TensorFlow笔记三:从Minist数据集出发 两种经典训练方法
Minist数据集:MNIST_data 包含四个数据文件

一、方法一:经典方法 tf.matmul(X,w)+b
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import input_data
import time #define paramaters
learning_rate=0.01
batch_size=128
n_epochs=900 # 1.read from data file
#using TF learn built in function to load MNIST data to the folder data
mnist=input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data/',one_hot=True) # 2.creat placeholders for features and label
# each img in mnist data is 28*28 ,therefor need a 1*784 tensor
# 10 classes corresponding to 0-9
X=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[batch_size,784],name='X_placeholder')
Y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[batch_size,10 ],name='Y_placeholder') # 3.creat weight and bias ,w init to random variables with mean of 0 ;
# b init to 0 ,shape of b depends on Y ,shape of w depends on the dimension of X and Y_placeholder
w=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[784,10],stddev=0.01),name='weights')
b=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,10]),name="bias") # 4.build model to predict
# the model that returns the logits ,the logits will later passed through softmax layer
logits=tf.matmul(X,w)+b # 5.define lose function
# use cross entropy of softmax of logits as the loss function
entropy=tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=Y,name='loss')
loss=tf.reduce_mean(entropy) # 6.define training open
# using gradient descent with learning rate of 0.01 to minimize loss
optimizer=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss) with tf.Session() as sess:
writer=tf.summary.FileWriter('./my_graph/logistic_reg',sess.graph) start_time= time.time()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
n_batches=int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)
for i in range(n_epochs) : #train n_epochs times
total_loss=0 for _ in range(n_batches):
X_batch,Y_batch=mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
_,loss_batch=sess.run([optimizer,loss],feed_dict={X:X_batch,Y:Y_batch})
total_loss +=loss_batch
if i%100==0:
print('Average loss epoch {0} : {1}'.format(i,total_loss/n_batches)) print('Total time: {0} seconds'.format(time.time()-start_time))
