Vladik and Favorite Game CodeForces - 811D (思维+BFS+模拟+交互题)
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
This is an interactive problem.
Vladik has favorite game, in which he plays all his free time.
Game field could be represented as n × m matrix which consists of cells of three types:
- «.» — normal cell, player can visit it.
- «F» — finish cell, player has to finish his way there to win. There is exactly one cell of this type.
- «*» — dangerous cell, if player comes to this cell, he loses.
Initially player is located in the left top cell with coordinates (1, 1).
Player has access to 4 buttons "U", "D", "L", "R", each of them move player up, down, left and right directions respectively.
But it’s not that easy! Sometimes friends play game and change functions of buttons. Function of buttons "L" and "R" could have been swapped, also functions of buttons "U" and "D" could have been swapped. Note that functions of buttons can be changed only at the beginning of the game.
Help Vladik win the game!
First line contains two space-separated integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100) — number of rows and columns respectively.
Each of next n lines contains m characters describing corresponding row of field. Set of characters in field is described above.
Guaranteed that cell with coordinates (1, 1) is normal and there is at least one way from initial cell to finish cell without dangerous cells.
You can press buttons no more than 2·n·m times.
To press a button you should print "U", "D", "L", "R" in new line. It’s necessary to print newline character and flush output. After flushing buffer you should read answer from input data. Answer is the pair of space-separated integers x, y — new position of player. In case, if there is no cell in direction of moving, position will not change. If after any move player lost, in other words player move to dangerous cell, then x and y will be equal to - 1.
If after any move player is in finish or dangerous cell, then you should terminate your program.
To finish output buffer (i. e. for operation flush) right after printing direction and newline you should do next:
- fflush(stdout) in C++
- System.out.flush() in Java
- stdout.flush() in Python
- flush(output) in Pascal
- read documentation for other languages.
Hacks
To perform a hack you should use this format:
n m swapLR swapUD
a_1
a_2
...
a_n
Where n, m — number of rows and columns in game field. swapLR is equal to 1 in case, when directions "L’’ and "R’’ is swapped, and equal to 0 otherwise. swapUD is equal to 1, when directions "U’’ and "D’’ is swapped, and equal to 0 otherwise. a1, a2, ..., an — description of corresponding rows of game field.
4 3
...
**.
F*.
...
1 1
1 2
1 3
1 3
2 3
3 3
4 3
4 2
4 1
3 1
R
L
L
D
U
U
U
R
R
D
In first test case all four directions swapped with their opposite directions. Protocol of interaction In more convenient form:
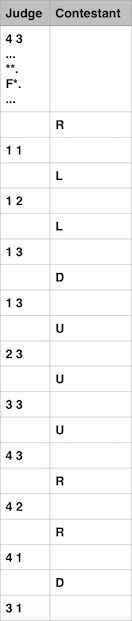
This test could be presenter for hack in following way:
4 3 1 1
...
**.
F*.
... 题意:
现在给你一个n*m大小的图,你输出一个方向之后,系统反馈给你一个坐标,表示走完这步之后到的位子,我们需要在2*n*m步之内走到终点,问怎样走才行(多解输出任意一个即可)。
我们一开始的位子是(1,1),终点位子是“F”,‘*’表示不能走的位子,游戏开始的时候,有一些小伙伴比较调皮,会将U和D互换,就是说假设我们操作了U,但是实际是走到了D.或者也可能将L和R互换,当然也可能都没有互换过,当然也可能都互换过。
然你模拟整个过程。
思路:
先根据迷宫用bfs找出一个可行路径,用pre[][]的二维数组来记录bfs中每一个位置的上一个位置。
然后从终点位置根据pre找到起点,中间的路径信息都加入栈中,然后从起点开始用栈的路径信息走向重点,
