02----python入门----基本数据类型
关于数据分类依据

一、数字型(int)
Python可以处理任意大小的正负整数,但是实际中跟我们计算机的内存有关,在32位机器上,整数的位数为32位,取值范围为-2**31~2**31-1,在64位系统上,整数的位数为64位,取值范围为-2**63~2**63-1。对于int类型,需要掌握的方法不多,看下面的几个例子:
Number 类型转换 |
|
| 语法 | 描述 |
int(x [,base ]) |
将x转换为一个整数 |
long(x [,base ]) |
将x转换为一个长整数 |
float(x ) |
将x转换到一个浮点数 |
complex(real [,imag ]) |
创建一个复数 |
str(x ) |
将对象 x 转换为字符串 |
repr(x ) |
将对象 x 转换为表达式字符串 |
eval(str ) |
用来计算在字符串中的有效Python表达式,并返回一个对象 |
tuple(s ) |
将序列 s 转换为一个元组 |
list(s ) |
将序列 s 转换为一个列表 |
chr(x ) |
将一个整数转换为一个字符 |
unichr(x ) |
将一个整数转换为Unicode字符 |
ord(x ) |
将一个字符转换为它的ascii码 |
hex(x ) |
将一个整数转换为一个十六进制字符串 |
oct(x ) |
将一个整数转换为一个八进制字符串 |
数字方法 |
|||
| 方法名 | 描述 | 语法 | 参数 |
| abs() | 返回数字的绝对值 |
abs( x ) |
x -- 数值表达式 |
print "abs(-45) : ", abs(-45) |
|||
| ceil() |
返回数字的上入整数,类似高斯函数 需要导入 math 模块,通过静态对象调用该方法 |
import math math.ceil( x ) |
x -- 数值表达式 |
import math # This will import math module print "math.ceil(-45.17) : ", math.ceil(-45.17) |
|||
| exp() |
返回x的指数 -> ex 需要导入 math 模块,通过静态对象调用该方法 |
import math math.exp( x ) |
x -- 数值表达式 |
import math # 导入 math 模块 print "math.exp(-45.17) : ", math.exp(-45.17) |
|||
| fabs() |
返回数字的绝对值 需要导入 math 模块,通过静态对象调用该方法 |
import math math.fabs( x ) |
x -- 数值表达式 |
import math # 导入数学模块 print "math.fabs(-45.17) : ", math.fabs(-45.17) |
|||
| floor() |
返回数字的下舍整数,与ceil相反 需要导入 math 模块,通过静态对象调用该方法 |
import math math.floor( x ) |
x -- 数值表达式 |
import math # This will import math module print "math.floor(-45.17) : ", math.floor(-45.17) |
|||
| log() |
返回 x 的自然对数 需要导入 math 模块,通过静态对象调用该方法 |
import math math.log(x[, base]) |
x -- 数值表达式。 base -- 可选底数,默认为 e |
import math # 导入 math 模块 print "math.log(100.12) : ", math.log(100.12) |
|||
| log10() |
返回以10为基数的x对数 需要导入 math 模块,通过静态对象调用该方法 |
import math math.log10( x ) |
x -- 数值表达式 |
print "math.log10(100.12) : ", math.log10(100.12) |
|||
| max() | 返回给定参数的最大值,参数可以为序列 |
max( x, y, z, .... ) |
x -- 数值表达式 y -- 数值表达式 z -- 数值表达式 |
print "max(80, 100, 1000) : ", max(80, 100, 1000) |
|||
| min() | 返回给定参数的最小值,参数可以为序列 |
min( x, y, z, .... ) |
x -- 数值表达式 y -- 数值表达式 z -- 数值表达式 |
print "min(80, 100, 1000) : ", min(80, 100, 1000) |
|||
| modf() |
返回x的整数部分与小数部分 两部分的数值符号与x相同,整数部分以浮点型表示 导入 math 模块,通过静态对象调用该方法 |
import math math.modf( x ) |
x -- 数值表达式 |
import math # This will import math module print "math.modf(100.12) : ", math.modf(100.12) |
|||
| pow() |
返回 xy(x的y次方) 的值 导入 math 模块,通过静态对象调用该方法 |
import math math.pow( x, y ) |
x -- 数值表达式 y -- 数值表达式 |
import math # 导入 math 模块 print "math.pow(100, 2) : ", math.pow(100, 2) |
|||
| round() | 返回浮点数x的四舍五入值 |
round( x [, n] ) |
x -- 数值表达式 n -- 数值表达式 |
print "round(80.23456, 2) : ", round(80.23456, 2) |
|||
| sqrt() |
返回数字x的平方根 需要导入 math 模块,通过静态对象调用该方法 |
import math math.sqrt( x ) |
x -- 数值表达式 |
