《机器学习Python实现_10_10_集成学习_xgboost_原理介绍及回归树的简单实现》
一.简介
xgboost在集成学习中占有重要的一席之位,通常在各大竞赛中作为杀器使用,同时它在工业落地上也很方便,目前针对大数据领域也有各种分布式实现版本,比如xgboost4j-spark,xgboost4j-flink等。xgboost的基础也是gbm,即梯度提升模型,它在此基础上做了进一步优化...
二.损失函数:引入二阶项
xgboost的损失函数构成如下,即一个经验损失项+正则损失项:
\]
这里\(n\)表示样本数,\(F_{m-1}\)表示前\(m-1\)轮模型,\(f_m\)表示第\(m\)轮新训练模型,所以\(F_m=F_{m-1}+f_m\),\(\Omega(f_m)\)是对第\(m\)轮新训练模型进行约束的正则化项,在前面第6小节做过探索,对损失函数近似做二阶泰勒展开,并对近似损失函数做优化,通常会收敛的更快更好,接下里看下对第\(i\)个样本的经验项损失函数做二阶展开:
\]
这里:
h_i=\frac{\partial^2 L(y_i,F_{m-1}(x_i))}{\partial {F_{m-1}(x_i)}^2}
\]
对于第\(m\)轮,\(L(y_i,F_{m-1}(x_i))\)为常数项,不影响优化,可以省略掉,所以损失函数可以表示为如下:
\]
这便是xgboost的学习框架,针对不同问题,比如回归、分类、排序,会有不同的\(L(\cdot)\)以及\(\Omega(\cdot)\),另外由于需要二阶信息,所以\(L(\cdot)\)必须要能二阶可微,接下来对基学习器为决策树的情况做推导
三.基学习器:回归决策树
下面推导一下基学习器为回归树的情况,当选择决策树时,它的正则化项如下:
\]
其中,\(j=1,2,...,T\)表达对应的叶节点编号,\(\omega_j\)表示落在第\(j\)个叶节点的样本的预测值,即:
\]
\(I_j\)表示第\(j\)个叶子节点所属区域,所以决策树的损失函数可以改写为如下:
\]
这其实是关于\(\omega\)的一元二次函数,直接写出它的最优解:
\]
这里\(G_j=\sum_{i\in I_j}g_i,H_j=\sum_{i\in I_j}h_i\),可见\(L_2\)正则项起到了缩小叶子节点权重的效果,减少其对整个预测结果的影响,从而防止过拟合,将\(\omega_j^*\)带入可得损失值:
\]
特征选择
很显然,上面的损失函数可以直接用于特征选择中,对某节点在分裂前的评分为:
\]
分裂后,左右子节点的评分和为:
\]
所以分裂所能带来的增益:
\]
这里\(G=G_L+G_R,H=H_L+H_R\)
四.代码实现
这部分对xgboost中的回归树做简单实现,大体流程其实与CART回归树差不多,下面说下它与CART回归树不一样的几个点:
(1)这里fit与之前的CART回归树有些不一样了,之前是fit(x,y),而现在需要fit(x,g,h);
(2)特征选择不一样了,之前是求平方误差的增益,现在需要利用一阶和二阶导数信息,见上面的\(Score\)
(3)叶子节点的预测值不一样了,之前是求均值,现在需利用一阶和二阶导数信息,见上面的\(w_j^*\)
接下来对xgboost所需要用到的回归树做简单实现
import os
os.chdir('../')
import numpy as np
from ml_models.wrapper_models import DataBinWrapper
"""
xgboost基模型:回归树的实现,封装到ml_models.ensemble
"""
class XGBoostBaseTree(object):
class Node(object):
"""
树节点,用于存储节点信息以及关联子节点
"""
def __init__(self, feature_index: int = None, feature_value=None, y_hat=None, score=None,
left_child_node=None, right_child_node=None, num_sample: int = None):
"""
:param feature_index: 特征id
:param feature_value: 特征取值
:param y_hat: 预测值
:param score: 损失函数值
:param left_child_node: 左孩子结点
:param right_child_node: 右孩子结点
:param num_sample:样本量
"""
self.feature_index = feature_index
self.feature_value = feature_value
self.y_hat = y_hat
self.score = score
self.left_child_node = left_child_node
self.right_child_node = right_child_node
self.num_sample = num_sample
def __init__(self, max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, min_samples_leaf=1, gamma=1e-2, lamb=1e-1,
max_bins=10):
"""
:param max_depth:树的最大深度
:param min_samples_split:当对一个内部结点划分时,要求该结点上的最小样本数,默认为2
:param min_samples_leaf:设置叶子结点上的最小样本数,默认为1
:param gamma:即损失函数中的gamma
:param lamb:即损失函数中lambda
"""
self.max_depth = max_depth
self.min_samples_split = min_samples_split
self.min_samples_leaf = min_samples_leaf
self.gamma = gamma
self.lamb = lamb
self.root_node: self.Node = None
self.dbw = DataBinWrapper(max_bins=max_bins)
def _score(self, g, h):
"""
计算损失损失评分
:param g:一阶导数
:param h: 二阶导数
:return:
"""
G = np.sum(g)
H = np.sum(h)
return -0.5 * G ** 2 / (H + self.lamb) + self.gamma
def _build_tree(self, current_depth, current_node: Node, x, g, h):
"""
递归进行特征选择,构建树
:param x:
:param y:
:param sample_weight:
:return:
"""
rows, cols = x.shape
# 计算G和H
G = np.sum(g)
H = np.sum(h)
# 计算当前的预测值
current_node.y_hat = -1 * G / (H + self.lamb)
current_node.num_sample = rows
# 判断停止切分的条件
current_node.score = self._score(g, h)
if rows < self.min_samples_split:
return
if self.max_depth is not None and current_depth > self.max_depth:
return
# 寻找最佳的特征以及取值
best_index = None
best_index_value = None
best_criterion_value = 0
