python德国信用评分卡建模(附代码AAA推荐)
Minimization of risk and maximization of profit on behalf of the bank.
To minimize loss from the bank’s perspective, the bank needs a decision rule regarding who to give approval of the loan and who not to. An applicant’s demographic and socio-economic profiles are considered by loan managers before a decision is taken regarding his/her loan application.
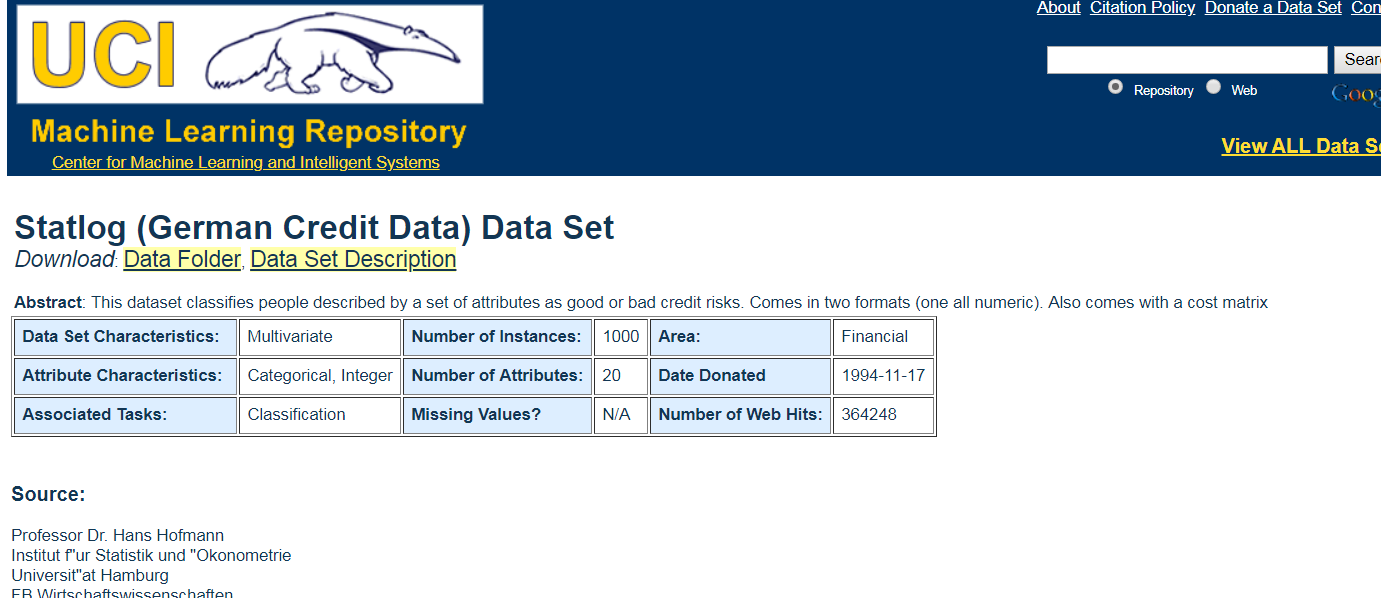
The German Credit Data contains data on 20 variables and the classification whether an applicant is considered a Good or a Bad credit risk for 1000 loan applicants. Here is a link to the German Credit data (right-click and "save as" ). A predictive model developed on this data is expected to provide a bank manager guidance for making a decision whether to approve a loan to a prospective applicant based on his/her profiles.
信用评分系统应用
http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Statlog+(German+Credit+Data)
account balance 账户余额
duration of credit

Data Set Information:
Two datasets are provided. the original dataset, in the form provided by Prof. Hofmann, contains categorical/symbolic attributes and is in the file "german.data".
For algorithms that need numerical attributes, Strathclyde University produced the file "german.data-numeric". This file has been edited and several indicator variables added to make it suitable for algorithms which cannot cope with categorical variables. Several attributes that are ordered categorical (such as attribute 17) have been coded as integer. This was the form used by StatLog.
This dataset requires use of a cost matrix (see below)
..... 1 2
----------------------------
1 0 1
-----------------------
2 5 0
(1 = Good, 2 = Bad)
The rows represent the actual classification and the columns the predicted classification.
It is worse to class a customer as good when they are bad (5), than it is to class a customer as bad when they are good (1).
Attribute Information:
Attribute 1: (qualitative)
Status of existing checking account
A11 : ... < 0 DM
A12 : 0 <= ... < 200 DM
A13 : ... >= 200 DM / salary assignments for at least 1 year
A14 : no checking account
Attribute 2: (numerical)
Duration in month
Attribute 3: (qualitative)
Credit history
A30 : no credits taken/ all credits paid back duly
A31 : all credits at this bank paid back duly
A32 : existing credits paid back duly till now
A33 : delay in paying off in the past
A34 : critical account/ other credits existing (not at this bank)
Attribute 4: (qualitative)
Purpose
A40 : car (new)
A41 : car (used)
A42 : furniture/equipment
A43 : radio/television
A44 : domestic appliances
A45 : repairs
A46 : education
A47 : (vacation - does not exist?)
