Deep Learning Tutorial - Multilayer perceptron
Multilayer perceptron:多层感知器
本节实现两层网络(一个隐层)作为分类器实现手写数字分类。引入的内容:激活函数(双曲正切、L1和L2正则化)、Theano的共享变量、grad、floatX等。损失函数和错误率沿用了上一节的LogisticRegression类。本节没有使用反向传播来更新参数,用的依旧是损失函数对参数求导(梯度下降法)。网络隐层的激活函数为tanh,输出层即采用LogisticRegression。更新参数的机制:损失函数为LogisticRegression中的损失函数+两层网络的正则化的和,参数为两层分别的W和b。
要点如下:
1.初始化权重,众所周知在使用sigmoid激活函数时权重初始为零可能导致学习缓慢、隐层神经元的饱和。有许多方法初始化权重,文中给出:
当激活函数为双曲正切时 :W取值为 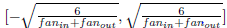 之间。
之间。
当激活函数为sigmoid时:W取值为: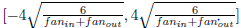 之间。
之间。
2.网络中的超参数一般来说不能用梯度下降法优化,严格地讲,找到这些参数的最优解不可行。首先,我们不能简单地独立的优化它们中的每一个参数,其次不能应用之前的梯度下降法,最后优化问题非凸很难找到局部最小值。一个好的解决办法是反向传播,由Yann LeCun提出的。
3.学习速率:简单的解决办法是设为定值,随着时间减小学习速率有时也很好,一个简单的法则是μ0/(1+d*t),μ0为初始设置的速率,d称为衰减常数控制衰减速率(10e-3或更小),t为迭代周期数。
总体代码如下:
# coding=UTF-8
# 两层网络、sgd优化(非bp)、early-stopping策略
import os
import sys
import timeit
import numpy
import theano
import theano.tensor as T
from Logistic_sgd import LogisticRegression, load_data #导入上一节的代码作为输出层 class HiddenLayer(object): #隐层类
def __init__(self, rng, input, n_in, n_out, W=None, b=None, activation=T.tanh):
self.input = input
if W is None:
W_values = numpy.asarray( #W非初始化为零
rng.uniform(
low=-numpy.sqrt(6. / (n_in + n_out)),
high=numpy.sqrt(6. / (n_in + n_out)),
size=(n_in, n_out)), dtype=theano.config.floatX)
if activation == theano.tensor.nnet.sigmoid:
W_values *= 4
W = theano.shared(value=W_values, name='W', borrow=True)
if b is None: #b初始化为零
b_values = numpy.zeros((n_out), dtype=theano.config.floatX)
b = theano.shared(value=b_values, name='b',borrow=True)
self.W = W
self.b = b
lin_output = T.dot(input, self.W) + self.b
self.output = (lin_output if activation is None else activation(lin_output))
self.params = [self.W, self.b] class MLP(object): #输出层
def __init__(self, rng, input, n_in, n_hidden, n_out):
self.hiddenLayer = HiddenLayer(rng=rng, input=input, n_in=n_in, n_out=n_hidden, activation=T.tanh)
self.logRegressionLayer = LogisticRegression(input=self.hiddenLayer.output, n_in=n_hidden, n_out=n_out) #引入输出层
self.L1 = (abs(self.hiddenLayer.W).sum()+ abs(self.logRegressionLayer.W).sum())
self.L2_sqr = ((self.hiddenLayer.W ** 2).sum() + (self.logRegressionLayer.W ** 2).sum()) #L1,L2正则化
self.negative_log_likelihood = (self.logRegressionLayer.negative_log_likelihood)
self.errors = self.logRegressionLayer.errors
self.params = self.hiddenLayer.params + self.logRegressionLayer.params #参数包括隐层和输出层
self.input = input def test_mlp(learning_rate=0.01, L1_reg=0.00, L2_reg=0.0001, n_epochs=1000,
dataset='data/mnist.pkl.gz', batch_size=20, n_hidden=500):
datasets = load_data(dataset)
train_set_x, train_set_y = datasets[0]
valid_set_x, valid_set_y = datasets[1]
test_set_x, test_set_y = datasets[2]
n_train_batches = train_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] / batch_size
n_valid_batches = valid_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] / batch_size
n_test_batches = test_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] / batch_size
print '...building the model'
index = T.lscalar()
x = T.matrix('x')
y = T.ivector('y')
rng = numpy.random.RandomState(1234) #随机数
classifier = MLP(rng=rng, input=x, n_in=28 * 28, n_hidden=n_hidden, n_out=10) #分类器
