TensorFlow初学教程(完整版)
1:你想要学习TensorFlow,首先你得安装Tensorflow,在你学习的时候你最好懂以下的知识:
a:怎么用python编程;
b:了解一些关于数组的知识;
c:最理想的情况是:关于机器学习,懂一点点;或者不懂也是可以慢慢开始学习的。
2:TensorFlow提供很多API,最低级别是API:TensorFlow Core,提供给你完成程序控制,还有一些高级别的API,它们是构建在
TensorFlow Core之上的,这些高级别的API更加容易学习和使用,于此同时,这些高级别的API使得重复的训练任务更加容易,
也使得多个使用者操作对他保持一致性,一个高级别的API像tf.estimator帮助你管理数据集合,估量,训练和推理。
3:TensorsTensorFlow的数据中央控制单元是tensor(张量),一个tensor由一系列的原始值组成,这些值被形成一个任意维数的数组。
一个tensor的列就是它的维度。
4:
import tensorflow as tf
上面的是TensorFlow 程序典型的导入语句,作用是:赋予Python访问TensorFlow类(classes),方法(methods),符号(symbols)
5:The Computational Graph TensorFlow核心程序由2个独立部分组成:
a:Building the computational graph构建计算图
b:Running the computational graph运行计算图
一个computational graph(计算图)是一系列的TensorFlow操作排列成一个节点图。
需要视频教程的小伙伴可点击进入扣群下载,群内不定期的会分享资料教程,点击直达链接:https://jq.qq.com/?_wv=1027&k=55fzJrT
最后打印结果是:
Tensor("Const:0", shape=(), dtype=float32) Tensor("Const_1:0",shape=(), dtype=float32)
要想打印最终结果,我们必须用到session:一个session封装了TensorFlow运行时的控制和状态

我们可以组合Tensor节点操作(操作仍然是一个节点)来构造更加复杂的计算,

打印结果是:

6:TensorFlow提供一个统一的调用称之为TensorBoard,它能展示一个计算图的图片;如下面这个截图就展示了这个计算图

7:一个计算图可以参数化的接收外部的输入,作为一个placeholders(占位符),一个占位符是允许后面提供一个值的。

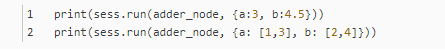
结果是:


8:我们可以增加另外的操作来让计算图更加复杂,比如

在TensorBoard,计算图类似于这样:

9:在机器学习中,我们通常想让一个模型可以接收任意多个输入,比如大于1个,好让这个模型可以被训练,在不改变输入的情况下,

:当你调用tf.constant时常量被初始化,它们的值是不可以改变的,而变量当你调用tf.Variable时没有被初始化,

11:要实现初始化所有全局变量的TensorFlow子图的的处理是很重要的,直到我们调用sess.run,这些变量都是未被初始化的。

12:我们已经创建了一个模型,但是我们至今不知道它是多好,在这些训练数据上对这个模型进行评估,我们需要一个
y占位符来提供一个期望的值,并且我们需要写一个loss function(损失函数),一个损失函数度量当前的模型和提供
的数据有多远,我们将会使用一个标准的损失模式来线性回归,它的增量平方和就是当前模型与提供的数据之间的损失
,linear_model - y创建一个向量,其中每个元素都是对应的示例错误增量。这个错误的方差我们称为tf.square。然后
,我们合计所有的错误方差用以创建一个标量,用tf.reduce_sum抽象出所有示例的错误。


14:tf.train APITessorFlow提供optimizers(优化器),它能慢慢改变每一个变量以最小化损失函数,最简单的优化器是
gradient descent(梯度下降),它根据变量派生出损失的大小,来修改每个变量。通常手工计算变量符号是乏味且容易出错的,
因此,TensorFlow使用函数tf.gradients给这个模型一个描述,从而能自动地提供衍生品,简而言之,优化器通常会为你做这个。例如:

15:tf.estimatortf.setimator是一个更高级别的TensorFlow库,它简化了机械式的机器学习,包含以下几个方面:
running training loops 运行训练循环
running evaluation loops 运行求值循环
managing data sets 管理数据集合
tf.setimator定义了很多相同的模型。
16:A custom modeltf.setimator没有把你限制在预定好的模型中,假设我们想要创建一个自定义的模型,它不是由
TensorFlow建成的。我还是能保持这些数据集合,输送,训练高级别的抽象;例如:tf.estimator;
17:现在你有了关于TensorFlow的一个基本工作知识,我们还有更多教程,它能让你学习更多。如果你是一个机器学习初学者,
你可以继续学习MNIST for beginners,否则你可以学习Deep MNIST for experts.
完整的代码:
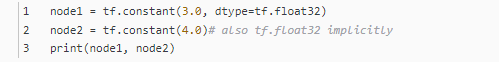
import tensorflow as tf
node1 = tf.constant(3.0, dtype=tf.float32)
node2 = tf.constant(4.0) # also tf.float32 implicitly
print(node1, node2)
sess = tf.Session()
print(sess.run([node1, node2]))
# from __future__ import print_function
node3 = tf.add(node1, node2)
print("node3:", node3)
print("sess.run(node3):", sess.run(node3))
# 占位符
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
adder_node = a + b # + provides a shortcut for tf.add(a, b)
print(sess.run(adder_node, {a: 3, b: 4.5}))
print(sess.run(adder_node, {a: [1, 3], b: [2, 4]}))
add_and_triple = adder_node * 3.
print(sess.run(add_and_triple, {a: 3, b: 4.5}))
# 多个变量求值
W = tf.Variable([.3], dtype=tf.float32)
b = tf.Variable([-.3], dtype=tf.float32)
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
linear_model = W*x + b
# 变量初始化
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
print(sess.run(linear_model, {x: [1, 2, 3, 4]}))
# loss function
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
squared_deltas = tf.square(linear_model - y)
loss = tf.reduce_sum(squared_deltas)
print("loss function", sess.run(loss, {x: [1, 2, 3, 4], y: [0, -1, -2, -3]}))
ss = (0-0)*(0-0) + (0.3+1)*(0.3+1) + (0.6+2)*(0.6+2) + (0.9+3)*(0.9+3) # 真实算法
print("真实算法ss", ss)
print(sess.run(loss, {x: [1, 2, 3, 4], y: [0, 0.3, 0.6, 0.9]})) # 测试参数
# ft.assign 变量重新赋值
fixW = tf.assign(W, [-1.])
fixb = tf.assign(b, [1.])
sess.run([fixW, fixb])
print(sess.run(linear_model, {x: [1, 2, 3, 4]}))
print(sess.run(loss, {x: [1, 2, 3, 4], y: [0, -1, -2, -3]}))
# tf.train API
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01) # 梯度下降优化器
train = optimizer.minimize(loss) # 最小化损失函数
sess.run(init) # reset values to incorrect defaults.
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(train, {x: [1, 2, 3, 4], y: [0, -1, -2, -3]})
print(sess.run([W, b]))
print("------------------------------------1")
# Complete program:The completed trainable linear regression model is shown here:完整的训练线性回归模型代码
# Model parameters
W = tf.Variable([.3], dtype=tf.float32)
b = tf.Variable([-.3], dtype=tf.float32)
# Model input and output
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
linear_model = W*x + b
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
# loss
loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(linear_model - y)) # sum of the squares
# optimizer
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01)
train = optimizer.minimize(loss)
# training data
x_train = [1, 2, 3, 4]
y_train = [0, -1, -2, -3]
# training loop
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init) # reset values to wrong
for i in range(1000):
sess.run(train, {x: x_train, y: y_train})
# evaluate training accuracy
curr_W, curr_b, curr_loss = sess.run([W, b, loss], {x: x_train, y: y_train})