A48 : retraining
A49 : business
A410 : others
Attribute 5: (numerical)
Credit amount
Attibute 6: (qualitative)
Savings account/bonds
A61 : ... < 100 DM
A62 : 100 <= ... < 500 DM
A63 : 500 <= ... < 1000 DM
A64 : .. >= 1000 DM
A65 : unknown/ no savings account
Attribute 7: (qualitative)
Present employment since
A71 : unemployed
A72 : ... < 1 year
A73 : 1 <= ... < 4 years
A74 : 4 <= ... < 7 years
A75 : .. >= 7 years
Attribute 8: (numerical)
Installment rate in percentage of disposable income
Attribute 9: (qualitative)
Personal status and sex
A91 : male : divorced/separated
A92 : female : divorced/separated/married
A93 : male : single
A94 : male : married/widowed
A95 : female : single
Attribute 10: (qualitative)
Other debtors / guarantors
A101 : none
A102 : co-applicant
A103 : guarantor
Attribute 11: (numerical)
Present residence since
Attribute 12: (qualitative)
Property
A121 : real estate
A122 : if not A121 : building society savings agreement/ life insurance
A123 : if not A121/A122 : car or other, not in attribute 6
A124 : unknown / no property
Attribute 13: (numerical)
Age in years
Attribute 14: (qualitative)
Other installment plans
A141 : bank
A142 : stores
A143 : none
Attribute 15: (qualitative)
Housing
A151 : rent
A152 : own
A153 : for free
Attribute 16: (numerical)
Number of existing credits at this bank
Attribute 17: (qualitative)
Job
A171 : unemployed/ unskilled - non-resident
A172 : unskilled - resident
A173 : skilled employee / official
A174 : management/ self-employed/
highly qualified employee/ officer
Attribute 18: (numerical)
Number of people being liable to provide maintenance for
Attribute 19: (qualitative)
Telephone
A191 : none
A192 : yes, registered under the customers name
Attribute 20: (qualitative)
foreign worker
A201 : yes
A202 : no
It is worse to class a customer as good when they are bad (5),
than it is to class a customer as bad when they are good (1).

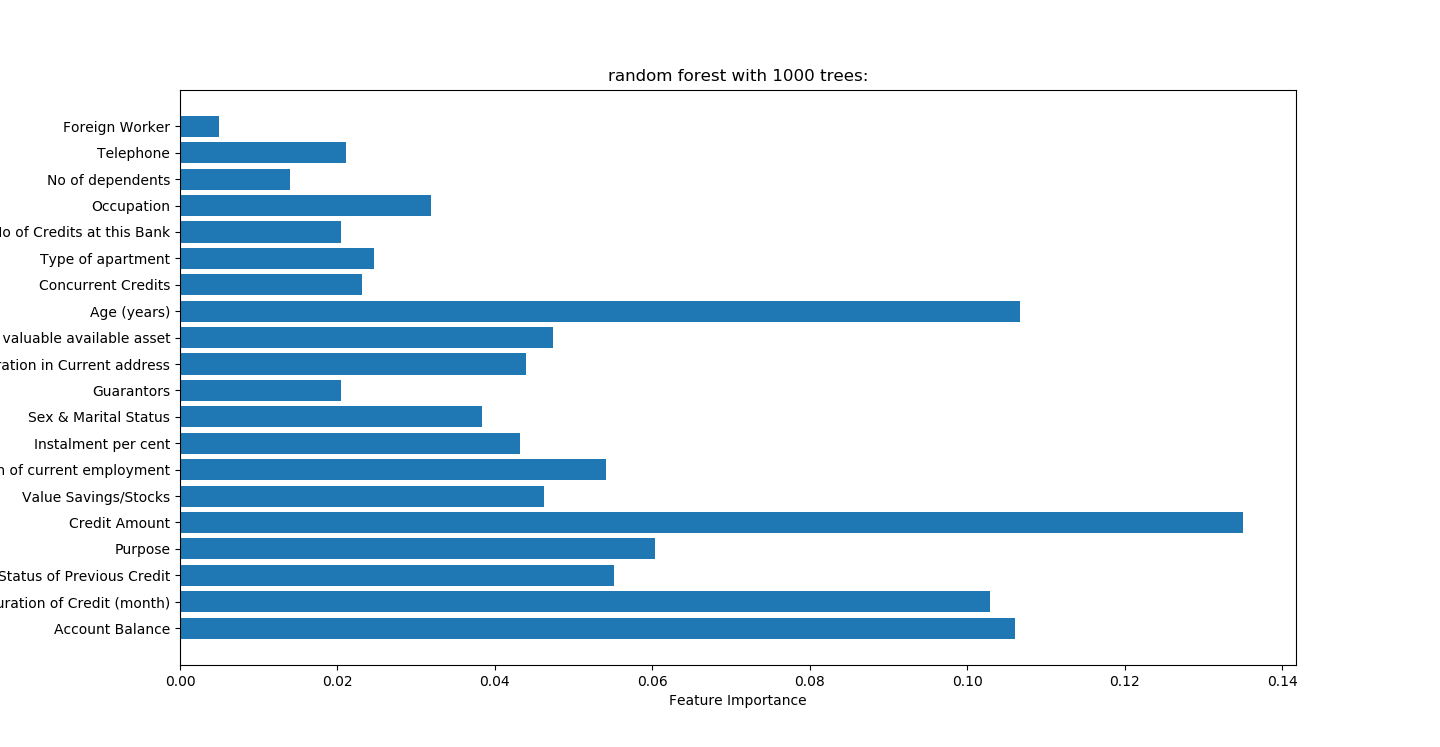
randomForest.py
random forest with 1000 trees:
accuracy on the training subset:1.000
accuracy on the test subset:0.772
准确性高于决策树
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Mar 31 09:30:24 2018 @author: Administrator
随机森林不需要预处理数据
"""
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split trees=1000
#读取文件
readFileName="German_credit.xlsx" #读取excel
df=pd.read_excel(readFileName)
list_columns=list(df.columns[:-1])
X=df.ix[:,:-1]
y=df.ix[:,-1]
names=X.columns x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,random_state=0)
#n_estimators表示树的个数,测试中100颗树足够
forest=RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=trees,random_state=0)