print('Optimization Finished!') # 7.test the model
n_batches=int(mnist.test.num_examples/batch_size)
total_correct_preds=0
for i in range(n_batches):
X_batch,Y_batch=mnist.test.next_batch(batch_size)
_,loss_batch,logits_batch=sess.run([optimizer,loss,logits],feed_dict={X:X_batch,Y:Y_batch})
preds=tf.nn.softmax(logits_batch)
correct_preds=tf.equal(tf.argmax(preds,1),tf.argmax(Y_batch,1))
accuracy=tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct_preds,tf.float32))
total_correct_preds+=sess.run(accuracy) print('Accuracy {0}'.format(total_correct_preds/mnist.test.num_examples)) writer.close()
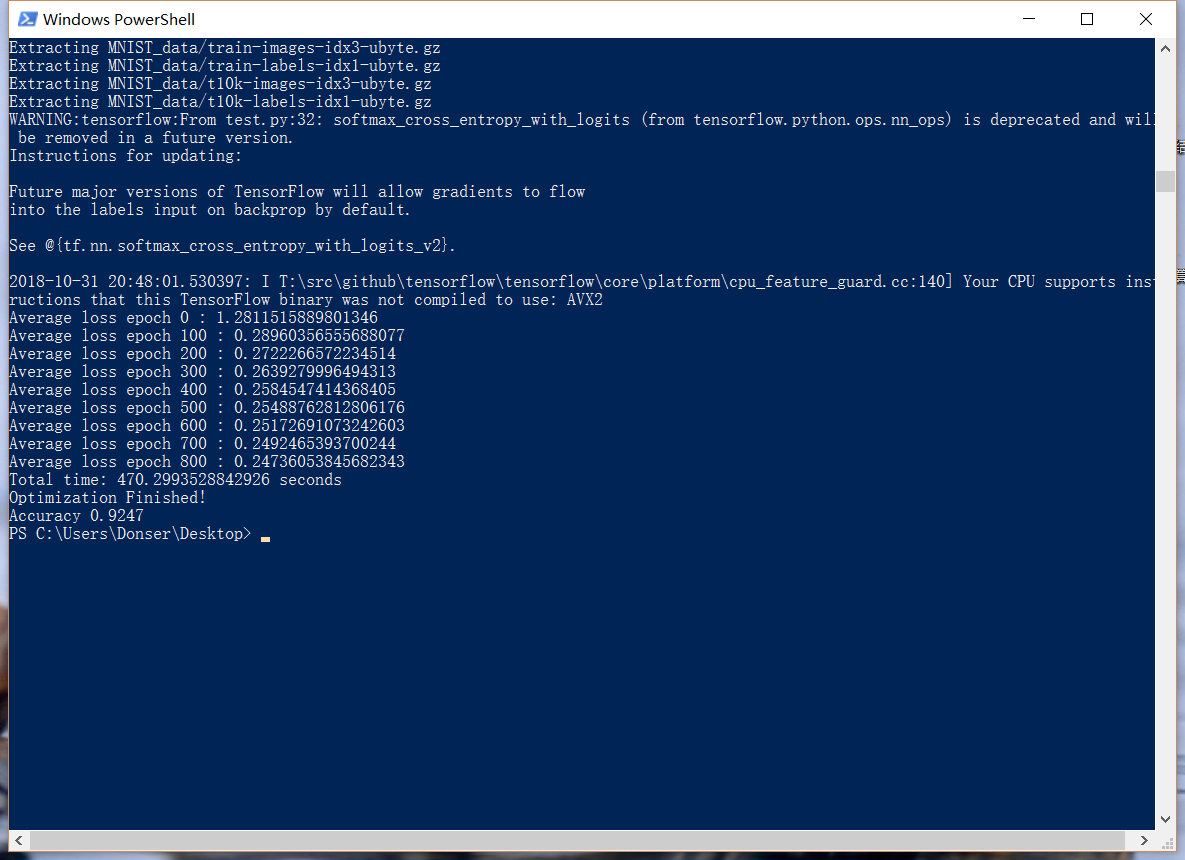
准确率大约是92%,TFboard:
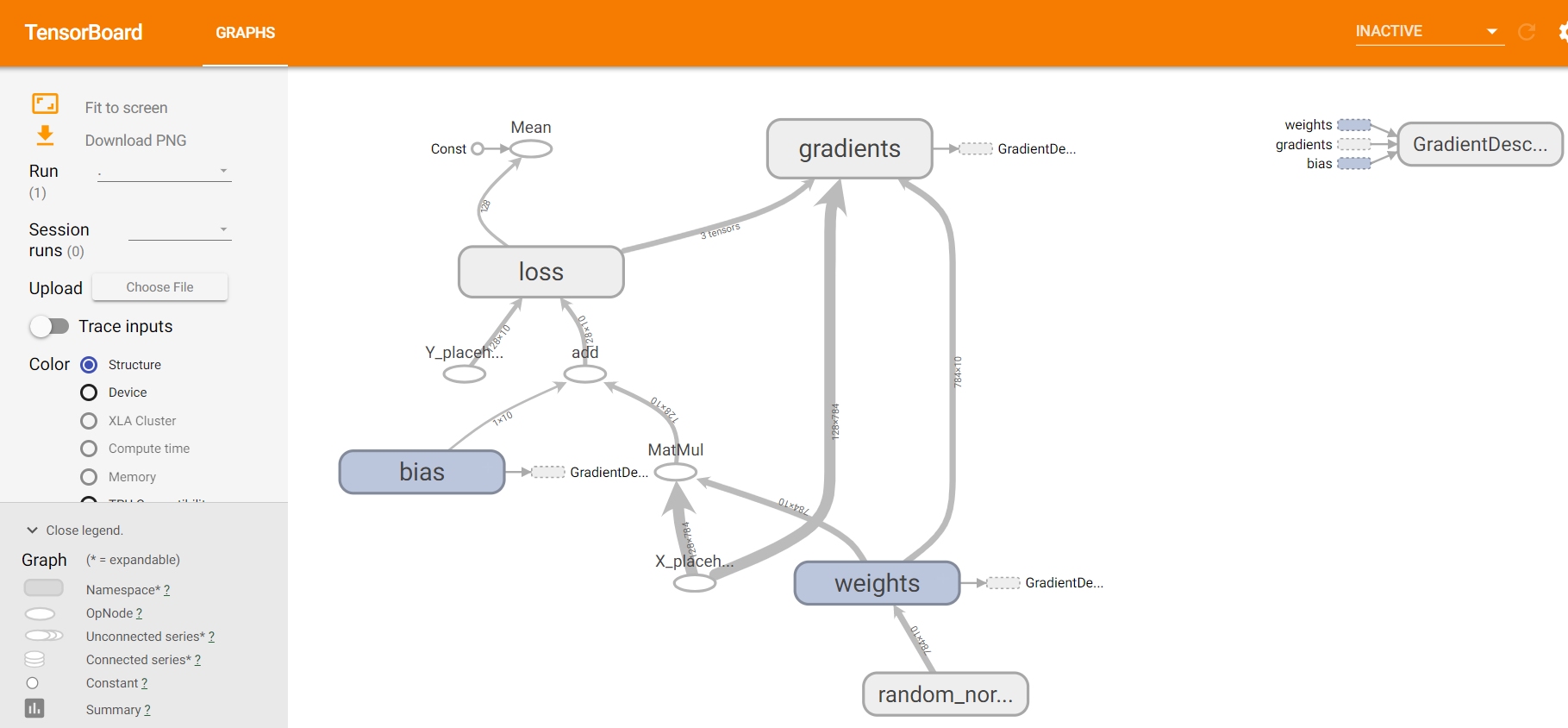
二、方法二:deep learning 卷积神经网络
# load MNIST data
import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True) # start tensorflow interactiveSession
import tensorflow as tf
sess = tf.InteractiveSession() # weight initialization
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial) def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape = shape)
return tf.Variable(initial) # convolution
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
# pooling
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') # Create the model
# placeholder
x = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 784])
y_ = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 10])
# variables
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,W) + b)
print (y)
# first convolutinal layer
w_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
print (x)
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
print (x_image)
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, w_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
print (h_conv1)
print (h_pool1)
# second convolutional layer
w_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, w_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
print (h_conv2)
print (h_pool2)
# densely connected layer
w_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024]) h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, w_fc1) + b_fc1)
print (h_fc1)
# dropout
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float")
