MyBatis 学习记录2 Mapper对象是如何生成的
主题
以前我一直有一个问题不懂.并且觉得很神奇.就是Mybatis我们开发的时候只需要定义接口,并没有写实现类,为什么我们运行的时候就可以直接使用? 现在我想分享下这部分大致是怎么实现的.
在启动的时候
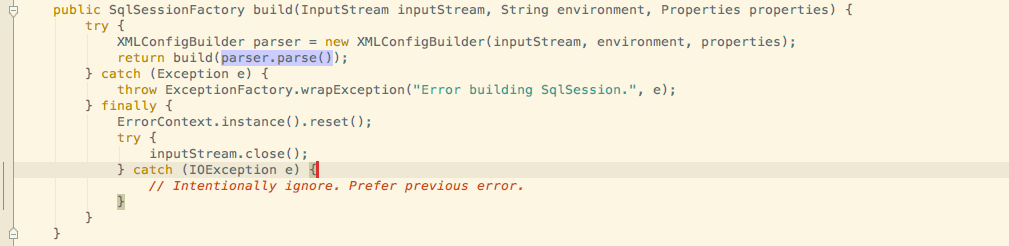
根据之前的分享,在初始化阶段Build SqlSessionFactory的时候需要用到XMLConfigBuilder去parse XML文件生成Configuration对象,在 parse的步骤中其中有一步就是parse mappers节点
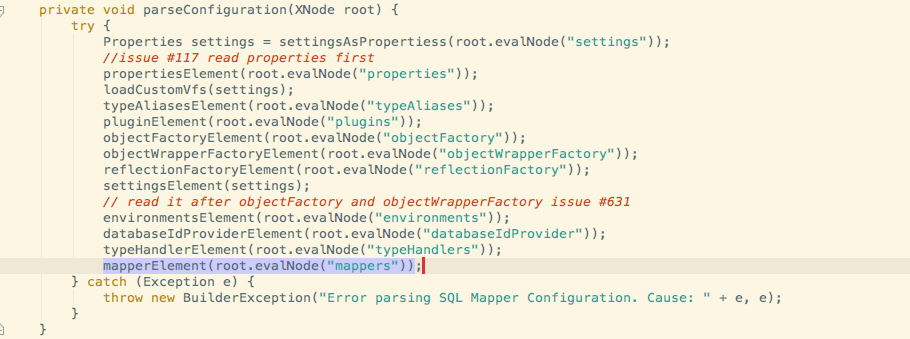
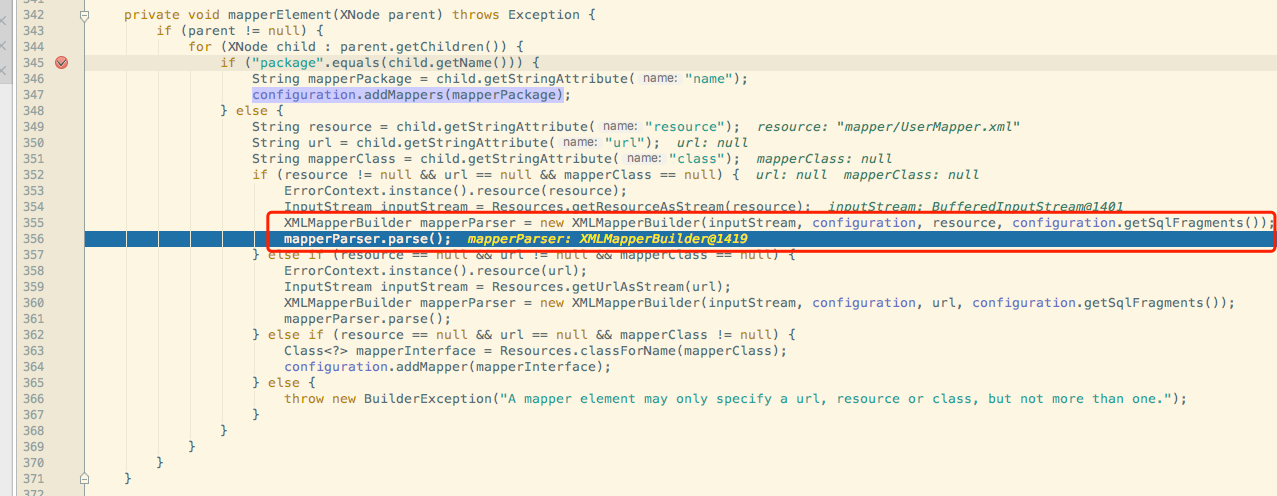
在parse mapper过程中会用到XMLMapperBuilder去parse.一步一步进入断点.