for index in range(0, cols):
for index_value in sorted(set(x[:, index])):
left_indices = np.where(x[:, index] <= index_value)
right_indices = np.where(x[:, index] > index_value)
criterion_value = current_node.score - self._score(g[left_indices], h[left_indices]) - self._score(
g[right_indices], h[right_indices])
if criterion_value > best_criterion_value:
best_criterion_value = criterion_value
best_index = index
best_index_value = index_value
# 如果减少不够则停止
if best_index is None:
return
# 切分
current_node.feature_index = best_index
current_node.feature_value = best_index_value
selected_x = x[:, best_index]
# 创建左孩子结点
left_selected_index = np.where(selected_x <= best_index_value)
# 如果切分后的点太少,以至于都不能做叶子节点,则停止分割
if len(left_selected_index[0]) >= self.min_samples_leaf:
left_child_node = self.Node()
current_node.left_child_node = left_child_node
self._build_tree(current_depth + 1, left_child_node, x[left_selected_index], g[left_selected_index],
h[left_selected_index])
# 创建右孩子结点
right_selected_index = np.where(selected_x > best_index_value)
# 如果切分后的点太少,以至于都不能做叶子节点,则停止分割
if len(right_selected_index[0]) >= self.min_samples_leaf:
right_child_node = self.Node()
current_node.right_child_node = right_child_node
self._build_tree(current_depth + 1, right_child_node, x[right_selected_index], g[right_selected_index],
h[right_selected_index])
def fit(self, x, g, h):
# 构建空的根节点
self.root_node = self.Node()
# 对x分箱
self.dbw.fit(x)
# 递归构建树
self._build_tree(1, self.root_node, self.dbw.transform(x), g, h)
# 检索叶子节点的结果
def _search_node(self, current_node: Node, x):
if current_node.left_child_node is not None and x[current_node.feature_index] <= current_node.feature_value:
return self._search_node(current_node.left_child_node, x)
elif current_node.right_child_node is not None and x[current_node.feature_index] > current_node.feature_value:
return self._search_node(current_node.right_child_node, x)
else:
return current_node.y_hat
def predict(self, x):
# 计算结果
x = self.dbw.transform(x)
rows = x.shape[0]
results = []
for row in range(0, rows):
results.append(self._search_node(self.root_node, x[row]))
return np.asarray(results)
下面简单测试一下功能,假设\(F_0(x)=0\),损失函数为平方误差的情况,则其一阶导为\(g=F_0(x)-y=-y\),二阶导为\(h=1\)
#构造数据
data = np.linspace(1, 10, num=100)
target1 = 3*data[:50] + np.random.random(size=50)*3#添加噪声
target2 = 3*data[50:] + np.random.random(size=50)*10#添加噪声
target=np.concatenate([target1,target2])
data = data.reshape((-1, 1))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
model=XGBoostBaseTree(lamb=0.1,gamma=0.1)
model.fit(data,-1*target,np.ones_like(target))
plt.scatter(data, target)
plt.plot(data, model.predict(data), color='r')
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x1d8fa8fd828>]

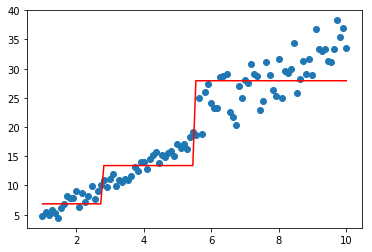
分别看看lambda和gamma的效果
model=XGBoostBaseTree(lamb=1,gamma=0.1)
model.fit(data,-1*target,np.ones_like(target))
plt.scatter(data, target)
plt.plot(data, model.predict(data), color='r')
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x1d8eb88cf60>]
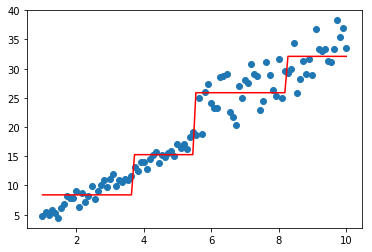
model=XGBoostBaseTree(lamb=0.1,gamma=100)
model.fit(data,-1*target,np.ones_like(target))
plt.scatter(data, target)
plt.plot(data, model.predict(data), color='r')
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x1d8fc9e3b38>]
《机器学习Python实现_10_10_集成学习_xgboost_原理介绍及回归树的简单实现》的更多相关文章
- 简单物联网:外网访问内网路由器下树莓派Flask服务器
最近做一个小东西,大概过程就是想在教室,宿舍控制实验室的一些设备. 已经在树莓上搭了一个轻量的flask服务器,在实验室的路由器下,任何设备都是可以访问的:但是有一些限制条件,比如我想在宿舍控制我种花 ...
