随笔3 HashMap<K,V>
equals、hashcode和==的区别
在介绍HashMap之前,我想先阐述一下我对这三者的理解,equals这个方法呢,就是在判断是否为同一对象(注意,这里的同一对象和相同的内存地址是不同的),是否为同一对象其实看一看做一种我们对事物的主观定义,如果我是个佛系青年,认为世间万物都是相同的,那么我只需要在equals里只return一个true。hashcode我们可以看做是一个对象的表示符,同一对象的表示符肯定是一样的,不同对象的表示符理论上来说应该是不同的,但是现实永远不太尽如人意,不同的对象hashcode相同,就是所谓的冲突。所以当我们重写Object中的equals方法的时候,一定要记得重写hashcode方法。==很好理解,它就表示是不是同一内存地址。
接下来我们就从原理和源码两方面去介绍一下hashcode,并且对hashcode的非线程安全进行一些简单的讨论,下文参考了https://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/7261111.html这篇文章
一、HashMap原理
在最初的HashMap中,其底层的实现数组加链表的数据结构,基本单元为Entry,但是在java8之后进行了优化,增加了红黑树,底层结构也由Entry变成了Node和TreeNode组合完成,但是TreeNode其实还是继承自Node。
数组的优缺点:优点是根据下标进行查找,十分迅速,缺点是在数组中插入元素,删除元素效率极低
链表的优缺点:优点是对于增删操作非常方便 ,但是查找起来却很慢
红黑树优缺点:优点是查找非常迅速,缺点是插入元素的时候又费时间又费空间
HashMap就是综合了以上几点,构成的一种数据结构:首先用一个数组来构成散列表,然后用链表来解决冲突,当冲突项大于默认值8时,会将链表转化成一颗红黑树,提高查询效率(链表就是一颗退化树)。
如下图所示:
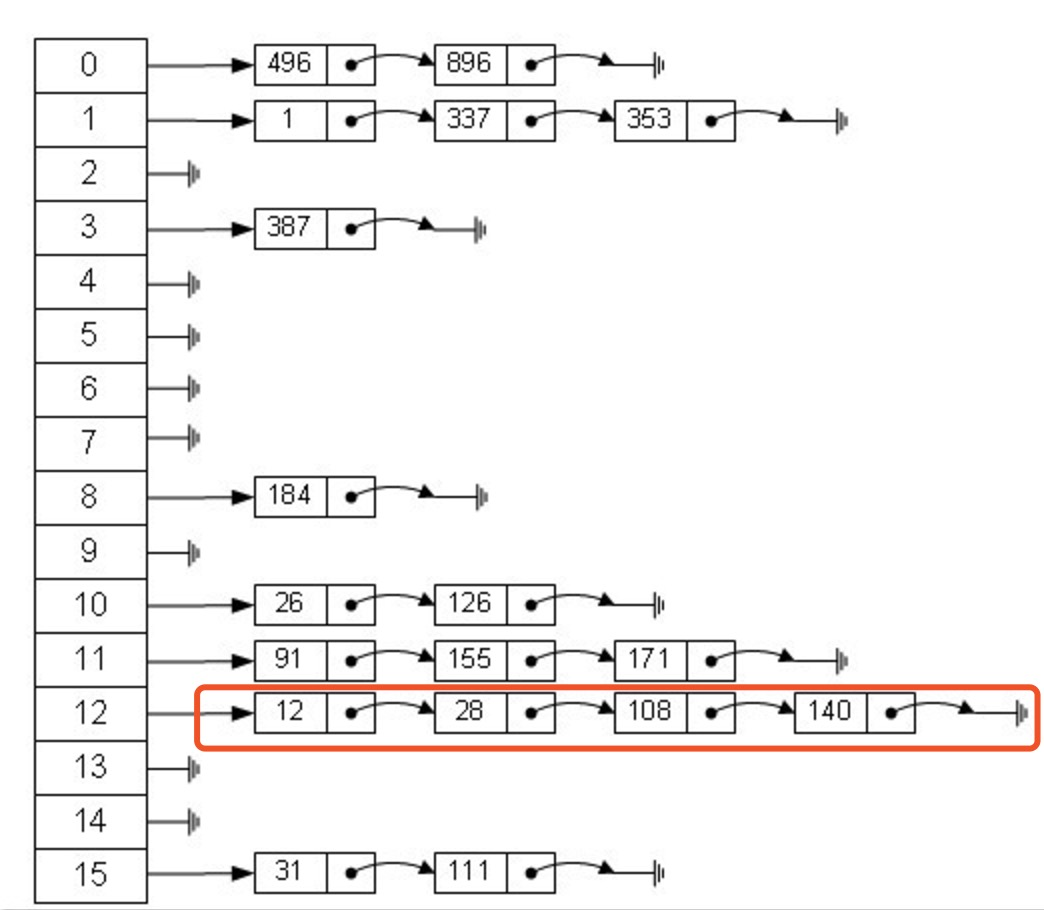
从上图我们可以发现HashMap是由Entry数组+链表组成的,一个长度为16的数组中,每个元素存储的是一个链表的头结点。那么这些元素是按照什么样的规则存储到数组中呢。一般情况是通过hash(key)%len获得,也就是元素的key的哈希值对数组长度取模得到。比如上述哈希表中,12%16=12,28%16=12,108%16=12,140%16=12。所以12、28、108以及140都存储在数组下标为12的位置。
二、源码分析
1、底层数据类
/**
* 这里可见,Node是实现了Entry
*/
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
/**
* 注意hash和key都是final修饰的,说明作为key需要是不可变值,比如String很常用
* 如果采用自己创建的对象
*/
final int hash;
final K key;
//value是可变的
V value;
//指向下一个节点的指针
Node<K,V> next; Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
} public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } /**
* key的hash值和value的hash值做与操作,所以key和value需要重写hashCode方法
*/