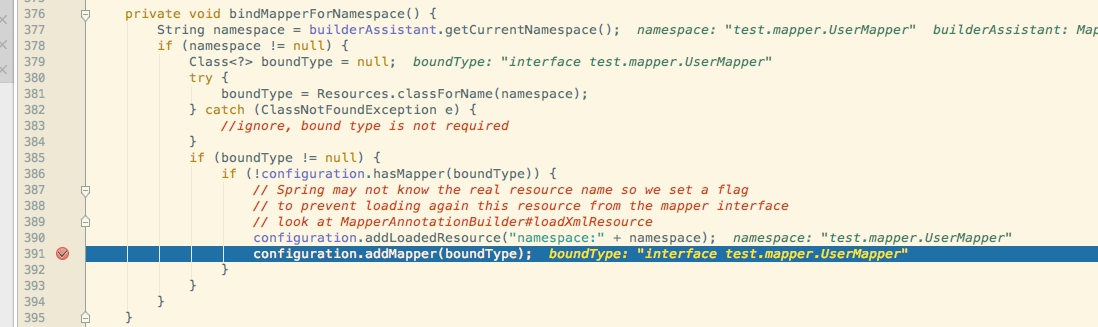
会发现后面会调用configuration的addMapper方法.它会调用MapperRegistry的addMapper方法
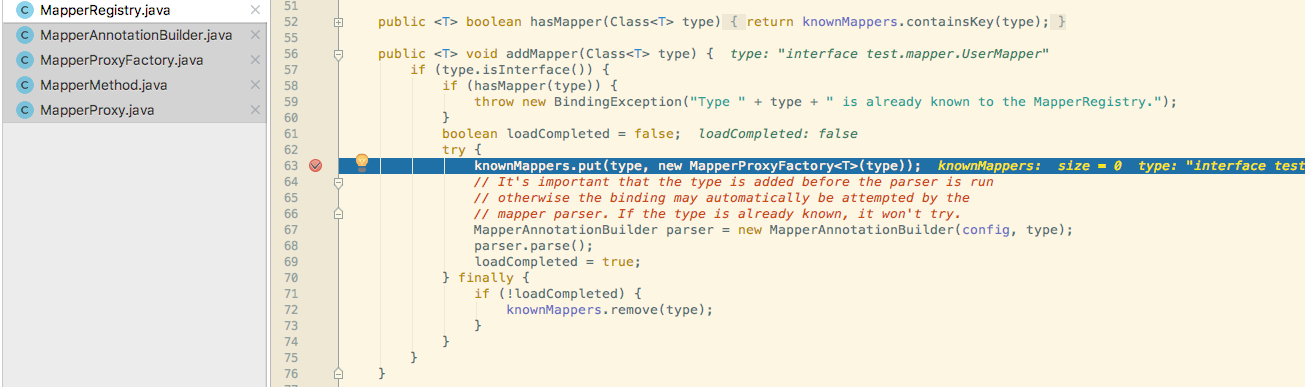
MapperRegistry相当用knownMappers这个hashmap于为每个Mapper注册一次,其中key是你自定义的Mapper接口的class,Value是MapperProxyFactory类的对象.