路上每一次输出一个方向的时候,如果走的结果和预期结果不一样,那么判定这个方向被恶搞了,我们做出相应的调整。
然后就根据出栈的信息一路走到终点了。
本题主要是细节过多,而且输出方向导致代码量较大,加上是交互题写起来不是很简单,希望大家多理解思路。
我的代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#define sz(a) int(a.size())
#define all(a) a.begin(), a.end()
#define rep(i,x,n) for(int i=x;i<n;i++)
#define repd(i,x,n) for(int i=x;i<=n;i++)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define pll pair<long long ,long long>
#define gbtb ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define MS0(X) memset((X), 0, sizeof((X)))
#define MSC0(X) memset((X), '\0', sizeof((X)))
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define eps 1e-6
#define gg(x) getInt(&x)
#define db(x) cout<<"== "<<x<<" =="<<endl;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
inline void getInt(int* p);
const int maxn=;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
/*** TEMPLATE CODE * * STARTS HERE ***/
int n,m;
int lrfan=;
int upfan=;
int lrok=;
int upok=;
int x,y;
char a[][];
pii pre[][];
void ask(int iiix)
{
// 1 2 3 4
// u d l r
if(iiix==)
{
if(upfan)
{
printf("D\n");
}else
{
printf("U\n");
}
}else if(iiix==)
{
if(upfan==)
{
printf("D\n");
}else
{
printf("U\n");
}
}else if(iiix==)
{
if(lrfan)
{
printf("R\n");
}else
{
printf("L\n");
}
}else
{
if(lrfan==)
{
printf("R\n");
}else
{
printf("L\n");
}
}
fflush(stdout);
scanf("%d %d",&x,&y);
}
int xx[]={,,-,};
int yy[]={,-,,};
int vis[][];
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
repd(i,,n)
{
scanf("%s",a[i]+);
}
queue<pii> q;
pre[][]=mp(-,-);
q.push(mp(,));
vis[][]=;
pii temp;
int ex,ey;
while(!q.empty())
{
temp=q.front();
q.pop();
if(a[temp.first][temp.second]=='F')
{
ex=temp.first;
ey=temp.second;
break;
// over
}
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
{
int gx=temp.fi+xx[i];
int gy=temp.second+yy[i];
if(gx>=&&gx<=n&&gy>=&&gy<=m&&vis[gx][gy]==&&a[gx][gy]=='.'||a[gx][gy]=='F')
{
q.push(mp(gx,gy));
vis[gx][gy]=;
pre[gx][gy]=temp;
}
} }
// repd(i,1,n)
// {
// repd(j,1,m)
// {
// printf("[ %d %d ] ",pre[i][j].first,pre[i][j].second);
// }
// printf("\n");
// }
stack<pii> path;
path.push(mp(ex,ey));
while(ex!=-)
{
path.push((pre[ex][ey]));
int tx=pre[ex][ey].first;
int ty=pre[ex][ey].second;
ex=tx;
ey=ty;
} int flag=;
x=;
y=;
path.pop();
path.pop();
while(flag)
{
temp=path.top();
path.pop();
int dx=x-temp.first;
int dy=y-temp.se;
if(dx==-&&dy==)
{
// 1 2 3 4
// u d l r
ask();
if(x!=temp.first||y!=temp.se)
{
upfan=;
ask();
} }else if(dx==&&dy==)
{
ask();
if(x!=temp.first||y!=temp.se)
{
upfan=;
ask();
}
}else if(dx==&&dy==-)
{
ask();
if(x!=temp.first||y!=temp.se)
{
lrfan=;
ask();
}
}else if(dx==&&dy==)
{
ask();
if(x!=temp.first||y!=temp.se)
{
lrfan=;
ask();
}
}
if(x==-||y==-||a[x][y]=='F')
{
flag=;
}
} return ;
} inline void getInt(int* p) {
char ch;
do {
ch = getchar();
} while (ch == ' ' || ch == '\n');
if (ch == '-') {
*p = -(getchar() - '');
while ((ch = getchar()) >= '' && ch <= '') {
*p = *p * - ch + '';
}
}
else {
*p = ch - '';
while ((ch = getchar()) >= '' && ch <= '') {
*p = *p * + ch - '';
}
}
}
Vladik and Favorite Game CodeForces - 811D (思维+BFS+模拟+交互题)的更多相关文章
- Vladik and Complicated Book CodeForces - 811B (思维实现)
Vladik had started reading a complicated book about algorithms containing n pages. To improve unders ...
- Codeforces 438D (今日gg模拟第二题) | 线段树 考察时间复杂度的计算 -_-|||
Codeforces 438D The Child and Sequence 给出一个序列,进行如下三种操作: 区间求和 区间每个数模x 单点修改 如果没有第二个操作的话,就是一棵简单的线段树.那么如 ...