import math # This will import math module print "math.sqrt(100) : ", math.sqrt(100) |
|||
随机数函数 |
|||
| 方法名 | 描述 | 语法 | 参数 |
| choice() |
返回一个列表,元组或字符串的随机项 需要导入 random 模块,然后通过 random 静态对象调用该方法 |
import random random.choice( seq ) |
seq -- 可以是一个列表,元组或字符串 |
import random
print ("从 range(100) 返回一个随机数 : ",random.choice(range(100)))
|
|||
| randrange() |
返回指定递增基数集合中的一个随机数,基数默认值为1 需要导入 random 模块,然后通过 random 静态对象调用该方法。 |
import random random.randrange ([start,] stop [,step]) |
start -- 指定范围内的开始值,包含在范围内。 stop -- 指定范围内的结束值,不包含在范围内。 step -- 指定递增基数。 |
import random # 从 1-100 中选取一个奇数 |
|||
| random() |
在[0,1)范围内,随机生成的一个实数 需要导入 random 模块,然后通过 random 静态对象调用该方法 |
import random random.random() |
无 |
import random # 第一个随机数 |
|||
| seed() |
改变随机数生成器的种子,可以在调用其他随机模块函数之前调用此函数 需要导入 random 模块,然后通过 random 静态对象调用该方法 |
import random random.seed ( [x] ) |
x -- 改变随机数生成器的种子seed 如果你不了解其原理,你不必特别去设定seed,Python会帮你选择seed |
import random random.seed() |
|||
| shuffle() |
将序列的所有元素随机排序 需要导入 random 模块,然后通过 random 静态对象调用该方法 |
import random random.shuffle (lst ) |
lst -- 列表 |
import random list = [20, 16, 10, 5]; |
|||
| uniform() |
随机生成下一个实数,它在 [x,y] 范围内 需要导入 random 模块,然后通过 random 静态对象调用该方法 |
import random random.uniform(x, y) |
x -- 随机数的最小值 y -- 随机数的最大值 |
import random
print ("uniform(5, 10) 的随机浮点数 : ", random.uniform(5, 10))
print ("uniform(7, 14) 的随机浮点数 : ", random.uniform(7, 14))
'''
|
|||
二、字符串(str)
字符串系列的小函数有很多,以下暂列几个
字符串方法 |
|||
| 方法名 | 描述 | 语法 | 参数 |
| capitalize() |
将字符串的第一个字母变成大写,其他字母变小写该方法。 返回一个首字母大写的字符串 |
s.capitalize() |
无 |
1 >>>s = 'a, B' |
|||
| center() |
原字符串居中,并使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串。 默认填充字符为空格。 |
s.center(width[, fillchar]) |
width -- 字符串的总宽度
fillchar -- 填充字符 |
1 >>>str = 'runoob' |
|||
| count() |
用于统计字符串里某个字符出现的次数。 可选参数为在字符串搜索的开始与结束位置。 |
s.count(sub, start= 0,end=len(string)) |
sub -- 搜索的子字符串
start -- 字符串开始搜索的位置。默认为第一个字符,第一个字符索引值为0 end -- 字符串中结束搜索的位置。字符中第一个字符的索引为 0。默认为字符串的最后一个位置 |
1 >>>str = 'national day' |
|||
| decode() |
encoding 指定的编码格式解码字符串。 默认编码为字符串编码。 |
s.decode(encoding='UTF-8',errors='strict') |
encoding -- 要使用的编码,如"UTF-8" errors -- 设置不同错误的处理方案。默认为 'strict',意为编码错误引起一个UnicodeError。 其他可能得值有 'ignore', 'replace', 'xmlcharrefreplace', 'backslashreplace' 以及通过 codecs.register_error() 注册的任何值 |
1 >>>str = "this is string example....wow!!!" |
|||
| encode() |
以 encoding 指定的编码格式编码字符串。 errors参数可以指定不同的错误处理方案。 |
s.encode(encoding='UTF-8',errors='strict') |
encoding -- 要使用的编码,如"UTF-8"
errors -- 设置不同错误的处理方案。默认为 'strict',意为编码错误引起一个UnicodeError。 其他可能得值有 'ignore', 'replace', 'xmlcharrefreplace', 'backslashreplace' 以及通过 codecs.register_error() 注册的任何值 |
1 >>>str = "this is string example....wow!!!" |
|||
| endswith() |
判断字符串是否以指定后缀结尾,如果是则返回True,否则返回False 可选参数"start"与"end"为检索字符串的开始与结束位置。 |