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
} //这里设置新值的时候会返回旧值
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
} //这里需要注意要重写equals方法
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* 这里介绍一下红黑树的五条性质
* 1、节点是红色或者是黑色;
* 2、根节点是黑色;
* 3、每个叶节点(NIL或空节点)是黑色;
* 4、每个红色节点的两个子节点都是黑色的(也就是说不存在两个连续的红色节点);
* 5、从任一节点到其没个叶节点的所有路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点;
*/
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
}
2、HashMap的常量和属性
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable { /**
* 默认初始化容量,必须是2的次方。这个容量就是table的长度
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 /**
* 这里指定了一个容量的上限,如果自己指定的值大于上限的话,就采用该默认值
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; /**
* 默认加载因子,当没有指定加载因子的时候会采用该值,这个值的意义在于,当有效值比容量大于加载因子时
* 会扩容table数组
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; /**
* 这个是一个链表在多长时转化为红黑树,默认为8
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; /**
* 当一颗树的节点少于6个的时候,将这棵树转化为链表
*/
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; /**
* 当哈希表中的容量大于这个值时,表中的桶才能进行树形化 否则桶内元素太多时会扩容,而不是树形化 为了
* 避免进行扩容、树形化选择的冲突,这个值不能小于 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD
*/
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
/**
* 这个数组会在第一次使用时初始化,并且在条件合适的时候重构,它的长度一定是2的整数次方
*/
transient Node<K,V>[] table; /**
* 一个包含所有节点的Set
*/
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet; /**
* Map中的当前元素数量
*/
transient int size; /**
* 这个是Map当中元素的修改次数(这里的修改只是说增加和减少元素时,该量会加一)
*/
transient int modCount; /**
* 当大于这个值的时候会执行重构数组操作(capacity * load factor).