forest.fit(x_train,y_train) print("random forest with %d trees:"%trees)
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(forest.score(x_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(forest.score(x_test,y_test)))
print('Feature importances:{}'.format(forest.feature_importances_)) n_features=X.shape[1]
plt.barh(range(n_features),forest.feature_importances_,align='center')
plt.yticks(np.arange(n_features),names)
plt.title("random forest with %d trees:"%trees)
plt.xlabel('Feature Importance')
plt.ylabel('Feature')
plt.show()
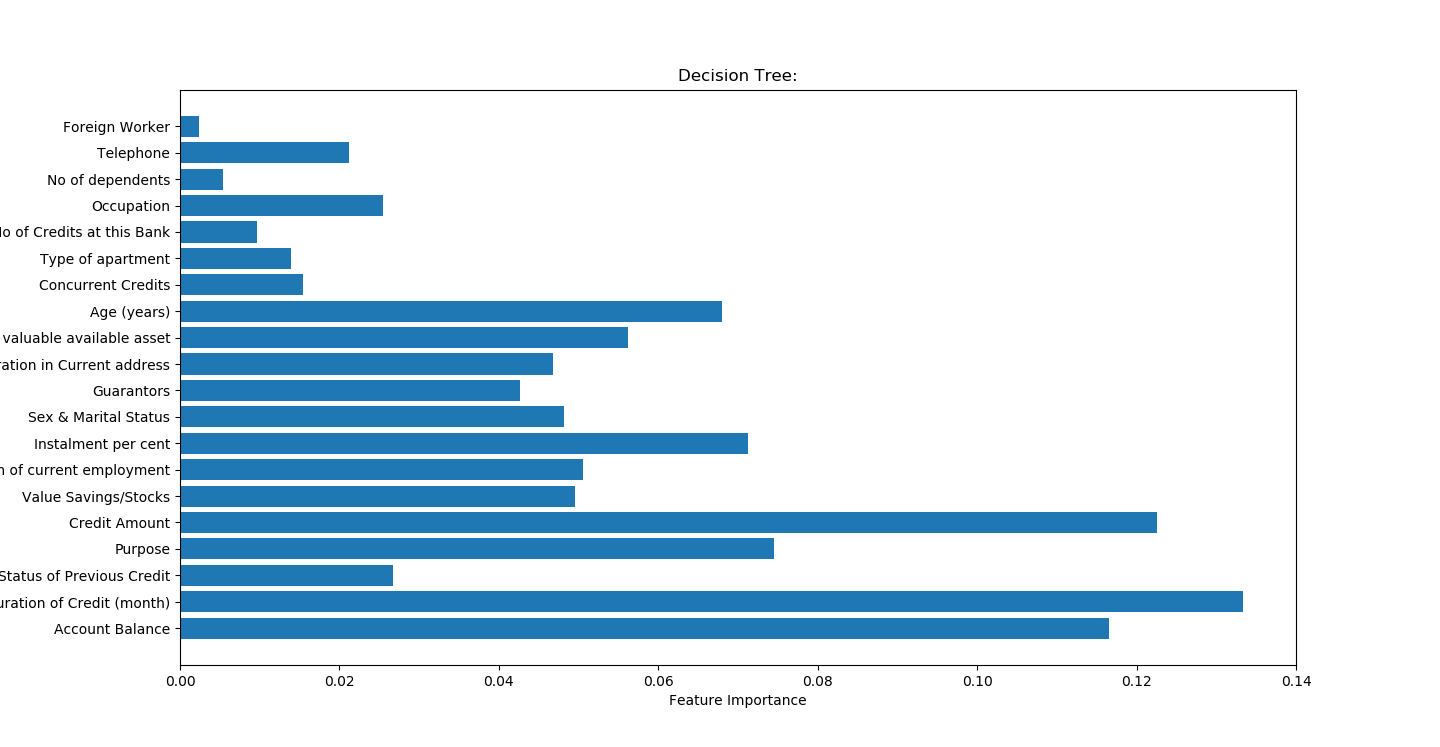
比较之前

自己绘制树图
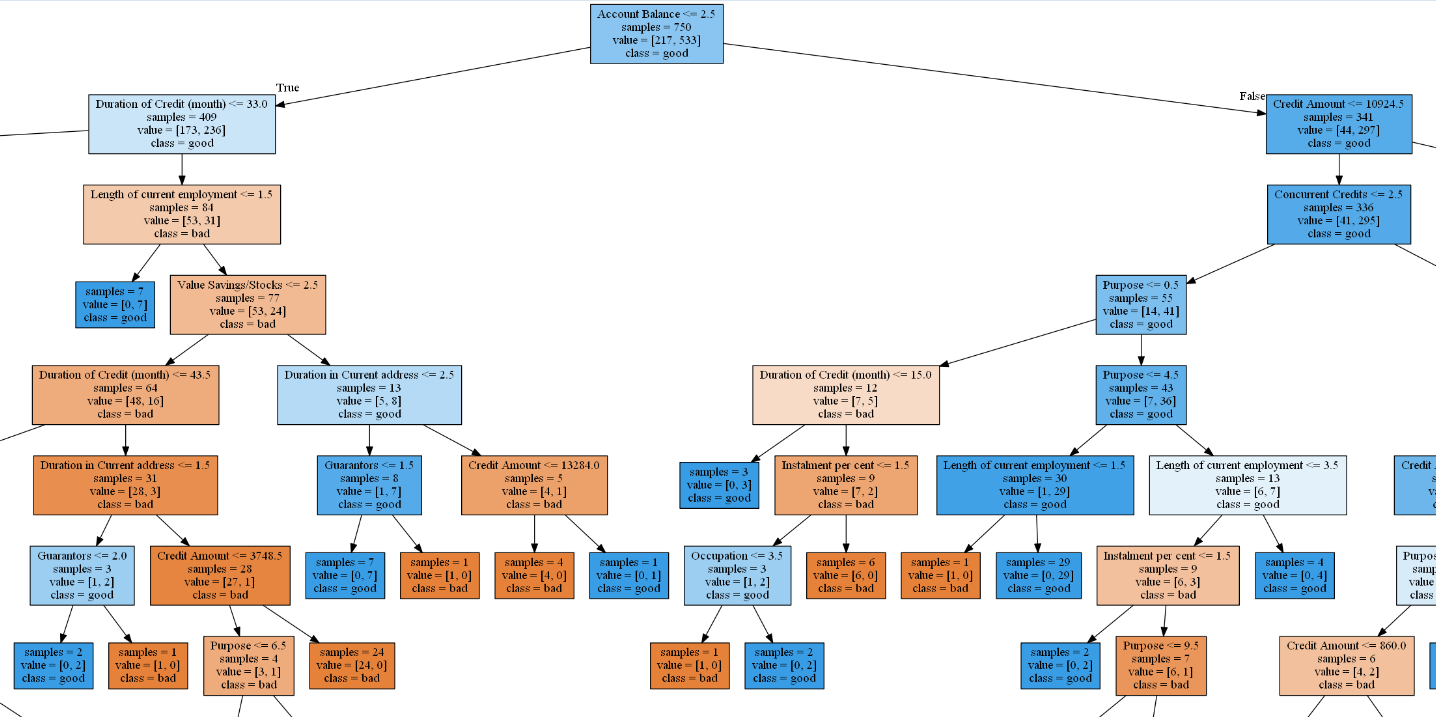
准确率不高,且严重过度拟合
accuracy on the training subset:0.991
accuracy on the test subset:0.680
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Apr 24 21:54:44 2018 @author: Administrator
""" import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pydotplus
from IPython.display import Image
import graphviz
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split trees=1000
#读取文件
readFileName="German_credit.xlsx" #读取excel
df=pd.read_excel(readFileName)
list_columns=list(df.columns[:-1])
x=df.ix[:,:-1]
y=df.ix[:,-1]
names=x.columns x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,random_state=0)
#调参
list_average_accuracy=[]
depth=range(1,30)
for i in depth:
#max_depth=4限制决策树深度可以降低算法复杂度,获取更精确值
tree= DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=i,random_state=0)
tree.fit(x_train,y_train)
accuracy_training=tree.score(x_train,y_train)
accuracy_test=tree.score(x_test,y_test)
average_accuracy=(accuracy_training+accuracy_test)/2.0
#print("average_accuracy:",average_accuracy)
list_average_accuracy.append(average_accuracy) max_value=max(list_average_accuracy)
#索引是0开头,结果要加1
best_depth=list_average_accuracy.index(max_value)+1
print("best_depth:",best_depth) best_tree= DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=best_depth,random_state=0)
best_tree.fit(x_train,y_train)
accuracy_training=best_tree.score(x_train,y_train)
accuracy_test=best_tree.score(x_test,y_test)
print("decision tree:")
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(best_tree.score(x_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(best_tree.score(x_test,y_test))) n_features=x.shape[1]
plt.barh(range(n_features),best_tree.feature_importances_,align='center')
plt.yticks(np.arange(n_features),names)
plt.title("Decision Tree:")
plt.xlabel('Feature Importance')
plt.ylabel('Feature')
plt.show() #生成一个dot文件,以后用cmd形式生成图片
