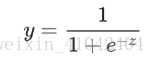学习笔记(七): Logistic Regression
目录
1.Loss function for Logistic Regression
2.Regularization in Logistic Regression
Calculating a Probability
Many problems require a probability estimate as output. Logistic regression is an extremely efficient mechanism for calculating probabilities. Practically speaking, you can use the returned probability in either of the following two ways:
"As is"
Converted to a binary category.
Let's consider how we might use the probability "as is." Suppose we create a logistic regression model to predict the probability that a dog will bark during the middle of the night. We'll call that probability:
p(bark | night)
If the logistic regression model predicts a p(bark | night) of 0.05, then over a year, the dog's owners should be startled awake approximately 18 times:
startled = p(bark | night) * nights
18 ~= 0.05 * 365
In many cases, you'll map the logistic regression output into the solution to a binary classification problem, in which the goal is to correctly predict one of two possible labels (e.g., "spam" or "not spam").
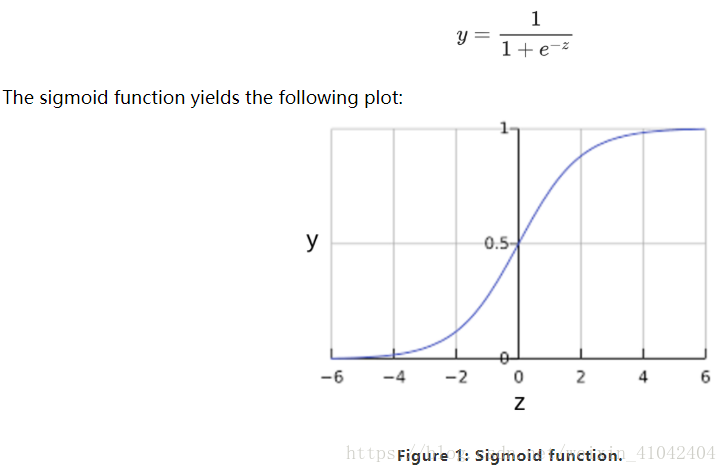
You might be wondering how a logistic regression model can ensure output that always falls between 0 and 1. As it happens, a sigmoid function, produces output having those same characteristics:
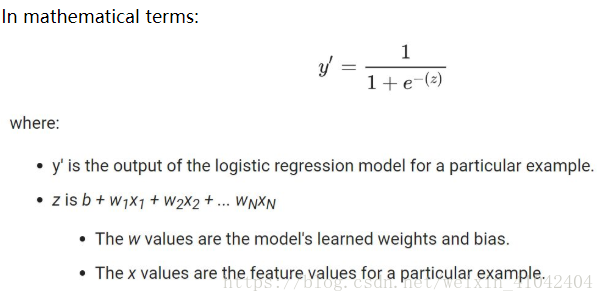
If z represents the output of the linear layer of a model trained with logistic regression, then sigmoid(z) will yield a value (a probability) between 0 and 1. 如果 z 表示使用逻辑回归训练的模型的线性层的输出,则 S 型(z) 函数会生成一个介于 0 和 1 之间的值(概率)。
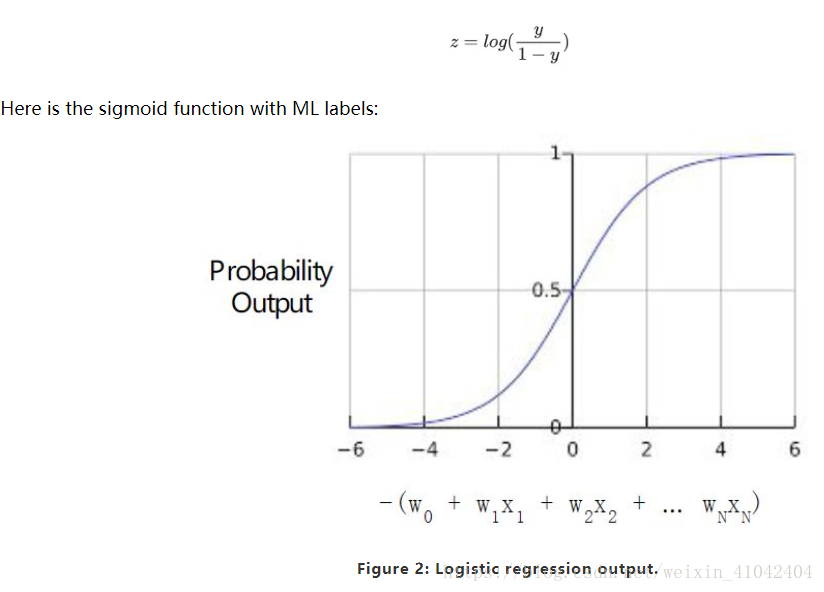
Note that z is also referred to as the log-odds 对数几率 because the inverse of the sigmoid S函数的反函数 states that z can be defined as the log of the probability of the "1" label (e.g., "dog barks") divided by the probability of the "0" label (e.g., "dog doesn't bark"):
Sample logistic regression inference calculation
Suppose we had a logistic regression model with three features that learned the following bias and weights:
b = 1,w1 = 2,w2 = -1,w3 = 5
Further suppose the following feature values for a given example:
x1 = 0,x2 = 10,x3 = 2
Therefore, the log-odds:
b+w1x1+w2x2+w3x3
will be:
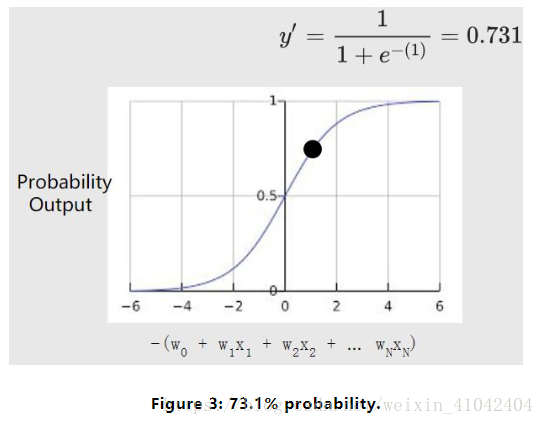
(1) + (2)(0) + (-1)(10) + (5)(2) = 1
Consequently, the logistic regression prediction for this particular example will be 0.731:
Model Training
1.Loss function for Logistic Regression
The loss function for linear regression is squared loss.
The loss function for logistic regression is Log Loss, which is defined as follows:
The equation for Log Loss is closely related to Shannon's Entropy measure from Information Theory.
对数损失函数的方程式与”Shannon 信息论中的熵测量“密切相关。
It is also the negative logarithm of the likelihood function, assuming a Bernoulli distribution of y.
它也是似然函数的负对数(假设“y”属于伯努利分布)。
Indeed, minimizing the loss function yields a maximum likelihood estimate.
最大限度地降低损失函数的值会生成最大的似然估计值。
2.Regularization in Logistic Regression
