Hibernate逍遥游记-第13章 映射实体关联关系-003单向多对多
0.


1.
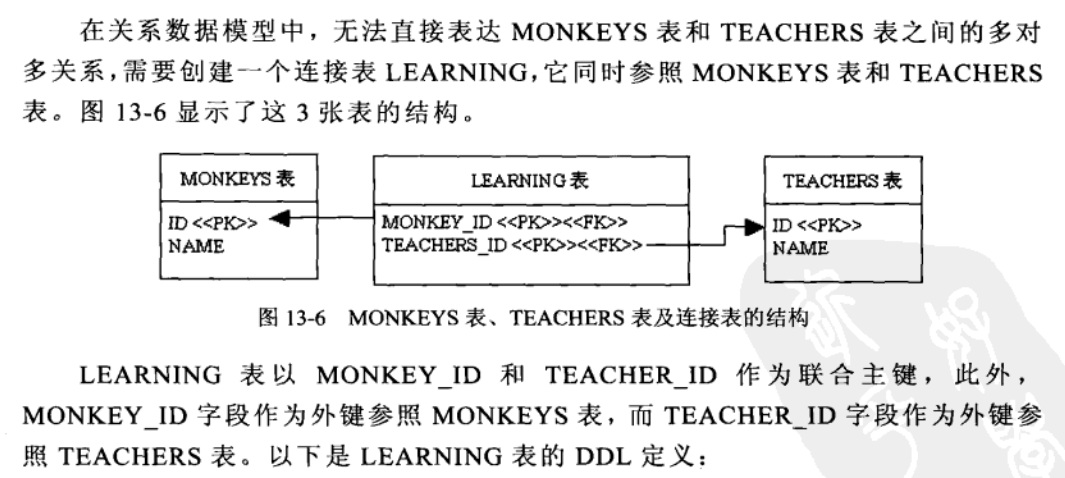
drop database if exists SAMPLEDB;
create database SAMPLEDB;
use SAMPLEDB; create table MONKEYS(
ID bigint not null,
NAME varchar(15),
primary key (ID)
); create table TEACHERS(
ID bigint not null,
NAME varchar(15),
primary key(ID)
); create table LEARNING(
MONKEY_ID bigint not null,
TEACHER_ID bigint not null,
primary key(MONKEY_ID,TEACHER_ID)
); alter table LEARNING add index IDX_MONKEY(MONKEY_ID),
add constraint FK_MONKEY foreign key (MONKEY_ID) references MONKEYS(ID); alter table LEARNING add index IDX_TEACHER(TEACHER_ID),
add constraint FK_TEACHER foreign key (TEACHER_ID) references TEACHERS(ID);
2.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping
PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping > <class name="mypack.Monkey" table="MONKEYS" >
<id name="id" type="long" column="ID">
<generator class="increment"/>
</id> <property name="name" column="NAME" type="string" /> <set name="teachers" table="LEARNING"
lazy="true"
cascade="save-update">
<key column="MONKEY_ID" />
<many-to-many class="mypack.Teacher" column="TEACHER_ID" />
</set> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
3.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping
PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping > <class name="mypack.Teacher" table="TEACHERS" >
<id name="id" type="long" column="ID">
<generator class="increment"/>
</id> <property name="name" column="NAME" type="string" /> </class>
</hibernate-mapping>
4.
package mypack;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.HashSet; public class Monkey { private Long id;
private String name;
private Set teachers=new HashSet(); public Monkey(String name, Set teachers) {
this.name = name;
this.teachers = teachers; } /** default constructor */
public Monkey() {
} public Long getId() {
return this.id;
} public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return this.name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public Set getTeachers() {
return this.teachers;
} public void setTeachers(Set teachers) {
this.teachers = teachers;
} }
5.
package mypack;
public class Teacher{
private Long id;
private String name; /** full constructor */
public Teacher(String name ) {
this.name = name;
} /** default constructor */
public Teacher() {
} public String getName() {
return this.name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public Long getId() {
return this.id;
} public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
} }
6.
