Codeforces Round #419 (Div. 2) A B C 暴力 区间更新技巧 +前缀和 模拟
2 seconds
512 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Karen is getting ready for a new school day!

It is currently hh:mm, given in a 24-hour format. As you know, Karen loves palindromes, and she believes that it is good luck to wake up when the time is a palindrome.
What is the minimum number of minutes she should sleep, such that, when she wakes up, the time is a palindrome?
Remember that a palindrome is a string that reads the same forwards and backwards. For instance, 05:39 is not a palindrome, because 05:39 backwards is 93:50. On the other hand, 05:50 is a palindrome, because 05:50 backwards is 05:50.
The first and only line of input contains a single string in the format hh:mm (00 ≤ hh ≤ 23, 00 ≤ mm ≤ 59).
Output a single integer on a line by itself, the minimum number of minutes she should sleep, such that, when she wakes up, the time is a palindrome.
05:39
11
13:31
0
23:59
1
In the first test case, the minimum number of minutes Karen should sleep for is 11. She can wake up at 05:50, when the time is a palindrome.
In the second test case, Karen can wake up immediately, as the current time, 13:31, is already a palindrome.
In the third test case, the minimum number of minutes Karen should sleep for is 1 minute. She can wake up at 00:00, when the time is a palindrome.
题意:给你一个24时制的时间 判断多少分钟后 是一个回文时间
题解:暴力
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int n;
char a[];
int hh,mm;
int main()
{
scanf("%s",a);
hh=(a[]-'')*+(a[]-'');
mm=(a[]-'')*+(a[]-'');
for(int i=;i<=(*);i++)
{
int nowmm;
int nowhh=hh;
nowmm=mm+i;
nowhh=nowhh+nowmm/;
nowhh%=;
nowmm%=;
nowhh=nowhh/+(nowhh%)*;
if(nowhh==nowmm)
{
printf("%d\n",i);
return ;
}
}
return ;
}
2.5 seconds
512 megabytes
standard input
standard output
To stay woke and attentive during classes, Karen needs some coffee!

Karen, a coffee aficionado, wants to know the optimal temperature for brewing the perfect cup of coffee. Indeed, she has spent some time reading several recipe books, including the universally acclaimed "The Art of the Covfefe".
She knows n coffee recipes. The i-th recipe suggests that coffee should be brewed between li and ri degrees, inclusive, to achieve the optimal taste.
Karen thinks that a temperature is admissible if at least k recipes recommend it.
Karen has a rather fickle mind, and so she asks q questions. In each question, given that she only wants to prepare coffee with a temperature between a and b, inclusive, can you tell her how many admissible integer temperatures fall within the range?
The first line of input contains three integers, n, k (1 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 200000), and q (1 ≤ q ≤ 200000), the number of recipes, the minimum number of recipes a certain temperature must be recommended by to be admissible, and the number of questions Karen has, respectively.
The next n lines describe the recipes. Specifically, the i-th line among these contains two integers li and ri (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ 200000), describing that the i-th recipe suggests that the coffee be brewed between li and ri degrees, inclusive.
The next q lines describe the questions. Each of these lines contains a and b, (1 ≤ a ≤ b ≤ 200000), describing that she wants to know the number of admissible integer temperatures between a and b degrees, inclusive.
For each question, output a single integer on a line by itself, the number of admissible integer temperatures between a and b degrees, inclusive.
3 2 4
91 94
92 97
97 99
92 94
93 97
95 96
90 100
3
3
0
4
2 1 1
1 1
200000 200000
90 100
0
In the first test case, Karen knows 3 recipes.
- The first one recommends brewing the coffee between 91 and 94 degrees, inclusive.
- The second one recommends brewing the coffee between 92 and 97 degrees, inclusive.
- The third one recommends brewing the coffee between 97 and 99 degrees, inclusive.
A temperature is admissible if at least 2 recipes recommend it.
She asks 4 questions.
In her first question, she wants to know the number of admissible integer temperatures between 92 and 94 degrees, inclusive. There are 3: 92, 93 and 94 degrees are all admissible.