- 利用ssh反向代理以及autossh实现从外网连接内网服务器
前言 最近遇到这样一个问题,我在实验室架设了一台服务器,给师弟或者小伙伴练习Linux用,然后平时在实验室这边直接连接是没有问题的,都是内网嘛.但是回到宿舍问题出来了,使用校园网的童鞋还是能连接上,使 ...
- 外网访问内网Docker容器
外网访问内网Docker容器 本地安装了Docker容器,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Docker容器? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Docker容器 ...
- 外网访问内网SpringBoot
外网访问内网SpringBoot 本地安装了SpringBoot,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地SpringBoot? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装Java 1 ...
- 外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB
外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB 本地安装了Elasticsearch,只能在局域网内访问其WEB,怎样从外网也能访问本地Elasticsearch? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Rails
外网访问内网Rails 本地安装了Rails,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Rails? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Rails 默认安装的Rails端口 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Memcached数据库
外网访问内网Memcached数据库 本地安装了Memcached数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Memcached数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网CouchDB数据库
外网访问内网CouchDB数据库 本地安装了CouchDB数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地CouchDB数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Cou ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网DB2数据库
外网访问内网DB2数据库 本地安装了DB2数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地DB2数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动DB2数据库 默认安装的DB2 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库
外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库 本地安装了OpenLDAP数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地OpenLDAP数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动 ...
随机推荐
- 吃透KVM创建虚机和KVM命令
1.创建虚拟机 1.1创建虚拟机磁盘 #使用qemu命令来创建磁盘 qemu-img create -f qcow2 /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos7.2.qcow2 2 ...
- [刷题] PTA 02-线性结构4 Pop Sequence
模拟栈进出 方法一: 1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #define MAXSIZE 1000 3 4 typedef struct{ 5 int data[MAXSIZE]; ...
- grub救援模式
http://www.jinbuguo.com/linux/grub.cfg.html
- 使用ps、top、ps_mem命令找出Linux中的最大内存消耗过程
使用ps.top.ps_mem命令找出Linux中的最大内存消耗过程 2020-02-08 16:06:59作者:自力稿源:云网牛站 您可能已经看到Linux系统多次消耗过多的内存,如果是这种情况,那 ...
- rsync同步遇到的报错和解决办法
rsync同步遇到的报错和解决办法 科技小能手 2017-11-12 18:27:00 浏览1125 配置 code 同步 open stream file read 在同步的客户端操作: [ ...
- ELK学习实验014:Nginx日志JSON格式收集
1 Kibana的显示配置 https://demo.elastic.co/app/kibana#/dashboard/welcome_dashboard 环境先处理干净 安装nginx和httpd- ...
- 11.20 yum:自动化RPM包管理工具
yum(Yellow dog Updater Modified)是多个Linux发行版的软件包管理器,例如Redhat RHEL.CentOS和Fedora.yum主要用于自动安装.升级rpm软件包, ...
- brk 和 sbrk 区别
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxuyuancc/p/3566710.html brk和sbrk的定义,在man手册中定义了这两个函数: 1 #include < ...
- SpringBoot打jar包-下载文件时报错-class path resource xxxxxx cannot be resolved to URL because it does not exist
一.问题由来 新项目的开发中,打包方式由war包改为了jar包的方式,这样在部署的时候更加的方便.测试环境使用pm2这个工具来管理项目的运行,停止,重启等等非常方便. 可是当测试人员在测试项目中的文件 ...
- .NET平台系列13 .NET5 统一平台
系列目录 [已更新最新开发文章,点击查看详细] 时机决定一切,对于 .NET5 也是如此.实际上微软.NET团队在开始开发 .NET Core 时,对 .NET Framework 的全面重写 ...
