tensorflow之曲线拟合
视频链接:https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/machine-learning/ML-intro/
1.定义层
定义 add_layer()
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1)
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b)
return outputs
解释
add_layer函数有四个形参。分别是
intputs 代表输入值,是这个神经元网络接收的数据,比如第二层网络的inputs就是第一层网络的outputs
in_size 代表输入的数据有几个特征,比如给苹果分类的话,特征可能有 大小、颜色、品种...
out_size 代表输出几个特征
activation_function 默认为None,即 f(x) = x
2.建造神经网络
建造神经网络代码
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
# add one more layer and return the output of this layer
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1)
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b)
return outputs
# Make up some real data
x_data = np.linspace(-1,1,300)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape)
y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise
# define placeholder for inputs to network
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
# add hidden layer
l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
# add output layer
prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, activation_function=None)
# the error between prediction and real data
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction),
reduction_indices=[1]))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
# important step
# tf.initialize_all_variables() no long valid from
# 2017-03-02 if using tensorflow >= 0.12
if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
else:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
for i in range(1000):
# training
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})
if i % 50 == 0:
# to see the step improvement
print(sess.run(loss, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data}))
解释
1. y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise ,可以看到样本数据是个二次函数
2. l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
① 这里添加了一个神经网络层,这一层为隐藏层(实际上这个工程一共三层),输入数据为xs ,xs 为 若干行,一列,代表这里有若干个样本数据,每个样本数据提供一个特征
所以这里in_size 为 1
② 输出10个特征,这个数值是自己添加的(你想写成12也可以,不过要和后边的代码吻合),所以这里out_size 为 10
③ 第四个参数为激励函数 , 激励函数的作用可以打开在这里看一下:https://blog.csdn.net/tyhj_sf/article/details/79932893
文中最后也说 “这个问题目前没有确定的方法,凭一些经验吧。” [无奈脸] 这里使用的relu 函数
④ 这个函数返回这若干个样本的10 个特征,赋值给l1,l1扔给后面的函数
3. prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, activation_function=None) ,这就是那个后面的函数,也是添加层,这一层为输出层。
① l1是前面函数传递过来的,作为本函数的输入数据
② 这里的10 也是前边函数输出的10 个特征,这里作为输入
③ 这里的1 表示最总输出数据的列数,输入层当时提供的每个样本数据特征值为1个,作为预测,输出多个特征是不合理的/莫名其妙的,所以这里的1取决于输入样本值的特征。
④ 激励函数为None,即f(x) = x
这段代码其他地方没什么好说的
3.结果可视化
安装
matplotlib,tkinter.sudo pip3 install matplotlib
sudo apt-get install pyhon-tk
代码全文
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1)
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b)
return outputs
# Make up some real data
x_data = np.linspace(-1, 1, 300)[:, np.newaxis]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape)
y_data = np.square(x_data) - 0.5 + noise
##plt.scatter(x_data, y_data)
##plt.show()
# define placeholder for inputs to network
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
# add hidden layer
l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