In her second question, she wants to know the number of admissible integer temperatures between 93 and 97 degrees, inclusive. There are 3: 93, 94 and 97 degrees are all admissible.
In her third question, she wants to know the number of admissible integer temperatures between 95 and 96 degrees, inclusive. There are none.
In her final question, she wants to know the number of admissible integer temperatures between 90 and 100 degrees, inclusive. There are 4: 92, 93, 94 and 97 degrees are all admissible.
In the second test case, Karen knows 2 recipes.
- The first one, "wikiHow to make Cold Brew Coffee", recommends brewing the coffee at exactly 1 degree.
- The second one, "What good is coffee that isn't brewed at at least 36.3306 times the temperature of the surface of the sun?", recommends brewing the coffee at exactly 200000 degrees.
A temperature is admissible if at least 1 recipe recommends it.
In her first and only question, she wants to know the number of admissible integer temperatures that are actually reasonable. There are none.
题意:给你 n个区间 q个查询[l,r] 问l~r有多少个值 属于 大于等于k个区间
题解:区间更新姿势+前缀和
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int n,k,q;
map<int,int>l;
int r[];
int ans[];
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&k,&q);
int s,t;
l.clear();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&s,&t);
l[s]++;
l[t+]--;
}
int now=;
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
{
now+=l[i];
r[i]=now;
}
int jishu=;
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
{
if(r[i]>=k)
jishu++;
ans[i]=jishu;
}
for(int i=;i<=q;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&s,&t);
printf("%d\n",ans[t]-ans[s-]);
}
return ;
}
2 seconds
512 megabytes
standard input
standard output
On the way to school, Karen became fixated on the puzzle game on her phone!

The game is played as follows. In each level, you have a grid with n rows and m columns. Each cell originally contains the number 0.
One move consists of choosing one row or column, and adding 1 to all of the cells in that row or column.
To win the level, after all the moves, the number in the cell at the i-th row and j-th column should be equal to gi, j.
Karen is stuck on one level, and wants to know a way to beat this level using the minimum number of moves. Please, help her with this task!
The first line of input contains two integers, n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100), the number of rows and the number of columns in the grid, respectively.
The next n lines each contain m integers. In particular, the j-th integer in the i-th of these rows contains gi, j (0 ≤ gi, j ≤ 500).
If there is an error and it is actually not possible to beat the level, output a single integer -1.
Otherwise, on the first line, output a single integer k, the minimum number of moves necessary to beat the level.
The next k lines should each contain one of the following, describing the moves in the order they must be done:
- row x, (1 ≤ x ≤ n) describing a move of the form "choose the x-th row".
- col x, (1 ≤ x ≤ m) describing a move of the form "choose the x-th column".
If there are multiple optimal solutions, output any one of them.
3 5
2 2 2 3 2
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 1 2 1
4
row 1
row 1
col 4
row 3
3 3
0 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 0
-1
3 3
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
3
row 1
row 2
row 3
In the first test case, Karen has a grid with 3 rows and 5 columns. She can perform the following 4 moves to beat the level:
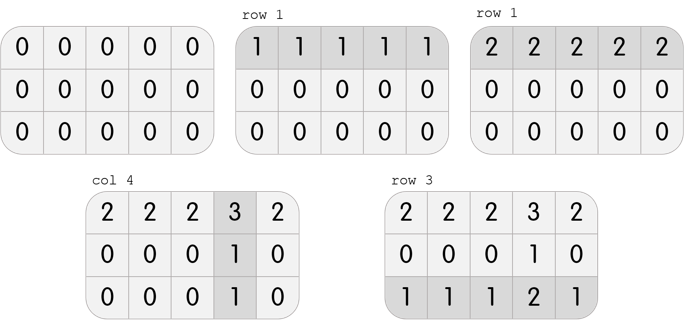
In the second test case, Karen has a grid with 3 rows and 3 columns. It is clear that it is impossible to beat the level; performing any move will create three 1s on the grid, but it is required to only have one 1 in the center.