cost = (classifier.negative_log_likelihood(y) + L1_reg * classifier.L1 + L2_reg * classifier.L2_sqr) #损失函数
test_model = theano.function(inputs=[index], outputs=classifier.errors(y), #测试模型
givens={x: test_set_x[index * batch_size:(index + 1) * batch_size],
y: test_set_y[index * batch_size:(index + 1) * batch_size]})
validate_model = theano.function(inputs=[index], outputs=classifier.errors(y), #验证模型
givens={x: valid_set_x[index * batch_size:(index + 1) * batch_size],
y: valid_set_y[index * batch_size:(index + 1) * batch_size]})
gparams = [T.grad(cost, param) for param in classifier.params]
updates = [(param, param - learning_rate * gparam) for param, gparam in zip(classifier.params, gparams)]
train_model = theano.function(inputs=[index], outputs=cost, updates=updates, #训练模型
givens={x: train_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: train_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]})
print '...training'
patience = 10000 #early stopping策略
patience_increase = 2
improvement_threshold = 0.995
validation_frequency = min(n_train_batches, patience / 2)
best_validation_loss = numpy.inf
best_iter = 0
test_score = 0.
start_time = timeit.default_timer()
epoch = 0
done_looping = False
while (epoch < n_epochs) and (not done_looping): #迭代优化过程(以下注释和上一节相同)
epoch = epoch + 1
for minibatch_index in xrange(n_train_batches):
minibatch_avg_cost = train_model(minibatch_index)
iter = (epoch - 1) * n_train_batches + minibatch_index
if (iter + 1) % validation_frequency == 0:
validation_losses = [validate_model(i) for i in xrange(n_valid_batches)]
this_validation_loss = numpy.mean(validation_losses)
print('epoch %i, minibatch %i / %i, validation error %f %%' % (
epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches, this_validation_loss * 100.))
if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss:
if (this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss * improvement_threshold):
patience = max(patience, iter * patience_increase)
best_validation_loss = this_validation_loss #最优解对应的验证损失值
best_iter = iter #最优解对应的迭代次数
test_losses = [test_model(i) for i in xrange(n_test_batches)]
test_score = numpy.mean(test_losses)
print(('epoch %i, minibatch %i / %i, test error of''best model %f %%') % (
epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches, test_score * 100.))
if patience <= iter:
done_looping = True
break
end_time = timeit.default_timer()
print(
('Optimization compelete.Best validation scores of % %%''obtained at iteration %i,with test performance %f %%')
% (best_validation_loss * 100., best_iter + 1, test_score * 100.)) if __name__ == '__main__':
test_mlp()
Deep Learning Tutorial - Multilayer perceptron的更多相关文章
- Deep Learning Tutorial - Classifying MNIST digits using Logistic Regression
Deep Learning Tutorial 由 Montreal大学的LISA实验室所作,基于Theano的深度学习材料.Theano是一个python库,使得写深度模型更容易些,也可以在GPU上训 ...
- 深度学习材料:从感知机到深度网络A Deep Learning Tutorial: From Perceptrons to Deep Networks
In recent years, there’s been a resurgence in the field of Artificial Intelligence. It’s spread beyo ...
- Deep Learning Tutorial - Convolutional Neural Networks(LENET)
CNN很多概述和要点在CS231n.Neural Networks and Deep Learning中有详细阐述,这里补充Deep Learning Tutorial中的内容.本节前提是前两节的内容 ...
