submissions for The Maze III.
#include "header.h"
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> dir = { { ,, },{ ,, },{ -,, },{ ,-, } };
vector<string> ds = { "d", "r", "u", "l" };
//d, r, u, l
string findShortestWay(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& ball, vector<int>& hole) {
//2018-12-18 解决了maze I and maze II,我觉得本质上还是BFS的问题,这个时候的destination只是说变成了如果掉进了hole,那么就不在运动了这样
//哈哈哈哈哈哈一次AC!赞!
if (maze.empty()) return "";
int m = maze.size();
int n = maze[].size();
vector<vector<pair<int, string> >> check(m, vector<pair<int, string> >(n, { INT_MAX, "" }));
check[ball[]][ball[]] = { , "" };
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({ ball[], ball[] });
while (!q.empty()) {
int len = q.size();
while (len) {
auto p = q.front(); q.pop(); len--;
for (auto d : dir) {
int steps = ;
int i = p.first; int j = p.second;
while (i + d[] >= && i + d[] < m && j + d[] >= && j + d[] < n && !maze[i + d[]][j + d[]]) {
i = i + d[]; j = j + d[]; steps++;
if (i == hole[] && j == hole[]) { break; }
}
if (check[i][j].first > check[p.first][p.second].first + steps) {
check[i][j].first = check[p.first][p.second].first + steps;
check[i][j].second = check[p.first][p.second].second + ds[d[]];
q.push({ i, j });
}
else if (check[i][j].first == check[p.first][p.second].first + steps) {
if (check[i][j].second > check[p.first][p.second].second + ds[d[]]) {
q.push({ i, j });
check[i][j].second = check[p.first][p.second].second + ds[d[]];
}
}
}
}
}
return check[hole[]][hole[]].first == INT_MAX ? "impossible" : check[hole[]][hole[]].second;
}
};
LC 499. The Maze III 【lock,hard】的更多相关文章
- LC 245. Shortest Word Distance III 【lock, medium】
Given a list of words and two words word1 and word2, return the shortest distance between these two ...
- LC 759. Employee Free Time 【lock, hard】
We are given a list schedule of employees, which represents the working time for each employee. Each ...
- Leetcode: The Maze III(Unsolved Lock Problem)
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolli ...
- LeetCode 499. The Maze III
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/the-maze-iii/ 题目: There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces ...
- [LeetCode] 499. The Maze III 迷宫 III
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolli ...
- LC 871. Minimum Number of Refueling Stops 【lock, hard】
A car travels from a starting position to a destination which is target miles east of the starting p ...
- LC 660. Remove 9 【lock, hard】
Start from integer 1, remove any integer that contains 9 such as 9, 19, 29... So now, you will have ...
- LC 656. Coin Path 【lock, Hard】
Given an array A (index starts at 1) consisting of N integers: A1, A2, ..., AN and an integer B. The ...
- LC 244. Shortest Word Distance II 【lock, Medium】
Design a class which receives a list of words in the constructor, and implements a method that takes ...
随机推荐
- JavaWeb【六、JavaBean】
简介 JavaBean是符合设计原则的Java类.好处是提高可复用性,减少冗余,增强可维护性. JavaBean设计原则 共有类 无参共有构造 属性私有 getter和setter方法 JSP动作元素 ...
- U盘加载速度慢的解决方法
在日常的生活和工作中,我们经常用U盘存储一些文件和程序.然而,一些朋友发现U盘有时候在使用过程中的识别加载速度非常缓慢.是U盘出故障了吗?其实不尽然,下面就为大家分享一下如何快速解决U盘加载缓慢的方法 ...
- 如何解决Win10电脑网速慢的问题?
很多Win10系统用户反映自己的电脑配置并不算低,却比有些旧电脑上网速度还要慢,不知道是什么原因. 其实,除了运营商网速的原因外,我们的电脑设置也会对网速有所影响.下面好系统U盘启动就来介绍一个Win ...
- (十二)Linux Kernel suspend and resume
一.对于休眠(suspend)的简单介绍 在Linux中,休眠主要分三个主要的步骤: 1) 冻结用户态进程和内核态任务 2) 调用注册的设备的suspend的回调函数, 顺序是按照注册顺序 ...
- tp5将查询数据返回为对象转为数组
use think\Model; collection()->toArray(); $result = collection(model("Menu")->order( ...
- PAT Basic 1023 组个最小数 (20 分)
给定数字 0-9 各若干个.你可以以任意顺序排列这些数字,但必须全部使用.目标是使得最后得到的数尽可能小(注意 0 不能做首位).例如:给定两个 0,两个 1,三个 5,一个 8,我们得到的最小的数就 ...
- Maven编译
多模块 只有需要编译成jar的模块才设置build <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springfram ...
- 今日理解之js
JavaScript 是前端的一门编程语言(也是有逻辑) node.js 支持前端js代码 跑在后端服务器上 Js跟Java什么关系? Js跟Java半毛钱关系都没有!!! 原因是当初Java特别火 ...
- 解决mysql提示服务无法启动问题
1.管理员权限打开命令,进入mysql下bin文件夹 删除根目录下data文件夹没有不用管,重新安装 2. ---------------------------------------------- ...
- java.sql.SQLException: Unknown column 'user0_.user_name' in 'field list' 报错问题
报错信息: java.sql.SQLException: Unknown column 'user0_.user_name' in 'field list'Query is: select user0 ...