In the third test case, Karen has a grid with 3 rows and 3 columns. She can perform the following 3 moves to beat the level:
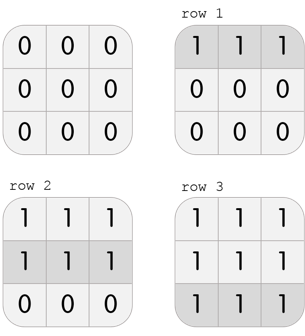
Note that this is not the only solution; another solution, among others, is col 1, col 2, col 3.
题意:给你一个n*m的矩阵 现在希望用最少的操作 每次操作能使得某一行或者某一列全部减少1 输出最小的操作数 以及操作的过程 无法实现则输出-1
题解:先处理行再处理列 先处理列再处理行 暴力跑两遍 取最优;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
int a[][];
int b[][];
int ans[];
int re[];
int ans1[];
int re1[];
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=; j<=m; j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
b[i][j]=a[i][j];
}
}
int jishu=;
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
int minx=;
for(int j=; j<=m; j++)
minx=min(minx,a[i][j]);
for(int j=; j<=minx; j++)
{
ans[jishu]=;
re[jishu]=i;
jishu++;
}
for(int j=; j<=m; j++)
{
a[i][j]-=minx;
}
}
for(int i=; i<=m; i++)
{
int minx=;
for(int j=; j<=n; j++)
{
minx=min(minx,a[j][i]);
}
for(int j=; j<=minx; j++)
{
ans[jishu]=;
re[jishu]=i;
jishu++;
}
for(int j=; j<=n; j++)
{
a[j][i]-=minx;
}
}
int flag1=;
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=; j<=m; j++)
{
if(a[i][j]!=)
{
flag1=;
break;
}
}
} for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=; j<=m; j++)
{
a[i][j]=b[i][j];
}
}
int jish=;
for(int i=; i<=m; i++)
{
int minx=;
for(int j=; j<=n; j++)
{
minx=min(minx,a[j][i]);
}
for(int j=; j<=minx; j++)
{
ans1[jish]=;
re1[jish]=i;
jish++;
}
for(int j=; j<=n; j++)
{
a[j][i]-=minx;
}
}
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
int minx=;
for(int j=; j<=m; j++)
{
minx=min(minx,a[i][j]);
}
for(int j=; j<=minx; j++)
{
ans1[jish]=;
re1[jish]=i;
jish++;
}
for(int j=; j<=m; j++)
{
a[i][j]-=minx;
}
}
int flag2=;
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=; j<=m; j++)
{
if(a[i][j]!=)
{
flag2=;
break;
}
}
}
if(flag1==&&flag2==)
{
printf("-1\n");
return ;
}
if(flag1==&&flag2==)
{
if(jishu<jish)
{
printf("%d\n",jishu-);
for(int i=; i<jishu; i++)
{
if(ans[i]==)
printf("row ");
else
printf("col ");
printf("%d\n",re[i]);
}
}
else
{
printf("%d\n",jish-);
for(int i=; i<jish; i++)
{
if(ans1[i]==)
printf("row ");
else
printf("col ");
printf("%d\n",re1[i]);
}
}
return ;
}
if(flag1==)
{
printf("%d\n",jishu-);
for(int i=; i<jishu; i++)
{
if(ans[i]==)
printf("row ");
else
printf("col ");
printf("%d\n",re[i]);
}
return ;
}
if(flag2==)
{
printf("%d\n",jish-);
for(int i=; i<jish; i++)
{
if(ans1[i]==)
printf("row ");
else
printf("col ");
printf("%d\n",re1[i]);
}
}
return ;
}
/*
3 2
1 1
2 2
2 2
2 3
2 1 2
2 1 2
*/
Codeforces Round #419 (Div. 2) A B C 暴力 区间更新技巧 +前缀和 模拟的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #169 (Div. 2) A水 B C区间更新 D 思路
A. Lunch Rush time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- Codeforces Round #538 (Div. 2) F 欧拉函数 + 区间修改线段树
https://codeforces.com/contest/1114/problem/F 欧拉函数 + 区间更新线段树 题意 对一个序列(n<=4e5,a[i]<=300)两种操作: 1 ...
