LeNet训练MNIST
jupyter notebook: https://github.com/Penn000/NN/blob/master/notebook/LeNet/LeNet.ipynb
LeNet训练MNIST
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # 不打印 warning
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import os
加载MNIST数据集
分别加载MNIST训练集、测试集、验证集
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
X_train, y_train = mnist.train.images, mnist.train.labels
X_test, y_test = mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels
X_validation, y_validation = mnist.validation.images, mnist.validation.labels
Extracting MNIST_data/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz Extracting MNIST_data/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz Extracting MNIST_data/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz Extracting MNIST_data/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
print("Image Shape: {}".format(X_train.shape))
print("label Shape: {}".format(y_train.shape))
print()
print("Training Set: {} samples".format(len(X_train)))
print("Validation Set: {} samples".format(len(X_validation)))
print("Test Set: {} samples".format(len(X_test)))
Image Shape: (55000, 784) label Shape: (55000, 10) Training Set: 55000 samples Validation Set: 5000 samples Test Set: 10000 samples
数据处理
由于LeNet的输入为32x32xC(C为图像通道数),而MNIST每张图像的尺寸为28x28,所以需要对图像四周进行填充,并添加一维,使得每幅图像的形状为32x32x1。
# 使用0对图像四周进行填充
X_train = np.array([np.pad(X_train[i].reshape((28, 28)), (2, 2), 'constant')[:, :, np.newaxis] for i in range(len(X_train))])
X_validation = np.array([np.pad(X_validation[i].reshape((28, 28)), (2, 2), 'constant')[:, :, np.newaxis] for i in range(len(X_validation))])
X_test = np.array([np.pad(X_test[i].reshape((28, 28)), (2, 2), 'constant')[:, :, np.newaxis] for i in range(len(X_test))])
print("Updated Image Shape: {}".format(X_train.shape))
Updated Image Shape: (55000, 32, 32, 1)
MNIST数据展示
import random import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline index = random.randint(0, len(X_train)) image = X_train[index].squeeze().reshape((32, 32)) plt.figure(figsize=(2,2)) plt.imshow(image, cmap="gray") print(y_train[index])
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0.]

LeNet网络结构

Input
The LeNet architecture accepts a 32x32xC image as input, where C is the number of color channels. Since MNIST images are grayscale, C is 1 in this case. LeNet的输入为32x32xC的图像,C为图像的通道数。在MNIST中,图像为灰度图,因此C等于1。
Architecture
Layer 1: Convolutional. 输出为28x28x6的张量。
Activation. 激活函数。
Pooling. 输出为14x14x6的张量。
Layer 2: Convolutional. 输出为10x10x16的张量。
Activation. 激活函数。
Pooling. 输出为5x5x16的张量。
Flatten. 将张量展平为一维向量,使用tf.contrib.layers.flatten可以实现。
Layer 3: Fully Connected. 输出为120长度的向量。
Activation. 激活函数。
Layer 4: Fully Connected. 输出为84长度的向量。
Activation. 激活函数。
Layer 5: Fully Connected (Logits). 输出为10长度的向量。
# 卷积层
def conv_layer(x, filter_shape, stride, name):
with tf.variable_scope(name):
W = tf.get_variable('weights', shape=filter_shape, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer())
b = tf.get_variable('biases', shape=filter_shape[-1], initializer=tf.zeros_initializer())
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=stride, padding='VALID', name=name) + b
# 全连接层
def fc_layer(x, in_size, out_size, name):
with tf.variable_scope(name):
W = tf.get_variable('weights', shape=(in_size, out_size), initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer())
b = tf.get_variable('biases', shape=(out_size), initializer=tf.zeros_initializer())
return tf.nn.xw_plus_b(x, W, b, name=name)
def relu_layer(x, name):
return tf.nn.relu(x, name=name)
from tensorflow.contrib.layers import flatten
def LeNet(x):
