二分类模型之logistic
liner classifiers
逻辑回归用在2分类问题上居多。它是一个非线性的回归模型,其最大的好处恰恰是可以解决二元类问题,目前在金融行业,基本都是使用Logistic回归来预判一个用户是否为好客户,因为它还弥补了其他黑盒模型(SVM、神经网络、随机森林等)不具解释性的缺点。知乎
1.logistic
- 逻辑回归其实是一个分类算法而不是回归算法。通常是利用已知的自变量来预测一个离散型因变量的值(像二进制值0/1,是/否,真/假)。简单来说,它就是通过拟合一个逻辑函数(logit fuction)来预测一个事件发生的概率。所以它预测的是一个概率值,自然,它的输出值应该在0到1之间。--计算的是单个输出
1.2 sigmoid
逻辑函数
\(g(z)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-z}}\)
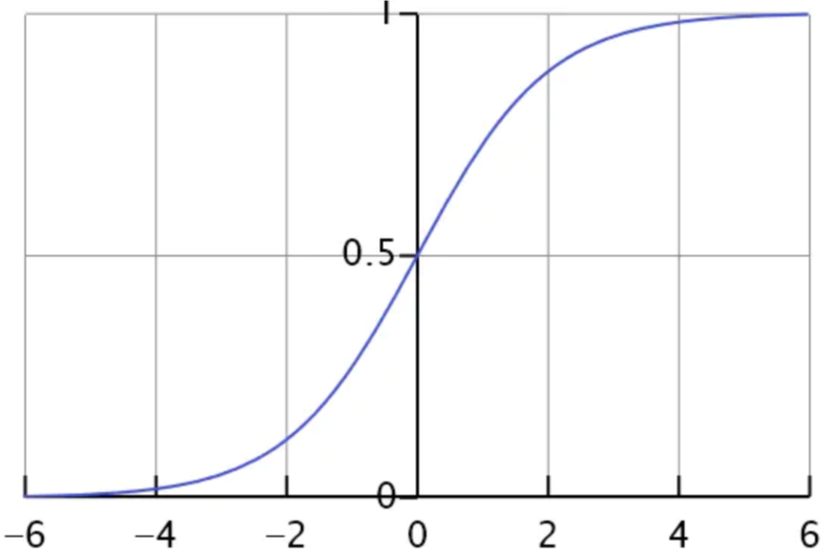
- sigmoid函数是一个s形的曲线,它的取值在[0, 1]之间,在远离0的地方函数的值会很快接近0或者1。它的这个特性对于解决二分类问题十分重要
- 二分类中,输出y的取值只能为0或者1,所以在线性回归的假设函数外包裹一层Sigmoid函数,使之取值范围属于(0,1),完成了从值到概率的转换。逻辑回归的假设函数形式如下
\(h_{\theta}(x)=g\left(\theta^{T} x\right)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-\theta^{T} x}}=P(y=1 | x ; \theta)\)
则若\(P(y=1 | x ; \theta)=0.7\),则表示输入为x的时候,y=1的概率为0.7
1.3 决策边界
决策边界,也称为决策面,是用于在N维空间,将不同类别样本分开的直线或曲线,平面或曲面
根据以上假设函数表示概率,我们可以推得
if \(h_{\theta}(x) \geqslant 0.5 \Rightarrow y=1\)
if \(h_{\theta}(x)<0.5 \Rightarrow y=0\)
1.3.1 线性决策边界
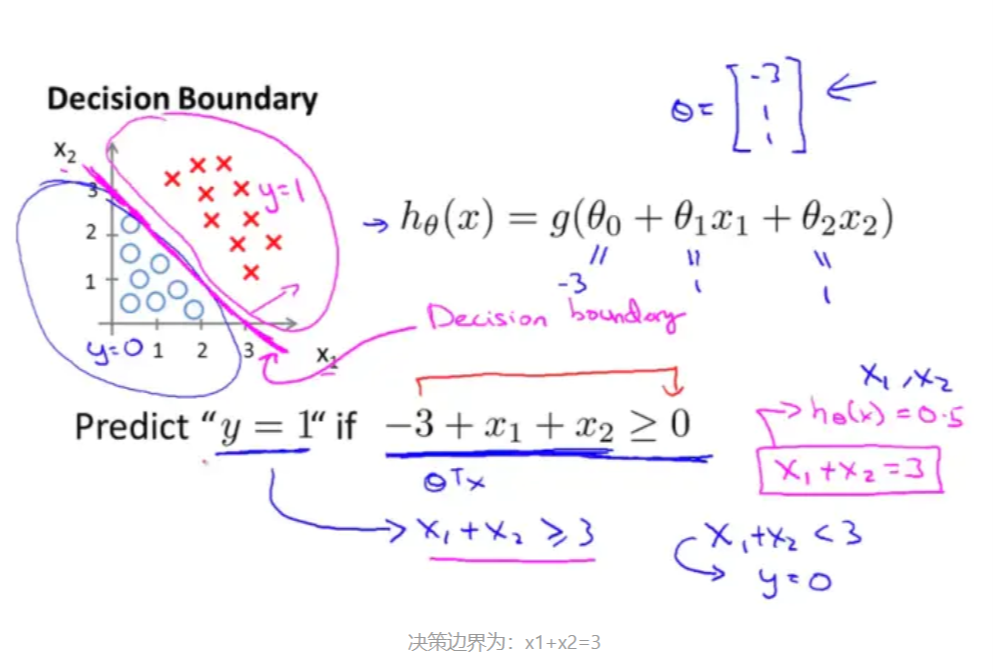
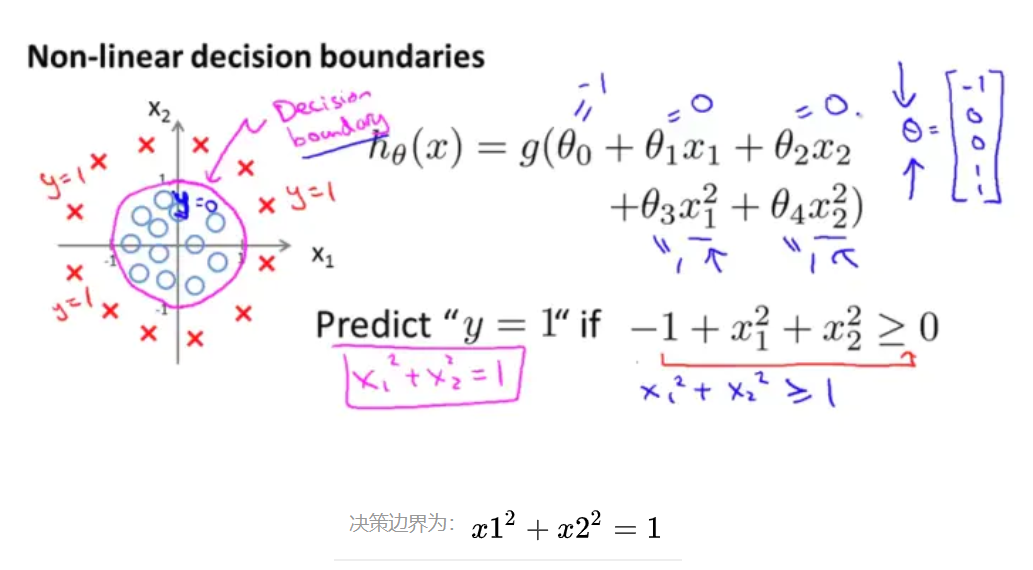
1.3.2 非线性决策边界
1.4 代价函数/损失函数
在线性回归中的代价函数为
\(J(\theta)=\frac{1}{2 m} \sum_{i=1}^{m}\left(h_{\theta}\left(x^{(i)}\right)-y^{(i)}\right)^{2}\)
- 因为它是一个凸函数,所以可用梯度下降直接求解,局部最小值即全局最小值
- 只有把函数是或者转化为凸函数,才能使用梯度下降法进行求导哦
- 在逻辑回归中,\(h_{\theta }(x)\)是一个复杂的非线性函数,属于非凸函数,直接使用梯度下降会陷入局部最小值中。类似于线性回归,逻辑回归的\(J(\theta )\)的具体求解过程如下
- 对于输入x,分类结果为类别1和类别0的概率分别为:
\(P(y=1 | x ; \theta)=h(x) ; \quad P(y=0 | x ; \theta)=1-h(x)\) - 因此化简为一个式子可以写为
