Java基础(四)线程快速了解
开始整理线程之前,之前有个命令忘记整理了,先整理一下jar命令的使用
Jar包
其实可以理解是java的压缩包
方便使用,只要在classpath设置jar路径即可
数据库驱动,ssh框架等都是以jar包体现的
打包方式一:将指定的class文件打入到jar包中
jar cvf xxx.jar Xxx.class yyy.class
打包方式二:将某个目录下的所有文件打入到jar包中
jar cvf xxx.jar -C xxx/.
查看jar文件:
jar -tf xxx.jar
运行jar包中的类:
java -cp xxx.jar xx.xx.xx(完整的类名)
常用的jar命令参数:
c:创建压缩文件
f:指定存档名称
v:显示详细信息
m:加入自定义清单
指定清单文件(xxx.jar/META-INF/MNIFEST.MF)的入口类
jar cvfe classess.jar com.zhaofan.PackagDemo1 classes/.
这样我们就可以通过java -jar xxx.jar直接执行
线程
进程:运行时概念,运行的应用程序
线程:应用程序内部并发执行的代码段,共享内存
这里几个关键词
yield: 放弃cpu抢占权
join:等待指定的线程执行完
sleep:静态方法,让线程休眠毫秒数
daemo:守护线程
最简单的线程代码:
package study_java.ex9;
public class ThreadDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Mythread t1 = new Mythread();
t1.start();
}
}
class Mythread extends Thread{
public void run(){
while (true){
System.out.println("MyThread");
}
}
}
join的一个简单实用例子:
package study_java.ex9;
public class ThreadDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Player p1 = new Player("aa",5000);
Player p2 = new Player("bb",8000);
Player p3 = new Player("cc",2000);
Player p4 = new Player("dd",3000);
p1.start();
p2.start();
p3.start();
p4.start();
try{
p1.join();
p2.join();
p3.join();
p3.join();
}
catch (Exception e){
}
System.out.println("人到了,开始玩游戏");
}
}
class Player extends Thread{
private String name;
private int time;
public Player(String name, int time){
this.name = name;
this.time = time;
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("玩家:"+name + "出发了");
try{
Thread.sleep(time);
}
catch (Exception e){
}
System.out.println("玩家:"+name + "到了");
}
}
守护线程的一个使用例子
package study_java.ex9;
import java.util.Date;
public class ThraedDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Room r1 = new Room("no1",15000);
Waiter w1 = new Waiter();
//w1.setDaemon(true); 设置守护线程
r1.start();
w1.start();
}
}
class Room extends Thread{
private String no;
private int time;
public Room(String no, int time){
this.no = no;
this.time = time;
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("no" + "号房间正在唱歌");
try{
Thread.sleep(time);
}
catch (Exception e){
}
System.out.println("no" + "买单");
}
}
class Waiter extends Thread{
public Waiter(){
this.setDaemon(true);
}
public void run(){
while (true){
System.out.println(new java.util.Date());
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
catch (Exception e){
}
}
}
}
任何一个对象都可以是锁,信号灯,其实就是一个参照物
一个锁的代码例子:
package study_java.ex9;
public class ThreadDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Saler s1 = new Saler("a1");
Saler s2 = new Saler("a2");
s1.start();
s2.start();
}
}
class Saler extends Thread{
// 锁
static Object lock = new Object();
static int tickts = 100;
private String name;
public Saler(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void run(){
while (true){
int tick = getTickts();
if (tick > 0){
System.out.println(name+":"+ tick);
}
else {
return;
}
}
}
// 取票
public int getTickts(){
synchronized (lock){
int currTicket = tickts;
tickts --;
return currTicket;
}
}
}
还有一种方法是:
public static synchronized int getTickts(){
int currTicket = tickts;
tickts --;
return currTicket;
}
这样也能实现锁的机制,但是注意这里必须是static
我们整理一个新的写法,把票池单独写出来
public class ThreadDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
TicketPool pool = new TicketPool();
Saler s1 = new Saler("s1",pool);
Saler s2 = new Saler("s2",pool);
s1.start();
s2.start();
}
}
// 票池
class TicketPool {
private int tickets = 100;
// 从票池取票
public synchronized int getTickets(){
int ticket = tickets;
tickets -= 1;
return ticket;
}
}
// 售票员
class Saler extends Thread{
private TicketPool pool = null;
private String name;
public Saler(String name, TicketPool tp){
this.name = name;
this.pool = tp;
}
public void run(){
while (true){
int no = pool.getTickets();
if (no > 0 ){
System.out.println(name + ":" + no);
}
else {
return;
}
}
}
}
两个小的练习熟悉上面知识点的使用:
车过山洞的问题,山洞同时只允许一个车通过,现在有多辆车,不同的车通过的时间不同,代码实现如下:
package study_java.ex11;
public class CarCave {
public static void main(String[] args){
Cave cave = new Cave();
Car car1 = new Car(cave,10000,"奥迪");
Car car2 = new Car(cave,8000,"奔驰");
Car car3 = new Car(cave,6000,"宝马");
Car car4 = new Car(cave,2000,"悍马");
car1.start();
car2.start();
car3.start();
car4.start();
}
}
class Cave{
public synchronized void crossCar(Car car){
try{
System.out.println(car.name+":开始过山洞了");
Thread.sleep(car.time);
System.out.println(car.name+":开始出山洞了");
}
catch (Exception e){
}
}
}
class Car extends Thread{
public Cave cave;
public int time;
public String name;
public Car(Cave cave ,int time,String name){
this.cave = cave;
this.time = time;
this.name = name;
}
public void run(){
cave.crossCar(this);
}
}
第二个小练习是我们经常遇到的场景,取票问题,现在有一个取票机,但是有五十个人要取票,实现代码如下:
package study_java.ex11;
public class TicketDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
TicketMachine m = new TicketMachine();
for (int i=0;i<50;i++){
new Person(m,"tom"+i).start();
}
}
}
// 取票机
class TicketMachine{
private int ticketNo = 1;
// 打印票号
public synchronized int printTicktNo(){
int currTicketNo = ticketNo;
ticketNo ++;
return currTicketNo;
}
}
class Person extends Thread{
private TicketMachine m;
private String name;
public Person(TicketMachine m,String name) {
this.m = m;
this.name = name;
}
public void run(){
int no = m.printTicktNo();
System.out.println(name+ ":" + no);
}
}
生产者消费者模型
通过上面的知识点,写一个生产者好消费者模型
package study_java.ex11; import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List; public class PCDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
MyList myList = new MyList(); Productor p = new Productor(myList);
Consumer c = new Consumer(myList);
Consumer c2 = new Consumer(myList);
Consumer c3 = new Consumer(myList);
p.start();
c.start();
c2.start();
c3.start();
} } class MyList{
private int Max = 100;
private List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
public void addLast(Integer i){
while (true){
synchronized (list){
if (list.size() < Max){
list.add(i);
return;
}
}
} }
public Integer removeFirst(){
while (true){
synchronized (list){
if(!list.isEmpty()){
return list.remove(0);
}
}
}