Regularization is extremely important in logistic regression modeling. Without regularization, the asymptotic nature渐进性 of logistic regression would keep driving loss towards 0 in high dimensions. Consequently, most logistic regression models use one of the following two strategies to dampen model complexity:
L2 regularization.
Early stopping, that is, limiting the number of training steps or the learning rate.
L1 regularization.
Imagine that you assign a unique id to each example, and map each id to its own feature. If you don't specify a regularization function, the model will become completely overfit. That's because the model would try to drive loss to zero on all examples and never get there, driving the weights for each indicator feature to +infinity or -infinity.
This can happen in high dimensional data with feature crosses, when there’s a huge mass of rare crosses that happen only on one example each.当有大量罕见的特征组合且每个样本中仅一个时,包含特征组合的高维度数据会出现这种情况。
Fortunately, using L2 or early stopping will prevent this problem.
Summary
Logistic regression models generate probabilities.
Log Loss is the loss function for logistic regression.
Logistic regression is widely used by many practitioners.
Glossay
1.sigmoid function:
A function that maps logistic or multinomial regression output (log odds) to probabilities, returning a value between 0 and 1:
where z in logistic regression problems is simply:
z=b+w1x1+w2x2+…wnxn
In other words, the sigmoid function converts z into a probability between 0 and 1.
In some neural networks, the sigmoid function acts as the activation function.
2.binary classification:
A type of classification task that outputs one of two mutually exclusive互斥 classes.
For example, a machine learning model that evaluates email messages and outputs either "spam" or "not spam" is a binary classifier.
3.logistic regression:
A model that generates a probability for each possible discrete label value in classification problems by applying a sigmoid function to a linear prediction.
Although logistic regression is often used in binary classification problems, it can also be used in multi-class classification problems (where it becomes called multi-class logistic regression or multinomial多项 regression).
4.Log Loss:
The loss function used in binary logistic regression二元逻辑回归.
5.log-odds对数几率:
The logarithm of the odds of some event.
If the event refers to a binary probability, then odds refers to the ratio of the probability of success (p) to the probability of failure (1-p).
For example, suppose that a given event has a 90% probability of success and a 10% probability of failure. In this case, odds is calculated as follows:
odds=p/(1-p)=.9/.1=9
The log-odds is simply the logarithm of the odds.
By convention, "logarithm" refers to natural logarithm, but logarithm could actually be any base greater than 1. 按照惯例,“对数”是指自然对数,但对数实际上可以是大于1的任何基数。
Sticking to convention, the log-odds of our example is therefore:
log-odds=ln(9) =2.2
The log-odds are the inverse of the sigmoid function.
