PyQt5教程——布局管理(4)
PyQt5中的布局管理
布局管理是GUI编程中的一个重要方面。布局管理是一种如何在应用窗口上防止组件的一种方法。我们可以通过两种基础方式来管理布局。我们可以使用绝对定位和布局类。
绝对定位
程序指定了组件的位置并且每个组件的大小用像素作为单位来丈量。当你使用了绝对定位,我们需要知道下面的几点限制:
- 如果我们改变了窗口大小,组件的位置和大小并不会发生改变。
- 在不同平台上,应用的外观可能不同
- 改变我们应用中的字体的话可能会把应用弄得一团糟。
- 如果我们决定改变我们的布局,我们必须完全重写我们的布局,这样非常乏味和浪费时间。
下面的例子中,使用了绝对坐标来定位组件
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """
ZetCode PyQt5 tutorial This example shows three labels on a window
using absolute positioning. author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: January 2015
""" import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QWidget, QLabel, QApplication class Example(QWidget): def __init__(self):
super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): lbl1 = QLabel('Zetcode', self)
lbl1.move(15, 10) lbl2 = QLabel('tutorials', self)
lbl2.move(35, 40) lbl3 = QLabel('for programmers', self)
lbl3.move(55, 70) self.setGeometry(300, 300, 250, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Absolute')
self.show() if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
我们使用move()方法来定位我们的组件。在上面的例子中我们使用move()方法定位了一些标签组件。在使用move()方法时,我们给move()方法提供了x和y坐标作为参数。move()使用的坐标系统是从左上角开始计算的。x值从左到右增长。y值从上到下增长。
lbl1 = QLabel('Zetcode', self)
lbl1.move(15, 10)
将标签组件定位在x=15,y=10的坐标位置。
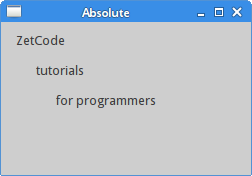 Figure: Absolute positioning
Figure: Absolute positioning
箱布局
布局管理器的布局管理类非常灵活,实用。它是将组件定位在窗口上的首选方式。QHBoxLayout和QVBoxLayout是两个基础布局管理类,他们水平或垂直的线性排列组件。想象一下我们需要在右下角排列两个按钮。为了使用箱布局,我们将使用一个水平箱布局和垂直箱布局来实现。同样为了使用一些必要的空白,我们将添加一些拉伸因子。
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """
ZetCode PyQt5 tutorial In this example, we position two push
buttons in the bottom-right corner
of the window. author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: January 2015
""" import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QPushButton,
QHBoxLayout, QVBoxLayout, QApplication) class Example(QWidget): def __init__(self):
super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): okButton = QPushButton("OK")
cancelButton = QPushButton("Cancel") hbox = QHBoxLayout()
hbox.addStretch(1)
hbox.addWidget(okButton)
hbox.addWidget(cancelButton) vbox = QVBoxLayout()
vbox.addStretch(1)
vbox.addLayout(hbox) self.setLayout(vbox) self.setGeometry(300, 300, 300, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Buttons')
self.show() if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
例子在右下角放置了两个按钮。当我们改变应用窗口大小时,它们会相对于应用窗口不改变位置。在这个例子中我们使用了QHBoxLayout和QVBoxLayout两个布局类。
okButton = QPushButton("OK")
cancelButton = QPushButton("Cancel")
在这里我们创建了两个按钮。
hbox = QHBoxLayout()
hbox.addStretch(1)
hbox.addWidget(okButton)
hbox.addWidget(cancelButton)
这里我们创建了一个水平箱布局,并且增加了一个拉伸因子和两个按钮。拉伸因子在两个按钮之前增加了一个可伸缩空间。这会将按钮推到窗口的右边。
vbox = QVBoxLayout()
vbox.addStretch(1)
vbox.addLayout(hbox)
为了创建必要的布局,我们把水平布局放置在垂直布局内。拉伸因子将把包含两个按钮的水平箱布局推到窗口的底边。
self.setLayout(vbox)
最后,我们设置一下窗口的主布局。
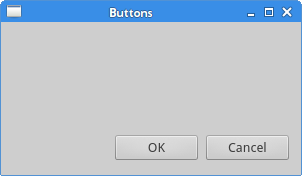 Figure: Buttons
Figure: Buttons
网格布局
最常用的布局类是网格布局。这个布局使用行了列分割空间。要创建一个网格布局,我们需要使用QGridLayout类。
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """
ZetCode PyQt5 tutorial In this example, we create a skeleton
of a calculator using a QGridLayout. author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: January 2015
""" import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QGridLayout,
QPushButton, QApplication) class Example(QWidget): def __init__(self):
super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): grid = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(grid) names = ['Cls', 'Bck', '', 'Close',
'7', '8', '9', '/',
'4', '5', '6', '*',
'1', '2', '3', '-',
'0', '.', '=', '+'] positions = [(i,j) for i in range(5) for j in range(4)] for position, name in zip(positions, names): if name == '':
continue
button = QPushButton(name)
grid.addWidget(button, *position) self.move(300, 150)
self.setWindowTitle('Calculator')
self.show() if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
在我们的例子中,我们创建了一个全是按钮的网格布局。
grid = QGridLayout()
self.setLayout(grid)
实例化QGridLayout类,并且把这个类设为应用窗口的布局。
names = ['Cls', 'Bck', '', 'Close',
'7', '8', '9', '/',
'4', '5', '6', '*',
'1', '2', '3', '-',
'0', '.', '=', '+']
这些标签会在之后的按钮中使用。
positions = [(i,j) for i in range(5) for j in range(4)]
我们创建了一个网格的定位列表。
for position, name in zip(positions, names):
if name == '':
continue
button = QPushButton(name)
grid.addWidget(button, *position)
创建出按钮组件,并使用addWidget()方法向布局中添加按钮。
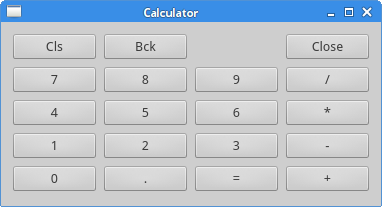 Figure: Calculator skeleton
Figure: Calculator skeleton
文本审阅窗口示例
在网格中,组件可以跨多列或多行。在这个例子中,我们对它进行一下说明。
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """
ZetCode PyQt5 tutorial In this example, we create a bit
more complicated window layout using
the QGridLayout manager. author: Jan Bodnar
website: zetcode.com
last edited: January 2015
""" import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import (QWidget, QLabel, QLineEdit,
QTextEdit, QGridLayout, QApplication) class Example(QWidget): def __init__(self):
super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): title = QLabel('Title')
author = QLabel('Author')
review = QLabel('Review') titleEdit = QLineEdit()
authorEdit = QLineEdit()
reviewEdit = QTextEdit() grid = QGridLayout()
grid.setSpacing(10) grid.addWidget(title, 1, 0)
grid.addWidget(titleEdit, 1, 1) grid.addWidget(author, 2, 0)
grid.addWidget(authorEdit, 2, 1) grid.addWidget(review, 3, 0)
grid.addWidget(reviewEdit, 3, 1, 5, 1) self.setLayout(grid) self.setGeometry(300, 300, 350, 300)
self.setWindowTitle('Review')
self.show() if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Example()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
我们创建了包含三个标签,两个单行编辑框和一个文本编辑框组件的窗口。布局使用了QGridLayout布局。
grid = QGridLayout()
grid.setSpacing(10)
我们创建了一个网格布局并且设置了组件之间的间距。
grid.addWidget(reviewEdit, 3, 1, 5, 1)
如果我们向网格布局中增加一个组件,我们可以提供组件的跨行和跨列参数。在这个例子中,我们让reviewEdit组件跨了5行。
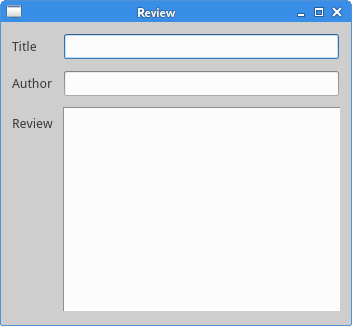 Figure: Review example
Figure: Review example
这部分的PyQt5教程专门用于讲述布局管理。
PyQt5教程——布局管理(4)的更多相关文章
- PyQt5之布局管理
目录 一 写在开头 1.1 本文内容 二 绝对布局 三 布局类 3.1 水平布局(QHBoxLayout)和垂直布局(QVBoxLayout) 3.2 水平布局和垂直布局实例 3.3 网格布局(QGr ...