s.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) |
suffix -- 该参数可以是一个字符串或者是一个元素
start -- 字符串中的开始位置 end -- 字符中结束位置 |
1 >>>str = "this is string example....wow!!!" |
|||
|
expandtabs() |
把字符串中的 tab 符号('\t')转为空格, tab 符号('\t')默认的空格数是 8 |
s.expandtabs(tabsize=8) |
tabsize -- 指定转换字符串中的 tab 符号('\t')转为空格的字符数。 |
1 >>>str = "this is\tstring example....wow!!!" |
|||
| find() |
检测字符串中是否包含子字符串 str 可指定范围,若含子字符串返回索引值,否则返回-1 |
s.find(str, beg=0, end=len(string)) |
str -- 指定检索的字符串
beg -- 开始索引,默认为0。 end -- 结束索引,默认为字符串的长度。 |
1 >>>str1 = "this is string example....wow!!!" |
|||
|
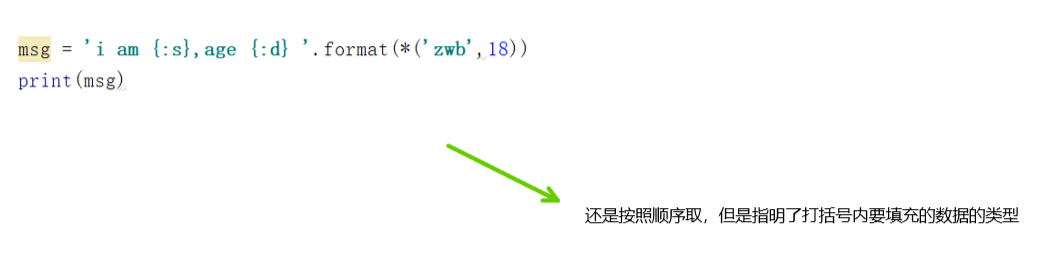
format() |
通过 {} 和 : 来代替以前的 % format 函数可以接受不限个参数,位置可以不按顺序 |
s.format(*args, **kwargs) |
|
1 >>>"{} {}".format("hello", "world") # 不设置指定位置,按默认顺序
1 print("网站名:{name}, 地址 {url}".format(name="菜鸟教程", url="www.runoob.com"))
1 #str.format() 格式化数字 1 #使用大括号 {} 来转义大括号
|
|||
| index() |
检测字符串中是否包含子字符串 str 可指定范围,类似find(),如果不在就报错 |
s.index(str, beg=0, end=len(string)) |
str -- 指定检索的字符串
beg -- 开始索引,默认为0。 end -- 结束索引,默认为字符串的长度。 |
1 >>>str1 = "this is string example....wow!!!" |
|||
| isalnum() | 检测字符串是否由字母和数字组成 |
s.isalnum() |
无 |
1 >>>str = "this2009" # 字符中没有空格 |
|||
| isalpha() | 检测字符串是否只由字母组成 |
s.isalpha() |
无 |
1 str = "runoob" |
|||
| isdigit() | 检测字符串是否只由数字组成 |
s.isdigit() |
无 |
1 >>>str = "123456" # Only digit in this string |
|||
| isdecimal() |
检查字符串是否只包含十进制字符 |
s.isdecimal() |
无 |
str = "runoob2016" |
|||
| islower() |
检测字符串是否由小写字母组成 |
s.islower() |
无 |
1 >>>str = "THIS is string example....wow!!!" |
|||
| isnumeric() |
检测字符串是否只由数字组成 只针对unicode对象 定义一个字符串为Unicode,只需要在字符串前添加 'u' 前缀即可 |
s.isnumeric() |
无 |
1 >>>str = u"this2009" |
|||
|
isspace() |
检测字符串是否只由空格组成 |
s.isspace() |
无 |
1 >>>str = " " |
|||
|
istitle() |
检测字符串中所有的单词拼写首字母是否为大写,且其他字母为小写 |
s.istitle() |
无 |
1 >>>str = "This Is String Example...Wow!!!" |
|||
| isupper() | 检测字符串中所有的字母是否都为大写 |
s.isupper() |
无 |
1 >>>str = "THIS IS STRING EXAMPLE....WOW!!!"; |
|||
| join() | 将序列中的元素以指定的字符连接生成一个新的字符串 |
s.join(sequence) |
sequence -- 要连接的元素序列 |
1 >>>str = "-" |
|||
| len() | 返回对象(字符、列表、元组等)长度或项目个数 |
len( s ) |
s -- 对象 |
1 >>>str = "runoob" |
|||
| ljust() |
返回一个原字符串左对齐,默认使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 如果指定的长度小于原字符串的长度则返回原字符串。 |
s.ljust(width[, fillchar]) |
width -- 指定字符串长度。 fillchar -- 填充字符,默认为空格。 |
1 >>>str = "this is string example....wow!!!" |
|||
| lower() | 转换字符串中所有大写字符为小写 |
s.lower() |
无 |
1 >>>str = "THIS IS STRING EXAMPLE....WOW!!!" |
|||
| lstrip() | 截掉字符串左边的空格或指定字符 |
s.lstrip([chars]) |
chars --指定截取的字符 |
1 >>>str = " this is string example....wow!!! " |
|||
| maketrans() |
创建字符映射的转换表 两个字符串的长度必须相同,一一对应 |
s.maketrans(intab, outtab) |
intab -- 字符串中要替代的字符组成的字符串 outtab -- 相应的映射字符的字符串 |
