线段树(Segment Tree)(转)
原文链接:线段树(Segment Tree)
1、概述
线段树,也叫区间树,是一个完全二叉树,它在各个节点保存一条线段(即“子数组”),因而常用于解决数列维护问题,基本能保证每个操作的复杂度为O(lgN)。
线段树是一种二叉搜索树,与区间树相似,它将一个区间划分成一些单元区间,每个单元区间对应线段树中的一个叶结点。
对于线段树中的每一个非叶子节点[a,b],它的左儿子表示的区间为[a,(a+b)/2],右儿子表示的区间为[(a+b)/2+1,b]。因此线段树是平衡二叉树,最后的子节点数目为N,即整个线段区间的长度。
使用线段树可以快速的查找某一个节点在若干条线段中出现的次数,时间复杂度为O(logN)。而未优化的空间复杂度为2N,因此有时需要离散化让空间压缩。
本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/archimedes/p/segment-tree.html,转载请注明源地址。
2、线段树基本操作
线段树的基本操作主要包括构造线段树,区间查询和区间修改。
(1)线段树构造
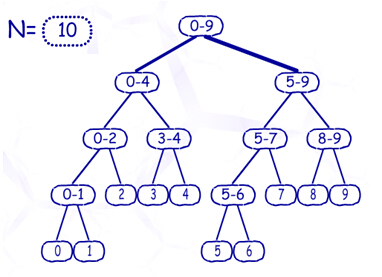
首先介绍构造线段树的方法:让根节点表示区间[0,N-1],即所有N个数所组成的一个区间,然后,把区间分成两半,分别由左右子树表示。不难证明,这样的线段树的节点数只有2N-1个,是O(N)级别的,如图:
节点定义如下:
typedef struct node {
int l; //线段的左端点
int r; //线段的左端点
int value; //线段上的值
}node;
线段树的构建
bulid//以节点v为根建树、v对应区间为[l,r]
{
对节点v初始化
if (l!=r) {
以v的左孩子为根建树,区间为[l,(l+r)/2]
以v的右孩子为根建树,区间为[(l+r)/2+1,r]
}
}
完整的建树代码如下:
#define N 10000
node tree[N];
void bulid(int l, int r, int v) //对结点v进行建立,区间为l~r
{
tree[v].l = l;
tree[v].r = r;
if(l == r) {
//进行结点的初始化
tree[v].value = a[r];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
bulid(v * 2, l, mid);
bulid(v * 2 + 1, mid + 1, r);
//根据左右儿子更新当前结点
tree[v].value = tree[v * 2].value + tree[v * 2 + 1].value;
}
更新
当在a[i]~a[j]上的所有的元素都加上一个值c的时候
如果a[i]~a[j]刚还是一个完整段的时候,直接将这个段的value值加上c*(r-l+1)
当更新的区间不是一个完整段的时候,采用一种记录增量的方法:给每个节点增加一个域:int add,记录更新操作的增量c,初始的时候add均为0,比如当对2~5区间更新后,给该结点的add加上一个值c,再下次要对2~3结点进行更新或查询时,再将add传递到下面的孩子结点中去
完整的更新树代码如下:
typedef struct node {
int l; //线段的左端点
int r; //线段的左端点
int value; //线段上的值
int add;
}node;
void update(int v, int r, int l, int m)//更新区间l~r加上数m
{
if(tree[v].l == l && tree[v].r == r) { //找到,更新并记录增量
tree[v].value += m * (r - l + 1);
tree[v].add = m;
return;
}
if(tree[v].add) {
tree[2 * v].add += tree[v].add;
tree[2 * v + 1].add += tree[v].add;
tree[v].add = 0;
}
int mid = (tree[v].l + tree[v].r) / 2;
if(r <= mid) {
update(v * 2, l, r, m); //只对左儿子更新
} else {
if(l > mid) {
update(v * 2 + 1, l, r, m); //只对右儿子更新
} else { //区间横跨左右儿子区间,对其两者均进行更新
update(v * 2, l, mid, m);
update(v * 2 + 1, mid + 1, r, m);
}
}
}
查询
查询区间l~r上的value值
void query(int v, int l, int r) //当前查询结点为v,要查询的区间为l~r
{
if(tree[v].l == l && tree[v].r == r) {
ans += tree[v].value;
return;
}
if(tree[v].add) {
tree[v * 2].add += tree[v].add;
tree[v * 2 + 1].add += tree[v].add;
tree[v].add = 0;
}
int mid = (tree[v].l + tree[v].r) / 2;
if(r <= mid) {
query(v * 2, l, r); //要查询的区间都在左儿子
} else {
if(l > mid) {
query(v * 2 + 1, l, r); //要查询的区间都在左儿子
} else { //要查询的区间横跨左右孩子
query(v * 2, l, mid);
query(v * 2 + 1, mid + 1, r);
}
}
}
编程实践
Description N (2 <= N <= 8,000) cows have unique brands in the range 1..N. In a spectacular display of poor judgment, they visited the neighborhood 'watering hole' and drank a few too many beers before dinner. When it was time to line up for their evening meal, they did not line up in the required ascending numerical order of their brands. Regrettably, FJ does not have a way to sort them. Furthermore, he's not very good at observing problems. Instead of writing down each cow's brand, he determined a rather silly statistic: For each cow in line, he knows the number of cows that precede that cow in line that do, in fact, have smaller brands than that cow. Given this data, tell FJ the exact ordering of the cows.
