COCO数据集深入理解
Object segmentation
Recognition in context
Superpixel stuff segmentation
330K images (>200K labeled)
1.5 million object instances
object categories
stuff categories
captions per image
, people with keypoints
1. 对stuff任务:118282(118K)训练,5k验证
2. 对instance任务:118k训练,instances_minival2014.json(5k)测试
3. 全景分割任务:40890(40k)训练,5k测试
数据格式
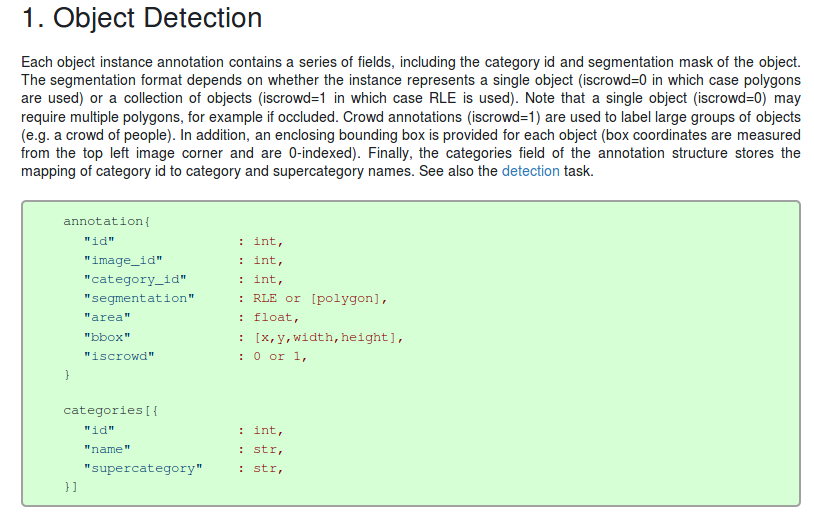
All annotations share the same basic data structure below:
{
"info": info,
"images": [image],
"annotations": [annotation],
"licenses": [license],
}
2. Stuff Segmentation
The stuff annotation format is identical and fully compatible to the object detection format above (except iscrowd is unnecessary and set to 0 by default). We provide annotations in both JSON and png format for easier access, as well as conversion scripts between the two formats. In the JSON format, each category present in an image is encoded with a single RLE annotation (see the Mask API for more details). The category_id represents the id of the current stuff category. For more details on stuff categories and supercategories see the stuff evaluation page. See also the stuff task.
注: instance和stuff任务都categorise没有isthing和color字段;

For a class-aware detector, if you feed it an image, it will return a set of bounding boxes, each box associated with the class of the object inside (i.e. dog, cat, car). It means that by the time the detector finished detecting, it knows what type of object was detected.
For class-agnostic detector, it detects a bunch of objects without knowing what class they belong to. To put it simply, they only detect “foreground” objects. Foreground is a broad term, but usually it is a set that contains all specific classes we want to find in an image, i.e. foreground = {cat, dog, car, airplane, …}. Since it doesn’t know the class of the object it detected, we call it class-agnostic.
Class-agnostic detectors are often used as a pre-processor: to produce a bunch of interesting bounding boxes that have a high chance of containing cat, dog, car, etc. Obviously, we need a specialized classifier after a class-agnostic detector to actually know what class each bounding box contains
COCO api: coco.py
def __init__(self, annotation_file=None):
"""
Constructor of Microsoft COCO helper class for reading and visualizing annotations.
:param annotation_file (str): location of annotation file
:param image_folder (str): location to the folder that hosts images.