1 >>>intab = "aeiou" |
|||
| max() | 返回字符串中最大的字母 |
max(str) |
str -- 字符串 |
1 >>>str = "this is really a string example....wow!!!" |
|||
| min() | 返回字符串中最小的字母 |
min(str) |
str -- 字符串 |
1 >>>str = "this-is-real-string-example....wow!!!" |
|||
| partition() |
根据指定的分隔符将字符串进行分割 如果字符串包含指定的分隔符,则返回一个3元的元组,第一个为分隔符左边的子串,第二个为分隔符本身,第三个为分隔符右边的子串 |
s.partition(str) |
str -- 指定的分隔符 |
1 >>>str = "www.runoob.com" |
|||
| replace() |
把旧字符串替换成新字符串 可指定替换次数 |
s.replace(old, new[, max]) |
old -- 将被替换的子字符串。 new -- 新字符串,用于替换old子字符串。 max -- 可选字符串, 替换不超过 max 次 |
1 >>>str = "this is string example....wow!!! this is really string" |
|||
| rfind() |
返回字符串最后一次出现的位置(从右向左查询), 如果没有匹配项则返回-1 |
s.rfind(str, beg=0 end=len(string)) |
str -- 查找的字符串 beg -- 开始查找的位置,默认为 0 end -- 结束查找位置,默认为字符串的长度。 |
1 >>>str = "this is really a string example....wow!!!" |
|||
| rindex() |
返回子字符串 str 在字符串中最后出现的位置 可指定范围,如果没有匹配的字符串会报异常 |
s.rindex(str, beg=0 end=len(string)) |
str -- 查找的字符串 beg -- 开始查找的位置,默认为0 end -- 结束查找位置,默认为字符串的长度。 |
1 >>>str1 = "this is string example....wow!!!" |
|||
| rjust() |
返回一个原字符串右对齐,默认使用空格填充至长度 width 的新字符串 如果指定的长度小于字符串的长度则返回原字符串。 |
s.rjust(width[, fillchar]) |
width -- 指定填充指定字符后中字符串的总长度. fillchar -- 填充的字符,默认为空格。 |
1 >>>str = "this is string example....wow!!!" |
|||
| rstrip() | 截掉字符串右边的空格或指定字符 |
s.rstrip([chars]) |
chars -- 指定删除的字符(默认为空格) |
1 >>>str = " this is string example....wow!!! " |
|||
| split() |
通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片 如果参数 num 有指定值,则分隔num处 |
s.split(str="", num=string.count(str)) |
str -- 分隔符,默认为所有的空字符,包括空格、换行(\n)、制表符(\t)等。 num -- 分割次数。默认为 -1, 即分隔所有。 |
1 >>>str = "Line1-abcdef \nLine2-abc \nLine4-abcd" |
|||
| splitlines() |
按照行('\r', '\r\n', \n')分隔 默认不保留换行符,若参数为 True,则保留 |
s.splitlines([keepends]) |
keepends -- 明确输出结果内是否保留换行符,默认为 False,不保留,若为 True,则保留。 |
1 >>>str1 = 'ab c\n\nde fg\rkl\r\n' |
|||
| startswith() |
检查字符串是否是以指定子字符串开头 可指定范围 |
s.startswith(str, beg=0,end=len(string)) |
str -- 检测的字符串。 strbeg -- 可设置字符串检测的起始位置。 strend -- 可设置字符串检测的结束位置。 |
1 >>>str = "this is string example....wow!!!" |
|||
| strip() |
移除字符串头尾指定的字符 默认为空格或换行符,可设置为字符序列 |
s.strip([chars]) |
chars -- 移除字符串头尾指定的字符序列 |
1 >>>str = "00000003210Runoob01230000000" |
|||
| swapcase() | 对字符串的大小写字母进行转换 |
s.swapcase() |
无 |
1 >>>str = "this is string example....wow!!!" |
|||
| title() | 所有单词都是以大写开始,其余字母均为小写 |
s.title() |
无 |
1 >>>str = "this is string example....wow!!!" |
|||
| translate() |
根据给出的表转换字符 要过滤掉的字符放到 del 参数中 |
s.translate(table[, deletechars]) |
table -- 翻译表,通过maketrans转换而deletechars -- 字符串中要过滤的字符列表 |
1 >>>intab = "aeiou" |
|||
| upper() | 将字符串中的小写字母转为大写字母 |
s.upper() |
无 |
1 >>>str = "this is string example....wow!!!" |
|||
格式化输入
百分号拼接字符串
print ("我叫 %s 今年 %d 岁!" % ('小明', 10))
'''
我叫 小明 今年 10 岁!