# add output layer
prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, activation_function=None)
# the error between prediction and real data
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys-prediction), reduction_indices=[1]))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
# important step
sess = tf.Session()
# tf.initialize_all_variables() no long valid from
# 2017-03-02 if using tensorflow >= 0.12
if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
else:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# plot the real data
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.scatter(x_data, y_data)
plt.ion()
plt.show()
for i in range(1000):
# training
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={xs: x_data, ys: y_data})
if i % 50 == 0:
# to visualize the result and improvement
try:
ax.lines.remove(lines[0])
except Exception:
pass
prediction_value = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: x_data})
# plot the prediction
lines = ax.plot(x_data, prediction_value, 'r-', lw=5)
plt.pause(1)
拟合曲线展示
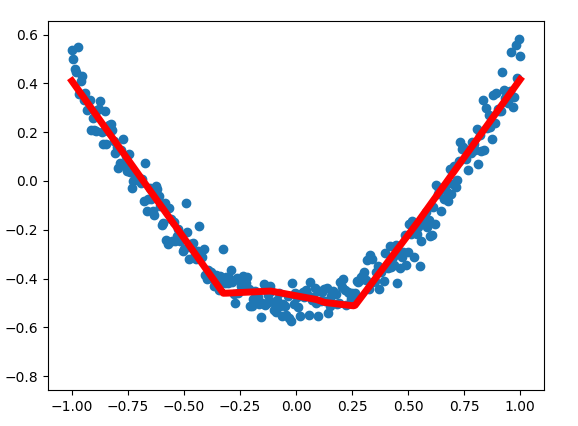
解释
程序中有两次作图,一次是散点的展示,用的函数是
ax.scatter(x_data, y_data),另一次是画出拟合的曲线ax.plot(x_data, prediction_value,),注意,这两个函数分别对应 点 和 线 。ax.lines.remove(lines[0]) ,你和图像的过程是逐渐向正确方向靠拢的过程,所以拟合的曲线也是动态变化的,新的曲线绘制出来的前一瞬间,需要把上一次绘制的拟合曲线删除,就是这句代买的作用
prediction_value = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={xs: x_data}) 获取本次最新训练的预测结果
lines = ax.plot(x_data, prediction_value, 'r-', lw=5) , 将样本数据x,预测结果进行拟合,得到曲线图
plt.pause(1) ,图像暂停1s ,以供程序员观察图像
总结
神奇的激励函数
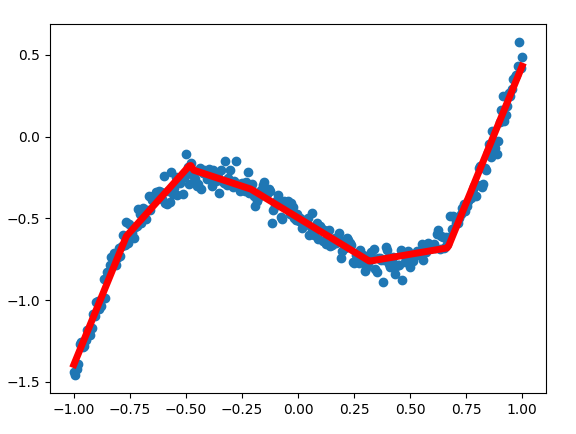
我用这套代码拟合曲线 y_data = 2*x_data*np.square(x_data) - x_data - 0.5 + noise ,发现拟合的也不错,两个样本差别不小的。上边的图像为U行,这里为N形。如下图。
思考
这套代码差不多是我最初接触到的完整代码,但是随着看其他教程推演,第三次看这套代码才看明白。
不能说全明白,比如
- 问题1: 什么情况下使用什么样的激励函数 这个问题,就没有答案。
- 问题2:在这个demo中怎么叫训练好的模型。整个拟合过程也没有可以输出的中间参数
这个问题已经解决了
训练好的模型,就是输出中间权重参数(Weights),和偏差参数(biases)
基本原理:上面提供的代码神经网络共三层,输入层,隐藏层,输出层,其中隐藏层和输出层使用了add_layer()函数,也就是这两层有各自的权重参数和偏差参数。因为这两层的输入(in_size)和输出(out_size)不同,所以这两层的参数的行列数(shape)也是相应不同的。
接下来我们把训练好的参数取出来
① 添加全局变量。在add_layer 函数前边添加
Weights = tf.Variable([-1,-1],dtype = tf.float32)
biases = tf.Variable([-1,-1],dtype = tf.float32)
Weights2 = tf.Variable([-1,-1],dtype = tf.float32)
biases2 = tf.Variable([-1,-1],dtype = tf.float32)
② 改返回,把
return outputs
改为
return outputs,Weights,biases
③ 改接收,把
l1 = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
prediction = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, activation_function=None)
改为
l1,Weights,biases = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function=tf.nn.relu)
prediction,Weights2,biases2 = add_layer(l1, 10, 1, activation_function=None)
④ 在最后添加代码打印这些参数
print("Weights")
print(Weights)
print("biases")
print(biases)
print("Weights2")
print(Weights2)
print("biases2")
print(biases2)
打印参数结果
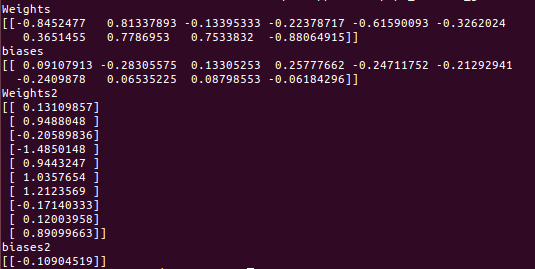
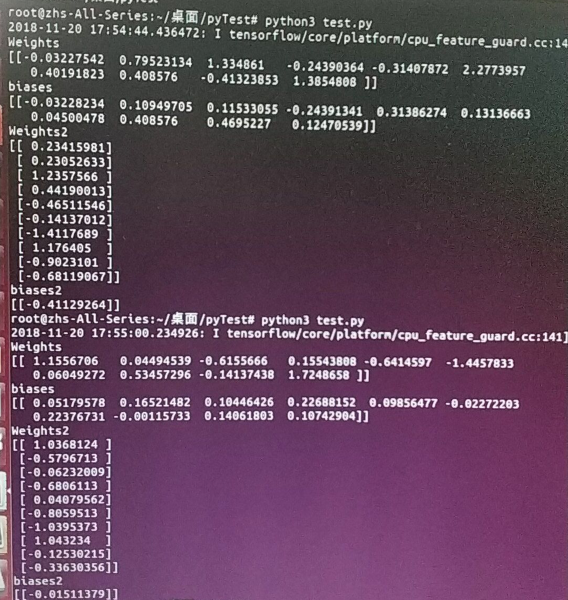
- 问题3:新的结果产生新的问题。在解决问题2之后,运行代码可以得到解,但是带有隐藏层和激励函数的代码每次循行之后得到的结果不同。如以上代码,去掉noise,连续运行两次,得到的是差别比较大的两组解。
之后就什么心得体会或者思考的话再想着回来补充吧
tensorflow之曲线拟合的更多相关文章
- tensorflow之分类学习
写在前面的话 MNIST教程是tensorflow中文社区的第一课,例程即训练一个 手写数字识别 模型:http://www.tensorfly.cn/tfdoc/tutorials/mnist_be ...