\(\left.P(y | x ; \theta)=(h(x))^{y}(1-h(x))^{(} 1-y\right)\)
1.4.1 似然函数
\(\begin{aligned} L(\theta) &=\prod_{i=1}^{m} P\left(y^{(i)} | x^{(i)} ; \theta\right) \\ &=\prod_{i=1}^{m}\left(h_{\theta}\left(x^{(i)}\right)\right)^{y^{(0)}}\left(1-h_{\theta}\left(x^{(i)}\right)\right)^{1-y^{(i)}} \end{aligned}\)
似然函数取对数之后
\(\begin{aligned} l(\theta) &=\log L(\theta) \\ &=\sum_{i=1}^{m}\left(y^{(i)} \log h_{\theta}\left(x^{(i)}\right)+\left(1-y^{(i)}\right) \log \left(1-h_{\theta}\left(x^{(i)}\right)\right)\right) \end{aligned}\)
- 根据最大似然估计,需要使用梯度上升法求最大值,因此,为例能够使用梯度下降法,需要将代价函数构造成为凸函数
因此
\(J(\theta )=-\frac{1}{m} l(\theta )\)
此时可以使用梯度下降求解了 - \(\theta_{j}\)更新过程为
\(\theta_{j}:=\theta_{j}-\alpha \frac{\partial}{\partial \theta_{j}} J(\theta)\)
中间求导过程省略
\(\theta_{j}:=\theta_{j}-\alpha \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m}\left(h_{\theta}\left(\mathrm{x}^{(i)}\right)-y^{(i)}\right) x_{j}^{(i)}, \quad(j=0 \ldots n)\)
1.5正则化
损失函数中增加惩罚项:参数值越大惩罚越大–>让算法去尽量减少参数值
损失函数 \(J(β)\)的简写形式:
\(J(\beta)=\frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m} \cos (y, \beta)+\frac{\lambda}{2 m} \sum_{j=1}^{n} \beta_{j}^{2}\)
- 当模型参数 β 过多时,损失函数会很大,算法要努力减少 β 参数值来让损失函数最小。
- λ 正则项重要参数,λ 越大惩罚越厉害,模型越欠拟合,反之则倾向过拟合
1.5.1 lasso
l1正则化
\(J(\beta)=\frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{\mathrm{m}} \cos t(y, \beta)+\frac{\lambda}{2 m} \sum_{j=1}^{n}\left|\beta_{j}\right|\)
1.5.2 ridge
l2正则化