'''
'''
%c 格式化字符及其ASCII码
%s 格式化字符串
%d 格式化整数
%u 格式化无符号整型
%o 格式化无符号八进制数
%x 格式化无符号十六进制数
%X 格式化无符号十六进制数(大写)
%f 格式化浮点数字,可指定小数点后的精度
%e 用科学计数法格式化浮点数
%E 作用同%e,用科学计数法格式化浮点数
%g %f和%e的简写
%G %f 和 %E 的简写
%p 用十六进制数格式化变量的地址 '''
python字符串格式化符号


format字符串格式化






python三引号允许一个字符串跨多行,字符串中可以包含换行符、制表符以及其他特殊字符
para_str = """这是一个多行字符串的实例
多行字符串可以使用制表符
TAB ( \t )。
也可以使用换行符 [ \n ]。
""" print (para_str) '''
这是一个多行字符串的实例
多行字符串可以使用制表符
TAB ( )。
也可以使用换行符 [
]。 '''
三、列表(list)
列表是Python内置的一种数据类型是列表,是一种有序的集合,可以随时添加和删除其中的元素。
列表方法 |
|||
| 方法名 | 描述 | 语法 | 参数 |
| cmp() |
比较两个列表的元素 如果比较的元素是同类型的,则比较其值,返回结果 如果两个元素不是同一种类型,则检查它们是否是数字 两方全是数字则转换成int值比较,一方是数字则它小 否则,通过类型名字的字母顺序进行比较 |
cmp(list1, list2) |
st1 -- 比较的列表。 list2 -- 比较的列表 |
>>>list1, list2 = [123, 'xyz'], [456, 'abc'] >>>print(cmp(list1, list2)) |
|||
| len() | 返回列表元素个数 |
len(list) |
list -- 要计算元素个数的列表 |
>>>list1, list2 = [123, 'xyz', 'zara'], [456, 'abc']
>>>print("First list length : ", len(list1))
|
|||
| max() | 返回列表元素中的最大值 |
max(list) |
list -- 要返回最大值的列表 |
>>>list1, list2 = ['123', 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc'], [456, 700, 200]
>>>print("Max value element : ", max(list1))
|
|||
| min() | 返回列表元素中的最小值 |
min(list) |
list -- 要返回最小值的列表 |
>>>list1, list2 = [123, 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc'], [456, 700, 200]
>>>print("min value element : ", min(list1))
|
|||
| list() | 将元组或字符串转换为列表 |
list( tup ) |
tup -- 要转换为列表的元组 |
aTuple = (123, 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc') |
|||
| append() | 在列表末尾添加新的对象 |
list.append(obj) |
obj -- 添加到列表末尾的对象 |
>>>aList = [123, 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc'] |
|||
| count() | 统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数 | list.count(obj) | obj -- 列表中统计的对象 |
>>>aList = [123, 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc', 123]
>>>print("Count for 123 : ", aList.count(123))
|
|||
| extend() |
在列表末尾一次性追加另一个序列中的多个值 用新列表扩展原来的列表 |
list.extend(seq) | seq -- 元素列表 |
aList = [123, 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc', 123] |
|||
| index() | 从列表中找出与某个值第一个匹配项的索引位置 | list.index(x[, start[, end]]) | x-- 查找的对象
start-- 可选,起始位置 end-- 可选,结束位置 |
>>>aList = [123, 'xyz', 'runoob', 'abc']
>>>print("xyz 索引位置: ", aList.index( 'xyz' ))
|
|||
| insert() | 将指定对象插入列表的指定位置 | list.insert(index, obj) |
index -- 需要插入的位置 obj -- 要插入的对象 |
>>>aList = [123, 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc'] |
|||
| pop() |
用于移除列表中的一个元素,并且返回该元素的值 默认最后一个元素 |
list.pop([index]) | index -- 要移除的元素的索引值 |
>>>list1 = ['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao'] |
|||
| remove() | 移除列表中某个值的第一个匹配项 | list.remove(obj) | obj -- 列表中要移除的对象 |
>>>aList = [123, 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc', 'xyz'] |
|||
| reverse() | 反转列表中元素 | list.reverse() | 无 |
>>>aList = [123, 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc', 'xyz'] |
|||
| sort() |
对原列表进行排序 默认降序,可指定排序方法 |
list.sort(cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False) |
cmp --指定排序方法 key -- 指定可迭代对象中的一个元素来进行排序 reverse -- 排序规则reverse = True 降序reverse = False 升序(默认) |