- tensorflow 曲线拟合
tensorflow 曲线拟合 Python代码: import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ...
- 机器学习&深度学习基础(tensorflow版本实现的算法概述0)
tensorflow集成和实现了各种机器学习基础的算法,可以直接调用. 代码集:https://github.com/ageron/handson-ml 监督学习 1)决策树(Decision Tre ...
- LSTM(长短期记忆网络)及其tensorflow代码应用
本文主要包括: 一.什么是LSTM 二.LSTM的曲线拟合 三.LSTM的分类问题 四.为什么LSTM有助于消除梯度消失 一.什么是LSTM Long Short Term 网络即为LSTM,是一种 ...
- Tensorflow 官方版教程中文版
2015年11月9日,Google发布人工智能系统TensorFlow并宣布开源,同日,极客学院组织在线TensorFlow中文文档翻译.一个月后,30章文档全部翻译校对完成,上线并提供电子书下载,该 ...
- tensorflow学习笔记二:入门基础
TensorFlow用张量这种数据结构来表示所有的数据.用一阶张量来表示向量,如:v = [1.2, 2.3, 3.5] ,如二阶张量表示矩阵,如:m = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], ...
- 用Tensorflow让神经网络自动创造音乐
#————————————————————————本文禁止转载,禁止用于各类讲座及ppt中,违者必究————————————————————————# 前几天看到一个有意思的分享,大意是讲如何用Ten ...
- tensorflow 一些好的blog链接和tensorflow gpu版本安装
pading :SAME,VALID 区别 http://blog.csdn.net/mao_xiao_feng/article/details/53444333 tensorflow实现的各种算法 ...
- tensorflow中的基本概念
本文是在阅读官方文档后的一些个人理解. 官方文档地址:https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/r0.12/get_started/basic_usage.html#ba ...
随机推荐
- debian系统,启动Wireshark,出现Couldn't run /usr/bin/dumpcap in child process:权限不够
这是由于当前用户没有权限运行/usr/bin/dumpcap造成的./usr/bin/dumpcap是Wireshark的包捕获引擎. 先用ls命令看一下dumpcap的权限情况:xy@debian- ...
- jquery实现复选框的全选、全不选、反选
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- golang总结-并发
目录 2.7 并发编程 go协程 go管道 2.7 并发编程 go协程 golang 通过一个go关键字就可以开启一个协程. func main() { //两个交错输出 go sayHello() ...
- 关于虚拟机linux网络的一个问题(基于cntos7)
刚刚开始学习搭建Linux集群,目前出现的比较麻烦的一个问题是Linux网络ip问题.其实网上好多出现类似问题的解答大部分说是因为克隆的问题,但实际情况先克隆产生的问题应该是很好排查的.所幸,有博主针 ...
- python学习第二天 -----2019年4月17日
第二周-第02章节-Python3.5-模块初识 #!/usr/bin/env python #-*- coding:utf-8 _*- """ @author:chen ...
- 第三章:文件I/O
本章开始讨论UNIX系统的文件I/O函数,包括打开文件.读文件.写文件等. UNIX系统中的大多数文件I/O只需要用到5个函数:open.read.write.lseek和close.它们每执行一次都 ...
- Asp.Net Core跨域配置
在没有设置跨域配置的时候,Ajax请求时会报以下错误 已拦截跨源请求:同源策略禁止读取位于 http://localhost:5000/Home/gettime 的远程资源.(原因:CORS 头缺少 ...
- PAT (Advanced Level) Practice 1003 Emergency
思路:用深搜遍历出所有可达路径,每找到一条新路径时,对最大救援人数和最短路径数进行更新. #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #includ ...
- SSM-CRUD入门项目——查询
查询 1.基础查询 分析:访问项目主页 index.jsp 时应该跳转到列表页 我们可以在index.jsp发出查询员工列表请求,来到 list.jsp 使用插件 pageHelper 完成分页功能— ...
- 20155236 《信息安全概论》实验二(Windows系统口令破解)实验报告
20155236 <信息安全概论>实验二(Windows系统口令破解)实验报告 北京电子科技学院(BESTI) 实验报告 课程:信息安全概论 班级:1552 姓名:范晨歌 学号:20155 ...