*/
int threshold; /**
* 自定义的加载因子
*/
final float loadFactor;
}
3、HashMap的resize
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
//将原来的table指针保存
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
//获取原来数组的长度,oldTab为null说明还没有进行初始化
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
//保存以前重构table的阈值
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
//oldCap > 0表示已经初始化过了
if (oldCap > 0) {
//当原来的容量已经达到最大容量的时候,将阈值设置为Integer.MAX_VALUE,这样就不会再发生重构的情况
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
//否则将旧的容量扩大两倍,当它小于最大容量,并且旧的容量大于初始化最小容量的时候,将新的阈值设置为旧的阈值的两倍
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) //虽然还没有初始化,但是设置过了阈值,将旧的阈值设置为新的容量
newCap = oldThr;
else { //没有初始化阈值的时候采用默认算法计算阈值
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {//对应oldCap = 0 && oldThr > 0的情况
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
//将旧数组中的元素全部取出,重新映射到新数组中
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
//(newCap - 1)是一个尾部全部为1的数
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)//判断旧的节点是一个树节点,则对树进行操作,重构树或者变成链表等等
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else {
// 对原来的链表部分进行重构
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> 所以新索引要么是原索引,要不就是原索引+oldCap = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
//在重新计算hash之后,因为n变为2倍,那么n-1的mask范围在高位多1bit
//对原来的链表部分进行重构
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
举个例子(例子来自https://blog.csdn.net/lianhuazy167/article/details/66967698)
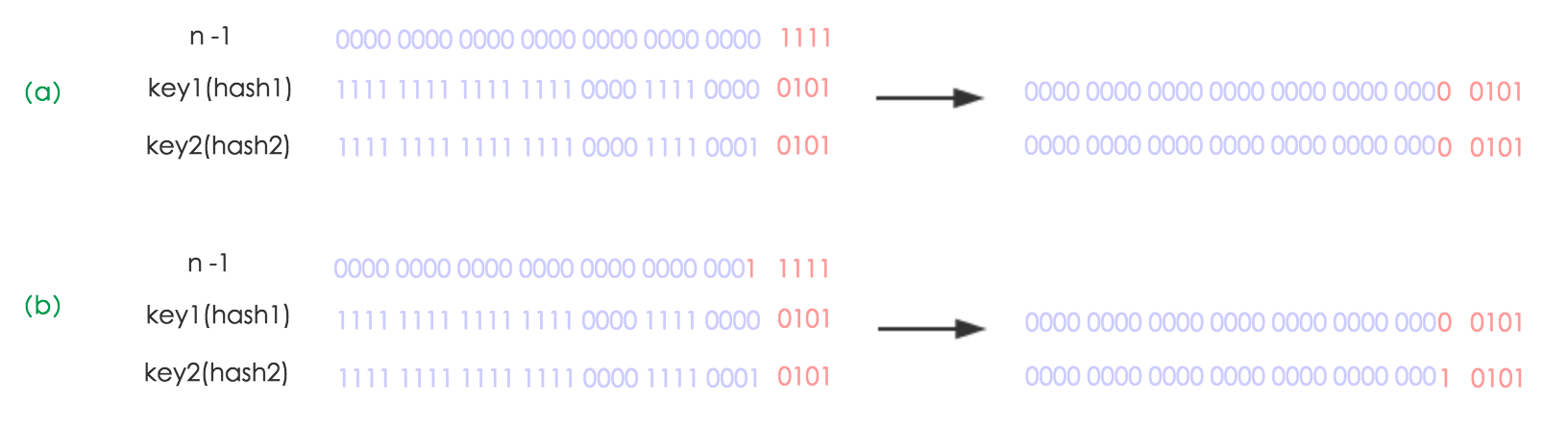
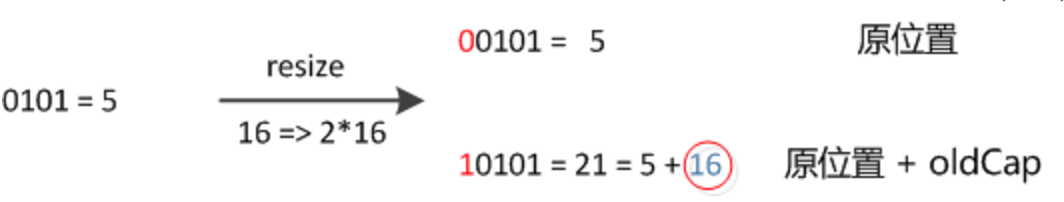
4、修改方法
4.1、put
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
/**
* @param hash 计算出来key的hash值
* @param key key的值
* @param value value的值
* @param onlyIfAbsent 当为true的时候,如果key对应有值,则不修改这个值
* @param evict 当为false时,表示这个处于创建模式,现在由于afterNodeInsertion中什么都没有,这里没有实际意
* evict参数用于LinkedHashMap中的尾部操作
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
//判断当table为null或者tab的长度为0时,即table尚未初始化,此时通过resize()方法得到初始化的table
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//当p为null时,表明tab[i]上没有任何元素,那么接下来就new第一个Node节点,调用newNode方法返回新节点赋值给tab[i]
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//HashMap中判断key相同的条件是key的hash相同,并且符合equals方法。这里判断了p.key是否和插入的key相等,如果相等,则将p的引用赋给e
//这里为什么要把p赋值给e,而不是直接覆盖原值呢?答案很简单,现在我们只判断了第一个节点,后面还可能出现key相同,所以需要在最后一并处理
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
//现在开始了第一种情况,p是红黑树节点,那么肯定插入后仍然是红黑树节点,所以我们直接强制转型p后调用TreeNode.putTreeVal方法,返回的引用赋给e
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
//最后一个参数为新节点的next,这里传入null,保证了新节点继续为该链表的末端
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//插入成功后,要判断是否需要转换为红黑树,因为插入后链表长度加1,而binCount并不包含新节点,所以判断时要将临界阈值减1
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
//在遍历链表的过程中,我之前提到了,有可能遍历到与插入的key相同的节点,此时只要将这个节点引用赋值给e,最后通过e去把新的value覆盖掉就可以了
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
//左边注释为jdk自带注释,说的很明白了,针对已经存在key的情况做处理
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
//收尾工作,值得一提的是,对key相同而覆盖oldValue的情况,在前面已经return,不会执行这里,所以那一类情况不算数据结构变化,并不改变modCount值
++modCount;
//当HashMap中存在的node节点大于threshold时,hashmap进行扩容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
4.2、putAll
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
putMapEntries(m, true);
}
/**
* @param m 需要放入的Map
* @param evict 在此处并无意义
*/
final void putMapEntries(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m, boolean evict) {
//获取添加元素的数量
int s = m.size();
//添加的Map中有元素
if (s > 0) {
//table == null表达现在还没有被初始化
if (table == null) { // pre-size
//通过加载因子计算出大概需要初始化的空间
float ft = ((float)s / loadFactor) + 1.0F;
//检查这个需要的空间有没有大于最大容量MAXIMUM_CAPACITY
int t = ((ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);
//如果大于了当前resize()的阈值,就要重新计算
if (t > threshold)
//这里会得到一个比t大的最小的2的整数次幂的值
threshold = tableSizeFor(t);
}
else if (s > threshold)//在已经创建Map的情况下,s如果直接大于阈值,直接重构现在的Map
resize();
//将传入的Map的每个值都插入到现在的Map中
for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) {
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, evict);
}
}
}
4.3、remove
public V remove(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?
null : e.value;
}
/**
* @param hash key的hash值
* @param key key的值
* @param value 传入匹配的value值,如果matchValue=false,直接忽略
* @param matchValue 为true时,会去进一步匹配value
* @param movable if false do not move other nodes while removing
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,
boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, index;
//确定table已经被初始化,并且其中有元素,并且对应的 hash值有元素