- 读《Deep Learning Tutorial》(台湾大学 李宏毅 深度学习教学ppt)后杂记
原ppt下载:pan.baidu.com/s/1nv54p9R,密码:3mty 需深入实践并理解的重要概念: Deep Learning: SoftMax Fuction(输出层归一化函数,与sigm ...
- Deep Learning Tutorial
http://www.slideshare.net/tw_dsconf/ss-62245351?qid=c0f0f97a-6ca8-4df0-97e2-984452215ee7&v=& ...
- 读李宏毅《一天看懂深度学习》——Deep Learning Tutorial
大牛推荐的入门用深度学习导论,刚拿到有点懵,第一次接触PPT类型的学习资料,但是耐心看下来收获还是很大的,适合我这种小白入门哈哈. 原PPT链接:http://www.slideshare.net/t ...
- Deep Learning Tutorial 李宏毅(一)深度学习介绍
大纲 深度学习介绍 深度学习训练的技巧 神经网络的变体 展望 深度学习介绍 深度学习介绍 深度学习属于机器学习的一种.介绍深度学习之前,我们先大致了解一下机器学习. 机器学习,拿监督学习为例,其本质上 ...
- Deep Learning(深度学习)学习笔记整理
申明:本文非笔者原创,原文转载自:http://www.sigvc.org/bbs/thread-2187-1-3.html 4.2.初级(浅层)特征表示 既然像素级的特征表示方法没有作用,那怎样的表 ...
- 【转载】Deep Learning(深度学习)学习笔记整理
http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09/article/details/8775360 一.概述 Artificial Intelligence,也就是人工智能,就像长生不老和星际漫 ...
随机推荐
- -bash: /tyrone/jdk/jdk1.8.0_91/bin/java: cannot execute binary file
问题描述:今天在linux环境下安装了一下JDK,安装成功后,打算输入java -version去测试一下,结果却出错了. 错误信息:-bash: /tyrone/jdk/jdk1.8.0_91/bi ...
- 2017-12-15python全栈9期第二天第七节之布尔值转数字
#!/user/bin/python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-print(int(True))print(int(False))
- Python 排序和numpy排序,得到排序后索引序列(及源list的序列)
Python list 排序 & np list 排序 nums = [1.25, 0.98, 6.13, 7.62] li = np.array(nums) print(li) out = ...
- Journal Storage Directory not formatted
类型一: 当你从异常信息中看到JournalNode not formatted,如果在异常中看到三个节点都提示需要格式化JournalNode. 如果你是新建集群,你可以重新格式化NameNode, ...
- JAVA核心技术I---JAVA基础知识(格式化相关类)
一:格式化相关类 (一)java.text包java.text.Format的子类 –NumberFormat:数字格式化,抽象类 DecimalFormat –MessageFormat:字符串格式 ...
- Hudson持续集成管理平台搭建
IP: 10.0.70.106 8G 内存 (Hudson 多 个 工程 在 同 时 构建 的情况下 比 较耗内存) 环 境: CentOS 6.5 . JDK7 注:Hudson 只是一个持续集成 ...
- vs code配置git
在项目目录执行 git init 修改.git文件夹下的config文件 [core] repositoryformatversion = 0 filemode = false bare = fals ...
- 细说tomcat之类加载器
官网:http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-7.0-doc/class-loader-howto.htmlJava类加载与Tomcat类加载器层级关系对比 Java Clas ...
- MySQL C API概述
以下列表总结了C API中可用的功能.有关更多详细信息,请参见 第27.8.7节“C API函数描述”中的说明. my_init():在线程安全程序中初始化全局变量和线程处理程序 mysql_affe ...
- DotNetBar的一个MDIView不正常显示的问题
现象,使用tabStrip MDIView后,子窗体会被遮挡一部分,两种解决办法 1.tabStrip的 MdiAutoHide=False 2.tabStrip 设置MultilineWithNav ...