export_graphviz(best_tree,out_file="creditTree.dot",class_names=['bad','good'],feature_names=names,impurity=False,filled=True) '''
best_depth: 12
decision tree:
accuracy on the training subset:0.991
accuracy on the test subset:0.680
'''
支持向量最高预测率
accuracy on the scaled training subset:0.867
accuracy on the scaled test subset:0.800
效果高于随机森林0.8-0.772=0.028
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Fri Mar 30 21:57:29 2018 @author: Administrator
SVM需要标准化数据处理
"""
#标准化数据
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd #读取文件
readFileName="German_credit.xlsx" #读取excel
df=pd.read_excel(readFileName)
list_columns=list(df.columns[:-1])
x=df.ix[:,:-1]
y=df.ix[:,-1]
names=x.columns #random_state 相当于随机数种子
X_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,stratify=y,random_state=42)
svm=SVC()
svm.fit(X_train,y_train)
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(svm.score(X_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(svm.score(x_test,y_test))) '''
accuracy on the training subset:1.000
accuracy on the test subset:0.700 ''' #观察数据是否标准化
plt.plot(X_train.min(axis=0),'o',label='Min')
plt.plot(X_train.max(axis=0),'v',label='Max')
plt.xlabel('Feature Index')
plt.ylabel('Feature magnitude in log scale')
plt.yscale('log')
plt.legend(loc='upper right') #标准化数据
X_train_scaled = preprocessing.scale(X_train)
x_test_scaled = preprocessing.scale(x_test)
svm1=SVC()
svm1.fit(X_train_scaled,y_train)
print("accuracy on the scaled training subset:{:.3f}".format(svm1.score(X_train_scaled,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the scaled test subset:{:.3f}".format(svm1.score(x_test_scaled,y_test)))
'''
accuracy on the scaled training subset:0.867
accuracy on the scaled test subset:0.800
''' #改变C参数,调优,kernel表示核函数,用于平面转换,probability表示是否需要计算概率
svm2=SVC(C=10,gamma="auto",kernel='rbf',probability=True)
svm2.fit(X_train_scaled,y_train)
print("after c parameter=10,accuracy on the scaled training subset:{:.3f}".format(svm2.score(X_train_scaled,y_train)))
print("after c parameter=10,accuracy on the scaled test subset:{:.3f}".format(svm2.score(x_test_scaled,y_test)))
'''
after c parameter=10,accuracy on the scaled training subset:0.972
after c parameter=10,accuracy on the scaled test subset:0.716
''' #计算样本点到分割超平面的函数距离
#print (svm2.decision_function(X_train_scaled)) #print (svm2.decision_function(X_train_scaled)[:20]>0)
#支持向量机分类
#print(svm2.classes_) #malignant和bening概率计算,输出结果包括恶性概率和良性概率
#print(svm2.predict_proba(x_test_scaled))
#判断数据属于哪一类,0或1表示
#print(svm2.predict(x_test_scaled))
神经网络
效果不如支持向量和随机森林
最好概率
accuracy on the training subset:0.916
accuracy on the test subset:0.720