- Codeforces Round #419 (Div. 2) E. Karen and Supermarket(树形dp)
http://codeforces.com/contest/816/problem/E 题意: 去超市买东西,共有m块钱,每件商品有优惠卷可用,前提是xi商品的优惠券被用.问最多能买多少件商品? 思路 ...
- Codeforces Round #419 (Div. 2) B. Karen and Coffee(经典前缀和)
http://codeforces.com/contest/816/problem/B To stay woke and attentive during classes, Karen needs s ...
- Codeforces Round #419 (Div. 2) A. Karen and Morning(模拟)
http://codeforces.com/contest/816/problem/A 题意: 给出一个时间,问最少过多少时间后是回文串. 思路: 模拟,先把小时的逆串计算出来: ① 如果逆串=分钟, ...
- Codeforces Round #419 (Div. 2)
1.题目A:Karen and Morning 题意: 给出hh:mm格式的时间,问至少经过多少分钟后,该时刻为回文字符串? 思路: 简单模拟,从当前时刻开始,如果hh的回文rh等于mm则停止累计.否 ...
- Codeforces Round #419 Div. 1
A:暴力枚举第一列加多少次,显然这样能确定一种方案. #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #in ...
- Codeforces Round #419 (Div. 2) ABC
python 2.7,用来熟悉Python 由于都是智障题,所以我也不讲述题意和题解,直接贴代码了-- A import sys h,m = map(int,raw_input().split(&qu ...
- Codeforces Round #419 (Div. 2) C. Karen and Game
C. Karen and Game time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 512 megabytes input standard i ...
随机推荐
- 大O算法
大O计法:根据执行次数计算#sum = (1+n)*n/2://执行了一次,即为O(1)#for(i=0;i<n;i++);//执行了n次,即为O(n)#算法的时间复杂度:T(n) = O(f( ...
- Python异常(基础) except
为什么要异常处理机制:在程序调用层数较深时,向主调函数传递错误信息需要层层return 返回比较麻烦,用异常处理机制可以较简单的传送错误信息 什么是错误 错误是指由于逻辑或语法等导致一个程序已无法正常 ...
- 转:为什么说招到合适的人比融到钱更加重要 - Hiring Great Talent is More Important Than Fund Raising
我在猎头行业工作了 20 多年,一直在帮助创业公司招聘优秀的人才.我服务过的客户既有 VC 投资的初创企业,也有即将 IPO 的公司.我和 200 多个 VC 合作过,也见过 300 多个客户失败的案 ...
- 亚马逊CEO贝索斯致股东信:阐述公司未来计划
亚马逊CEO 杰夫·贝索斯(Jeff Bezos)今天发布年度股东信, 详细描述了亚马逊的产品.服务和未来计划,当然,信中并没有任何的硬数据,比如说亚马逊Kindle的销量等等.但这封信也包括一些颇令 ...
- [笔记] mysql5.6一些编译参数
cmake \ -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local/mysql \ -DSYSCONFDIR=/etc \ -DWITH_INNOBASE_STORAGE_ENGINE ...
- underscore.js源码解析(三)
最近工作比较忙,做不到每周两篇了,周末赶着写吧,上篇我针对一些方法进行了分析,今天继续. 没看过前两篇的可以猛戳这里: underscore.js源码解析(一) underscore.js源码解析(二 ...
- 经验之谈:10位顶级PHP大师的开发原则
导读:在Web开发世界里,PHP是最流行的语言之一,从PHP里,你能够很容易的找到你所需的脚本,遗憾的是,很少人会去用“最佳做法”去写一个PHP程序.这里,我们向大家介绍PHP的10种最佳实践,当然, ...
- 进击的SDN
SDN是什么? 不再是OSI七层模型,全新的SDN三层模型. 起源于斯坦福大学博士生领导的一个项目Ethane:通过一个集中式控制器(NOX),网络管理员可以定义基于网络流的控制策略,并将这个策略用于 ...
- TCP系列49—拥塞控制—12、DSACK下的拥塞撤销
一.概述 DSACK下的虚假重传的检测我们之前重传部分的文章已经介绍过了,这里简单说一下拥塞控制部分的实现. linux内部会维护一个undo_retrans状态变量,其值为已经重传的次数减掉被DSA ...
- 倒计时60s 代码
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