>>>aList = [123, 'Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao', 'Facebook'] |
|||
四、元组(tuple)
tuple和list非常类似,但是tuple一旦初始化就不能修改,tuple也是有序的,tuple使用的是小括号标识。
元组方法 |
|||
| 方法名 | 描述 | 语法 | 参数 |
| cmp() |
用于比较两个元组元素 类似列表 |
cmp(tuple1, tuple2) |
tuple1 -- 比较的元组 tuple2 -- 比较的另外一个元组 |
>>>tuple1, tuple2 = (123, 'xyz'), (456, 'abc') >>>print(cmp(tuple1, tuple2)) |
|||
| tuple() | 将列表或字符串转换为元组 |
tuple( iterable ) |
iterable -- 要转换为元组的可迭代序列 |
(1, 2, 3, 4)
>>> tuple({1:2,3:4}) #针对字典 会返回字典的key组成的tuple
(1, 3)
>>> tuple((1,2,3,4)) #元组会返回元组自身
(1, 2, 3, 4)
>>>aList = [123, 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc'] |
|||
五、字典(dict)
字典是另一种可变容器模型,且可存储任意类型对象,如其他容器模型。
字典由键和对应值成对组成。字典也被称作关联数组或哈希表。
键必须独一无二,但值则不必,可以取任何数据类型
但键必须是不可变的,可以是字符串,数字,元组,布尔值
字典方法 |
|||
| 方法名 | 描述 | 语法 | 参数 |
| clear() | 删除字典内所有元素 |
dict.clear() |
无 |
>>>dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7}
>>>print("Start Len : " , len(dict))
>>>dict.clear()
>>>print("End Len : " , len(dict))
'''
|
|||
| copy() | 返回一个字典的浅复制 |
dict.copy() |
无 |
>>>dict1 = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7};
>>>dict1 = {'user':'runoob','num':[1,2,3]}
>>>dict2 = dict1 # 浅拷贝: 引用对象
|
|||
| fromkeys() |
创建一个新字典 以序列 seq 中元素做字典的键 value 为字典所有键对应的初始值 |
dict.fromkeys(seq[, value]) |
seq -- 字典键值列表 value -- 可选,设置键序列的值。 |
>>>seq = ('Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao')
|
|||
| get() |
返回指定键的值 如果值不在字典中返回设定值,默认为None |
dict.get(key, default=None) |
key -- 要查找的键。 default -- 若指定键不存在,返回该值 |
>>>dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 27}
>>>print("Value : ",dict.get('Age'))
|
|||
| has_key() | 判断键是否存在于字典中 |
dict.has_key(key) |
key -- 要查找的键 |
>>>dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7}
>>>print("Value : " , dict.has_key('Age'))
|
|||
| items() | 以列表返回所有的键值对 |
dict.items() |
无 |
>>>dict = {'Google': 'www.google.com', 'Runoob': 'www.runoob.com', 'taobao': 'www.taobao.com'}
>>>print("字典值 : " , dict.items())
# 遍历字典列表
|
|||
| keys() | 以列表返回所有的键 |
dict.keys() |
无 |
>>>dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7}
>>>print("Value :" , dict.keys())
'''
|
|||
| setdefault() |
添加键值对 若键已存在,仅返回对应的值 若键未存在,创建键值对并返回设置后的值,默认为None |
dict.setdefault(key, default=None) |
key -- 查找的键 default -- 键不存在时,设置的值 |
>>>dict = {'runoob': '菜鸟教程', 'google': 'Google 搜索'}
>>>print(“Value : " , dict.setdefault('runoob', None))
|
|||
| update() |
把字典dict2的键/值对更新到dict 还有一种 =表达式 -> k1 = 'abc' 有相同的键会直接替换成 update 的值 |
dict.update(dict2) |
dict2 -- 添加到指定字典dict里的字典 |
>>>dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7}
|
|||
| values() | 以列表返回字典中的所有值 |
dict.values() |
无 |
>>>dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7}
>>>print("Value : " , dict.values())
'''
|
|||
| pop() |
删除给定键及对应的值 返回值为被删除的值 key 值必须给出,否则返回 default 值 |
pop(key[,default]) |
key: 要删除的键值 default: 如果没有 key,返回 default 值 |
>>>site= {'name': '菜鸟教程', 'alexa': 10000, 'url': 'www.runoob.com'}
|
|||
| popitem() |
随机删除字典中的一个键值对 (key,value)的形式返回该键值对 |
popitem() |
无 |
>>>d = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3, 'd': 4}
|
|||
六、集合(set)