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Apr 1 11:49:50 2018 @author: Administrator
神经网络需要预处理数据
"""
#Multi-layer Perceptron 多层感知机
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
#标准化数据,否则神经网络结果不准确,和SVM类似
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import mglearn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd #读取文件
readFileName="German_credit.xlsx" #读取excel
df=pd.read_excel(readFileName)
list_columns=list(df.columns[:-1])
x=df.ix[:,:-1]
y=df.ix[:,-1]
names=x.columns #random_state 相当于随机数种子
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,stratify=y,random_state=42)
mlp=MLPClassifier(random_state=42)
mlp.fit(x_train,y_train)
print("neural network:")
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(mlp.score(x_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(mlp.score(x_test,y_test))) scaler=StandardScaler()
x_train_scaled=scaler.fit(x_train).transform(x_train)
x_test_scaled=scaler.fit(x_test).transform(x_test) mlp_scaled=MLPClassifier(max_iter=1000,random_state=42)
mlp_scaled.fit(x_train_scaled,y_train)
print("neural network after scaled:")
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(mlp_scaled.score(x_train_scaled,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(mlp_scaled.score(x_test_scaled,y_test))) mlp_scaled2=MLPClassifier(max_iter=1000,alpha=1,random_state=42)
mlp_scaled2.fit(x_train_scaled,y_train)
print("neural network after scaled and alpha change to 1:")
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(mlp_scaled2.score(x_train_scaled,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(mlp_scaled2.score(x_test_scaled,y_test))) #绘制颜色图,热图
plt.figure(figsize=(20,5))
plt.imshow(mlp_scaled.coefs_[0],interpolation="None",cmap="GnBu")
plt.yticks(range(30),names)
plt.xlabel("columns in weight matrix")
plt.ylabel("input feature")
plt.colorbar() '''
neural network:
accuracy on the training subset:0.700
accuracy on the test subset:0.700
neural network after scaled:
accuracy on the training subset:1.000
accuracy on the test subset:0.704
neural network after scaled and alpha change to 1:
accuracy on the training subset:0.916
accuracy on the test subset:0.720
'''
xgboost
区分能力还可以
AUC: 0.8134
ACC: 0.7720
Recall: 0.9521
F1-score: 0.8480
Precesion: 0.7644
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Apr 24 22:42:47 2018 @author: Administrator
出现module 'xgboost' has no attribute 'DMatrix'的临时解决方法
初学者或者说不太了解Python才会犯这种错误,其实只需要注意一点!不要使用任何模块名作为文件名,任何类型的文件都不可以!我的错误根源是在文件夹中使用xgboost.*的文件名,当import xgboost时会首先在当前文件中查找,才会出现这样的问题。
所以,再次强调:不要用任何的模块名作为文件名!