:return:
"""
# load dataset
self.dataset,self.anns,self.cats,self.imgs = dict(),dict(),dict(),dict()
self.imgToAnns, self.catToImgs = defaultdict(list), defaultdict(list)
if not annotation_file == None:
print('loading annotations into memory...')
tic = time.time()
dataset = json.load(open(annotation_file, 'r')) # 加载进内存
assert type(dataset)==dict, 'annotation file format {} not supported'.format(type(dataset))
print('Done (t={:0.2f}s)'.format(time.time()- tic))
self.dataset = dataset
self.createIndex() def createIndex(self):
# create index
print('creating index...')
anns, cats, imgs = {}, {}, {} # 这几个都是根据字段一一对应,没有重复
imgToAnns,catToImgs = defaultdict(list),defaultdict(list)
if 'annotations' in self.dataset:
for ann in self.dataset['annotations']:
imgToAnns[ann['image_id']].append(ann) # 同一image_id可能有很多标注框
anns[ann['id']] = ann if 'images' in self.dataset:
for img in self.dataset['images']:
imgs[img['id']] = img if 'categories' in self.dataset:
for cat in self.dataset['categories']:
cats[cat['id']] = cat if 'annotations' in self.dataset and 'categories' in self.dataset:
for ann in self.dataset['annotations']:
catToImgs[ann['category_id']].append(ann['image_id']) # 将有某一种类别标注-->和所有image_id对应 print('index created!') # create class members
self.anns = anns
self.imgToAnns = imgToAnns
self.catToImgs = catToImgs
self.imgs = imgs
self.cats = cats
- 主要是实例化一个cocco对象,利用json文件初始化各种对应关系:其中图像,标注,类别id都唯一建立映射;图像id->标注,类别id->图像,存在一对多映射;
- 在通过一些其他接口处理数据
# The following API functions are defined:
# COCO - COCO api class that loads COCO annotation file and prepare data structures.
# decodeMask - Decode binary mask M encoded via run-length encoding.
# encodeMask - Encode binary mask M using run-length encoding.
# getAnnIds - Get ann ids that satisfy given filter conditions. #annotations
# getCatIds - Get cat ids that satisfy given filter conditions. #category
# getImgIds - Get img ids that satisfy given filter conditions.
# loadAnns - Load anns with the specified ids.
# loadCats - Load cats with the specified ids.
# loadImgs - Load imgs with the specified ids.
# annToMask - Convert segmentation in an annotation to binary mask.
# showAnns - Display the specified annotations.
# loadRes - Load algorithm results and create API for accessing them.
# download - Download COCO images from mscoco.org server.
- 其中loadRes将训练结果转换为coco对象(json格式);
网络输出:
[{"image_id": 139, "category_id": 1, "bbox": [418.3974914550781, 159.67330932617188, 47.4359130859375, 137.63726806640625], "score": 0.9947304725646973}, ...]
[{"image_id": 139, "category_id": 1, "segmentation": {"size": [426, 640], "counts": "cia53R==kCEj:a0mDFP;c0cDC[;X1N1O1O2N2N2N4L3M2N1O0110107YE`ML0o9Y3K5K0O3M10O0O2O1N1O2N4L5K5XNmEOY:CVF6R:^OWF=m9]O[F=g9_OdF7a9CURY2"}, "score": 0.9947304725646973}, ...]
MS COCO数据集目标检测评估(Detection Evaluation)
- 调用方法:cocoGt,cocoDt分别为coco对象
# running evaluation
cocoEval = COCOeval(cocoGt,cocoDt,annType)
cocoEval.evaluate()
cocoEval.accumulate()
cocoEval.summarize()
- cocoeval.py:
- 调试理解:
class COCOeval:
# Interface for evaluating detection on the Microsoft COCO dataset.
#
# The usage for CocoEval is as follows:
# cocoGt=..., cocoDt=... # load dataset and results
# E = CocoEval(cocoGt,cocoDt); # initialize CocoEval object
# E.params.recThrs = ...; # set parameters as desired
# E.evaluate(); # run per image evaluation
# E.accumulate(); # accumulate per image results
# E.summarize(); # display summary metrics of results
# For example usage see evalDemo.m and http://mscoco.org/.
#
# The evaluation parameters are as follows (defaults in brackets):
# imgIds - [all] N img ids to use for evaluation
# catIds - [all] K cat ids to use for evaluation
# iouThrs - [.5:.05:.95] T=10 IoU thresholds for evaluation
# recThrs - [0:.01:1] R=101 recall thresholds for evaluation
# areaRng - [...] A=4 object area ranges for evaluation
# maxDets - [1 10 100] M=3 thresholds on max detections per image
# iouType - ['segm'] set iouType to 'segm', 'bbox' or 'keypoints'
# iouType replaced the now DEPRECATED useSegm parameter.
# useCats - [1] if true use category labels for evaluation
# Note: if useCats=0 category labels are ignored as in proposal scoring.
# Note: multiple areaRngs [Ax2] and maxDets [Mx1] can be specified.
#
# evaluate(): evaluates detections on every image and every category and
# concats the results into the "evalImgs" with fields:
# dtIds - [1xD] id for each of the D detections (dt)
# gtIds - [1xG] id for each of the G ground truths (gt)
# dtMatches - [TxD] matching gt id at each IoU or 0
# gtMatches - [TxG] matching dt id at each IoU or 0
# dtScores - [1xD] confidence of each dt
# gtIgnore - [1xG] ignore flag for each gt
# dtIgnore - [TxD] ignore flag for each dt at each IoU
#
# accumulate(): accumulates the per-image, per-category evaluation
# results in "evalImgs" into the dictionary "eval" with fields:
# params - parameters used for evaluation
# date - date evaluation was performed
# counts - [T,R,K,A,M] parameter dimensions (see above)
# precision - [TxRxKxAxM] precision for every evaluation setting
# recall - [TxKxAxM] max recall for every evaluation setting
# Note: precision and recall==-1 for settings with no gt objects.
#
# See also coco, mask, pycocoDemo, pycocoEvalDemo
#
# Microsoft COCO Toolbox. version 2.0
# Data, paper, and tutorials available at: http://mscoco.org/
# Code written by Piotr Dollar and Tsung-Yi Lin, 2015.
# Licensed under the Simplified BSD License [see coco/license.txt]
def __init__(self, cocoGt=None, cocoDt=None, iouType='segm'):
'''
Initialize CocoEval using coco APIs for gt and dt
:param cocoGt: coco object with ground truth annotations
:param cocoDt: coco object with detection results
:return: None
'''
if not iouType:
print('iouType not specified. use default iouType segm')
self.cocoGt = cocoGt # ground truth COCO API
self.cocoDt = cocoDt # detections COCO API
self.params = {} # evaluation parameters
self.evalImgs = defaultdict(list) # per-image per-category evaluation results [KxAxI] elements
self.eval = {} # accumulated evaluation results
self._gts = defaultdict(list) # gt for evaluation
self._dts = defaultdict(list) # dt for evaluation
self.params = Params(iouType=iouType) # parameters
self._paramsEval = {} # parameters for evaluation
self.stats = [] # result summarization
self.ious = {} # ious between all gts and dts
if not cocoGt is None:
self.params.imgIds = sorted(cocoGt.getImgIds())
self.params.catIds = sorted(cocoGt.getCatIds())
COCO数据集深入理解的更多相关文章
- COCO数据集使用
一.简介 官方网站:http://cocodataset.org/全称:Microsoft Common Objects in Context (MS COCO)支持任务:Detection.Keyp ...
- COCO 数据集的使用
Windows 10 编译 Pycocotools 踩坑记 COCO数据库简介 微软发布的COCO数据库, 除了图片以外还提供物体检测, 分割(segmentation)和对图像的语义文本描述信息. ...
- COCO 数据集使用说明书
下面的代码改写自 COCO 官方 API,改写后的代码 cocoz.py 被我放置在 Xinering/cocoapi.我的主要改进有: 增加对 Windows 系统的支持: 替换 defaultdi ...
- Pascal VOC & COCO数据集介绍 & 转换
目录 Pascal VOC & COCO数据集介绍 Pascal VOC数据集介绍 1. JPEGImages 2. Annotations 3. ImageSets 4. Segmentat ...