conv1 = conv_layer(x, filter_shape=(5, 5, 1, 6), stride=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv1')
relu1 = relu_layer(conv1, 'relu1')
max_pool1 = max_pool_layer(relu1, kernel_size=[1, 2, 2, 1], stride=[1, 2, 2, 1], name='max_pool1')
conv2 = conv_layer(max_pool1, filter_shape=(5, 5, 6, 16), stride=[1, 1, 1, 1], name='conv2')
relu2 = relu_layer(conv2, 'relu2')
max_pool2 = max_pool_layer(relu2, kernel_size=[1, 2, 2, 1], stride=[1, 2, 2, 1], name='max_pool1')
flat = flatten(max_pool2)
fc3 = fc_layer(flat, 400, 120, name='fc3')
relu3 = relu_layer(fc3, 'relu3')
fc4 = fc_layer(relu3, 120, 84, name='fc4')
relu4 = relu_layer(fc4, 'relu4')
logits = fc_layer(relu4, 84, 10, name='fc5')
return logits
TensorFlow设置
EPOCHS = 10 BATCH_SIZE = 128 log_dir = './log/' x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None, 32, 32, 1)) y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, (None, 10)) # 定义损失函数 logits = LeNet(x) cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y, logits=logits) loss = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy) train = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(loss)
训练
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
import shutil
log_dir = './logs/'
if os.path.exists(log_dir):
shutil.rmtree(log_dir)
os.makedirs(log_dir)
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(log_dir+'train/')
valid_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(log_dir+'valid/')
ckpt_path = './ckpt/'
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
n_samples = len(X_train)
step = 0
for i in range(EPOCHS):
X_train, y_train = shuffle(X_train, y_train) # 打乱数据
# 使用mini-batch训练
for offset in range(0, n_samples, BATCH_SIZE):
end = offset + BATCH_SIZE
batch_x, batch_y = X_train[offset:end], y_train[offset:end]
sess.run(train, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y})
train_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y})
train_summary = tf.Summary(value=[
tf.Summary.Value(tag="loss", simple_value=train_loss)
])
train_writer.add_summary(train_summary, step)
train_writer.flush()
step += 1
# 每个epoch使用验证集对网络进行验证
valid_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x: X_validation, y: y_validation})
valid_summary = tf.Summary(value=[
tf.Summary.Value(tag="loss", simple_value=valid_loss)
])
valid_writer.add_summary(valid_summary, step)
valid_writer.flush()
print('epoch', i, '>>> loss:', valid_loss)
# 保存模型
saver.save(sess, ckpt_path + 'model.ckpt')
print("Model saved")
epoch 0 >>> validation loss: 39.530758 epoch 1 >>> validation loss: 19.649899 epoch 2 >>> validation loss: 11.780323 epoch 3 >>> validation loss: 8.7316675 epoch 4 >>> validation loss: 6.396747 epoch 5 >>> validation loss: 5.4544454 epoch 6 >>> validation loss: 4.5326686 epoch 7 >>> validation loss: 3.5578024 epoch 8 >>> validation loss: 3.2353864 epoch 9 >>> validation loss: 3.5096574 Model saved
训练和验证的loss曲线
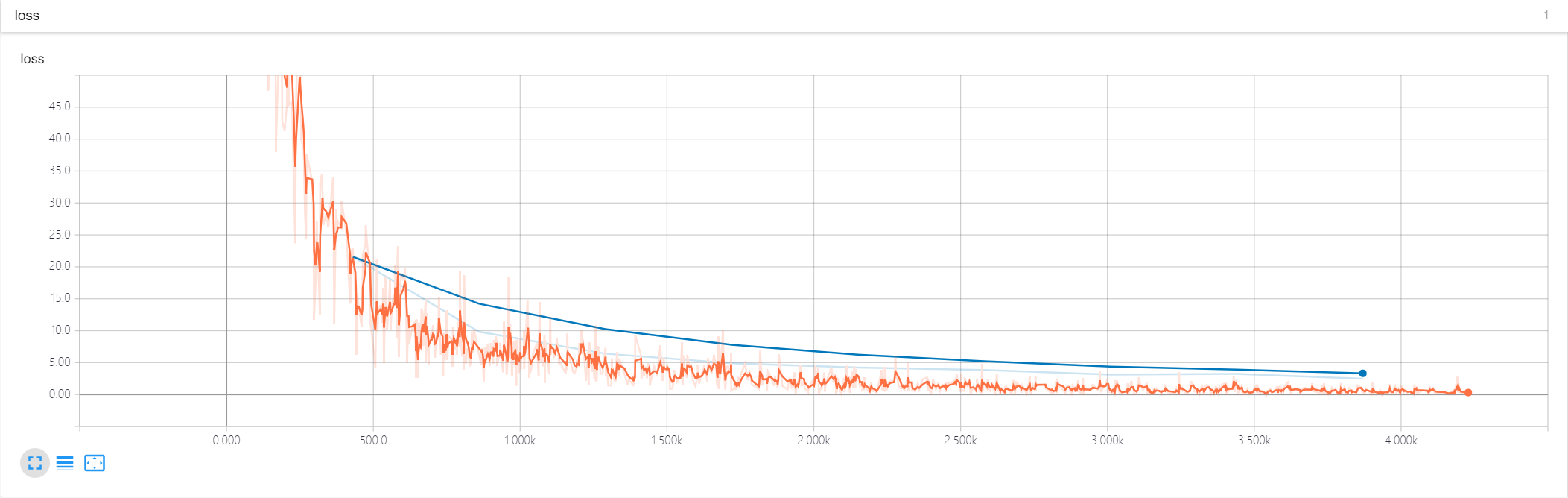
测试
correct = tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.argmax(y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct, tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver.restore(sess, tf.train.latest_checkpoint('./ckpt'))
test_accuracy = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: X_test, y: y_test})
print("Test Accuracy = {}".format(test_accuracy))
INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from ./ckpt/model.ckpt Test Accuracy = 0.9574000239372253
LeNet训练MNIST的更多相关文章
- Window10 上MindSpore(CPU)用LeNet网络训练MNIST
本文是在windows10上安装了CPU版本的Mindspore,并在mindspore的master分支基础上使用LeNet网络训练MNIST数据集,实践已训练成功,此文为记录过程中的出现问题: ( ...