\(J(\beta)=\frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{\mathrm{m}} \cos t(y, \beta)+\frac{\lambda}{2 m} \sum_{j=1}^{n} \beta_{j}^{2}\)
1.6 python实现
class sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression(penalty='l2', dual=False, tol=0.0001, C=1.0, fit_intercept=True, intercept_scaling=1, class_weight=None, random_state=None, solver='lbfgs', max_iter=100, multi_class='auto', verbose=0, warm_start=False, n_jobs=None, l1_ratio=None
1.6.1 参数
- penalty:{‘l1’, ‘l2’, ‘elasticnet’, ‘none’}, default=’l2’ 正则项,默认是l2
- The ‘newton-cg’, ‘sag’ and ‘lbfgs’ solvers support only l2 penalties. ‘elasticnet’ is only supported by the ‘saga’ solver. If ‘none’ (not supported by the liblinear solver), no regularization is applied.LogisticRegression
- dual:bool, default=False
-Dual formulation is only implemented for l2 penalty with liblinear solver. Prefer dual=False when n_samples > n_features,一般情况下是false - tol:float, default=1e-4 阈值,迭代终止条件按
- C:float, default=1.0
- Inverse of regularization strength; must be a positive float. Like in support vector machines, smaller values specify stronger regularization,正则化强度的倒数;必须是正浮点数。与支持向量机一样,较小的值指定更强的正则化
-solver:{‘newton-cg’, ‘lbfgs’, ‘liblinear’, ‘sag’, ‘saga’}, default=’lbfgs’ - Algorithm to use in the optimization problem.
- For small datasets, ‘liblinear’ is a good choice, whereas ‘sag’ and ‘saga’ are faster for large ones.
- For multiclass problems, only ‘newton-cg’, ‘sag’, ‘saga’ and ‘lbfgs’ handle multinomial loss; ‘liblinear’ is limited to one-versus-rest schemes.