集合(set)由不同元素组成(自动去重),无序排列(不可索引),元素为可hash值(不可变类型:数字、字符串、元组)
可以使用大括号 { } 或者 set() 函数创建集合
注意:创建一个空集合必须用 set() 而不是 { },因为 { } 是用来创建一个空字典。
| 运算 | 符号 |
| 交集 | & |
| 并集 | | |
| 交叉补集 | ^ |
| 差集 | - |
集合方法 |
|||
| 方法名 | 描述 | 语法 | 参数 |
| add() |
给集合添加元素 如果添加的元素在集合中已存在,则不执行任何操作 |
set.add(elmnt) |
elmnt -- 必需,要添加的元素 |
fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
|
|||
| clear() | 移除集合中的所有元素 |
set.clear() |
无 |
fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
|
|||
| copy() | 拷贝一个集合 |
set.copy() |
无 |
fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
|
|||
| difference() |
返回集合的差集 即返回的集合元素包含在第一个集合中,但不包含在第二个集合(参数)中 |
set.difference(set) |
set -- 必需,用于计算差集的集合 |
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
|
|||
| difference_update() |
移除两个集合中都存在的元素 |
set.difference_update(set) |
set -- 必需,用于计算差集的集合 |
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
|
|||
| discard() |
移除指定的集合元素 元素不存在时不报错 |
set.discard(value) |
value -- 必需,要移除的元素 |
fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
|
|||
| intersection() |
返回两个或更多集合中都包含的元素,即交集 |
set.intersection(set1, set2 ... etc) |
set1 -- 必需,要查找相同元素的集合 set2 -- 可选,其他要查找相同元素的集合,可以多个,多个使用逗号 , 隔开 |
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
x = {"a", "b", "c"}
|
|||
| intersection_update() |
获取两个或更多集合中都重叠的元素,即交集 在原始的集合上移除不重叠的元素 |
set.intersection_update(set1, set2 ... etc) |
set1 -- 必需,要查找相同元素的集合
set2 -- 可选,其他要查找相同元素的集合,可以多个,多个使用逗号 , 隔开 |
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
x = {"a", "b", "c"}
|
|||
| isdisjoint() | 判断两个集合是否包含相同的元素 |
set.isdisjoint(set) |
set -- 必需,要比较的集合 |
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
|
|||
| issubset() |
判断前者是否为子集 |
set.issubset(set) | set -- 必需,要比查找的集合 |
x = {"a", "b", "c"}
|
|||
| issuperset() | 判断前者是否为父集 |
set.issuperset(set) |
set -- 必需,要比查找的集合 |
x = {"f", "e", "d", "c", "b", "a"}
|
|||
| pop() |
随机移除一个元素 因为集合是无序的 |
set.pop() |
无 |
fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
fruits.pop()
print(fruits)
'''
|
|||
| remove() |
移除集合中的指定元素 元素不存在时会报错 |
set.remove(item) |
item -- 要移除的元素 |
fruits = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
fruits.remove("banana")
print(fruits)
'''
|
|||
| symmetric_difference() | 返回两个集合中不重复的元素集合,即会移 除两个集合中都存在的元素 |
set.symmetric_difference(set) |
set -- 集合 |
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
|
|||
| symmetric_difference_update() |
移除当前集合中在另外一个指定集合相 同的元素 并将另外一个指定集合中不同的元素插 入到当前集合中 |
set.symmetric_difference_update(set) |
set -- 要检测的集合 |
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
|
|||
| union() |
返回两个集合的并集, 即包含了所有集合的元素,重复的元素 只会出现一次 |
set.union(set1, set2...) |
set1 -- 必需,合并的目标集合 set2 -- 可选,其他要合并的集合,可以多个,多个使用逗号 , 隔开 |
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
x = {"a", "b", "c"}
|
|||
| update() |
修改当前集合 可以添加新的元素或集合到当前集合 中,重复的元素会忽略。 |
set.update(set) |
set -- 必需,可以是元素或集合 |
x = {"apple", "banana", "cherry"}
|
|||
02----python入门----基本数据类型的更多相关文章
- Python 入门之数据类型之间的相互转换 以及 在编程中会遇到的数据类型的坑
Python 入门之数据类型之间的相互转换 以及 在编程中会遇到的数据类型的坑 1.数据类型总结: 可变,不可变,有序,无序 (1)可变的数据类型:list dict set (2)不可变的数据类型: ...