"""
import xgboost as xgb
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pylab as plt #读取文件
readFileName="German_credit.xlsx" #读取excel
df=pd.read_excel(readFileName)
list_columns=list(df.columns[:-1])
x=df.ix[:,:-1]
y=df.ix[:,-1]
names=x.columns train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y=train_test_split(x,y,random_state=0) dtrain=xgb.DMatrix(train_x,label=train_y)
dtest=xgb.DMatrix(test_x) params={'booster':'gbtree',
#'objective': 'reg:linear',
'objective': 'binary:logistic',
'eval_metric': 'auc',
'max_depth':4,
'lambda':10,
'subsample':0.75,
'colsample_bytree':0.75,
'min_child_weight':2,
'eta': 0.025,
'seed':0,
'nthread':8,
'silent':1} watchlist = [(dtrain,'train')] bst=xgb.train(params,dtrain,num_boost_round=100,evals=watchlist) ypred=bst.predict(dtest) # 设置阈值, 输出一些评价指标
y_pred = (ypred >= 0.5)*1 #模型校验
from sklearn import metrics
print ('AUC: %.4f' % metrics.roc_auc_score(test_y,ypred))
print ('ACC: %.4f' % metrics.accuracy_score(test_y,y_pred))
print ('Recall: %.4f' % metrics.recall_score(test_y,y_pred))
print ('F1-score: %.4f' %metrics.f1_score(test_y,y_pred))
print ('Precesion: %.4f' %metrics.precision_score(test_y,y_pred))
metrics.confusion_matrix(test_y,y_pred) print("xgboost:")
#print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(bst.get_score(train_x,train_y)))
#print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(bst.get_score(test_x,test_y)))
print('Feature importances:{}'.format(bst.get_fscore())) '''
AUC: 0.8135
ACC: 0.7640
Recall: 0.9641
F1-score: 0.8451
Precesion: 0.7523 #特征重要性和随机森林差不多
Feature importances:{'Account Balance': 80, 'Duration of Credit (month)': 119,
'Most valuable available asset': 54, 'Payment Status of Previous Credit': 84,
'Value Savings/Stocks': 66, 'Age (years)': 94, 'Credit Amount': 149,
'Type of apartment': 20, 'Instalment per cent': 37,
'Length of current employment': 70, 'Sex & Marital Status': 29,
'Purpose': 67, 'Occupation': 13, 'Duration in Current address': 25,
'Telephone': 15, 'Concurrent Credits': 23, 'No of Credits at this Bank': 7,
'Guarantors': 28, 'No of dependents': 6}
'''
最终结论:
xgboost 有时候特征重要性分析比随机森林还准确,可见其强大之处
随机森林重要因子排序 xgboost权重指数
Credit amount信用保证金 149
age 年龄 94
account balance 账户余额 80
duration of credit持卡时间 119 (信用卡逾期时间,每个银行有所不同,以招商银行为例,两个月就会被停卡)
2018-9-18数据更新
逻辑回归验证数据和catboost验证数据差不多,可见逻辑回归稳定性
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
作者邮箱 231469242@qq.com 技术文档
https://www.cnblogs.com/webRobot/p/7216614.html
model accuracy is: 0.755
model precision is: 0.697841726618705
model sensitivity is: 0.3233333333333333
f1_score: 0.44191343963553525
AUC: 0.7626619047619048 根据iv值删除后预测结果没有变量完全保留的高
model accuracy is: 0.724
model precision is: 0.61320754717
model sensitivity is: 0.216666666667
f1_score: 0.320197044335
AUC: 0.7031
good classifier 带入German_credit原始数据结果
accuracy on the training subset:0.777
accuracy on the test subset:0.740
A: 6.7807190511263755
B: 14.426950408889635
model accuracy is: 0.74
model precision is: 0.7037037037037037
model sensitivity is: 0.38
f1_score: 0.49350649350649356
AUC: 0.7885
"""
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model.logistic import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.cross_validation import cross_val_score
import statsmodels.api as sm
#混淆矩阵计算
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc,roc_auc_score
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.metrics import recall_score
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score #df_german=pd.read_excel("german_woe.xlsx")
df_german=pd.read_excel("german_credit.xlsx")
#df_german=pd.read_excel("df_after_vif.xlsx")
y=df_german["target"]
x=df_german.ix[:,"Account Balance":"Foreign Worker"]
#x=df_german.ix[:,"Credit Amount":"Purpose"]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=0) classifier = LogisticRegression()
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions = classifier.predict(X_test) #验证
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(classifier.score(X_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(classifier.score(X_test,y_test))) #得分公式
'''
P0 = 50
PDO = 10
theta0 = 1.0/20
B = PDO/np.log(2)
A = P0 + B*np.log(theta0)
'''
def Score(probability):
#底数是e
score = A-B*np.log(probability/(1-probability))
return score
#批量获取得分
def List_score(pos_probablity_list):
list_score=[]
for probability in pos_probablity_list:
score=Score(probability)
list_score.append(score)
return list_score P0 = 50
PDO = 10
theta0 = 1.0/20
B = PDO/np.log(2)
A = P0 + B*np.log(theta0)
print("A:",A)
print("B:",B)
list_coef = list(classifier.coef_[0])
intercept= classifier.intercept_ #获取所有x数据的预测概率,包括好客户和坏客户,0为好客户,1为坏客户
probablity_list=classifier.predict_proba(x)
#获取所有x数据的坏客户预测概率
pos_probablity_list=[i[1] for i in probablity_list]
#获取所有客户分数
list_score=List_score(pos_probablity_list)
list_predict=classifier.predict(x)