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
Node<K,V> node = null, e; K k; V v;
//判断当前这个找到的元素是不是目标元素,如果是的话赋值给node
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
node = p;
//不是的话,就从相同hash值的所有元素中去查找
else if ((e = p.next) != null) {
if (p instanceof TreeNode)
//该列表已经转换成红黑树的情况
node = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
//在列表中查找的情况
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key ||
(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
node = e;
break;
}
p = e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
//找到了目标节点
if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||
(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {
if (node instanceof TreeNode)//是红黑树节点的情况
((TreeNode<K,V>)node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);
else if (node == p)//是一个链表开头元素的情况
tab[index] = node.next;
else
p.next = node.next;//是一个链表中间元素的情况
++modCount;//结构改变,需要加一
--size;
afterNodeRemoval(node);
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
4.4、clear
public void clear() {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
modCount++;//对table结构修改加一
if ((tab = table) != null && size > 0) {
size = 0;
//释放数组的每一个指针
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i)
tab[i] = null;
}
}
5、查询方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
public boolean containsKey(Object key) {
return getNode(hash(key), key) != null;
}
/**
* Implements Map.get and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @return the node, or null if none
*/
final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
//根据输入的hash值,可以直接计算出对应的下标(n - 1)& hash,缩小查询范围,如果存在结果,则必定在table的这个位置上
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
//判断第一个存在的节点的key是否和查询的key相等。如果相等,直接返回该节点
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
//遍历该链表/红黑树直到next为null
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
//当这个table节点上存储的是红黑树结构时,在根节点first上调用getTreeNode方法,在内部遍历红黑树节点,查看是否有匹配的TreeNode
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
//当这个table节点上存储的是链表结构时,方法同上
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
6、静态方法
/**
* 对于这个函数,我想说两点,第一点是支持key==null,返回位置为0
* 第二点是(h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16),一个int32bit
* 这里正好将高16位移到了低16位,然后产生的hash值即包含了高位信息又包含了低位信息
* 还解决了地址空间不够引起的冲突问题
*/
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
} /**
* 当x的类型为X,且X直接实现了Comparable接口(比较类型必须为X类本身)时,返回x的运行时类型;否则返回null。
*/
static Class<?> comparableClassFor(Object x) {
if (x instanceof Comparable) {// 判断是否实现了Comparable接口
Class<?> c; Type[] ts, as; Type t; ParameterizedType p;
if ((c = x.getClass()) == String.class) // bypass checks
return c; // 如果是String类型,直接返回String.class
if ((ts = c.getGenericInterfaces()) != null) {// 判断是否有直接实现的接口
for (int i = 0; i < ts.length; ++i) { // 遍历直接实现的接口
if (((t = ts[i]) instanceof ParameterizedType) &&// 该接口实现了泛型
((p = (ParameterizedType)t).getRawType() ==// 获取接口不带参数部分的类型对象
Comparable.class) &&// 该类型是Comparable
(as = p.getActualTypeArguments()) != null && // 获取泛型参数数组
as.length == 1 && as[0] == c) // 只有一个泛型参数,且该实现类型是该类型本身
return c;
}
}
}
return null;
} /**
* kc是k的类型,并且可以比较
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) // for cast to Comparable
static int compareComparables(Class<?> kc, Object k, Object x) {
return (x == null || x.getClass() != kc ? 0 :
((Comparable)k).compareTo(x));
} /**
* 返回不小于cap的最小的2的整次幂
*/
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
7、迭代器
/**
* 这里我感觉设计的还挺好的,这里是编写了一个Node节点的迭代器,这是一个抽象类,虽然是个抽象类,但是没哟抽象方法
* 留下了next方法去给子类实现,因为子类只有nest返回的东西是不同的
*/
abstract class HashIterator {
Node<K,V> next; // next entry to return
Node<K,V> current; // current entry
int expectedModCount; // for fast-fail
int index; // current slot HashIterator() {
expectedModCount = modCount;
Node<K,V>[] t = table;
current = next = null;
index = 0;
if (t != null && size > 0) { // advance to first entry
do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
} public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
} final Node<K,V> nextNode() {
Node<K,V>[] t;
Node<K,V> e = next;
//注意,这里在生成迭代器后,如果原来的图不是通过迭代器进行对图结构修改,那么就会报错
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
if ((next = (current = e).next) == null && (t = table) != null) {
do {} while (index < t.length && (next = t[index++]) == null);
}
return e;
} public final void remove() {
Node<K,V> p = current;
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
//在不是通过remove修改之前,通过其他方式是不允许修改图的结构的