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
print (h_fc1_drop)
# readout layer
w_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10]) y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, w_fc2) + b_fc2) # train and evaluate the model
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y_conv))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(1e-3).minimize(cross_entropy)
#train_step = tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
writer=tf.summary.FileWriter('./my_graph/mnist_deep',sess.graph) # Train
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
for i in range(1000):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
#print (batch_xs.shape,batch_ys)
if i % 100 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys, keep_prob:0.5})
print (("step %d, train accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy)))
train_step.run({x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys, keep_prob:0.5})
#print(accuracy.eval({x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels})) # Test trained model
print( ("python_base accuracy %g" % accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images[0:500], y_:mnist.test.labels[0:500], keep_prob:0.5}))) writer.close()
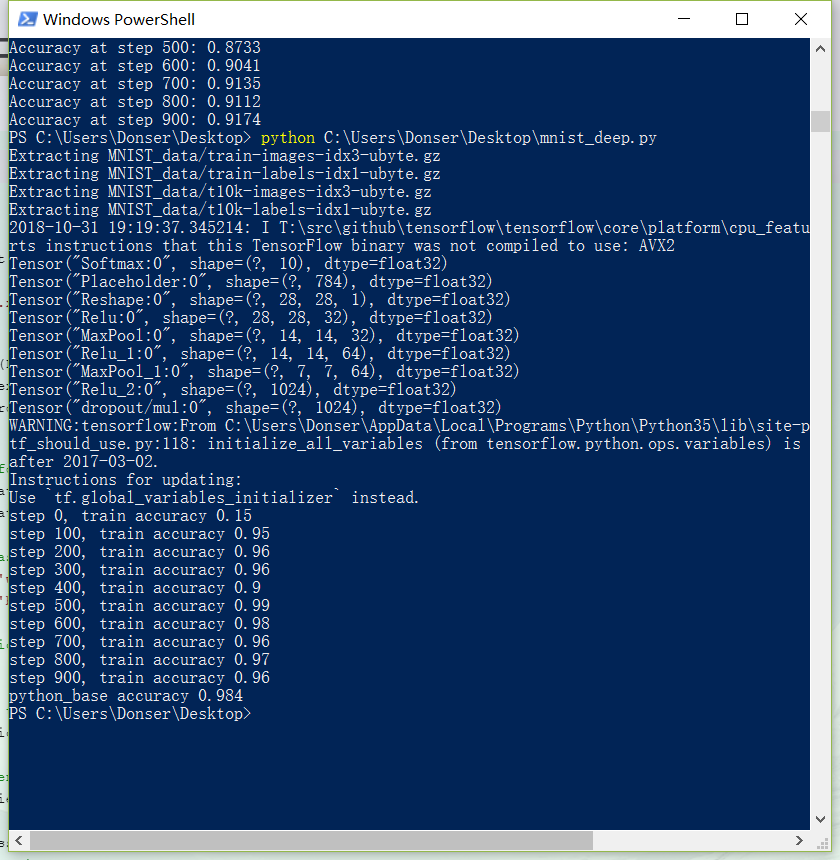
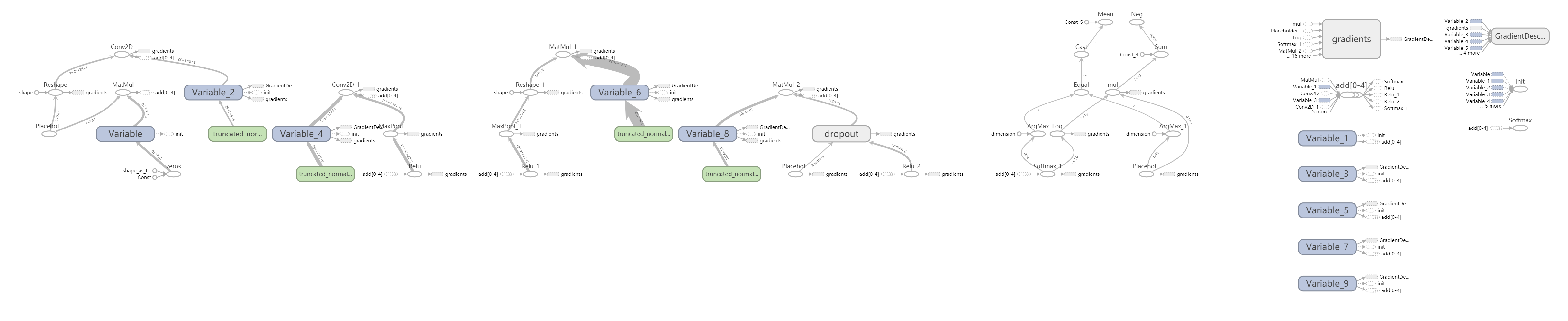
准确率达到98%,Board:
三、第三种 使用minist数据集做图像去噪
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.layers import Input, Dense
from keras.models import Model
from keras.layers import Input, Dense, Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, UpSampling2D
import numpy as np
from keras.callbacks import TensorBoard
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt (x_train, _), (x_test, _) = mnist.load_data() x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255.
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255.
x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (len(x_train), 28, 28, 1)) # adapt this if using `channels_first` image data format
x_test = np.reshape(x_test, (len(x_test), 28, 28, 1)) # adapt this if using `channels_first` image data format noise_factor = 0.5
x_train_noisy = x_train + noise_factor * np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=x_train.shape)