df_result=pd.DataFrame({"label":y,"predict":list_predict,"pos_probablity":pos_probablity_list,"score":list_score}) df_result.to_excel("score_proba.xlsx") #变量名列表
list_vNames=df_german.columns
#去掉第一个变量名target
list_vNames=list_vNames[1:]
df_coef=pd.DataFrame({"variable_names":list_vNames,"coef":list_coef})
df_coef.to_excel("coef.xlsx") y_true=y_test
y_pred=classifier.predict(X_test)
accuracyScore = accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)
print('model accuracy is:',accuracyScore) #precision,TP/(TP+FP) (真阳性)/(真阳性+假阳性)
precision=precision_score(y_true, y_pred)
print('model precision is:',precision) #recall(sensitive)敏感度,(TP)/(TP+FN)
sensitivity=recall_score(y_true, y_pred)
print('model sensitivity is:',sensitivity) #F1 = 2 x (精确率 x 召回率) / (精确率 + 召回率)
#F1 分数会同时考虑精确率和召回率,以便计算新的分数。可将 F1 分数理解为精确率和召回率的加权平均值,其中 F1 分数的最佳值为 1、最差值为 0:
f1Score=f1_score(y_true, y_pred)
print("f1_score:",f1Score) def AUC(y_true, y_scores):
auc_value=0
#auc第二种方法是通过fpr,tpr,通过auc(fpr,tpr)来计算AUC
fpr, tpr, thresholds = metrics.roc_curve(y_true, y_scores, pos_label=1)
auc_value= auc(fpr,tpr) ###计算auc的值
#print("fpr:",fpr)
#print("tpr:",tpr)
#print("thresholds:",thresholds)
if auc_value<0.5:
auc_value=1-auc_value
return auc_value def Draw_roc(auc_value):
fpr, tpr, thresholds = metrics.roc_curve(y, list_score, pos_label=0)
#画对角线
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], '--', color=(0.6, 0.6, 0.6), label='Diagonal line')
plt.plot(fpr,tpr,label='ROC curve (area = %0.2f)' % auc_value)
plt.title('ROC curve')
plt.legend(loc="lower right") #评价AUC表现
def AUC_performance(AUC):
if AUC >=0.7:
print("good classifier")
if 0.7>AUC>0.6:
print("not very good classifier")
if 0.6>=AUC>0.5:
print("useless classifier")
if 0.5>=AUC:
print("bad classifier,with sorting problems") #Auc验证,数据采用测试集数据
auc_value=AUC(y, list_score)
print("AUC:",auc_value)
#评价AUC表现
AUC_performance(auc_value)
#绘制ROC曲线
Draw_roc(auc_value)
catboost脚本
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
作者邮箱 231469242@qq.com 技术文档
https://www.cnblogs.com/webRobot/p/7216614.html
catboost-
accuracy on the training subset:1.000
accuracy on the test subset:0.763
test数据指标
accuracy on the test subset:0.757
model accuracy is: 0.7566666666666667
model precision is: 0.813953488372093
model sensitivity is: 0.35
f1_score: 0.48951048951048953
AUC: 0.7595999999999999
"""
import catboost as cb
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model.logistic import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.cross_validation import cross_val_score
import statsmodels.api as sm
#混淆矩阵计算
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc,roc_auc_score
from sklearn.metrics import precision_score
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.metrics import recall_score
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score #df_german=pd.read_excel("german_woe.xlsx")
df_german=pd.read_excel("german_credit.xlsx")
#df_german=pd.read_excel("df_after_vif.xlsx")
y=df_german["target"]
x=df_german.ix[:,"Account Balance":"Foreign Worker"]
#x=df_german.ix[:,"Credit Amount":"Purpose"]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=0) classifier = cb.CatBoostClassifier()
classifier.fit(X_train, y_train) list_score=classifier.predict_proba(X_test)
list_score=[i[1] for i in list_score] #验证
print("accuracy on the training subset:{:.3f}".format(classifier.score(X_train,y_train)))
print("accuracy on the test subset:{:.3f}".format(classifier.score(X_test,y_test))) list_predict=classifier.predict(x)
y_true=y_test
y_pred=classifier.predict(X_test)
accuracyScore = accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)
print('model accuracy is:',accuracyScore) #precision,TP/(TP+FP) (真阳性)/(真阳性+假阳性)
precision=precision_score(y_true, y_pred)
print('model precision is:',precision) #recall(sensitive)敏感度,(TP)/(TP+FN)
sensitivity=recall_score(y_true, y_pred)
print('model sensitivity is:',sensitivity) #F1 = 2 x (精确率 x 召回率) / (精确率 + 召回率)
#F1 分数会同时考虑精确率和召回率,以便计算新的分数。可将 F1 分数理解为精确率和召回率的加权平均值,其中 F1 分数的最佳值为 1、最差值为 0:
f1Score=f1_score(y_true, y_pred)
print("f1_score:",f1Score) def AUC(y_true, y_scores):
auc_value=0
#auc第二种方法是通过fpr,tpr,通过auc(fpr,tpr)来计算AUC
fpr, tpr, thresholds = metrics.roc_curve(y_true, y_scores, pos_label=1)
auc_value= auc(fpr,tpr) ###计算auc的值
#print("fpr:",fpr)
#print("tpr:",tpr)
#print("thresholds:",thresholds)
if auc_value<0.5:
auc_value=1-auc_value
return auc_value #Auc验证,数据采用测试集数据
auc_value=AUC(y_test, list_score)
print("AUC:",auc_value)
sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博主亲自录制视频)
https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&utm_campaign=commission&utm_source=cp-400000000398149&utm_medium=share
欢迎关注博主主页,学习python视频资源,还有大量免费python经典文章

机器学习,统计项目可联系QQ:231469242
python德国信用评分卡建模(附代码AAA推荐)的更多相关文章
- 基于Python的信用评分卡模型分析(二)
上一篇文章基于Python的信用评分卡模型分析(一)已经介绍了信用评分卡模型的数据预处理.探索性数据分析.变量分箱和变量选择等.接下来我们将继续讨论信用评分卡的模型实现和分析,信用评分的方法和自动评分 ...