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
current = null;
K key = p.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
} final class KeyIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<K> {
public final K next() { return nextNode().key; }
} final class ValueIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<V> {
public final V next() { return nextNode().value; }
} final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextNode(); }
}
8、并行遍历迭代器
/**
* jdk1.8发布后,对于并行处理的能力大大增强,Spliterator就是为了并行遍历元素而设计的一个迭代器,
* jdk1.8中的集合框架中的数据结构都默认实现了spliterator
*
*/
static class HashMapSpliterator<K,V> {
final HashMap<K,V> map;
Node<K,V> current; // 当前节点
int index; // 当前节点下标,advance/split会修改这个值
int fence; // 最后一个节点的下标,注意这里不是元素个数,而是数组下标
int est; // 预测还有多少个元素
int expectedModCount; // 得到当前Map的结构修改次数 HashMapSpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin,
int fence, int est,
int expectedModCount) {
this.map = m;
this.index = origin;
this.fence = fence;
this.est = est;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
} final int getFence() { // initialize fence and size on first use
int hi;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {//当小于0的时候说明还没有初始化
HashMap<K,V> m = map;
est = m.size;
expectedModCount = m.modCount;
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table;
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length;//这里可以看到给出的是数组长度
}
return hi;
} public final long estimateSize() {
getFence(); // 这里是防止还没有初始化的情况
return (long) est;
}
} static final class KeySpliterator<K,V>
extends HashMapSpliterator<K,V>
implements Spliterator<K> {
KeySpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin, int fence, int est,
int expectedModCount) {
super(m, origin, fence, est, expectedModCount);
} /**
* 这个方法相当于把未遍历的元素分成两半,然后将前一半生成一个KeySpliterator,当前这个KeySpliterator
* 处理后一半数据
*/
public KeySpliterator<K,V> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid || current != null) ? null :
new KeySpliterator<>(map, lo, index = mid, est >>>= 1,//est >>>= 1的意思是est = est >>> 1
expectedModCount);
} /**
* 这个方法就是通过action方法处理还没有处理的元素
*/
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super K> action) {
int i, hi, mc;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
HashMap<K,V> m = map;
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {//如果还没有被初始化
mc = expectedModCount = m.modCount;
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;//这个mc就是为了在KeySpliterator调用的过程中确认没有通过其他的方式改变Map的结构
if (tab != null && tab.length >= hi &&
(i = index) >= 0 && (i < (index = hi) || current != null)) {
Node<K,V> p = current;
current = null;
do {
if (p == null)//这里是处理数组
p = tab[i++];
else {//这里是处理链表
action.accept(p.key);
p = p.next;
}
} while (p != null || i < hi);
if (m.modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} //单个对元素执行给定的动作,如果有剩下元素未处理返回true,否则返回false
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super K> action) {
int hi;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Node<K,V>[] tab = map.table;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= (hi = getFence()) && index >= 0) {
while (current != null || index < hi) {
if (current == null)
current = tab[index++];
else {
K k = current.key;
current = current.next;
action.accept(k);
if (map.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} //返回当前对象有哪些特征值
public int characteristics() {
return (fence < 0 || est == map.size ? Spliterator.SIZED : 0) |
Spliterator.DISTINCT;
}
} //下面的就不再赘述,只是用方法处理的对象不一样,其他的都和上面一样
static final class ValueSpliterator<K,V>
extends HashMapSpliterator<K,V>
implements Spliterator<V> {
ValueSpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin, int fence, int est,
int expectedModCount) {
super(m, origin, fence, est, expectedModCount);
} public ValueSpliterator<K,V> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid || current != null) ? null :
new ValueSpliterator<>(map, lo, index = mid, est >>>= 1,
expectedModCount);
} public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super V> action) {
int i, hi, mc;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
HashMap<K,V> m = map;
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = expectedModCount = m.modCount;
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= hi &&
(i = index) >= 0 && (i < (index = hi) || current != null)) {
Node<K,V> p = current;
current = null;
do {
if (p == null)
p = tab[i++];
else {