- [Tkinter 教程] 布局管理 (Pack Place Grid)
原系列地址: Python Tkinter 简介: 本文讲述如何使用 tkinter 的布局管理 (被称作 layout managers 或 geometry managers). tkinter ...
- PyQT5基础布局管理
绝对定位布局 使用move(x, y)可以对窗口进行布局,以窗口左上角为原点,向右为 x 轴正方向,向下为 y 轴正方向,移动(x,y); import sys from PyQt5.QtGui im ...
- PyQT5速成教程-3 布局管理
本文由 沈庆阳 所有,转载请与作者取得联系! 布局(Layout)管理 Qt Designer中,在工具箱中最上方可以看到有4种布局.分别是垂直布局.水平布局.栅格布局和表单布局. 四种布局 布局 ...
- PyQt5——布局管理
PyQt5布局管理使用方法详见:https://blog.csdn.net/jia666666/article/list/3?t=1& PyQt5布局管理汇总: 1.QHBoxLayout 2 ...
- 四、PyQt5布局管理(绝对&相对、水平、垂直、格栅、表单)
目录 一.绝对布局 二.盒布局 三.格栅布局 四.格栅布局跨行跨列显示 布局管理即设置窗体上各个控件的位置,对于新手来说,这是学习的难点. 布局管理根据绝对坐标是否变动分为绝对布局和相对布局两大类.采 ...
- PyQt5(2)——调整布局(布局管理器)第一个程序
我们拖拽一个UI文件,转为PY文件后生成一个类Ui_MainWindow 此时,我们新建一个文件,用来控制业务逻辑(继承界面中的类),跟界面分开,这样我们就完成了界面和逻辑相分离(这段代码使用率基本1 ...
- PyQt5笔记之布局管理
代码:界面与逻辑分离 这是使用Designer做出的GUI,然后通过转换得到的Py代码.(界面文件) # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Form implementation gen ...
- PyQt5布局管理器
布局分类 绝对定位:使用move方法将空间直接定死在某个坐标,不会随着窗口大小的改变而改变 可变布局:使用各种布局管理器,实现组件的位置和大小随着窗口的变化而变化 布局管理器 QHBoxLayout: ...
随机推荐
- 移动端适配之雪碧图(sprite)背景图片定位
为了减少网络请求个数量,提高网站的访问速度,我们一般都会把一些小的图片合并成一张sprite图,然后根据background-position来进行定位.在web端由于是固定的大小与left .top ...
- 你的C/C++程序为什么无法运行?揭秘Segmentation fault (1)
什么让你对C/C++如此恐惧? 晦涩的语法?还是优秀IDE的欠缺? 我想那都不是问题,最多的可能是一个类似这样的错误: 段错误(Segmentation fault) 这是新手无法避免的错误,也是老手 ...
- CentOS 7 下编译安装lnmp之nginx篇详解
一.安装环境 宿主机=> win7,虚拟机 centos => 系统版本:CentOS Linux release 7.5.1804 (Core),ip地址 192.168.1.168 ...
- 重温PHP面向对象的三大特性
PHP面向对象的三大特性:封装性.继承性.多态性. 1. 封装性: 也称为信息隐藏,就是将一个类的使用和实现分开,只保留部分接口和方法与外部联系,或者说只公开了一些供开发人员使用的方法. 于是开发人员 ...
- SPOJ 1811. Longest Common Substring (LCS,两个字符串的最长公共子串, 后缀自动机SAM)
1811. Longest Common Substring Problem code: LCS A string is finite sequence of characters over a no ...
- Tasker to detect and vibrate once the ougoing call is being answered
I happen to find that for GSM standard phone, call duration would be created into sql database only ...
- MVC自定义路由02-实现IRouteConstraint限制控制器名
通过实现IRouteConstraint接口,实现对某个控制名进行限制.本篇把重点放在自定义约束,其余部分参考: MVC自定义路由01-为什么需要自定义路由 自定义约束前 using Syste ...
- jQuery插件——可以动态改动颜色的jQueryColor
1.请选择代码框中所有代码后, 保存为 jquery.color.js /*! * jQuery Color Animations v@VERSION * https://github.com/jqu ...
- Nginx和Tomcat负载均衡实现session共享
以前的项目使用Nginx作为反向代理实现了多个Tomcat的负载均衡,为了实现多个Tomcat之间的session共享,使用了开源的Memcached-Session-Manager框架. 此框架的优 ...
- java执行ping命令
public static void get() throws IOException{ String address="10.132.118.110"; Process proc ...
