Exercise: PCA in 2D
Step 0: Load data
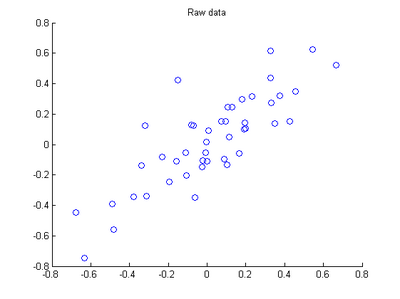
The starter code contains code to load 45 2D data points. When plotted using the scatter function, the results should look like the following:
Step 1: Implement PCA
In this step, you will implement PCA to obtain xrot, the matrix in which the data is "rotated" to the basis comprising
made up of the principal components
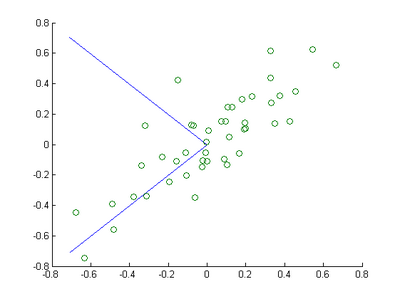
Step 1a: Finding the PCA basis
Find
and
, and draw two lines in your figure to show the resulting basis on top of the given data points.
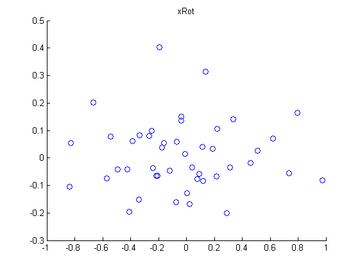
Step 1b: Check xRot
Compute xRot, and use the scatter function to check that xRot looks as it should, which should be something like the following:
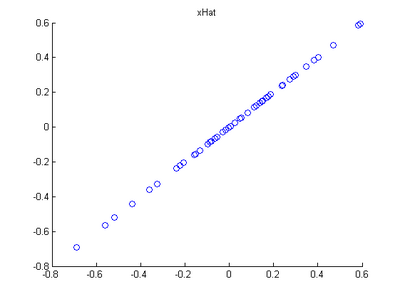
Step 2: Dimension reduce and replot
In the next step, set k, the number of components to retain, to be 1
Step 3: PCA Whitening
Step 4: ZCA Whitening
Code
close all %%================================================================
%% Step : Load data
% We have provided the code to load data from pcaData.txt into x.
% x is a * matrix, where the kth column x(:,k) corresponds to
% the kth data point.Here we provide the code to load natural image data into x.
% You do not need to change the code below. x = load('pcaData.txt','-ascii'); % 载入数据
figure();
scatter(x(, :), x(, :)); % 用圆圈绘制出数据分布
title('Raw data'); %%================================================================
%% Step 1a: Implement PCA to obtain U
% Implement PCA to obtain the rotation matrix U, which is the eigenbasis
% sigma. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
u = zeros(size(x, )); % You need to compute this
[n m]=size(x);
% x=x-repmat(mean(x,),,m); %预处理,均值为零 —— 2维,每一维减去该维上的均值
sigma=(1.0/m)*x*x'; % 协方差矩阵
[u s v]=svd(sigma); % --------------------------------------------------------
hold on
plot([ u(,)], [ u(,)]); % 画第一条线
plot([ u(,)], [ u(,)]); % 画第二条线
scatter(x(, :), x(, :));
hold off %%================================================================
%% Step 1b: Compute xRot, the projection on to the eigenbasis
% Now, compute xRot by projecting the data on to the basis defined
% by U. Visualize the points by performing a scatter plot. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xRot = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
xRot=u'*x; % -------------------------------------------------------- % Visualise the covariance matrix. You should see a line across the
% diagonal against a blue background.
figure();
scatter(xRot(, :), xRot(, :));
title('xRot'); %%================================================================
%% Step : Reduce the number of dimensions from to .
% Compute xRot again (this time projecting to dimension).
% Then, compute xHat by projecting the xRot back onto the original axes
% to see the effect of dimension reduction % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
k = ; % Use k = and project the data onto the first eigenbasis
xHat = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
xHat = u*([u(:,),zeros(n,)]'*x); % 降维
% 使特征点落在特征向量所指的方向上而不是原坐标系上 % --------------------------------------------------------
figure();
scatter(xHat(, :), xHat(, :));
title('xHat'); %%================================================================
%% Step : PCA Whitening
% Complute xPCAWhite and plot the results. epsilon = 1e-;
% -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xPCAWhite = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
xPCAWhite = diag(./sqrt(diag(s)+epsilon))*u'*x; % 每个特征除以对应的特征向量,以使每个特征有一致的方差
% --------------------------------------------------------
figure();
scatter(xPCAWhite(, :), xPCAWhite(, :));
title('xPCAWhite'); %%================================================================
%% Step : ZCA Whitening
% Complute xZCAWhite and plot the results. % -------------------- YOUR CODE HERE --------------------
xZCAWhite = zeros(size(x)); % You need to compute this
xZCAWhite = u*diag(./sqrt(diag(s)+epsilon))*u'*x; % --------------------------------------------------------
figure();
scatter(xZCAWhite(, :), xZCAWhite(, :));
title('xZCAWhite'); %% Congratulations! When you have reached this point, you are done!