action.accept(p.value);
p = p.next;
}
} while (p != null || i < hi);
if (m.modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super V> action) {
int hi;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Node<K,V>[] tab = map.table;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= (hi = getFence()) && index >= 0) {
while (current != null || index < hi) {
if (current == null)
current = tab[index++];
else {
V v = current.value;
current = current.next;
action.accept(v);
if (map.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} public int characteristics() {
return (fence < 0 || est == map.size ? Spliterator.SIZED : 0);
}
} static final class EntrySpliterator<K,V>
extends HashMapSpliterator<K,V>
implements Spliterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
EntrySpliterator(HashMap<K,V> m, int origin, int fence, int est,
int expectedModCount) {
super(m, origin, fence, est, expectedModCount);
} public EntrySpliterator<K,V> trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid || current != null) ? null :
new EntrySpliterator<>(map, lo, index = mid, est >>>= 1,
expectedModCount);
} public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super Map.Entry<K,V>> action) {
int i, hi, mc;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
HashMap<K,V> m = map;
Node<K,V>[] tab = m.table;
if ((hi = fence) < 0) {
mc = expectedModCount = m.modCount;
hi = fence = (tab == null) ? 0 : tab.length;
}
else
mc = expectedModCount;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= hi &&
(i = index) >= 0 && (i < (index = hi) || current != null)) {
Node<K,V> p = current;
current = null;
do {
if (p == null)
p = tab[i++];
else {
action.accept(p);
p = p.next;
}
} while (p != null || i < hi);
if (m.modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super Map.Entry<K,V>> action) {
int hi;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Node<K,V>[] tab = map.table;
if (tab != null && tab.length >= (hi = getFence()) && index >= 0) {
while (current != null || index < hi) {
if (current == null)
current = tab[index++];
else {
Node<K,V> e = current;
current = current.next;
action.accept(e);
if (map.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} public int characteristics() {
return (fence < 0 || est == map.size ? Spliterator.SIZED : 0) |
Spliterator.DISTINCT;
}
}
9、JDK1.8新增的方法部分
@Override
public V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {//如果没有key的情况下会返回defaultValue
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? defaultValue : e.value;
} @Override
public V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {//当存在key的时候,不会用value去覆盖
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, true, true);
} @Override
public boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {//当key和value都相同时,才去删除这个值
return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null;
} @Override
public boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {//当key和oldValue都相同时,用newValue去代替oldValue
Node<K,V> e; V v;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) != null &&
((v = e.value) == oldValue || (v != null && v.equals(oldValue)))) {
e.value = newValue;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return true;
}
return false;
} @Override
public V replace(K key, V value) {//这个和上面方法不同在于,不用确定旧的值,直接覆盖,并且返回oldValue
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
return null;
} /**
* 这个方法就类似于get方法,但是不同之处在于当key不存在时不时返回null,而是通过mappingFunction计算出一个值返回
*/
@Override
public V computeIfAbsent(K key,
Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {
if (mappingFunction == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key);
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first; int n, i;
int binCount = 0;
TreeNode<K,V> t = null;
Node<K,V> old = null;
if (size > threshold || (tab = table) == null ||
(n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((first = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
old = (t = (TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
Node<K,V> e = first; K k;
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
old = e;
break;
}
++binCount;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
V oldValue;
if (old != null && (oldValue = old.value) != null) {
afterNodeAccess(old);
return oldValue;
}
}
V v = mappingFunction.apply(key);
if (v == null) {
return null;
} else if (old != null) {
old.value = v;
afterNodeAccess(old);
return v;
}