- ‘newton-cg’, ‘lbfgs’, ‘sag’ and ‘saga’ handle L2 or no penalty
- ‘liblinear’ and ‘saga’ also handle L1 penalty
- ‘saga’ also supports ‘elasticnet’ penalty
- ‘liblinear’ does not support setting penalty='none'
- Inverse of regularization strength; must be a positive float. Like in support vector machines, smaller values specify stronger regularization,正则化强度的倒数;必须是正浮点数。与支持向量机一样,较小的值指定更强的正则化
- multi_class:{‘auto’, ‘ovr’, ‘multinomial’}, default=’auto’ 这个参数是多元分类中用到的,二分类中不涉及
- If the option chosen is ‘ovr’, then a binary problem is fit for each label.
- For ‘multinomial’ the loss minimised is the multinomial loss fit across the entire probability distribution, even when the data is binary. **‘multinomial’ is unavailable when solver=’liblinear’. **
-‘auto’ selects ‘ovr’ if the data is binary, or if solver=’liblinear’, and otherwise selects ‘multinomial’.
1.6.1 属性
- classes_:ndarray of shape (n_classes, )属性数组
A list of class labels known to the classifier. - coef_:ndarray of shape (1, n_features) or (n_classes, n_features)属性和特征分类的数组
- Coefficient of the features in the decision function.
- coef_ is of shape (1, n_features) when the given problem is binary. In particular, when multi_class='multinomial', coef_ corresponds to outcome 1 (True) and -coef_ corresponds to outcome 0 (False).
- intercept_:ndarray of shape (1,) or (n_classes,)
Intercept (a.k.a. bias) added to the decision function.
If fit_intercept is set to False, the intercept is set to zero. intercept_ is of shape (1,) when the given problem is binary. In particular, when multi_class='multinomial', intercept_ corresponds to outcome 1 (True) and -intercept_ corresponds to outcome 0 (False).
n_iter_:ndarray of shape (n_classes,) or (1, )
Actual number of iterations for all classes. If binary or multinomial, it returns only 1 element. For liblinear solver, only the maximum number of iteration across all classes is given.
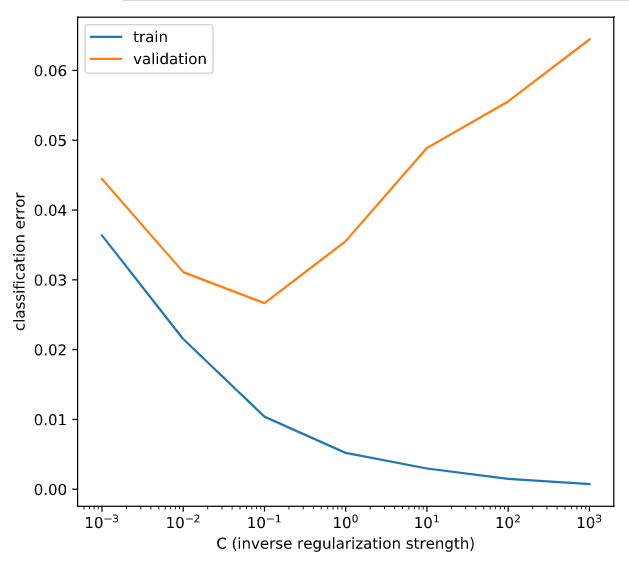
# Create LogisticRegression object and fit
lr = LogisticRegression(C=C_value)
lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Evaluate error rates and append to lists
train_errs.append( 1.0 - lr.score(X_train, y_train) )
valid_errs.append( 1.0 - lr.score(X_valid, y_valid) )
# Plot results
plt.semilogx(C_values, train_errs, C_values, valid_errs)
plt.legend(("train", "validation"))
plt.show()
二分类模型之logistic的更多相关文章
- 【AUC】二分类模型的评价指标ROC Curve
AUC是指:从一堆样本中随机抽一个,抽到正样本的概率比抽到负样本的概率大的可能性! AUC是一个模型评价指标,只能用于二分类模型的评价,对于二分类模型,还有很多其他评价指标,比如logloss,acc ...
- Logistic回归二分类Winner or Losser----台大李宏毅机器学习作业二(HW2)
一.作业说明 给定训练集spam_train.csv,要求根据每个ID各种属性值来判断该ID对应角色是Winner还是Losser(0.1分类). 训练集介绍: (1)CSV文件,大小为4000行X5 ...