print("W: %s b: %s loss: %s"%(curr_W, curr_b, curr_loss))
print("------------------------------------2")
# tf.estimator 使用tf.estimator实现上述训练
# Notice how much simpler the linear regression program becomes with tf.estimator:
# NumPy is often used to load, manipulate and preprocess data.
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
# Declare list of features. We only have one numeric feature. There are many
# other types of columns that are more complicated and useful.
feature_columns = [tf.feature_column.numeric_column("x", shape=[1])]
# An estimator is the front end to invoke training (fitting) and evaluation
# (inference). There are many predefined types like linear regression,
# linear classification, and many neural network classifiers and regressors.
# The following code provides an estimator that does linear regression.
estimator = tf.estimator.LinearRegressor(feature_columns=feature_columns)
# TensorFlow provides many helper methods to read and set up data sets.
# Here we use two data sets: one for training and one for evaluation
# We have to tell the function how many batches
# of data (num_epochs) we want and how big each batch should be.
x_train = np.array([1., 2., 3., 4.])
y_train = np.array([0., -1., -2., -3.])
x_eval = np.array([2., 5., 8., 1.])
y_eval = np.array([-1.01, -4.1, -7, 0.])
input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
{"x": x_train}, y_train, batch_size=4, num_epochs=None, shuffle=True)
train_input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
{"x": x_train}, y_train, batch_size=4, num_epochs=1000, shuffle=False)
eval_input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
{"x": x_eval}, y_eval, batch_size=4, num_epochs=1000, shuffle=False)
# We can invoke 1000 training steps by invoking the method and passing the
# training data set.
estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn, steps=1000)
# Here we evaluate how well our model did.
train_metrics = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=train_input_fn)
eval_metrics = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=eval_input_fn)
print("train metrics: %r"% train_metrics)
print("eval metrics: %r"% eval_metrics)
print("------------------------------------3")
# A custom model:客户自定义实现训练
# Declare list of features, we only have one real-valued feature
def model_fn(features, labels, mode):
# Build a linear model and predict values
W = tf.get_variable("W", [1], dtype=tf.float64)
b = tf.get_variable("b", [1], dtype=tf.float64)
y = W*features['x'] + b
# Loss sub-graph
loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(y - labels))
# Training sub-graph
global_step = tf.train.get_global_step()
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01)
train = tf.group(optimizer.minimize(loss),
tf.assign_add(global_step, 1))
# EstimatorSpec connects subgraphs we built to the
# appropriate functionality.
return tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec(
mode=mode,
predictions=y,
loss=loss,
train_op=train)
estimator = tf.estimator.Estimator(model_fn=model_fn)
# define our data sets
x_train = np.array([1., 2., 3., 4.])
y_train = np.array([0., -1., -2., -3.])
x_eval = np.array([2., 5., 8., 1.])