else if (t != null)
t.putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, v);
else {
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, v, first);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1)
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
}
++modCount;
++size;
afterNodeInsertion(true);
return v;
} //这个方法和尚一个方法不同的是,这个方法在key存在时,通过key和value算出一个新的value返回,如果不存在,返回null
public V computeIfPresent(K key,
BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
if (remappingFunction == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Node<K,V> e; V oldValue;
int hash = hash(key);
if ((e = getNode(hash, key)) != null &&
(oldValue = e.value) != null) {
V v = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);
if (v != null) {
e.value = v;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return v;
}
else
removeNode(hash, key, null, false, true);
}
return null;
} @Override
//这个方法综合了上面的两个方法,都会带入remappingFunction进行运算新值,并且替换旧值
public V compute(K key,
BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
if (remappingFunction == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key);
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first; int n, i;
int binCount = 0;
TreeNode<K,V> t = null;
Node<K,V> old = null;
if (size > threshold || (tab = table) == null ||
(n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((first = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
old = (t = (TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
Node<K,V> e = first; K k;
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
old = e;
break;
}
++binCount;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
V oldValue = (old == null) ? null : old.value;
V v = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);
if (old != null) {
if (v != null) {
old.value = v;
afterNodeAccess(old);
}
else
removeNode(hash, key, null, false, true);
}
else if (v != null) {
if (t != null)
t.putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, v);
else {
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, v, first);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1)
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
}
++modCount;
++size;
afterNodeInsertion(true);
}
return v;
} @Override
//这个函数就是将oldVAlue和value通过remappingFunction进行一下混合,然后代替旧值
public V merge(K key, V value,
BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (remappingFunction == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key);
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first; int n, i;
int binCount = 0;
TreeNode<K,V> t = null;
Node<K,V> old = null;
if (size > threshold || (tab = table) == null ||
(n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((first = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
old = (t = (TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
else {
Node<K,V> e = first; K k;
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
old = e;
break;
}
++binCount;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
if (old != null) {
V v;
if (old.value != null)
v = remappingFunction.apply(old.value, value);
else
v = value;
if (v != null) {
old.value = v;
afterNodeAccess(old);
}
else
removeNode(hash, key, null, false, true);
return v;
}
if (value != null) {
if (t != null)
t.putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, first);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1)
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
}
++modCount;
++size;
afterNodeInsertion(true);
}
return value;
} @Override
//对于Map中的每一项,进行action运算
public void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
int mc = modCount;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
action.accept(e.key, e.value);
}
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
} @Override
//Map中所有的值,都会被function(key,value)替换为新值
public void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
if (function == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
int mc = modCount;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
e.value = function.apply(e.key, e.value);
}
}
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
三、HashMap的非线程安全(见博客https://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/7261111.html)
随笔3 HashMap<K,V>的更多相关文章
- Java集合源码分析(七)HashMap<K, V>
一.HashMap概述 HashMap基于哈希表的 Map 接口的实现.此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用 null 值和 null 键.(除了不同步和允许使用 null 之外,HashMap ...