x_test_noisy = x_test + noise_factor * np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=x_test.shape) x_train_noisy = np.clip(x_train_noisy, 0., 1.)
x_test_noisy = np.clip(x_test_noisy, 0., 1.)
x_train_noisy = x_train_noisy.astype(np.float)
x_test_noisy = x_test_noisy.astype(np.float) input_img = Input(shape=(28, 28, 1)) # adapt this if using `channels_first` image data format x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(input_img)
x = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x)
x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
encoded = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x) # at this point the representation is (7, 7, 32) x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(encoded)
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(x)
x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x)
x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(x)
decoded = Conv2D(1, (3, 3), activation='sigmoid', padding='same')(x) autoencoder = Model(input_img, decoded)
autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adadelta', loss='binary_crossentropy') autoencoder.fit(x_train_noisy, x_train,
epochs=100,
batch_size=128,
shuffle=True,
validation_data=(x_test_noisy, x_test),
callbacks=[TensorBoard(log_dir='/tmp/tb', histogram_freq=0, write_graph=True)]) n = 10
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4))
for i in range(n):
#noisy data
ax = plt.subplot(3, n, i+1)
plt.imshow(x_test_noisy[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
#predict
ax = plt.subplot(3, n, i+1+n)
decoded_img = autoencoder.predict(x_test_noisy)
plt.imshow(decoded_img[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.gray()
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
#original
ax = plt.subplot(3, n, i+1+2*n)
plt.imshow(x_test[i].reshape(28, 28))
plt.gray()
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()
使用了keras,见官网 https://blog.keras.io/building-autoencoders-in-keras.html
第一行是加了噪声的图,第二行是去噪以后的图,第三行是原图,回复效果较好

125s跑一个epoch,100组三个半小时搞定
tensorboard --logdir=/tmp/tb
TensorFlow笔记三:从Minist数据集出发 两种经典训练方法的更多相关文章
- angular学习笔记(三)-视图绑定数据的两种方式
绑定数据有两种方式: <!DOCTYPE html> <html ng-app> <head> <title>2.2显示文本</title> ...
