在进行神经网络训练时需要使用的显存空间大小的预估——300MB的神经网络在训练时最少需要占用多大的显存空间
以Tensorflow为例。
=======================================
神经网络(TensorFlow举例)在GPU中训练时需要占用的内存大概有下面几部分组成:
1. TensorFlow的自身的计算库导入显存时所在内存,一般在session初始化时就会自动导入,这部分大小与TensorFlow的版本有关,这里大概估计普遍为450MB大小;
2. 神经网络的本身模型大小;
3. 优化器对神经网络模型进行优化时自身参数大小,一般一阶优化器的自身参数大小和神经网络模型本身大小相同,二阶优化器一般为模型本身大小的两倍(如:RMSProp优化器);
4. 神经网络前向计算时所产生的临时Tensor,这部分Tensor需要被临时保存,以便在反传计算梯度时使用,这部分Tensor的大小和模型的每一层结构形状有关(必须根据具体模型的每层形状来计算)也和具体的batch_size大小以及输入数据input_data的大小有关;
5. 神经网络向后性计算时被人为设定的一些负责监督运行状态或其他操作的Tensor,如:某些层的反传计算出的梯度进行正则化后或进行求mean/std/max/min等操作产生的Tensor,某些层前传时计算该层输出的一些统计Tensor(求mean/std/max/min等操作产生的Tensor);
--------------------------------------------
在估计一个模型在训练时所需的显存空间一般可以考虑将上面1, 2, 3部分的大小加总即可;4部分的大小难以计算,毕竟这个大小还和输入数据的大小和batch_size有关,而且每层的输出结构也是差异极大的;5部分的大小一般有限,可以不主要考虑。
PS:
这里需要说明一下,有些时候我们在跑模型训练的时候发现显存不够报错的时候我们可以通过调小batch_size的方式来解决,这时候我们就是通过调小第4部分显存大小来解决的;但是有些时候即使把batch_size设置为1也无法满足,那么就应该是第1,2,3部分所占显存空间已经超出了可用空间大小。
--------------------------------------------
关于第一部分显存大小,下面给出TensorFlow1.14版本的情况:


查看显存占用:

可以看到导入库后所占显存大小为104MB。
--------------------------------------------
关于第2, 3部分的大小,我们使用例子:(只给出项目中进行修改的文件)
https://gitee.com/devilmaycry812839668/paac/blob/master/actor_learner.py
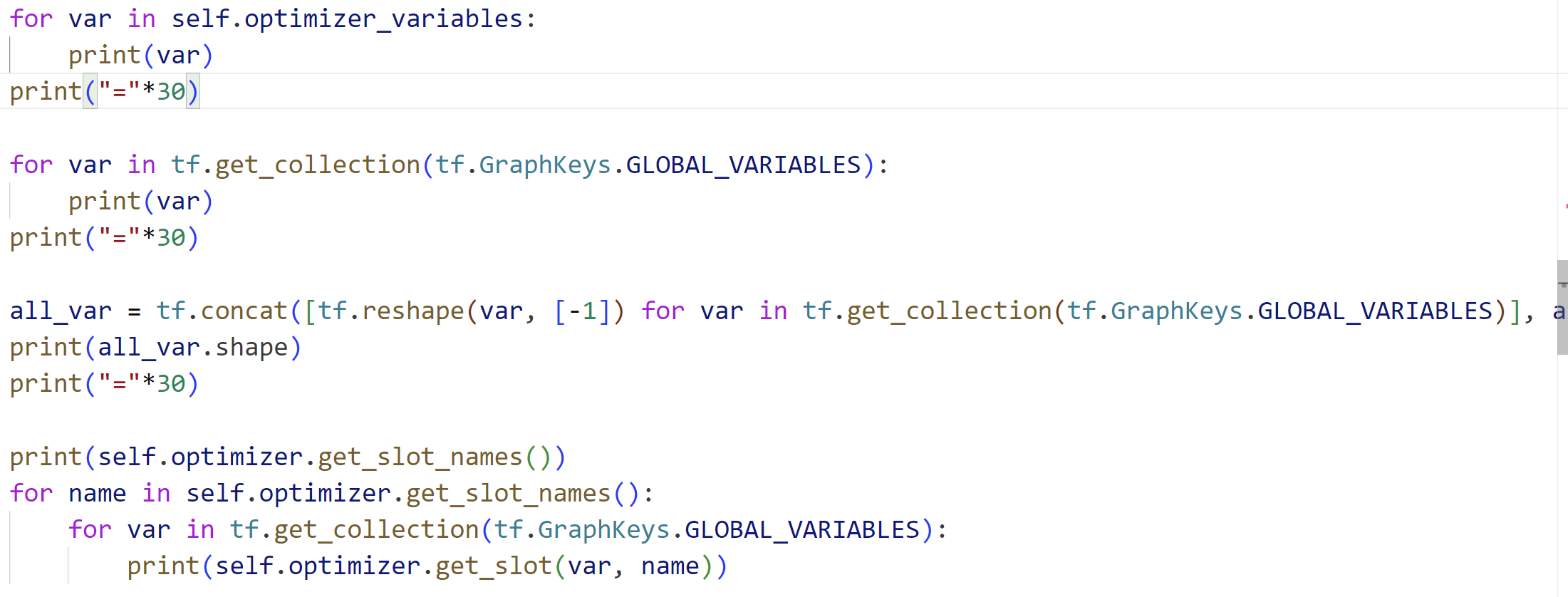
我们在__init__函数中添加下面代码:
for var in self.optimizer_variables:
print(var)
print("="*30) for var in tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES):
print(var)
print("="*30) all_var = tf.concat([tf.reshape(var, [-1]) for var in tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES)], axis=0)
print(all_var.shape)
print("="*30) print(self.optimizer.get_slot_names())
for name in self.optimizer.get_slot_names():
for var in tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES):
print(self.optimizer.get_slot(var, name))
运行结果:
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(8, 8, 4, 16) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(8, 8, 4, 16) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(16,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(16,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(4, 4, 16, 32) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(4, 4, 16, 32) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(32,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(32,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(2592, 256) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(2592, 256) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256, 6) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256, 6) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(6,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(6,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256, 1) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256, 1) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(1,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(1,) dtype=float32_ref>
==============================
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_weights:0' shape=(8, 8, 4, 16) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_biases:0' shape=(16,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_weights:0' shape=(4, 4, 16, 32) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_biases:0' shape=(32,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_weights:0' shape=(2592, 256) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_biases:0' shape=(256,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_weights:0' shape=(256, 6) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_biases:0' shape=(6,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_weights:0' shape=(256, 1) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_biases:0' shape=(1,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(8, 8, 4, 16) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(8, 8, 4, 16) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(16,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(16,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(4, 4, 16, 32) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(4, 4, 16, 32) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(32,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(32,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(2592, 256) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(2592, 256) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256, 6) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256, 6) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(6,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(6,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256, 1) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256, 1) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(1,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(1,) dtype=float32_ref>
==============================
(2033829,)
==============================
['momentum', 'rms']
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(8, 8, 4, 16) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(16,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(4, 4, 16, 32) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(32,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(2592, 256) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256, 6) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(6,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256, 1) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(1,) dtype=float32_ref>
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(8, 8, 4, 16) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(16,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(4, 4, 16, 32) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(32,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(2592, 256) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256, 6) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(6,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256, 1) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(1,) dtype=float32_ref>
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
None
通过结果我们可以知道,第2部分显存为模型的参数,即10个Tensor Variable所占,第3部分为20个针对模型参数的优化器参数,即20个Tensor Variable所占;其中模型参数(10个Variable)大小总共为(MB):

优化器的参数时模型参数的两倍,所以总共的Variable参数为3倍的模型参数(MB):

模型参数,10个Variable:
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_weights:0' shape=(8, 8, 4, 16) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_biases:0' shape=(16,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_weights:0' shape=(4, 4, 16, 32) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_biases:0' shape=(32,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_weights:0' shape=(2592, 256) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_biases:0' shape=(256,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_weights:0' shape=(256, 6) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_biases:0' shape=(6,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_weights:0' shape=(256, 1) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_biases:0' shape=(1,) dtype=float32_ref>
优化器参数(二阶),20个Variable:
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(8, 8, 4, 16) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(8, 8, 4, 16) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(16,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(16,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(4, 4, 16, 32) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(4, 4, 16, 32) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(32,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(32,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(2592, 256) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(2592, 256) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256, 6) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256, 6) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(6,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(6,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256, 1) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256, 1) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(1,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(1,) dtype=float32_ref>
其中,这20个优化器参数在槽['momentum']中的有:
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(8, 8, 4, 16) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(16,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(4, 4, 16, 32) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(32,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(2592, 256) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256, 6) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(6,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_weights/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(256, 1) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_biases/OptimizerVariables_1:0' shape=(1,) dtype=float32_ref>
其中,这20个优化器参数在槽['rms']中的有:
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv1_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(16,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(4, 4, 16, 32) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/conv2_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(32,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(2592, 256) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_1/fc3_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256, 6) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/actor_output_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(6,) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_weights/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(256, 1) dtype=float32_ref>
<tf.Variable 'local_learning_2/critic_output_biases/OptimizerVariables:0' shape=(1,) dtype=float32_ref>
判断优化器中参数是否可以训练:



查询结果:

------------------------------------------------------
可以看到,在例子中,第2部分和第3部分的显存大小共为:7.7584MB
而第1部分的显存占用为104MB,那么我们运行下例子所在的项目,看下总共在训练时占用显存大小:

由此我们可以知道,即使是一些模型大小特别小的模型(模型参数加优化器参数共7.7584MB)也可以在运行时占用大量显存,这时候所占用显存的主要为第4部分和第5部分所占,我们将batch_size设置为1,然后再看下:
此时项目启动命令:python3 train.py -g pong -df logs/ -ec 1 -ew 1 --max_local_steps 1

PS:
通过这个例子,我们可以知道,即使一个模型特别小(优化器参数也随之很小,共7.7584MB),但是计算过程中所需导入显存的lib库和训练过程中产生的临时Tensor、用于检测的Tensor所占的空间大小也可以是很大的,甚至是近百倍于模型参数大小;所以说一个模型在训练过程中所需最小显存空间并不由模型参数大小所完全决定,有时候训练过程中的临时Tensor大小会大于模型参数大小;通过修改batch_size可以缩小训练过程中的临时Tensor大小,但是这个缩小程度毕竟有限,例子中通过减小batch size所获增加的空余显存空间为832-592=240MB。
------------------------------------------------------
RMSProp优化器:

参考:
https://www.coder.work/article/93009
=======================================
在进行神经网络训练时需要使用的显存空间大小的预估——300MB的神经网络在训练时最少需要占用多大的显存空间的更多相关文章
- 交叉熵代价函数——当我们用sigmoid函数作为神经元的激活函数时,最好使用交叉熵代价函数来替代方差代价函数,以避免训练过程太慢
交叉熵代价函数 machine learning算法中用得很多的交叉熵代价函数. 1.从方差代价函数说起 代价函数经常用方差代价函数(即采用均方误差MSE),比如对于一个神经元(单输入单输出,sigm ...
- 用SQL语句实现:当A列大于B列时选择A列否则选择B列,当B列大于C列时选择B列否则选择C列。
数据库中有A B C三列,用SQL语句实现:当A列大于B列时选择A列否则选择B列,当B列大于C列时选择B列否则选择C列. 方法一: select (case when a>b then a el ...
- 设置一个div网页滚动时,使其固定在头部,当页面滚动到距离头部300px时,隐藏该div,另一个div在底部,此时显示;当页面滚动到起始位置时,头部div出现,底部div隐藏
设置一个div网页滚动时,使其固定在头部,当页面滚动到距离头部300px时,隐藏该div,另一个div在底部,此时显示: 当页面滚动到起始位置时,头部div出现,底部div隐藏 前端代码: <! ...
- 在mvc返回JSON时出错:序列化类型为“System.Data.Entity.DynamicProxies.Photos....这个会的对象时检测到循环引用 的解决办法
在MVC中返回JSON时出错,序列化类型为“System.Data.Entity.DynamicProxies.Photos....这个会的对象时检测到循环引用. public ActionResul ...
- 题目:企业发放的奖金根据利润提成。 利润(I)低于或等于10万元时,奖金可提10%; 利润高于10万元,低于20万元时,低于10万元的部分按10%提成,高于10万元的部分,可可提成7.5%; 20万到40万之间时,高于20万元的部分,可提成5%; 40万到60万之间时高于40万元的部分,可提成 3%; 60万到100万之间时,高于60万元的部分,可提成1.5%; 高于100万元时,超过
题目:企业发放的奖金根据利润提成. 利润(I)低于或等于10万元时,奖金可提10%: 利润高于10万元,低于20万元时,低于10万元的部分按10%提成,高于10万元的部分,可可提成7.5%: 20万到 ...
- SQL语句实现:当A列大于B列时选择A列否则选择B列,当B列大于C列时选择B列否则选择C列
分享一道今天的面试题:SQL语句实现:数据库中有A B C三列,当A列大于B列时选择A列否则选择B列,当B列大于C列时选择B列否则选择C列 第一种:使用case when...then...else ...
- 代码实现:企业发放的奖金根据利润提成。利润(I)低于或等于10万元时,奖金可提10%; 利润高于10万元,低于20万元时,低于10万元的部分按10%提成,高于10万元的部分,可可提成7.5%; 20万到40万之间时,高于20万元的部分,可提成5%;40万到60万之间时高于40万元的部分,可提成3%; 60万到100万之间时,高于60万元的部分,可提成1.5%,高于100万元时,超过100万元
import java.util.Scanner; /* 企业发放的奖金根据利润提成.利润(I)低于或等于10万元时,奖金可提10%: 利润高于10万元,低于20万元时,低于10万元的部分按10%提成 ...
- iOS开发之UIImage在压缩时失真问题,压缩图片的大小
今天遇到UIImage在压缩时失真问题,压缩图片的大小图片模糊 错误的方案 /** * 压缩图片 * image:将要压缩的图片 size:压缩后的尺寸 */ -(UIImage*) OriginIm ...
- 深度学习原理与框架-猫狗图像识别-卷积神经网络(代码) 1.cv2.resize(图片压缩) 2..get_shape()[1:4].num_elements(获得最后三维度之和) 3.saver.save(训练参数的保存) 4.tf.train.import_meta_graph(加载模型结构) 5.saver.restore(训练参数载入)
1.cv2.resize(image, (image_size, image_size), 0, 0, cv2.INTER_LINEAR) 参数说明:image表示输入图片,image_size表示变 ...
- 【神经网络与深度学习】Caffe使用step by step:使用自己数据对已经训练好的模型进行finetuning
在经过前面Caffe框架的搭建以及caffe基本框架的了解之后,接下来就要回到正题:使用caffe来进行模型的训练. 但如果对caffe并不是特别熟悉的话,从头开始训练一个模型会花费很多时间和精力,需 ...
随机推荐
- 【干货分享】.NET人脸识别解决方案
前言 前段时间有同学在DotNetGuide技术社区交流群提问:.NET做人脸识别功能有什么好的解决方案推荐的吗?今天大姚给大家推荐2款.NET开源.免费.跨平台.使用简单的人脸识别库,希望可以帮助到 ...
- @Valid + BindingResult 拦截接口错误信息
@Valid + BindingResult 拦截接口错误信息###测试发现: HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, 需要 ...
- idea部署运行tomcat项目方法
在导航栏点击Add Configuration-或者(打开菜单Run->Edit Configuration) 点击+号,选择Tomcat Server ->选择Local->在Na ...
- @Async异步方法对异常的处理,从内层向外层抛出机制
@Async异步方法对异常的处理,从内层向外层抛出机制 @RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.GET) p ...
- 如何使用 Dump 文件?
引言 本文概述了使用 WinDbg 的一些必要步骤. 准备工作 第一步,你必须更改系统的配置使其能够生成 PDB 文件,包括 Release 版本.近期的 Visual C++ 编译器默认启用此配置, ...
- 数据分析---matplotlib模块的使用
1.摘要 在数据可视化.统计绘图和图表生成领域,Python 被广泛使用,其中 Matplotlib 是一个极其重要的基础三方库.本博客旨在介绍 Python 及其三方库 Matplotlib 的详细 ...
- 你了解Vim的增删改查吗 ?
增: 在Vim的Normal模式中输入A/I/O,a/i/o字符进行对应的增加操作. 删 在Vim的Normal模式中, 输入x 删除光标对应的一个字符(4x代表删除4个字符): 输入dd删除光标所在 ...
- Oracle自动化编译无效对象
问题描述:使用存储过程的方式对oracle数据库的无效对象,如视图或者同义词进行定期的编译,让他变成一个有效的对象,加上定时任务可以实现自动化的处理.同时在数据库内部创建一个记录表,用来记录被编译过的 ...
- B码对时方案,基于TI AM62x异构多核工业处理器实现!
什么是IRIG-B码对时 IRIG-B(inter-range instrumentationgroup-B)码是一种时间同步标准,通常用于精确的时间测量和数据同步,广泛应用于电力.通信.航空等领域. ...
- 树莓派4B-MAX9814麦克风模块
树莓派4B-MAX9814麦克风模块 硬件需求 树莓派 MAX9814模块 杜邦线 MAX9814模块 电子特性 实验电路板 实验电路局部 典型工作特性 引角接线 代码展示 import RPi.GP ...
