FreeRTOS --(6)内存管理 heap5
转载自https://blog.csdn.net/zhoutaopower/article/details/106748308
FreeRTOS 中的 heap 5 内存管理,相对于 heap 4《FreeRTOS --(5)内存管理 heap4》 只增加了对非连续内存区域的管理,什么叫非连续区域内存呢?比如一款芯片,它即支持了内部的 RAM,也支持了外挂 RAM,那么这两个内存就可能在地址上不是连续的,比如 RAM1、RAM2、RAM3,如下所示:
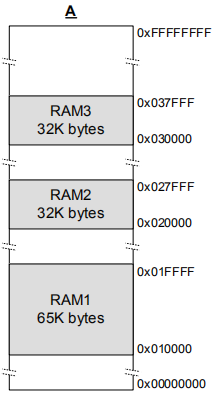
针对这种情况,就可以使用 heap 5 来管理;
不同于之前的 heap 管理,heap 5 引入了一个结构体来管理这些非连续的区域:
typedef struct HeapRegion
{
/* The start address of a block of memory that will be part of the heap.*/
uint8_t *pucStartAddress;
/* The size of the block of memory in bytes. */
size_t xSizeInBytes;
} HeapRegion_t;
一个块连续的内存用一个 HeapRegion_t 表示,多个连续内存通过 HeapRegion_t 数组的形式组织成为了所有的内存;
heap 5 要求,在调用正式的内存分配函数之前,需要定义 HeapRegion,并调用 vPortDefineHeapRegions 来初始化它;
官方给了一个 demo:
/* Define the start address and size of the three RAM regions. */
#define RAM1_START_ADDRESS ( ( uint8_t * ) 0x00010000 )
#define RAM1_SIZE ( 65 * 1024 ) #define RAM2_START_ADDRESS ( ( uint8_t * ) 0x00020000 )
#define RAM2_SIZE ( 32 * 1024 ) #define RAM3_START_ADDRESS ( ( uint8_t * ) 0x00030000 )
#define RAM3_SIZE ( 32 * 1024 ) /* Create an array of HeapRegion_t definitions, with an index for each of the three
RAM regions, and terminating the array with a NULL address. The HeapRegion_t
structures must appear in start address order, with the structure that contains the
lowest start address appearing first. */
const HeapRegion_t xHeapRegions[] =
{
{ RAM1_START_ADDRESS, RAM1_SIZE },
{ RAM2_START_ADDRESS, RAM2_SIZE },
{ RAM3_START_ADDRESS, RAM3_SIZE },
{ NULL, 0 } /* Marks the end of the array. */
};
int main( void ) {
/* Initialize heap_5. */
vPortDefineHeapRegions( xHeapRegions );
/* Add application code here. */
}
如果有 3 个 RAM 区域的话,那么这样去定义他们;
需要注意的几点是:
1、定义 HeapRegion_t 数组的时候,最后一定要定义成为 NULL 和 0,这样接口才知道这是终点;
2、被定义的 RAM 区域,都会去参与内存管理;
那么问题就来了,在真实使用的时候,有可能你很难去定义部分 RAM 的 Start Address!
比如,一款芯片,它告诉你,它的第一块 RAM 有 64KB,第二块 RAM 有 32KB,第三块 RAM 有 32KB,那么你显然不能够直接将这些内存信息,按照上面 demo 代码的形式,定义到这个表格中,因为在编译阶段,有可能你相关的代码和数据等等(.text,.data,.bss,等)都会占用一部分的 RAM,但凡是定义到这个 HeapRegion_t 数组表格的,都会参与内存管理的行为,这显然是我们不愿意的;
也就是说,比如你芯片的 RAM 起始地址 0x2000_0000,你编译你的 Source Code 后,相关的代码和数据要占用 20KB,也就是 0x5000;那么你定义的 RAM1_START_ADDRESS 起始地址,就必须要大于 0x2000_0000+0x5000,这样才不会踩到你的其他数据;但是呢?你总不可能每次编译完都去改你的这个表吧?这是很痛苦的事情;
所有考虑到实际的使用,官方给出参考 demo 的方法是:
/* Define the start address and size of the two RAM regions not used by the
linker. */
#define RAM2_START_ADDRESS ( ( uint8_t * ) 0x00020000 )
#define RAM2_SIZE ( 32 * 1024 ) #define RAM3_START_ADDRESS ( ( uint8_t * ) 0x00030000 )
#define RAM3_SIZE ( 32 * 1024 ) /* Declare an array that will be part of the heap used by heap_5. The array will be
placed in RAM1 by the linker. */
#define RAM1_HEAP_SIZE ( 30 * 1024 ) static uint8_t ucHeap[ RAM1_HEAP_SIZE ]; /* Create an array of HeapRegion_t definitions. Whereas in Listing 6 the first entry
described all of RAM1, so heap_5 will have used all of RAM1, this time the first
entry only describes the ucHeap array, so heap_5 will only use the part of RAM1 that
contains the ucHeap array. The HeapRegion_t structures must still appear in start
address order, with the structure that contains the lowest start address appearing
first. */ const HeapRegion_t xHeapRegions[] =
{
{ ucHeap, RAM1_HEAP_SIZE },
{ RAM2_START_ADDRESS, RAM2_SIZE },
{ RAM3_START_ADDRESS, RAM3_SIZE },
{ NULL, 0 } /* Marks the end of the array. */
};
即,将链接的代码数据,根据链接器(Linker)配置后,这些都放置在第一段的区域,ucHeap 也放在一样的地方,这样就避免去根据 map 文件去硬编码这个表格;
通过 beyond compare 可以知道,heap 5 和 heap 4 的代码在分配内存的 pvPortMalloc,和释放内存的 vPortFree,以及插入节点合并空闲内存 prvInsertBlockIntoFreeList 的部分,几乎完全一样,唯一不一样的地方在于:
heap 4 的内存初始化用的是 prvHeapInit
