PCI Express(四) - The transaction layer
原文出处:http://www.fpga4fun.com/PCI-Express4.html
感觉没什么好翻译的,都比较简单,主要讲了TLP的帧结构
In the transaction layer, we receive "packets". There is a 32-bits bus and the packets arrive on the bus (packet lengths are always multiples of 32-bits). Maybe one packet will says "write data 0x1234 at address 0xABCD", and another will say "read from address 0xDCBA (and return a response packet)".
There are many types of packets: memory read, memory write, I/O read, I/O write, message, completion, etc... Our job in the transaction layer is to accept packets and issue packets. The packets are presented to us in a specific format called "transaction layer packets" (TLPs), and each 32-bits data arriving on the bus is called a "double word" (or DW in short).
So a packet (oops sorry, a TLP) is a bunch of DWs.
How a TLP looks
TLPs are pretty simple to interpret. Here's a general view of their structure.
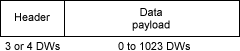
The header contains 3 or 4 DWs but the most important fields are part of the first DW.

The "Fmt" field tells how long is the header, and if a data payload is present.
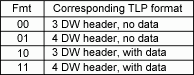
Then together with "Type", it describes the TLP operation. The remainder of the TLP header content depends of the TLP operation.
For example, here's a 32-bits memory write TLP header, where you can see that the write address is at the end of the header (and the write data is not shown as it is in the payload after the header).
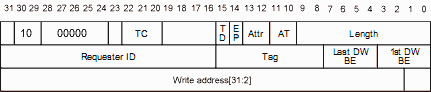
The "Fmt" field is "10" which means "3 DW, with data". That makes sense, a memory write needs data to write, so upon getting the data payload after the header, we write that data to some memory (or use it somehow) and we are done with it. The Field "Length" tells how many DWs are in the payload (from 0 to 1023). Commonly, it's a single DW to write, in which case length is equal to 1 and the total TLP length is 4 DWs (3 for the header and 1 of the payload).
Now what about a memory read? Somehow we have to return data.
Completion with data
If the TLP is a memory read instead of a write, we have to execute the read and then respond. There is a special TLP for that response, it is called CplD (completion with data) and its payload contains the data that we want to return.
Let's take a closer look at the 32-bit memory read TLP header - it is very similar to the 32-bit memory write we had previously.
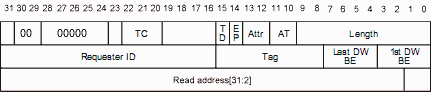
One difference is the Fmt=00, which means "no data". Makes sense, we don't need data to do a read, just an address. But we now have to respond with data. And as important, the response will need to be routed back to whoever asked for the read... Do you see the problem?
Ok, we received a read request. Did it come from the CPU? Or from the interrupt controller? Or from a graphic card? After all, many devices are capable of issuing such request. The answer is given in the "Requester ID" - it shows who requested the read. So when we create the CplD TLP, we have to recopy the "Requester ID" in it. This way, it'll be routed where it belongs by the PCI Express bridge(s). BTW, we also have to recopy the "Tag" (which is useful in case of multiple reads pending).
TLP size
A typical 32-bit address/data memory read TLP is made of 3 DWs in the header and no payload (so 96 bits total), while a similar memory write is made of 4 DWs (3 for the header and 1 for the payload). That's not very efficient in term of bandwidth because of the TLP header overhead, so it is better to use bigger TLP payloads when possible. A TLP payload can theoretically be as big as 1023 DWs, pretty handy for burst reads and writes, although PCs can limit the maximum size to a lower value (32 DWs is typical).
For more information, check the official PCI Express specification by googling something like PCI_Express_Base_11.pdf
Enough with theory, let's have some fun and play with the Xilinx PCI Express wizard.
PCI Express(四) - The transaction layer的更多相关文章
- PCI Express(六) - Simple transactions
原文地址:http://www.fpga4fun.com/PCI-Express6.html Let's try to control LEDs from the PCI Express bus. X ...
- PCI Express(三) - A story of packets, stack and network
原文出处:http://www.fpga4fun.com/PCI-Express3.html Packetized transactions PCI express is a serial bus. ...