学习笔记(七): Logistic Regression的更多相关文章
- (转)Qt Model/View 学习笔记 (七)——Delegate类
Qt Model/View 学习笔记 (七) Delegate 类 概念 与MVC模式不同,model/view结构没有用于与用户交互的完全独立的组件.一般来讲, view负责把数据展示 给用户,也 ...
- Learning ROS for Robotics Programming Second Edition学习笔记(七) indigo PCL xtion pro live
中文译著已经出版,详情请参考:http://blog.csdn.net/ZhangRelay/article/category/6506865 Learning ROS forRobotics Pro ...
- Typescript 学习笔记七:泛型
中文网:https://www.tslang.cn/ 官网:http://www.typescriptlang.org/ 目录: Typescript 学习笔记一:介绍.安装.编译 Typescrip ...
- 机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————05.Logistic回归
机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————05.Logistic回归 关键字:Logistic回归.python.源码解析.测试作者:米仓山下时间:2018- ...
- [ML学习笔记] 回归分析(Regression Analysis)
[ML学习笔记] 回归分析(Regression Analysis) 回归分析:在一系列已知自变量与因变量之间相关关系的基础上,建立变量之间的回归方程,把回归方程作为算法模型,实现对新自变量得出因变量 ...
- python3.4学习笔记(七) 学习网站博客推荐
python3.4学习笔记(七) 学习网站博客推荐 深入 Python 3http://sebug.net/paper/books/dive-into-python3/<深入 Python 3& ...
- Go语言学习笔记七: 函数
Go语言学习笔记七: 函数 Go语言有函数还有方法,神奇不.这有点像python了. 函数定义 func function_name( [parameter list] ) [return_types ...
- iOS 学习笔记七 【博爱手把手教你使用2016年gitHub Mac客户端】
iOS 学习笔记七 [博爱手把手教你使用gitHub客户端] 第一步:首先下载git客户端 链接:https://desktop.github.com 第二步:fork 大神的代码[这里以我的代码为例 ...
- 【opencv学习笔记七】访问图像中的像素与图像亮度对比度调整
今天我们来看一下如何访问图像的像素,以及如何改变图像的亮度与对比度. 在之前我们先来看一下图像矩阵数据的排列方式.我们以一个简单的矩阵来说明: 对单通道图像排列如下: 对于双通道图像排列如下: 那么对 ...
- Linux学习笔记(七) 查询系统
1.查看命令 (1)man 可以使用 man 命令名称 命令查看某个命令的详细用法,其显示的内容如下: NAME:命令名称 SYNOPSIS:语法 DESCRIPTION:说明 OPTIONS:选项 ...
随机推荐
- Luogu P4551 最长异或路径 01trie
做一个树上前缀异或和,然后把前缀和插到$01trie$里,然后再对每一个前缀异或和整个查一遍,在树上从高位向低位贪心,按位优先选择不同的,就能贪出最大的答案. #include<cstdio&g ...
- IfmContextHolder(ThreadLocal)
package com.yundaex.wms.config; public class IfmContextHolder { private static final ThreadLocal< ...
- SpringBoot源码篇:深度分析SpringBoot如何省去web.xml
一.前言 从本博文开始,正式开启Spring及SpringBoot源码分析之旅.这可能是一个漫长的过程,因为本人之前阅读源码都是很片面的,对Spring源码没有一个系统的认识.从本文开始我会持续更新, ...
- DNS跳转
switch (window.location.hostname) { case "www.zcom.gov.cn" ://确定域名为 www.zcom.gov.cn //wind ...
- Visual Studio 2015 实用插件推荐
-1000.EntityFramework Reverse POCO Generator(EF Code First 的必备神器) Reverse engineers an existing data ...
- flask --db-Column属性
db.Column 中其余的参数指定属性的配置选项. 选项名 说 明 primary_key 如果设为 True,这列就是表的主键 unique 如果设为 True,这列不允许出现重复的值 index ...
- Sublime Text插件列表
本文由 伯乐在线 - 艾凌风 翻译,黄利民 校稿.英文出处:ipestov.com.欢迎加入翻译组. 本文收录了作者辛苦收集的Sublime Text最佳插件,很全. 最佳的Sublime Text ...
- Ubuntu下eclipse无法识别手机驱动(以小米2S为例子)
google官方开发向导里对Android手机已经设置了允许安装非market程序,并且处于usb调试模式,但是仍然在usb连接电脑后无法被识别的问题作了解释. 在Ubuntu Linux环境下需要添 ...
- 从零开始的全栈工程师——js篇2.9(this详解)
this 一.this是js的一个关键字 指定一个对象然后去替代他 只研究函数内的this 分两种 函数内的this和函数外的this1)函数内的this指向行为发生的主体2)函数外的this都 ...
- js 数组操作常用方法
push():在数组后面加入元素,并返回数组的长度: unshift():在数组前面就如元素,并返回数组的长度: pop():删除最后一个元素: var arr =[1,2,3,4,5] ; arr. ...