package mypack; import org.hibernate.*;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import java.util.*; public class BusinessService{
public static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
static{
try{
Configuration config = new Configuration().configure();
sessionFactory = config.buildSessionFactory();
}catch(RuntimeException e){e.printStackTrace();throw e;}
} public void saveMonkey(Monkey monkey){
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
session.save(monkey);
tx.commit(); }catch (RuntimeException e) {
if (tx != null) {
tx.rollback();
}
throw e;
} finally {
session.close();
}
} public Monkey loadMonkey(Long id){
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
Monkey monkey=(Monkey)session.get(Monkey.class,id);
Hibernate.initialize(monkey.getTeachers());
tx.commit(); return monkey; }catch (RuntimeException e) {
if (tx != null) {
tx.rollback();
}
throw e;
} finally {
session.close();
}
} public void printMonkey(Monkey monkey){
Set teachers=monkey.getTeachers();
Iterator it=teachers.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Teacher teacher=(Teacher)it.next();
System.out.println(monkey.getName()+" "+teacher.getName());
} } public void test(){ Teacher teacher1=new Teacher("¶þÀÉÉñ");
Teacher teacher2=new Teacher("ºìº¢¶ù"); Monkey monkey1=new Monkey();
monkey1.setName("ÖǶàÐÇ");
monkey1.getTeachers().add(teacher1);
monkey1.getTeachers().add(teacher2); Monkey monkey2=new Monkey();
monkey2.setName("ÀÏÍçͯ");
monkey2.getTeachers().add(teacher1); saveMonkey(monkey1);
saveMonkey(monkey2); monkey1=loadMonkey(monkey1.getId());
printMonkey(monkey1); } public static void main(String args[]){
new BusinessService().test();
sessionFactory.close();
}
}

7.
Hibernate逍遥游记-第13章 映射实体关联关系-003单向多对多的更多相关文章
- Hibernate逍遥游记-第13章 映射实体关联关系-006双向多对多(分解为一对多)
1. 2. <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate ...
- Hibernate逍遥游记-第13章 映射实体关联关系-005双向多对多(使用组件类集合\<composite-element>\)
1. <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hi ...
- Hibernate逍遥游记-第13章 映射实体关联关系-004双向多对多(inverse="true")
1. <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hi ...
- Hibernate逍遥游记-第13章 映射实体关联关系-002用主键映射一对一(<one-to-one constrained="true">、<generator class="foreign">)
1. <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hi ...
- Hibernate逍遥游记-第13章 映射实体关联关系-001用外键映射一对一(<many-to-one unique="true">、<one-to-one>)
1. <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hi ...
- Hibernate逍遥游记-第10章 映射继承关系-003继承关系树中的每个类对应一个表(joined-subclass)
1. 2. <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate ...
- Hibernate逍遥游记-第5章映射一对多-01单向<many-to-one>、cascade="save-update"、lazy、TransientObjectException
1. <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hi ...
- Hibernate逍遥游记-第12章 映射值类型集合-005对集合排序Map(<order-by>\<sort>)
1. <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hi ...
- Hibernate逍遥游记-第12章 映射值类型集合-005对集合排序(<order-by>\<sort>)
1. 2. <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate ...
随机推荐
- 51nod 1021 石头归并
1021 石子归并 基准时间限制:1 秒 空间限制:131072 KB 分值: 20 难度:3级算法题 收藏 关注 N堆石子摆成一条线.现要将石子有次序地合并成一堆.规定每次只能选相邻的2堆石子合 ...
- java web 路径 --转载
主题:java(Web)中相对路径,绝对路径问题总结 1.基本概念的理解 绝对路径:绝对路径就是你的主页上的文件或目录在硬盘上真正的路径,(URL和物理路径)例如:C:\xyz\test.txt 代表 ...
- js读取json数据(php传值给js)
<?php $array =array('fds','fdsa','fdsafasd'); // json_encode($array); ?> <html> <hea ...
- 为checkboxSelectionModel赋值
store.on('load', function(store, records, options) { sm.clearSelections(); //清空数据 Ext.each(records ...
- Python中Cookie的处理(二)cookielib库
Python中cookielib库(python3中为http.cookiejar)为存储和管理cookie提供客户端支持. 该模块主要功能是提供可存储cookie的对象.使用此模块捕获cookie并 ...
- 1099. Build A Binary Search Tree (30)
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following propertie ...
- 博主教你制作类似9patch效果的iOS图片拉伸
下面张图片,本来是设计来做按钮背景的: button.png,尺寸为:24x60 现在我们把它用作为按钮背景,按钮尺寸是150x50: // 得到view的尺寸 CGSize viewSize = ...
- mysql数据库本地化操作
<?php if(!defined('SITE_PATH')){ define('SITE_PATH',dirname(dirname(__FILE__))); } $dbconfig=incl ...
- Notes of the scrum meeting(10/28)
meeting time:4:00~6:00p.m.,October 28th,2013 meeting place:雕刻时光 attendees: 顾育豪 ...
- error:LNK2005 已经在*.obj中定义
为什么会出现这个错误??“error LNK2005: 已经在*.obj中定义” 编程中经常能遇到LNK2005错误——重复定义错误,其实LNK2005错误并不是一个很难解决的错误,弄清楚它形成的原 ...