- 基于Python的信用评分卡模型分析(一)
信用风险计量体系包括主体评级模型和债项评级两部分.主体评级和债项评级均有一系列评级模型组成,其中主体评级模型可用“四张卡”来表示,分别是A卡.B卡.C卡和F卡:债项评级模型通常按照主体的融资用途,分为 ...
- 信用评分卡 (part 4 of 7)
python信用评分卡(附代码,博主录制) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005214003&utm_camp ...
- 信用评分卡 (part 2of 7)
python信用评分卡(附代码,博主录制) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005214003&utm_camp ...
- 信用评分卡 (part 1 of 7)
python信用评分卡(附代码,博主录制) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005214003&utm_camp ...
- 信用评分卡 (part 7 of 7)
python信用评分卡(附代码,博主录制) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005214003&utm_camp ...
- 信用评分卡 (part 6 of 7)
python信用评分卡(附代码,博主录制) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005214003&utm_camp ...
- 信用评分卡 (part 5 of 7)
python信用评分卡(附代码,博主录制) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005214003&utm_camp ...
- 信用评分卡 (part 3of 7)
python信用评分卡(附代码,博主录制) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005214003&utm_camp ...
随机推荐
- 洛谷P1395 会议 题解
$题目$ 为什么这个题会有图论的标签啊,虽然图论也包括找树的重心,可是这很容易让人联想到最短路,但不得不说,这是一个典型的找树的重心模板题. 树的重心是什么? 找到一个点,其所有的子树中最大的子树节点 ...
- 杨辉三角(java实现)
package lizi; import java.util.Scanner; public class Yanghui { private static Scanner input; public ...
- Matplotlib学习---用seaborn画直方图,核密度图(histogram, kdeplot)
由于直方图受组距(bin size)影响很大,设置不同的组距可能会产生完全不同的可视化结果.因此我们可以用密度平滑估计来更好地反映数据的真实特征.具体可参见这篇文章:https://blog.csdn ...
- 【UOJ349】【WC2018】即时战略 LCT 动态点分治
这是一道交互题 题目大意 有一棵\(n\)个点的树.最开始\(1\)号点是白的,其他点是黑的. 每次你可以执行一个操作:\(explore(x,y)\).要求\(x\)是一个白点.该函数会返回从\(x ...
- #565. 「LibreOJ Round #10」mathematican 的二进制(期望 + 分治NTT)
题面 戳这里,题意简单易懂. 题解 首先我们发现,操作是可以不考虑顺序的,因为每次操作会加一个 \(1\) ,每次进位会减少一个 \(1\) ,我们就可以考虑最后 \(1\) 的个数(也就是最后的和) ...
- python3 集合set
set是一种集合的数据类型,使用{}表示 集合中元素是无序的,并且不可重复,集合最重要的作用就是可以去重 set是不可哈希的,set中的元素必须是可哈希的 可以切片,可以迭代 交集.并集.差集.对称差 ...
- 【BZOJ4890】[TJOI2017]城市(动态规划)
[BZOJ4890][TJOI2017]城市(动态规划) 题面 BZOJ 洛谷 题解 数据范围都这样了,显然可以暴力枚举断开哪条边. 然后求出两侧直径,暴力在直径上面找到一个点,使得其距离直径两端点的 ...
- 【UOJ#236】[IOI2016]railroad(欧拉回路,最小生成树)
[UOJ#236][IOI2016]railroad(欧拉回路,最小生成树) 题面 UOJ 题解 把速度看成点,给定的路段看成边,那么现在就有了若干边,然后现在要补上若干边,以及一条\([inf,\) ...
- iptables(2)
MASQUERADE同样是做源地址转换,只不过防火墙会根据该策略自动查找可用的公网IP地址,适应变化的情况•若接口使用ppp+,表示匹配ppp0.ppp1……中任意可用的拨号连接•若需要演示操作,可以 ...
- LVS负载均衡集群(DR)
-----构建DR模式的LVS群集----- --client---------------------LVS------------------------WEB1----------------- ...