- Codeforces 1254C/1255F Point Ordering (交互题)
题目链接 http://codeforces.com/contest/1254/problem/C 题解 sb题. 第一次,通过\((n-2)\)次询问2确定\(p[2]\),也就是从\(1\)来看& ...
- Codeforces 631A Interview【模拟水题】
题意: 模拟模拟~~ 代码: #include<iostream> using namespace std; const int maxn = 1005; int a[maxn], b[m ...
- codeforces 1019B The hat 【交互题+二分搜索】
题目链接:戳这里 学习题解:戳这里
- Codeforces 1137D - Cooperative Game - [交互题+思维题]
题目链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1137/problem/D 题意: 交互题. 给定如下一个有向图: 现在十个人各有一枚棋子(编号 $0 \sim 9$),在不 ...
- Codeforces Round #523 (Div. 2) F. Katya and Segments Sets (交互题+思维)
https://codeforces.com/contest/1061/problem/F 题意 假设存在一颗完全k叉树(n<=1e5),允许你进行最多(n*60)次询问,然后输出这棵树的根,每 ...
- BFS+模拟 ZOJ 3865 Superbot
题目传送门 /* BFS+模拟:dp[i][j][p] 表示走到i,j,方向为p的步数为多少: BFS分4种情况入队,最后在终点4个方向寻找最小值:) */ #include <cstdio&g ...
- Codeforces Round #378 (Div. 2) D题(data structure)解题报告
题目地址 先简单的总结一下这次CF,前两道题非常的水,可是第一题又是因为自己想的不够周到而被Hack了一次(或许也应该感谢这个hack我的人,使我没有最后在赛后测试中WA).做到C题时看到题目情况非常 ...
随机推荐
- docker容器持久化卷讲解
docker容器自身存储数据效率比较低,因此我们为了提高磁盘IO的性能等,需要在容器中挂载一个外部存储设备.关于讲解大致如下: Docker中的数据可以存储在类似于虚拟机磁盘的介质中,在Docker中 ...
- Spring的IOC注解开发入门1
基本知识点如下: 引入注解约束,配置组件扫描 类上的注解: @Conponent @Controller @Service @Repository 普通属性的注解 @value 对象属性的注解 ...
- MySQL初识
1.MySQL版本 社区版:免费的,功能够用. 商业版:更能更加强大,更加稳定,但是收费的. 2.每个版本都分四个版本发布 Alpha版本:一般只在开发公司内部使用,不对外公开,测试.自我检查版本: ...
- Spring获取实现某接口的所有实例bean
1.获取 applicationContext,通过ApplicationAware自动注入 2.getBeansOfType.getBeanNamesForType Map<String, I ...
- [python] os.path.join() 与 sys.path
脚本文件本地目录挂入系统环境变量 import sys, os sys.path.append(os.pardir) print(sys.path) os.getcwd()获取当前目录路径 impor ...
- 转://Oracle 单引号转义
在ORACLE中,单引号有两个作用: 1:字符串是由单引号引用 2:转义. 单引号的使用是就近配对,即就近原则.而在单引号充当转义角色时相对不好理解 1.从第二个单引号开始被视为转义符,如果第二个单引 ...
- mongodb查询的语法(大于,小于,大于或等于,小于或等于等等)
1 ) . 大于,小于,大于或等于,小于或等于 $gt:大于$lt:小于$gte:大于或等于$lte:小于或等于 例子: db.collection.find({ "field" ...
- >/dev/null 2>&1和2>&1 >/dev/null区别
>/dev/null 2>&1和2>&1 >/dev/null区别 >/dev/null 2>&1 //会将标准输出,错误输出都重定向至/d ...
- DeeplabV3+ 在自己环境下跑出现的错误
1. no module named 'deeplab' 解决办法:把 models/research 和 models/research/slim 加到环境变量path中不管用,需要在 cmd 中运 ...
- Java多线程(十)——线程优先级和守护线程
一.线程优先级的介绍 java 中的线程优先级的范围是1-10,默认的优先级是5.“高优先级线程”会优先于“低优先级线程”执行. java 中有两种线程:用户线程和守护线程.可以通过isDaemon( ...