- Down to the TLP: How PCI express devices talk (Part I)
http://xillybus.com/tutorials/pci-express-tlp-pcie-primer-tutorial-guide-1 Down to the TLP: How PCI ...
- PCI Express
1.1课题研究背景 在目前高速发展的计算机平台上,应用软件的开发越来越依赖于硬件平台,尤其是随着大数据.云计算的提出,人们对计算机在各个领域的性能有更高的需求.日常生活中的视频和图像信息包含大量的数据 ...
- Down to the TLP: How PCI express devices talk (Part II)
http://xillybus.com/tutorials/pci-express-tlp-pcie-primer-tutorial-guide-2 Data Link Layer Packets A ...
- [中英对照]How PCI Express Works | PCIe工作原理
How PCI Express Works | PCIe工作原理 PCI Express is a high-speed serial connection that operates more li ...
- 002 PCI Express体系结构(二)
一.PCI总线的信号定义 PCI总线是一条共享总线,在一条PCI总线上可以挂接多个PCI设备.这些PCI设备通过一系列信号与PCI总线相连,这些信号由地址/数据信号.控制信号.仲裁信号.中断信号等多种 ...
- 001 PCI Express体系结构(一)
一 .PCI总线的基本知识 PCI总线作为处理器系统的局部总线,主要目的是为了连接外部设备,而不是作为处理器的系统总线连接Cache和主存储器.但是PCI总线.系统总线和处理器体系结构之间依然存在着紧 ...
- PCI Express(五) - Xilinx wizard
原文地址:http://www.fpga4fun.com/PCI-Express5.html Xilinx makes using PCI express easy - they provide a ...
随机推荐
- iOS学习之手势
UIGestureRecognizer 为了完成手势识别,必须借助于手势识别器--UIGestureRecognizer,利用UIGestureRecognizer,能轻松识别用户在某个view上面做 ...
- Maven安装本地jar
应用场景: 有时候一些jar包(比如oracle 的 ojdbc.jar)由于种种原因,比如版权等,导致maven中央库没有该jar文件,但是却有该jar的pom文件. 这个时候,如果私服也没这jar ...
- HttpClient(4.3.3)实例讲解
HttpClient的作用强大,真的是十分强大. 本实例是基于v4.3.3写的,,作用是模拟登陆后进行上下班打卡,,,使用htmlparser进行解析返回的html文件 关于HttpClient的一些 ...
- Jquery和Javascript 实际项目中写法基础-闭包 (2)
一.什么是闭包? 概念性的我就不去百度了,感兴趣的可以自己去搜下,我自己的理解,闭包就是一个封装的包,相当于类的概念,把乱七八糟的的东西封装到一起,然后统一使用一个对象来调用,实现代码部分对外开放,部 ...
- UVALive 7302 (最短路)
Probelm Terrorists 题目大意 给一张n个点,m条边的无向图.共有q个询问,每次询问u到v的最短路. n <= 100000 , n-1 <= m <= n + 5 ...
- bigworld源码分析(5)——BaseApp分析
BaseApp负载部分,核心代码缺失...网上的源码中都找不到,暂时没办法分析其核心内容,很遗憾,继续寻找吧,等找到了,再继续自己的分析.
- SVN提交碰到的问题奇怪的问题
svn提交遇到恶心的问题,可能是因为上次cleanup中断后,进入死循环了. 错误如下: 解决方法:清空svn的队列 1.下载sqlite3.exe 2.找到你项目的.svn文件,查看是否存在wc.d ...
- Sublime Text 3开启自动换行
在Submine Text 3中要开启自动换行功能只需要两个步骤: 1.找到查看(View) 2.点击弹出菜单中的自动换行即可 但是如果是在2中的话就相对麻烦少少,现在也说下其开启自动换行功能的步骤: ...
- Android 开发错误信息001
Error:Execution failed for task ':app:dexDebug'. > com.android.ide.common.process.ProcessExceptio ...
- AJAX部分---php-jquery-ajax;
AJAX的应用场景 1.异步搜索过滤内容数据 2.表单异步验证 3.异步加载页面“更多”数据 4.异步处理登录 5.异步处理用户名是否注册 AJAX的主要特点 1.在不刷新页面的情况下,与服务器进行异 ...