- python入门day02数据类型
字符串:数据类型的学习 #======================================基本使用====================================== #1.用途 ...
- python入门之数据类型及内置方法
目录 一.题记 二.整形int 2.1 用途 2.2 定义方式 2.3 常用方法 2.3.1 进制之间的转换 2.3.2 数据类型转换 3 类型总结 三.浮点型float 3.1 用途 3.2 定义方 ...
- python入门之数据类型之列表、元组、字典
list 格式: test_list = ["a",123,[1,"b"]] 索引: >>>print(test_list[0]) " ...
- python入门之数据类型之字符串
str方法 name.capitalize() 将name的首字母大写 name.center(20,'*') 将name居中,长度变为20,其余用*填充 name.count('chy') 返回na ...
- 02 . Python之数据类型
Python入门之数据类型 变量存储在内存中的值.这就意味着在创建变量时会在内存中开辟一个空间.基于变量的数据类型,解释器会分配指定内存,并决定什么数据可以被存储在内存中. 因此,变量可以指定不同的数 ...
- Python入门篇-基础数据类型之整型(int),字符串(str),字节(bytes),列表(list)和切片(slice)
Python入门篇-基础数据类型之整型(int),字符串(str),字节(bytes),列表(list)和切片(slice) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.Py ...
- python入门(8)数据类型和变量
python入门(8)数据类型和变量 数据类型 在Python中,能够直接处理的数据类型有以下几种: 整数 Python可以处理任意大小的整数,当然包括负整数,在程序中的表示方法和数学上的写法一模一样 ...
- Python入门学习:1.变量和简单的数据类型
python入门学习:1.变量和简单的数据类型 关键点:变量.字符串.数字 1.1 变量的命名和使用1.2 字符串1.3 数字1.4 注释 1.1 变量的命名和使用 变量,顾名思义是一个可变的量, ...
- Python 入门之基本数据类型
为什么我要学习Python这门语言呢?其实很简单,我想拓展技术面的同时,尝试更多的方向,可能最后会不了了之,谁知道呢?有可能的话,我会向爬虫和数据分析这个方向走.所以也就开始了我的Python学习之旅 ...
随机推荐
- Codeforces Round #307 (Div. 2) B. ZgukistringZ
Professor GukiZ doesn't accept string as they are. He likes to swap some letters in string to obtain ...
- Educational DP Contest F - LCS (LCS输出路径)
题意:有两个字符串,求他们的最长公共子序列并输出. 题解:首先跑个LCS记录一下dp数组,然后根据dp数组来反着还原路径,只有当两个位置的字符相同时才输出. 代码: char s[N],t[N]; i ...
- bfs输出路径 && 最短路(迪杰斯特拉)输出路径
问题描述 解决方法 1.像第一个问题那就是最短路问题(我代码采用迪杰斯特拉算法)实现 2.换乘次数最少,那就用bfs广搜来寻找答案.但是我的代码不能保证这个最少换乘是最短路程 代码 1 #includ ...
- 加密算法——RSA算法(c++简单实现)
RSA算法原理转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/idreamo/p/9411265.html C++代码实现部分为本文新加 RSA算法简介 RSA是最流行的非对称加密算法之一.也被 ...
- 正则指引 pdf 高清版
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Xeuma4toE_L-MxROvTGBxw 提取码:nqyj
- SpringBoot简单整合redis
Jedis和Lettuce Lettuce 和 Jedis 的定位都是Redis的client,所以他们当然可以直接连接redis server. Jedis在实现上是直接连接的redis serve ...
- Python基础--核心数据类型
python的核心数据类型: Number 数字(整数,浮点数,复数,布尔型数) String 字符串 List 列表 Tuple 元组 Dictionary 字典 Set 集合 1. 整数(整型数) ...
- MySQL 字符集及校验规则
字符集 Mysql 的字符集有4个级别的默认设置:服务器级,数据库级,表级和字段级,客户端交互时,也可以指定字符集 # 字符集:是一个系统支持的所有抽象字符的集合.字符是各种文字和符号的总称,包括各国 ...
- TensorFlow+restore读取模型
# 注意和前一或二篇Lenet训练并验证的文章从`y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(fc2)`起的不同 # 部分函数请参照前后2篇文章 import tensorflow as tf im ...
- 蓝湖 UI 设计稿上如何生成渐变色和复制渐变色
蓝湖 UI 设计稿上如何生成渐变色和复制渐变色 Sketch 生成渐变色 不要上传图片,切图 如果是切图,切图模式下就不会生成 css 代码了 复制渐变色 OK .button { width: 28 ...