y_eval = np.array([-1.01, -4.1, -7., 0.])
input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
{"x": x_train}, y_train, batch_size=4, num_epochs=None, shuffle=True)
train_input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
{"x": x_train}, y_train, batch_size=4, num_epochs=1000, shuffle=False)
eval_input_fn = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
{"x": x_eval}, y_eval, batch_size=4, num_epochs=1000, shuffle=False)
# train
estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn, steps=1000)
# Here we evaluate how well our model did.
train_metrics = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=train_input_fn)
eval_metrics = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=eval_input_fn)
print("train metrics: %r"% train_metrics)
print("eval metrics: %r"% eval_metrics)
TensorFlow初学教程(完整版)的更多相关文章
- Python入门教程完整版(懂中文就能学会)
前几天给大家分享<从零学会Photoshop经典教程300集>的教程受到了广泛的关注,有人不知道怎么领取,居然称小编为"骗子". 不过小编的内心是强大的,网友虐我千百遍 ...
- IIS下配置Php+Mysql+zend的图文教程(完整版)
网上有很多关于PHP在IIS下配置的教程,但都是一些很理性化的东西,我从里面整理出来这个教程 发出来为了方便参考,,有什么问题也可以大家一起交流,,如果有什么不对的地方,请指正.. 下面的教程都是在w ...
- es6入门教程完整版
ECMAScript 6入门 <ECMAScript 6入门>是一本开源的JavaScript语言教程,全面介绍ECMAScript 6新引入的语法特性. 作者:阮一峰 授权:署名-非商用 ...
- ajax教程完整版
第 1 页 Ajax 简介 Ajax 由 HTML.JavaScript™ 技术.DHTML 和 DOM 组成,这一杰出的方法可以将笨拙的 Web 界面转化成交互性的 Ajax 应用程序.本文的作者是 ...
- LoadRunner_11破解教程完整版
2017.12.17更正 qtm的LR11,如果是win10版本的电脑而且ie浏览器是11以上的请到loadrunner官网下载社区免费版,支持google,firefox,edge,ie11四大浏览 ...
- [Red5]Red5之Flash流媒体服务器的安装与使用教程完整版(组图)
参看下面链接:http://www.cuplayer.com/player/PlayerCode/Red5/2013/0319/760.html
- BootStrap教程完整版
http://www.runoob.com/bootstrap/bootstrap-navbar.html
- oracle11g安装教程完整版
来自: https://www.2cto.com/database/201701/588135.html 64位WIN7+oracle11g+plsql安装 1.下载Oracle 11g R2 for ...
- AspJpeg2.0组件教程完整版 aspjpeg教程...
AspJpeg是一款功能强大的基于Microsoft IIS环境的图片处理组件,网络上对其进行详细和深入介绍的中文文章并不多,即使有一般也只是牵涉到图片缩略图和图片水印,这与其为英文版本有着密切的关系 ...
随机推荐
- Mybaits-从零开始-Hello World(暂不考虑命名规范化)
1.mybatis-config.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE ...
- android字母索引实现ListView定位
最近闲的很,没什么事干 ,在玩手机的时间看到android系统自带的那个通讯录软件对联系人的快速定位功能. 感觉这个功能也比较实用自己就试着自己去实现. 虽然网络上还是有大牛封闭好了的框架,但是如果 ...
- ubuntu13 eclipse菜单栏失效解决
使用ubuntu13安装完eclipse和myeclipse后发现菜单栏单击时不显示下拉框只能通过快捷键显示. 百度了一下,找到以下解决办法. 打开终端运行下面的命令,打开eclipse后可正常显示菜 ...
- redis实践 —— redisReply简析
redisReply 定义如下: /* This is the reply object returned by redisCommand() */ typedef struct redisReply ...
- dede tag标签静态化
看回那2个文件夹即可,txt说明书我已经修改过. 下面说一下tag标签静态化之后在内容页.列表页中如何使用. 内容页中沿用之前的方法即可: {dede:tag sort='new' getall='0 ...
- ping通谷歌后发送QQ邮件通知
前言 国庆期间,据说是为了防止有人在重大节日发表不正当言论,很多可以kxsw的ip都被封了,可是什么时候才会解封呢,不能没事就去ping一下吧,所以我写了个定时任务,定时ping谷歌服务器,如果p ...
- 【每天一题】LeetCode 0020. 有效的括号
开源地址:https://github.com/jiauzhang/algorithms 题目 /* * https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-parenthe ...
- 快学Scala 第一课 (变量,类型,操作符)
Scala 用val定义常量,用var定义变量. 常量重新赋值就会报错. 变量没有问题. 注意:我们不需要给出值或者变量的类型,scala初始化表达式会自己推断出来.当然我们也可以指定类型. 多个值和 ...
- MongoDB 学习笔记之 游标
游标: 游标是查询的接口,可以逐条读取. var mycursor = db.bar.find(); mycursor.hasNext(); mycursor.next(); 示例: var mycu ...
- pycharm 2019/10 激活码 最新福利 (1)
MTW881U3Z5-eyJsaWNlbnNlSWQiOiJNVFc4ODFVM1o1IiwibGljZW5zZWVOYW1lIjoiTnNzIEltIiwiYXNzaWduZWVOYW1lIjoiI ...