- 逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)二分类原理及python实现
本文目录: 1. sigmoid function (logistic function) 2. 逻辑回归二分类模型 3. 神经网络做二分类问题 4. python实现神经网络做二分类问题 1. si ...
- Kaggle实战之二分类问题
0. 前言 1. MNIST 数据集 2. 二分类器 3. 效果评测 4. 多分类器与误差分析 5. Kaggle 实战 0. 前言 "尽管新技术新算法层出不穷,但是掌握好基础算法就能解决手 ...
- 分类模型的性能评价指标(Classification Model Performance Evaluation Metric)
二分类模型的预测结果分为四种情况(正类为1,反类为0): TP(True Positive):预测为正类,且预测正确(真实为1,预测也为1) FP(False Positive):预测为正类,但预测错 ...
- matlab 实现感知机线性二分类算法(Perceptron)
感知机是简单的线性分类模型 ,是二分类模型.其间用到随机梯度下降方法进行权值更新.参考他人代码,用matlab实现总结下. 权值求解过程通过Perceptron.m函数完成 function W = ...
- NLP(二十)利用BERT实现文本二分类
在我们进行事件抽取的时候,我们需要触发词来确定是否属于某个特定的事件类型,比如我们以政治上的出访类事件为例,这类事件往往会出现"访问"这个词语,但是仅仅通过"访问&q ...
- NLP(二十二)利用ALBERT实现文本二分类
在文章NLP(二十)利用BERT实现文本二分类中,笔者介绍了如何使用BERT来实现文本二分类功能,以判别是否属于出访类事件为例子.但是呢,利用BERT在做模型预测的时候存在预测时间较长的问题.因此 ...
- keras框架下的深度学习(二)二分类和多分类问题
本文第一部分是对数据处理中one-hot编码的讲解,第二部分是对二分类模型的代码讲解,其模型的建立以及训练过程与上篇文章一样:在最后我们将训练好的模型保存下来,再用自己的数据放入保存下来的模型中进行分 ...
随机推荐
- Spring 事件:Application Event
Spring Application Event Spring 的事件(Application Event)为 Bean 与 Bean 之间的消息通信提供了支持.当一个 Bean 处理完一个任务之后, ...
- java jdk1.8 32/64位 官方绿色版下载附安装教程
java jdk1.8 32/64位 官方绿色版下载附安装教程 地址:https://www.jb51.net/softs/691593.html
- java架构之路-(微服务专题)nacos集群精讲实战
上次回顾: 上次博客,我们主要说了微服务的发展历程和nacos集群单机的搭建,单机需要-m standalone启动,集群建议使用nginx做一下反向代理,自行保证mysql和ngxin的高可用. 本 ...
- 从Golang中open的实现方式看Golang的语言设计
Golang有很多优点: 开发高效:(C语言写一个hash查找很麻烦,但是go很简单) 运行高效:(Python的hash查找好写,但比Python高效很多) 很少的系统库依赖:(环境依赖少,一般不依 ...
- 如何开始阅读ASP.NET Core源代码
背景 当我们对ASP.Net Core内部的某些方法.类的实现感兴趣时,有很多方法可以去了解,看书,看各种文章,但是最直接也是最深入的办法就是去阅读源代码.ASP.NET Core的源代码托管在Git ...
- GNU make doc - 函数总结
$(value variable) 使用variable未展开状态的值 FOO = $(PATH) all: $(warning $(FOO)) $(warning $(value FOO)) #ou ...
- spring boot 打包jar后访问classes文件夹的文件提示地址不存在
报错内容:class path resource [client.p12] cannot be resolved to absolute file path because it does not r ...
- hadoop3自学入门笔记(2)—— HDFS分布式搭建
一些介绍 Hadoop 2和Hadoop 3的端口区别 Hadoop 3 HDFS集群架构 我的集群规划 name ip role 61 192.168.3.61 namenode,datanode ...
- CentOS、Ubuntu的安装
Linux使用最广泛的2个发行版:CentOS.Ubuntu. CentOS安全性高,常用作企业的服务器,Ubuntu常用作个人桌面. 常见的虚拟机有2个: VM VirtualBox,这个是Orac ...
- Nuget打包没有注释显示
1.选中项目-->属性-->生成-->选中 XML文档文件(xml路径和该项目相同) 2.选择生成序列化程序集:自动/开