Factory一个就是一个工厂类,它肯定需要生产对应的对象,从名字上也能发现它生产的就是MapperProxy
/**
* Copyright 2009-2015 the original author or authors.
* <p>
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
* <p>
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
* <p>
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.ibatis.binding; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; /**
* @author Lasse Voss
*/
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> { private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>(); public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
} public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
} public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{mapperInterface}, mapperProxy);
} public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
} }
/**
* Copyright 2009-2015 the original author or authors.
* <p>
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
* <p>
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
* <p>
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.ibatis.binding; import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ExceptionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Map; /**
* @author Clinton Begin
* @author Eduardo Macarron
*/
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache; public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
} @Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
} private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
} }
从代码中我们可以得知,这里是用了JDK动态代理,MapperProxy类implements了InvocationHandler,
如果是调用自定义Mapper的Object类中的方法,比如toString,那就直接调用,否则的话调用mapperMethod.execute去执行对应的方法(比如selectById).那么mapperMethod是什么呢?
这个类的对象其实就是对应你写的Mapper里的方法,你的每个方法对应1个MapperMethod,相当于是Java的Method的包装.
另外还包含了你在XML里定义的SQL字符串, 是select还是insert还是update,delete操作等信息.相当于融合了你定义的Mapper里的Method和你为每个Method在XML里的写的信息.
这样你调用mapperMethod.execute的时候就能找到对应的SQL去执行了.
通过SqlSession获取Mapper
初始化完成后就如同之前的介绍,会在confuguration的mapperRegistry里注册好了各种MapperFactory.那么通过SqlSession去获取Mapper的时候也是类似的.会调用configuration去获取Mapper,内部会调用mapperRegistry去获取Mapper

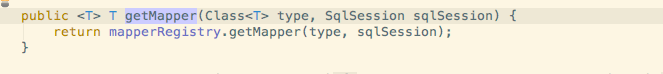
然后通过MapperProxyFactory去创建一个MapperProxy并返还

小结
1.说白了,其实就是利用JDK动态代理,返回给你1个实现了你写的Mapper接口的对象,而其中的Invocation接口的实现类就是MapperProxy.
2.在初始化阶段会为你写的每个Mapper在Configuration的MapperRegistry里注册一个MapperFactory,当你要获取Mapper实例的时候就通过这个Factory来new.
3.当你调用Mapper.XXX方法的时候,比如select,就会调用MapperProxy的invoke方法,获取你定义在Mapper里的xxx方法对应的MapperMethod对象,这个对象就是Method的封装,同时在XML里找到对应的select语句再执行.
4.你写的每个Mapper类的对象对应1个MapperProxyFactory生成1个MapperProxy,你在Mapper中定义的每个方法对应1个MapperMethod,它是Java的Method的封装
MyBatis 学习记录2 Mapper对象是如何生成的的更多相关文章
- MyBatis 学习记录5 MyBatis的二级缓存
主题 之前学习了一下MyBatis的一级缓存,主要涉及到BaseExecutor这个类. 现在准备学习记录下MyBatis二级缓存. 配置二级缓存与初始化发生的事情 首先二级缓存默认是不开启的,需要自 ...
- MyBatis 学习记录3 MapperMethod类
主题 之前学习了一下MapperProxy的生产过程,自定义Mapper类的对象是通过动态代理生产的,调用自定义方法的时候实际上是调用了MapperMethod的execute方法:mapperMet ...
- mybatis 学习记录1
起因 以前刚学习java三大框架的时候持久层框架我是自学的是hibernate..感觉蛮好用的,so easy..后来大三实习公司用的是jpa(hibernate外包装一层)...再后来工作1年多用的 ...
- MyBatis 学习记录7 一个Bug引发的思考
主题 这次学习MyBatis的主题我想记录一个使用起来可能会遇到,但是没有经验的话很不好解决的BUG,在特定情况下很容易发生. 异常 java.lang.IllegalArgumentExceptio ...