- [PocketFlow]解决TensorFLow在COCO数据集上训练挂起无输出的bug
1. 引言 因项目要求,需要在PocketFlow中添加一套PeleeNet-SSD和COCO的API,具体为在datasets文件夹下添加coco_dataset.py, 在nets下添加pelee ...
- 在ubuntu1604上使用aria2下载coco数据集效率非常高
简单的下载方法: 所以这里介绍一种能照顾大多数不能上外网的同学的一种简单便捷,又不会中断的下载方法:系统环境: Ubuntu 14.04 方法: a. 使用aria2 搭配命令行下载.需要先安装: s ...
- MS coco数据集下载
2017年12月02日 23:12:11 阅读数:10411 登录ms-co-co数据集官网,一直不能进入,FQ之后开看到下载链接.有了下载链接下载还是很快的,在我这儿晚上下载,速度能达到7M/s,所 ...
- coco数据集标注图转为二值图python(附代码)
coco数据集大概有8w张以上的图片,而且每幅图都有精确的边缘mask标注. 后面后分享一个labelme标注的json或xml格式转二值图的源码(以备以后使用) 而我现在在研究显著性目标检测,需要的 ...
- Microsoft COCO 数据集
本篇博客主要以介绍MS COCO数据集为目标,分为3个部分:COCO介绍,数据集分类和COCO展示. 本人主要下载了其2014年版本的数据,一共有20G左右的图片和500M左右的标签文件.标签文件标记 ...
随机推荐
- Windows7双系统的启动顺序怎样修改?
本着工作的原因或个人的原因,不过绝大部分还是因为个人怀旧的因素比较多.大家即使安装了新的Windows 7,可是又不想放弃原来的xp765系统,安装双系统就成为不少人的选择.不过有一个麻烦,那就是系统 ...
- web前端面试经历分享
十天前,我还在纠结这个暑假到底是呆在实验室研究技术好还是找一份实习见识世面好,而现在我已经接到offer准备工作了.这几天真是累得够呛,一方面需要拼命准备期末考试,另一方面,需要往公司里面跑接受面试. ...
- windows系统,联系人文件。个性化。
韩梦飞沙 韩亚飞 313134555@qq.com yue31313 han_meng_fei_sha ======= 文件下载链接:
- Activemq+Zookeeper集群
如果在同一台机器上请参考 http://blog.csdn.net/liuyifeng1920/article/details/50233067 http://blog.csdn.net/zuolj/ ...
- CSS选择符、属性继承、优先级算法以及CSS3新增伪类、新特性
CSS 选择符有哪些?哪些属性可以继承?优先级算法如何计算? CSS3新增伪类有那些?CSS新增了哪些特性?下面我整理了一些,仅供参考. CSS 选择符: 1) id选择器(# myid) ...
- Xcode 模拟器复制解决方案
网址:http://blog.csdn.net/zhangao0086/article/details/38491271
- java native方法与JNI实现
native方法定义: 简单地讲,一个Native Method就是一个java调用非java代码的接口.一个Native Method是这样一个java的方法:该方法的实现由非java语言实现,比如 ...
- ARM LDR/STR, LDM/STM 指令
这里比较下容易混淆的四条指令,已经在这4条指令的混淆上花费了很多精力,现在做个小结,LDR,STR,LDM,STM这四条指令, 关于LDM和STM的说明,见另外一个说明文件,说明了这两个文件用于栈操作 ...
- Xcode 统计项目代码行数及常用快捷键
1.统计Xcode项目代码行数 1 打开终端. 2 用ls和cd进到你项目的路径. 3 输入下面的指令: grep -r "\n" classes | wc -l (cl ...
- iOS 实现复选框 checkbox
-(void)checkboxClick:(UIButton *)btn{ btn.selected = !btn.selected;} - (void)viewDidLoad {UIButto ...