- 单向LSTM笔记, LSTM做minist数据集分类
单向LSTM笔记, LSTM做minist数据集分类 先介绍下torch.nn.LSTM()这个API 1.input_size: 每一个时步(time_step)输入到lstm单元的维度.(实际输入 ...
- LWJGL3的内存管理,第三篇,剩下的两种策略
LWJGL3的内存管理,第三篇,剩下的两种策略 上一篇讨论的基于 MemoryStack 类的栈上分配方式,是效率最高的,但是有些情况下无法使用.比如需要分配的内存较大,又或许生命周期较长.这时候就可 ...
- 中间自适应,左右定宽的两种经典布局 ---- 圣杯布局 VS 双飞翼布局
一.引子 最近学了些js框架,小有充实感,又深知如此节奏的前提需得基础扎实,于是回头想将原生CSS和Javascript回顾总结一番,先从CSS起,能集中它的就在基础的布局上,便查阅了相关资料,将布局 ...
- Android(java)学习笔记147:textView 添加超链接(两种实现方式,,区别于WebView)
1.方式1: LinearLayout layout = new LinearLayout(this); LinearLayout.LayoutParams params = new LinearLa ...
- react学习笔记1之声明组件的两种方式
//定义组件有两种方式,函数和类 function Welcome(props) { return <h1>Hello, {props.name}</h1>; } class ...
- 三,memcached服务的两种访问方式
memcached有两种访问方式,分别是使用telnet访问和使用php访问. 1,使用telnet访问memcacehd 在命令提示行输入, (1)连接memcached指令:telnet 127. ...
- TQ2440学习笔记——Linux上I2C驱动的两种实现方法(1)
作者:彭东林 邮箱:pengdonglin137@163.com 内核版本:Linux-3.14 u-boot版本:U-Boot 2015.04 硬件:TQ2440 (NorFlash:2M Na ...
- Android(java)学习笔记90:TextView 添加超链接(两种实现方式)
1. TextView添加超链接: TextView添加超链接有两种方式,它们有区别于WebView: (1)方式1: LinearLayout layout = new LinearLayout(t ...
随机推荐
- Java学习3之成员方法及函数重载
方法的定义:方法名称,返回值,参数列表,修饰符(权限修饰符,final,static),实现体. 参考自:<Java 程序设计与工程实践> 方法的签名: 唯一区别其他方法的元素:(1)方法 ...
- 聊聊、CA机构认证CSR生成
https://search.thawte.com/support/ssl-digital-certificates/index?page=content&id=SO832 https://s ...
- CSU 1809 Parenthesis(RMQ-ST+思考)
1809: Parenthesis Submit Description Bobo has a balanced parenthesis sequence P=p1 p2…pn of length n ...
- Linux系统——常见的系统调用
本文列出了大部分常见的Linux系统调用,并附有简要中文说明. 以下是Linux系统调用的一个列表,包含了大部分常用系统调用和由系统调用派生出的的函数.这可能是你在互联网上所能看到的唯一一篇中文注释的 ...
- php中session的生成机制、回收机制和存储机制探究
1.php中session的生成机制 我们先来分析一下PHP中是怎么生成一个session的.设计出session的目的是保持每一个用户的各种状态来弥补HTTP协议的不足(无状态).我们现在有一个疑问 ...
- Python 安装MySQLdb模块遇到报错及解决方案:_mysql.c(42) : fatal error C1083: Cannot open include file: 'config-win.h': No such file or directory
一.问题 系统:win7 64位 在下载MySQL-python-1.2.5.zip,使用python setup.py install 安装时,出现以下报错: _mysql.c(42) : fata ...
- Java Class 与 Object
平时看代码时,总是碰到这些即熟悉又陌生的名次,每天都与他们相见,但见面后又似曾没有任何的交集,所以今天我就来认识下这两个江湖侠客的背景: CLASS 在Java中,每个class都有一个相应的Clas ...
- mysql安装配置、主从复制配置详解【转】
仅限 centos7以下 版本 #yum install mysql #yum install mysql-server #yum install mysql-devel 启动服务 [root@loc ...
- 只能运行一个程序,禁止运行多个相同的程序 C#
原文发布时间为:2009-04-06 -- 来源于本人的百度文章 [由搬家工具导入] Program.cs 里面改成如下: static void Main() { ...
- C#获取二维数组的行数和列数及其多维。。。
原文发布时间为:2008-11-26 -- 来源于本人的百度文章 [由搬家工具导入] 有一个二维数组sz[,] 怎样获取sz 的行数和列数呢? sz.GetLength(0) 返回第一维的长度(即行数 ...