Input * Line 1: A single integer, N * Lines 2..N: These N-1 lines describe the number of cows that precede a given cow in line and have brands smaller than that cow. Of course, no cows precede the first cow in line, so she is not listed. Line 2 of the input describes the number of preceding cows whose brands are smaller than the cow in slot #2; line 3 describes the number of preceding cows whose brands are smaller than the cow in slot #3; and so on.
Output * Lines 1..N: Each of the N lines of output tells the brand of a cow in line. Line #1 of the output tells the brand of the first cow in line; line 2 tells the brand of the second cow; and so on.
Sample Input 5
1
2
1
0
Sample Output 2
4
5
3
1
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define N 10000
int small[N], ans[N];
struct segment {
int lc, rc, len;
};
struct segment s[ * N];
void bulid(int root, int lc, int rc) /*建树*/
{
s[root].lc = lc;
s[root].rc = rc;
s[root].len = rc - lc + ;
if(rc == lc) return;
bulid( * root, lc, (lc + rc) / );
bulid( * root + , (lc + rc) / + , rc);
}
int query(int root, int k)
{
s[root].len--;
if(s[root].lc == s[root].rc) return s[root].lc;
else if(k <= s[ * root].len) {
return query( * root, k);
} else {
return query( * root + , k - s[ * root].len);
}
} int main()
{
int n, i;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i = ; i <=n; i++)
scanf("%d", &small[i]);
small[] = ;
bulid(, , n);
for(i = n; i >= ; i--)
ans[i] = query(, small[i] + );
for(i = ; i <= n; i++)
printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
return ;
}
leetcode编程题307 Range Sum Query - Mutable
Given an integer array nums, find the sum of the elements between indices i and j (i ≤ j), inclusive. The update(i, val) function modifies nums by updating the element at index i to val. Example: Given nums = [1, 3, 5] sumRange(0, 2) -> 9
update(1, 2)
sumRange(0, 2) -> 8
Note: The array is only modifiable by the update function.
You may assume the number of calls to update and sumRange function is distributed evenly.
public class NumArray {
private class SegmentTreeNode{
int start;
int end;
int sum;
SegmentTreeNode left;
SegmentTreeNode right;
public SegmentTreeNode(int start, int end){
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.sum = 0;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
private SegmentTreeNode buildTree(int[] nums, int s, int e){
if(s>e)
return null;
SegmentTreeNode stn = new SegmentTreeNode(s,e);
if(s==e){
stn.sum = nums[s];
}else{
int mid = s+(e-s)/2;
stn.left = buildTree(nums, s, mid);
stn.right = buildTree(nums, mid+1, e);
stn.sum = stn.left.sum+stn.right.sum;
}
return stn;
}
private void update(SegmentTreeNode root, int i, int val){
if(root.start==root.end){
root.sum = val;
}else{
int mid = root.start + (root.end-root.start)/2;
if(i<=mid)
update(root.left, i, val);
else if(i>mid)
update(root.right, i, val);
root.sum = root.left.sum + root.right.sum;
}
}
private int sumRange(SegmentTreeNode root, int s, int e){
if(root.start==s&&root.end==e){
return root.sum;
}else{
int mid = root.start + (root.end-root.start)/2;
if(e<=mid)
return sumRange(root.left, s, e);
else if(s>mid)
return sumRange(root.right, s, e);
else
return sumRange(root.left, s, mid)+sumRange(root.right, mid+1, e);
}
}
SegmentTreeNode root;
public NumArray(int[] nums) {
root = buildTree(nums, 0, nums.length-1);
}
void update(int i, int val) {
update(root, i, val);
}
public int sumRange(int i, int j) {
return sumRange(root, i, j);
}
}
// Your NumArray object will be instantiated and called as such:
// NumArray numArray = new NumArray(nums);
// numArray.sumRange(0, 1);
// numArray.update(1, 10);
// numArray.sumRange(1, 2);
参考链接:
线段树(segment tree)
线段树(Segment Tree)(转)的更多相关文章
- 『线段树 Segment Tree』
更新了基础部分 更新了\(lazytag\)标记的讲解 线段树 Segment Tree 今天来讲一下经典的线段树. 线段树是一种二叉搜索树,与区间树相似,它将一个区间划分成一些单元区间,每个单元区间 ...