}
} class Productor extends Thread{
private MyList myList;
public Productor(MyList myList){
this.myList = myList;
}
public void run(){
int i = 1;
while (true){
myList.addLast(new Integer(i));
System.out.println("生产者生产了"+i+"号");
i++;
}
}
} class Consumer extends Thread{
private MyList myList;
public Consumer(MyList myList){
this.myList = myList;
}
public void run(){
while (true){
int no = myList.removeFirst();
System.out.println("消费者消费了"+no+"号");
}
}
}
生产者消费者而改进版本:
package study_java.ex11; import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List; public class PCDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args){
Pool pool = new Pool();
Producter p1 = new Producter(pool);
Consumer c1 = new Consumer(pool);
p1.start();
c1.start(); }
} class Pool{
private List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
private int Max = 100;
public void addLast(int n){
synchronized (this){
while (list.size() >= Max){
try{
this.wait();
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
list.add(new Integer(n)); this.notifyAll();
}
}
public int remove(){
synchronized (this){
while (list.size() == 0){
try{
this.wait();
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
} }
int no = list.remove(0); this.notifyAll();
return no;
}
} } // 生产者
class Producter extends Thread{
private Pool pool;
static int i = 1;
public Producter(Pool pool){
this.pool = pool;
}
public void run(){
while (true){
pool.addLast(i++);
System.out.println("生产者生产了"+i+"号");
}
} } // 消费者
class Consumer extends Thread{
private Pool pool;
public Consumer(Pool pool){
this.pool = pool;
}
public void run(){
while (true){
int no = pool.remove();
System.out.println("消费者消费了"+no+"号");
}
} }
wait():让当前线程进入到锁对象的等待队列里,同时释放锁旗标。这个方法是当前锁对象的方法
wait这里还可以添加参数wait(int n) :等待指定的时间片,等待队列中的线程最多等待n毫秒
notify():这个方法是当前锁对象的方法,注意这里并不会释放锁
notifyAll():通知等待队列中的所有线程都可以抢占cpu运行,通知需要获得对象的监控权
sleep:当前CPU的抢占权,和锁对象的监控权无关。
Thread.currentThread().getName():获取当前线程名字
Thread.currentThread().setName():设置当前线程名字
priority:1-10从低到高,默认是5
Thread.currentThread().getPriority():设置当前线程优先级
线程状态:
BLOCKED: 阻塞
NEW:新建
RUNNABL:执行
TERMINATED:已经终止
TIMED_WAITING:限时等待
WAITING:等待
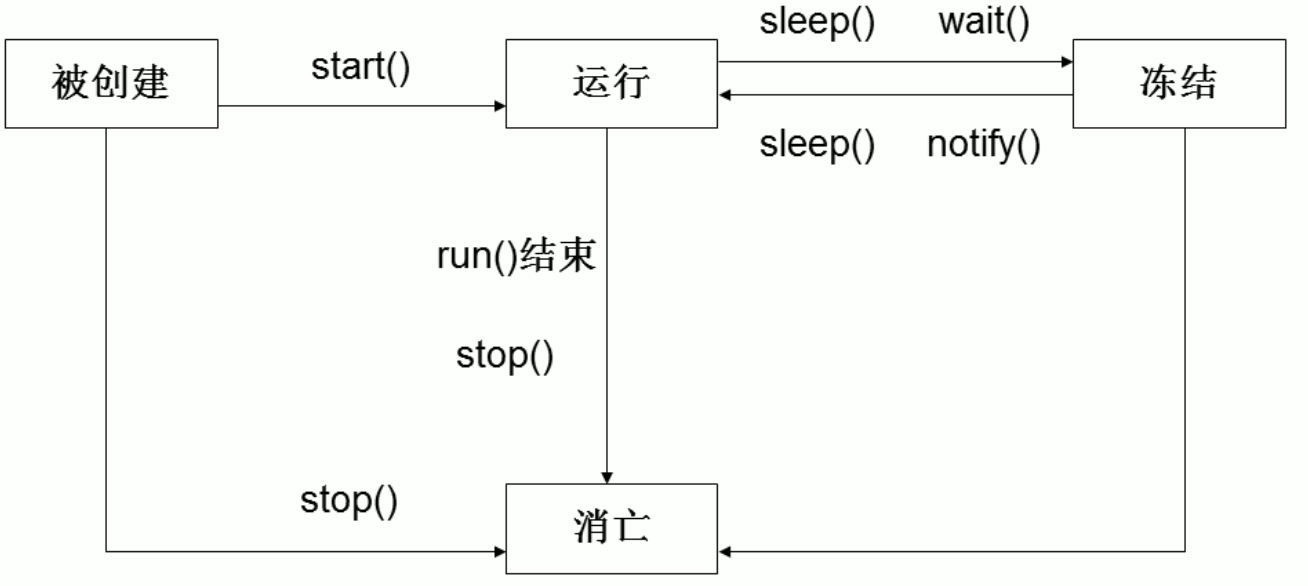
创建一个线程的另外一种方式:
实现Runnable接口
1. 子类覆盖接口中的run方法
2. 通过Thread类创建线程,并将实现了Runnable接口的子类对象作为参数传递给Thread类的构造函数
3. Thread类对象调用start方法开启线程
代码例子如下:
package study_java.ex11;
public class RunnableDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
MyRunnabl m = new MyRunnabl();
new Thread(m).start();
}
}
class MyRunnabl implements Runnable{
public void run(){
System.out.println("hello world");
}
}
同步(synchronized)
synchronized(对象)
{
需要同步的代码
}
同步的特点:
同步的前提是:
需要两个或者两个以上的线程
多个线程使用的同一个锁
同步的弊端:
当线程相当多时,因为每个线程都会去判断同步上的锁,这是很耗费资源的,无形中会降低程序的额运行效率
Java基础(四)线程快速了解的更多相关文章
- 重学JAVA基础(四):线程的创建与执行
1.继承Thread public class TestThread extends Thread{ public void run(){ System.out.println(Thread.curr ...
- Java基础(四) StringBuffer、StringBuilder原理浅析
StringBuilder与StringBuffer作用就是用来处理字符串,但String类本身也具备很多方法可以用来处理字符串,那么为什么还要引入这两个类呢? 关于String的讲解请看Java基础 ...