heap 5 的内存初始化用的是 vPortDefineHeapRegions
那我们就来看看这个 vPortDefineHeapRegions 的实现:
void vPortDefineHeapRegions( const HeapRegion_t * const pxHeapRegions )
{
BlockLink_t *pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion = NULL, *pxPreviousFreeBlock;
size_t xAlignedHeap;
size_t xTotalRegionSize, xTotalHeapSize = 0;
BaseType_t xDefinedRegions = 0;
size_t xAddress;
const HeapRegion_t *pxHeapRegion; /* Can only call once! */
configASSERT( pxEnd == NULL ); pxHeapRegion = &( pxHeapRegions[ xDefinedRegions ] ); while( pxHeapRegion->xSizeInBytes > 0 )
{
xTotalRegionSize = pxHeapRegion->xSizeInBytes; /* Ensure the heap region starts on a correctly aligned boundary. */
xAddress = ( size_t ) pxHeapRegion->pucStartAddress;
if( ( xAddress & portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK ) != 0 )
{
xAddress += ( portBYTE_ALIGNMENT - 1 );
xAddress &= ~portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK; /* Adjust the size for the bytes lost to alignment. */
xTotalRegionSize -= xAddress - ( size_t ) pxHeapRegion->pucStartAddress;
} xAlignedHeap = xAddress; /* Set xStart if it has not already been set. */
if( xDefinedRegions == 0 )
{
/* xStart is used to hold a pointer to the first item in the list of
free blocks. The void cast is used to prevent compiler warnings. */
xStart.pxNextFreeBlock = ( BlockLink_t * ) xAlignedHeap;
xStart.xBlockSize = ( size_t ) 0;
}
else
{
/* Should only get here if one region has already been added to the
heap. */
configASSERT( pxEnd != NULL ); /* Check blocks are passed in with increasing start addresses. */
configASSERT( xAddress > ( size_t ) pxEnd );
} /* Remember the location of the end marker in the previous region, if
any. */
pxPreviousFreeBlock = pxEnd; /* pxEnd is used to mark the end of the list of free blocks and is
inserted at the end of the region space. */
xAddress = xAlignedHeap + xTotalRegionSize;
xAddress -= xHeapStructSize;
xAddress &= ~portBYTE_ALIGNMENT_MASK;
pxEnd = ( BlockLink_t * ) xAddress;
pxEnd->xBlockSize = 0;
pxEnd->pxNextFreeBlock = NULL; /* To start with there is a single free block in this region that is
sized to take up the entire heap region minus the space taken by the
free block structure. */
pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion = ( BlockLink_t * ) xAlignedHeap;
pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion->xBlockSize = xAddress - ( size_t ) pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion;
pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion->pxNextFreeBlock = pxEnd; /* If this is not the first region that makes up the entire heap space
then link the previous region to this region. */
if( pxPreviousFreeBlock != NULL )
{
pxPreviousFreeBlock->pxNextFreeBlock = pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion;
} xTotalHeapSize += pxFirstFreeBlockInRegion->xBlockSize; /* Move onto the next HeapRegion_t structure. */
xDefinedRegions++;
pxHeapRegion = &( pxHeapRegions[ xDefinedRegions ] );
} xMinimumEverFreeBytesRemaining = xTotalHeapSize;
xFreeBytesRemaining = xTotalHeapSize; /* Check something was actually defined before it is accessed. */
configASSERT( xTotalHeapSize ); /* Work out the position of the top bit in a size_t variable. */
xBlockAllocatedBit = ( ( size_t ) 1 ) << ( ( sizeof( size_t ) * heapBITS_PER_BYTE ) - 1 );
}
经过一些对齐操作,将 demo 中的 3 块内存通过链表的方式挂接起来了,只不过内存地址不连续而已,但是对于连续的内存地址中,照样在释放的时候,可以进行合并操作;

FreeRTOS --(6)内存管理 heap5的更多相关文章
- 轻量级操作系统FreeRTOS的内存管理机制(一)
本文由嵌入式企鹅圈原创团队成员朱衡德(Hunter_Zhu)供稿. 近几年来,FreeRTOS在嵌入式操作系统排行榜中一直位居前列,作为开源的嵌入式操作系统之一,它支持许多不同架构的处理器以及多种编译 ...