- Java源码 HashMap<K,V>
HashMap类 https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/HashMap.html public class HashMap<K, ...
- 随笔4 Dictionary<K,V>
本来说是想介绍一下Hashtable的,但是发现HashMap和Hashtable最开始的不同就是在于HashMap继承了AbstractMap,而Hashtable继承了Dictionary< ...
- 随笔2 AbstractMap<K,V>
上一篇写了Map接口的源码分析,这一篇写一下Map接口的一个实现类AbstractMap,从名字就可以看出这是一个抽象类,提供了Map接口的骨架实现,为我们实现Map接口的时候提供了很大的便利.在这里 ...
- java:警告:[unchecked] 对作为普通类型 java.util.HashMap 的成员的put(K,V) 的调用未经检查
java:警告:[unchecked] 对作为普通类型 java.util.HashMap 的成员的put(K,V) 的调用未经检查 一.问题:学习HashMap时候,我做了这样一个程序: impor ...
- 统计字符串中每种字符出现的评率(HashMap中getOrDefault(K, V)方法的使用)
为了统计字符串中每种字符出现的频率,使用HashMap这种数据结构.其中,字符作为Key,出现的频率作为Value. 基本算法为: 1. 将字符串分成字符数组 2. (1)如果HashMap中的Key ...
- 随笔1 interface Map<K,V>
第一次写笔记就从map开始吧,如上图所示,绿色的是interface,黄色的是abstract class,蓝色的是class,可以看出所有和图相关的接口,抽象类和类的起源都是interface ma ...
- 关于jsp利用EL和struts2标签来遍历ValueStack的东东 ------> List<Map<K,V>> 以及 Map<K,<List<xxx>>> 的结构遍历
//第一种结构Map<K,<List<xxx>>> <body> <% //显示map<String,List<Object>& ...
- [编程语言][java][java se]java泛型中? T K V E含义(学习)
? 表示不确定的java类型,类型是未知的. T 表示java类型. K V 分别代表java键值中的Key Value. E 代表Element,特性是枚举. 1.意思 jdk中的K,V, ...
随机推荐
- AngularJS的基本概念和用法
mvc 为什么需要mvc(mvc只是手段,终极目标是模块化和复用) 代码规模越来越大,切分职责是大势所趋 为了复用 为了后期维护方便 前端mvc的困难 操作DOM的代码必须等待整个页面全部加载完成. ...
- 微信小程序、SSL证书、开启服务器TSL1.0、TSL1.1、TSL1.2服务
微信小程序.SSL证书.开启服务器TSL1.0.TSL1.1.TSL1.2服务 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_32933615/article/details/70143105
- React-Native 之 GD (九)POST 网络请求封装
1.POST /** * * POST请求 * * @param url * @param params {}包装 * @param headers * * @return {Promise} * * ...
- Zipf's law
w https://www.bing.com/knows/search?q=马太效应&mkt=zh-cn&FORM=BKACAI 马太效应(Matthew Effect),指强者愈强. ...
- (转)Jquery之ShowLoading遮罩组件
本文转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/eczhou/archive/2012/12/18/2822788.html 一.遮罩用途及效果 ShowLoading这个jQuery插件设 ...
- Vue知识整理4:v-html标签
可以在数据绑定中使用html标签,这样在变量里可以使用html标签输出结果,如下所示:
- Delphi XE2 之 FireMonkey 入门(29) - 数据绑定: TBindingsList: 表达式的 Evaluate() 方法
Delphi XE2 之 FireMonkey 入门(29) - 数据绑定: TBindingsList: 表达式的 Evaluate() 方法 TBindingsList 中可能不止一个表达式, 通 ...
- AngleSharp 网络数据采集 -- 使用AngleSharp做html解析
AngleSharp AngleSharp is a .NET library that gives you the ability to parse angle bracket bas ...
- create-react-app 创建react应用环境变量(env)配置
参考:https://facebook.github.io/create-react-app/docs/adding-custom-environment-variables What other . ...
- linux下vscode备忘
vscode如何自定义,如何方便地编写c/c++vscode支持vim.sublime快捷键,在设置->keymap可以安装相应插件vscode默认的快捷键支持自定义,打开keyboard sh ...