- 【Java基础】线程和并发机制
前言 在Java中,线程是一个很关键的名词,也是很高频使用的一种资源.那么它的概念是什么呢,是如何定义的,用法又有哪些呢?为何说Android里只有一个主线程呢,什么是工作线程呢.线程又存在并发,并发 ...
- Java基础-多线程-③线程同步之synchronized
使用线程同步解决多线程安全问题 上一篇 Java基础-多线程-②多线程的安全问题 中我们说到多线程可能引发的安全问题,原因在于多个线程共享了数据,且一个线程在操作(多为写操作)数据的过程中,另一个线程 ...
- java 基础 四种权限修饰符
/** * Java有四种权限修饰符: * public > protected > (default) > private * 同一个类 YES YES YES YES * 同一个 ...
- Java基础篇——线程、并发编程知识点全面介绍(面试、学习的必备索引)
原创不易,如需转载,请注明出处https://www.cnblogs.com/baixianlong/p/10739579.html,希望大家多多支持!!! 一.线程基础 1.线程与进程 线程是指进程 ...
- Java基础(四)-异常处理机制及其设计
本篇主要是记录自己所理解的Java异常处理机制(基于jdk1.7)以及怎么去处理和设计异常.还记得当初学习Java异常这块的时候都没怎么注意它的用途,以为就是简单的处理下异常,我避免程序出现这样错误就 ...
- Java多线程(四) 线程池
一个优秀的软件不会随意的创建.销毁线程,因为创建和销毁线程需要耗费大量的CPU时间以及需要和内存做出大量的交互.因此JDK5提出了使用线程池,让程序员把更多的精力放在业务逻辑上面,弱化对线程的开闭管理 ...
- Java多线程(四) —— 线程并发库之Atomic
一.从原子操作开始 从相对简单的Atomic入手(java.util.concurrent是基于Queue的并发包,而Queue,很多情况下使用到了Atomic操作,因此首先从这里开始). 很多情况下 ...
- java基础24 线程、多线程及线程的生命周期(Thread)
1.1.进程 正在执行的程序称作为一个进程.进程负责了内存空间的划分 疑问1:windows电脑称之为多任务的操作系统,那么Windows是同时运行多个应用程序呢? 从宏观的角度:windows确实在 ...
随机推荐
- [dotnet core]使用Peach简化Socket网络通讯协议开发
Peach是基于DotNetty的Socket网络通讯帮助类库,可以帮助开发者简化使用DotNetty,关于DotNetty可参考我之前的这篇文章. Peach内置实现了一个基于文本协议的Comman ...
- mongoose之操作mongoDB数据库
mongoose是node.js操作mongoDB数据库的一种工具,借助于mongoose,我们可以便捷的完成一些数据库的基本操作,基本使用如下: 1.安装 npm install mongoose ...
- ASP.NET Core的Data Protect(数据保护)的学习和应用
转载请注入出处: https://home.cnblogs.com/u/zhiyong-ITNote/ dotnet core中提供了一个新的身份验证框架Identity,它不同于dot net下的身 ...
- C# 正规则表达式
获取括号里的内容 public string GetRegexStr(string Str, string Symbol1, string Symbol2, bool needSymbol) { ]; ...
- webpack 入门踩坑
参考来源:知乎张轩 安装 先装好node和npm,因为webpack是一个基于node的项目.然后 npm install -g webpack 全局安装 还可以在当前项目里面也安装一个webpack ...
- LOJ.2718.[NOI2018]归程(Kruskal重构树 倍增)
LOJ2718 BZOJ5415 洛谷P4768 Rank3+Rank1无压力 BZOJ最初还不是一道权限题... Update 2019.1.5 UOJ上被hack了....好像是纯一条链的数据过不 ...
- set_include_path和get_include_path用法详解
首先set_include_path这个函数呢,是在脚本里动态地对PHP.ini中include_path进行修改的.而这个include_path呢,它可以针对下面的include和require的 ...
- Spring配置JDBCTemplate
案例:单测查询全部学生 项目结构: 1.导入部署jar包:spring-jdbc <!--spring-jdbc--> <dependency> <groupId> ...
- ACM/IOI 历年国家集训队论文集和论文算法分类整理
国家集训队1999论文集 陈宏:<数据结构的选择与算法效率--从IOI98试题PICTURE谈起> 来煜坤:<把握本质,灵活运用--动态规划的深入探讨> 齐鑫:<搜索方法 ...
- java第二周的学习知识
1.java基本运行单位是类,类的组成成员为成员变量和方法.成员变量的种类有public,default(就是不写),protected,private.public:public可以修饰类,数据成员 ...