- 使用caffe训练mnist数据集 - caffe教程实战(一)
个人认为学习一个陌生的框架,最好从例子开始,所以我们也从一个例子开始. 学习本教程之前,你需要首先对卷积神经网络算法原理有些了解,而且安装好了caffe 卷积神经网络原理参考:http://cs231 ...
- 实践详细篇-Windows下使用VS2015编译的Caffe训练mnist数据集
上一篇记录的是学习caffe前的环境准备以及如何创建好自己需要的caffe版本.这一篇记录的是如何使用编译好的caffe做训练mnist数据集,步骤编号延用上一篇 <实践详细篇-Windows下 ...
- CAFFE学习笔记(一)Caffe_Example之训练mnist
0.参考文献 [1]caffe官网<Training LeNet on MNIST with Caffe>; [2]薛开宇<读书笔记4学习搭建自己的网络MNIST在caffe上进行训 ...
- Caffe_Example之训练mnist
0.参考文献 [1]caffe官网<Training LeNet on MNIST with Caffe>; [2]薛开宇<读书笔记4学习搭建自己的网络MNIST在caffe上进行训 ...
- 【Caffe 测试】Training LeNet on MNIST with Caffe
Training LeNet on MNIST with Caffe We will assume that you have Caffe successfully compiled. If not, ...
- 2、TensorFlow训练MNIST
装载自:http://www.tensorfly.cn/tfdoc/tutorials/mnist_beginners.html TensorFlow训练MNIST 这个教程的目标读者是对机器学习和T ...
- TensorFlow训练MNIST报错ResourceExhaustedError
title: TensorFlow训练MNIST报错ResourceExhaustedError date: 2018-04-01 12:35:44 categories: deep learning ...
- mxnet卷积神经网络训练MNIST数据集测试
mxnet框架下超全手写字体识别—从数据预处理到网络的训练—模型及日志的保存 import numpy as np import mxnet as mx import logging logging. ...
随机推荐
- 为什么使用 Spring Boot?
Spring 是一个非常流行的基于Java语言的开发框架,此框架用来构建web和企业应用程序.与许多其他仅关注一个领域的框架不同,Spring框架提供了广泛的功能,通过其组合项目满足现代业务需求. S ...
- 基于APNs最新HTTP/2接口实现iOS的高性能消息推送(服务端篇)
1.前言 本文要分享的消息推送指的是当iOS端APP被关闭或者处于后台时,还能收到消息/信息/指令的能力. 这种在APP处于后台或关闭情况下的消息推送能力,通常在以下场景下非常有用: 1)IM即时通讯 ...
- Redis 配置内容总结
命令 Redis 的配置文件位于 Redis 安装目录下,文件名为 redis.conf. 你可以通过 CONFIG 命令查看或设置配置项. (1)config get config_setting_ ...
- display: table-cell的实用应用
概述 之前工作中碰到了一个垂直居中问题,最后通过查资料利用table-cell解决.于是打算总结一下有关table-cell的应用,记录下来,供以后开发时参考,相信对其他人也有用. 参考资料:我所知道 ...
- Kali学习笔记22:缓冲区溢出漏洞利用实验
实验机器: Kali虚拟机一台(192.168.163.133) Windows XP虚拟机一台(192.168.163.130) 如何用Kali虚拟机一步一步“黑掉”这个windowsXP虚拟机呢? ...
- Linux编程 22 shell编程(输出和输入重定向,管道,数学运算命令,退出脚本状态码)
1. 输出重定向 最基本的重定向是将命令的输出发送到一个文件中.在bash shell中用大于号(>) ,格式如下:command > inputfile.例如:将date命令的输出内容, ...
- win32程序之窗口程序,以及消息机制
win32程序值窗口程序,以及消息机制 一丶简介 通过上一讲.我们了解了窗口其实是绘制出来的.而且是不断绘制的过程. 所以窗口的本质是绘制. 但是我们现在看到的窗口程序.都可以点击关闭按钮. 使用鼠标 ...
- Chrome 浏览器最牛插件之一 Vimium
导航当页: ? 显示help,查询vimium的所有使用方法 h 向左滚动 j 向下滚动 k 向上滚动 l 向右滚动 gg 滚动到顶部 G 滚动到底部 d 向下滚动半页 u 向上滚动半页面 f 显示链 ...
- Dubbo 源码分析系列之三 —— 架构原理
1 核心功能 首先要了解Dubbo提供的三大核心功能: Remoting:远程通讯 提供对多种NIO框架抽象封装,包括"同步转异步"和"请求-响应"模式的信息交 ...
- NTP时间服务器实战应用详解-技术流ken
简介 在搭建集群服务中,要保证各节点时间一致,NTP时间服务器就成为了一个好帮手了. 系统环境 系统版本:centos6.7 服务器IP:10.220..5.166/24 客户端IP:10.220.5 ...