- MyBatis 学习记录6 TypeHandler
主题 因为对MyBatis在JDBC数据和Java对象之间数据转化比较感兴趣,所以就记录并学习一下TypeHandler. 使用场景 如上图所示,观察下接口方法就能明白.TypeHandler主要用于 ...
- MyBatis 学习记录4 MyBatis的一级缓存
主题 分享记录一下MyBatis的一级缓存相关的学习. Demo public static void firstLevelCache() { init("mybatis-config.xm ...
- mybatis学习记录六——一对一、一对多和多对多查询
9 订单商品数据模型 9.1 数据模型分析思路 1.每张表记录的数据内容 分模块对每张表记录的内容进行熟悉,相当 于你学习系统 需求(功能)的过程. 2.每张表重要的字段设置 非空 ...
- Mybatis学习记录(六)----Mybatis的高级映射
1.一对多查询 1.1 需求 查询订单及订单明细的信息. 1.2 sql语句 确定主查询表:订单表 确定关联查询表:订单明细表 在一对一查询基础上添加订单明细表关联即可. SELECT orders. ...
- Mybatis学习记录(五)----Mybatis的动态SQL
1. 什么是动态sql mybatis核心 对sql语句进行灵活操作,通过表达式进行判断,对sql进行灵活拼接.组装. 1.1 需求 用户信息综合查询列表和用户信息查询列表总数这两个statemen ...
随机推荐
- tab页面自动跳转原因【在控制ul和li的时候没有细分】
效果图 存储buy的tab跳转js代码 $(function() { $('.tabPanel ul li').click(function(){ $(this).addClass('hit').si ...
- Yahoo关于性能优化的N条规则
本来这是个老生常谈的问题,上周自成又分享了一些性能优化的建议,我这里再做一个全面的Tips整理,谨作为查阅型的文档,不妥之处,还请指正: 一. Yahoo的规则条例: 谨记:80%-90%的终端响应时 ...
- BZOJ4547 Hdu5171 小奇的集合 【矩阵快速幂优化递推】
BZOJ4547 Hdu5171 小奇的集合 Description 有一个大小为n的可重集S,小奇每次操作可以加入一个数a+b(a,b均属于S),求k次操作后它可获得的S的和的最大值.(数据保证这个 ...
- Built(最小生成树+构图离散化)
个人心得:看了题目很明确,最小生成树,但是但是周赛卡住了,因为10W的点若一个一个找出距离很明显内存和时间都炸了, 静下心来,画了下图,仔细一想,任意一个点都只会在她左右俩边选择建立联系,那么我们只要 ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example7.3
由图上可以看出,与幅度谱对应的相位谱是分段线性函数,而与振幅谱对应的相位谱是真正线性函数. 幅度谱和振幅谱的区别也很明显.
- 基于jquery 的ajax 文件下载
ajax 文件下载,实际上就是模拟表单提交,代码如下: function download(url, data, method){ //url and data options required if ...
- WebSocket的使用
WebSocket是长连接,如果客户端的程序没有数据实时同步的需求就没必要使用它.因为长连接会带来一定的服务器内存开销.如果Ajax就能轻松搞定的话就完全没必要兴师动众的搞WebSocket. htt ...
- 什么是Spark(三)数据的加载和保存
Spark内置了一些常见的文件格式的处理,包括text/json,csv,sequence等:Spark对于文件处理保持了开放性,还提供了可以通过InputFormat,OutputFormat来进行 ...
- NumPy-快速处理数据--ufunc运算--广播--ufunc方法
本文摘自<用Python做科学计算>,版权归原作者所有. 1. NumPy-快速处理数据--ndarray对象--数组的创建和存取 2. NumPy-快速处理数据--ndarray对象-- ...
- 【备忘】mysql主从设置
主(master)192.168.1.10机器设置: [root@vm-vagrant mysql]# vi my.cnf [mysqld]节点下添加以下配置server-id=1log-bin=my ...