% You can now move onto the next PCA exercise. :)
Exercise: PCA in 2D的更多相关文章
- 【DeepLearning】Exercise:PCA in 2D
Exercise:PCA in 2D 习题的链接:Exercise:PCA in 2D pca_2d.m close all %%=================================== ...
- 【DeepLearning】Exercise:PCA and Whitening
Exercise:PCA and Whitening 习题链接:Exercise:PCA and Whitening pca_gen.m %%============================= ...
- Deep Learning 4_深度学习UFLDL教程:PCA in 2D_Exercise(斯坦福大学深度学习教程)
前言 本节练习的主要内容:PCA,PCA Whitening以及ZCA Whitening在2D数据上的使用,2D的数据集是45个数据点,每个数据点是2维的.要注意区别比较二维数据与二维图像的不同,特 ...
- UFLDL教程笔记及练习答案二(预处理:主成分分析和白化)
首先将本节主要内容记录下来.然后给出课后习题的答案. 笔记: :首先我想推导用SVD求解PCA的合理性. PCA原理:如果样本数据X∈Rm×n.当中m是样本数量,n是样本的维数.PCA降维的目的就是为 ...
- Deep Learning 教程(斯坦福深度学习研究团队)
http://www.zhizihua.com/blog/post/602.html 说明:本教程将阐述无监督特征学习和深度学习的主要观点.通过学习,你也将实现多个功能学习/深度学习算法,能看到它们为 ...
- [Scikit-learn] 4.3 Preprocessing data
数据分析的重难点,就这么来了,欢迎欢迎,热烈欢迎. 4. Dataset transformations 4.3. Preprocessing data 4.3.1. Standardization, ...
- UFLDL教程之(三)PCA and Whitening exercise
Exercise:PCA and Whitening 第0步:数据准备 UFLDL下载的文件中,包含数据集IMAGES_RAW,它是一个512*512*10的矩阵,也就是10幅512*512的图像 ( ...
- PCA and kmeans MATLAB实现
MATLAB基础知识 l Imread: 读取图片信息: l axis:轴缩放:axis([xmin xmax ymin ymax zmin zmax cmin cmax]) 设置 x.y 和 ...
- Deep Learning 5_深度学习UFLDL教程:PCA and Whitening_Exercise(斯坦福大学深度学习教程)
前言 本文是基于Exercise:PCA and Whitening的练习. 理论知识见:UFLDL教程. 实验内容:从10张512*512自然图像中随机选取10000个12*12的图像块(patch ...
随机推荐
- 鼠标点击textarea后,在光标后追加内容
$("#insertMsg").on("click",function(){ //获取下拉选项框的值 var textFeildValue = $(" ...
- 使用sysbench 对mysql进行性能测试
使用sysbench 对mysql进行性能测试 sysbench是一个开源的.模块化的.跨平台的多线程性能测试工具,可以用来进行CPU.内存.磁盘I/O.线程.数据库的性能测试.目前支持的数据库有My ...
- vscode 调试vue.js程序
npm install -g vue-cli //安装vue-clivue init webpack projectName //创建项目 1.Ctrl+~ 打开命令行 ...
- 记intel杯比赛中各种bug与debug【其三】:intel chainer的安装与使用
现在在训练模型,闲着来写一篇 顺着这篇文章,顺利安装上intel chainer 再次感谢 大黄老鼠 intel chainer 使用 头一次使用chainer,本以为又入了一个大坑,实际尝试感觉非常 ...
- Java web application——基础
概述 一个WAR文件包含了构成一个Web应用程序所需要的文件.WAR文件作为一个单元部署在一个或多个WebLogic Server实例上. WebLogic Server上的Web存档始终包含以下文件 ...
- laravel中soapServer支持wsdl的例子
最近在对接客户的CRM系统,获取令牌时,要用DES方式加密解密,由于之前没有搞错这种加密方式,经过请教了"百度"和"谷歌"两个老师后,结合了多篇文档内容后,终于 ...
- HDU 4398 Template Library Management (最优页面调度算法)
中等偏易题.操作系统理论中的最优页面调度算法,贪心.当需要淘汰某个模版时,淘汰掉当前手中在最远的将来才会被用到(或者以后永远不再用到)的那个. 代码: #include <iostream> ...
- WHU 1537 Stones I
题目见: http://acm.whu.edu.cn/land/problem/detail?problem_id=1537 这个题相当无语,学长给的解法是:枚举取的个数k,然后对每个k贪心,取其中的 ...
- CodeForces 316c1 Tidying Up
Tidying Up Time Limit: 4000ms Memory Limit: 262144KB This problem will be judged on CodeForces. Orig ...
- java RSA加密算法
[转]RSA加密算法 RSA公钥加密算法是1977年由Ron Rivest.Adi Shamirh和LenAdleman在(美国麻省理工学院)开发的.RSA取名来自开发他们三者的名字.RSA是目前 ...