- FreeRTOS 动态内存管理
以下转载自安富莱电子: http://forum.armfly.com/forum.php 本章节为大家讲解 FreeRTOS 动态内存管理,动态内存管理是 FreeRTOS 非常重要的一项功能,前面 ...
- FreeRTOS的内存管理
FreeRTOS提供了几个内存堆管理方案,有复杂的也有简单的.其中最简单的管理策略也能满足很多应用的要求,比如对安全要求高的应用,这些应用根本不允许动态内存分配的. FreeRTOS也允许你自己实现内 ...
- freertos之内存管理
任务.信号量.邮箱才调度器开始调度之前就应该创建,所以它不可能像裸奔程序那样的函数调用能确定需要多少内存资源,RTOS提供了3种内存管理的方法: 1 方法一:确定性好适合于任务.信号量.队列都不被删除 ...
- FreeRTOS内存管理
简介 Freertos的内存管理分别在heap_1.c,heap_2.c,heap_3.c,heap_4.c,heap_5.c个文件中,选择合适的一种应用于嵌入式项目中即可. 本文的图片中 红色部分B ...
- FreeRTOS --(3)内存管理 heap2
在<FreeRTOS --(2)内存管理 heap1>知道 heap 1 的内存管理其实只是简单的实现了内存对齐的分配策略,heap 2 的实现策略相比 heap 1 稍微复杂一点,不仅仅 ...
- FreeRTOS --(2)内存管理 heap1
转载自https://blog.csdn.net/zhoutaopower/article/details/106631237 FreeRTOS 提供了5种内存堆管理方案,分别对应heap1/heap ...
- FreeRTOS --(5)内存管理 heap4
FreeRTOS 中的 heap 4 内存管理,可以算是 heap 2 的增强版本,在 <FreeRTOS --(3)内存管理 heap2>中,我们可以看到,每次内存分配后都会产生一个内存 ...
- FreeRTOS--堆内存管理
因为项目需要,最近开始学习FreeRTOS,一开始有些紧张,因为两个星期之前对于FreeRTOS的熟悉度几乎为零,经过对FreeRTOS官网的例子程序的摸索,和项目中问题的解决,遇到了很多熟悉的身影, ...
随机推荐
- Java并发机制(1)--线程状态与方法(转)
Java并发编程:Thread类的使用 个人总结:参考:博客园-海子-http://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3920357.html 参考:https://blog ...
- Java 语言如何进行异常处理,关键字:throws、throw、 try、catch、finally 分别如何使用?
Java 通过面向对象的方法进行异常处理,把各种不同的异常进行分类,并提供了良好的接口.在 Java 中,每个异常都是一个对象,它是 Throwable 类或其子类的实例.当一个方法出现异常后便抛出一 ...
- java-設計模式-原型模式
原型模式 是一种创建型设计模式, 使你能够复制已有对象, 而又无需使代码依赖它们所属的类. 問題: 如果我們要複製一個類實例: 首先, 你必须新建一个属于相同类的对象. 然后, 你必须遍历原始对象的所 ...
- Linux用户身份与文件权限学习笔记
用户身份 管理员UID为0:系统的管理员用户 系统用户UID为1~999:服务程序会有独立的系统用户负责运行:防止被黑客入侵进行提权,并有效控制被破坏的范围 普通用户UID从1000开始:是由管理员创 ...
- Redis 集群会有写操作丢失吗?为什么?
Redis 并不能保证数据的强一致性,这意味这在实际中集群在特定的条件下可能会丢失写操作.
- kafka producer 源码总结
kafka producer可以总体上分为两个部分: producer调用send方法,将消息存放到内存中 sender线程轮询的从内存中将消息通过NIO发送到网络中 1 调用send方法 其实在调用 ...
- Java 中堆和栈有什么区别?
JVM 中堆和栈属于不同的内存区域,使用目的也不同.栈常用于保存方法帧和局 部变量,而对象总是在堆上分配.栈通常都比堆小,也不会在多个线程之间共享, 而堆被整个 JVM 的所有线程共享.
- ctfhub rce 命令注入 过滤cat 过滤空格 过滤目录分隔符
命令注入 源码直接给了出来尝试127.0.0.1;ls 发现一串数字的php文件cat查看 127.0.0.1|cat 233382768628619.php 查看源码发现flag 过滤cat 这题和 ...
- AWS 6R
"The 6 R's": 6 Application Migration Strategies "The 6 R's": 6 Application Migra ...
- hbase增删查
代码: package cn.idcast.hbase; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.h ...