- BZOJ.4695.最假女选手(线段树 Segment tree Beats!)
题目链接 区间取\(\max,\ \min\)并维护区间和是普通线段树无法处理的. 对于操作二,维护区间最小值\(mn\).最小值个数\(t\).严格次小值\(se\). 当\(mn\geq x\)时 ...
- 【数据结构系列】线段树(Segment Tree)
一.线段树的定义 线段树,又名区间树,是一种二叉搜索树. 那么问题来了,啥是二叉搜索树呢? 对于一棵二叉树,若满足: ①它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值 ②若它的右子树不空, ...
- 线段树(segment tree)
线段树在一些acm题目中经常见到,这种数据结构主要应用在计算几何和地理信息系统中.下图就为一个线段树: (PS:可能你见过线段树的不同表示方式,但是都大同小异,根据自己的需要来建就行.) 1.线段树基 ...
- 浅谈线段树 Segment Tree
众所周知,线段树是algo中很重要的一项! 一.简介 线段树是一种二叉搜索树,与区间树相似,它将一个区间划分成一些单元区间,每个单元区间对应线段树中的一个叶结点. 使用线段树可以快速的查找某一个节点在 ...
- 线段树 Interval Tree
一.线段树 线段树既是线段也是树,并且是一棵二叉树,每个结点是一条线段,每条线段的左右儿子线段分别是该线段的左半和右半区间,递归定义之后就是一棵线段树. 例题:给定N条线段,{[2, 5], [4, ...
- 线段树(I tree)
Codeforces Round #254 (Div. 2)E题这题说的是给了一个一段连续的区间每个区间有一种颜色然后一个彩笔从L画到R每个区间的颜色都发生了 改变然后 在L和R这部分区间里所用的颜色 ...
- segment树(线段树)
线段树(segment tree)是一种Binary Search Tree或者叫做ordered binary tree.对于线段树中的每一个非叶子节点[a,b],它的左子树表示的区间为[a,(a+ ...
- RMQ问题(线段树+ST算法)
转载自:http://kmplayer.iteye.com/blog/575725 RMQ (Range Minimum/Maximum Query)问题是指:对于长度为n的数列A,回答若干询问RMQ ...
随机推荐
- ORA-**,oracle 12c操作问题
https://blog.csdn.net/typa01_kk/article/details/41924321
- Hadoop案例(三)找博客共同好友
找博客共同好友案例 1)数据准备 以下是博客的好友列表数据,冒号前是一个用户,冒号后是该用户的所有好友(数据中的好友关系是单向的) A:B,C,D,F,E,O B:A,C,E,K C:F,A,D,I ...
- 二安装Python
因为Python是跨平台的,它可以运行在Windows.Mac和各种Linux/Unix系统上.在Windows上写Python程序,放到Linux上也是能够运行的. 要开始学习Python编程,首先 ...
- centos6.5 下安装mysql5.7
http://blog.csdn.net/cryhelyxx/article/details/49757217 按步骤一路执行下去. 以下是补充: linux下,在mysql正常运行的情况下,输入my ...
- phantomjs2.1 初体验
上次看了一下scrapy1.1的新手指南 决定写个小爬虫实验一下 目标网站是http://www.dm5.com/manhua-huofengliaoyuan准备爬取漫画火凤燎原的已有章节,将图片保存 ...
- 使用fastadmin系统自带的图片上传plupload
首先,form表单需要具有如下代码 <form class="form-horizontal" role="form" method="POST ...
- [hdu3934] 凸包 旋转卡壳
大致题意: 求多边形的最大内接三角形 旋转卡壳 模板题 #include<cstdio> #include<iostream> #include<cstring> ...
- code forces 505A
Mr. Kitayuta's Gift Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:262144KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64 ...
- 几何:pick定理详解
一.概念 假设P的内部有I(P)个格点,边界上有B(P)个格点,则P的面积A(P)为:A(P)=I(P)+B(P)/2-1. 二.说明 Pick定理主要是计算格点多边形(定点全是格点的不自交图形)P的 ...
- AtcoderGrandContest 005 F. Many Easy Problems
$ >AtcoderGrandContest \space 005 F. Many Easy Problems<$ 题目大意 : 有一棵大小为 \(n\) 的树,对于每一个 \(k \i ...
