Spring Cloud Gateway实战之二:更多路由配置方式
欢迎访问我的GitHub
https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos
内容:所有原创文章分类汇总及配套源码,涉及Java、Docker、Kubernetes、DevOPS等;
本篇概览
- 本文是《Spring Cloud Gateway实战》系列的第二篇,通过前文咱们了解到Spring Cloud Gateway的核心是路由配置,然后在本地application.yml中配置了一条路由,但这种修改本地配置文件的方式缺乏灵活性,未必能满足灵活多变的业务需求,因此,本篇的目的就是找出本地配置之外的其他配置方式来,满足各种实际需求;
- 总的来说以下三种方式都是常用的:
- 目标地址支持用服务名(取代之前的IP+端口);
- 支持在nacos上配置;
- 支持写代码的方式配置;
- 另外还有一种更加灵活的配置方式:动态代理,因为涉及到不少的代码所以会单独出一篇文章详细介绍
源码下载
- 本篇实战中的完整源码可在GitHub下载到,地址和链接信息如下表所示(https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos):
| 名称 | 链接 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 项目主页 | https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos | 该项目在GitHub上的主页 |
| git仓库地址(https) | https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos.git | 该项目源码的仓库地址,https协议 |
| git仓库地址(ssh) | git@github.com:zq2599/blog_demos.git | 该项目源码的仓库地址,ssh协议 |
- 这个git项目中有多个文件夹,本篇的源码在spring-cloud-tutorials文件夹下,如下图红框所示:

准备工作
正式开始前需要再做一点准备工作,整个《Spring Cloud Gateway实战》系列中,所有请求最后都会被路由到provider-hello这个web上去,该服务目前只有一个web接口/hello/str,现在咱们再给它增加一个,后面的实战会用到
新增加的web接口来自LBTest.java,可见非常简单:
package com.bolingcavalry.provider.controller;
import com.bolingcavalry.common.Constants;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/lbtest")
public class LBTest {
private String dateStr(){
return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss").format(new Date());
}
/**
* 返回字符串类型
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/str")
public String helloStr() {
return Constants.LB_PREFIX + ", " + dateStr();
}
}
- 上述代码中的Constants.LB_PREFIX来自子工程common:
package com.bolingcavalry.common;
public interface Constants {
String HELLO_PREFIX = "Hello World";
String LB_PREFIX = "Load balance";
}
写完代码后,先确保nacos已经启动
在启动provider-hello工程,启动成功后去看nacos,确认已经注册:
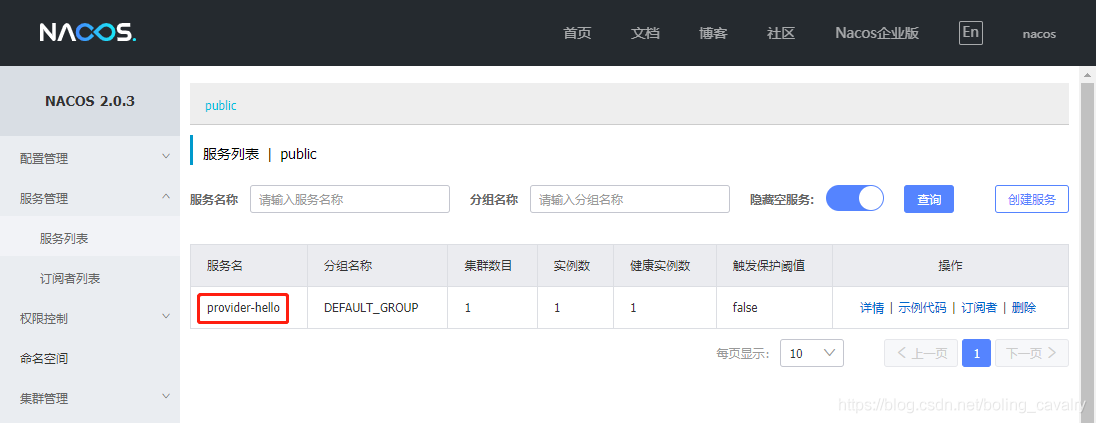
- 准备完毕,可以开始实战了
目标地址支持用服务名(取代之前的IP+端口)
- 咱们从最简单的开始,先看前文的路由配置,如下图红框,目标地址是IP+端口:
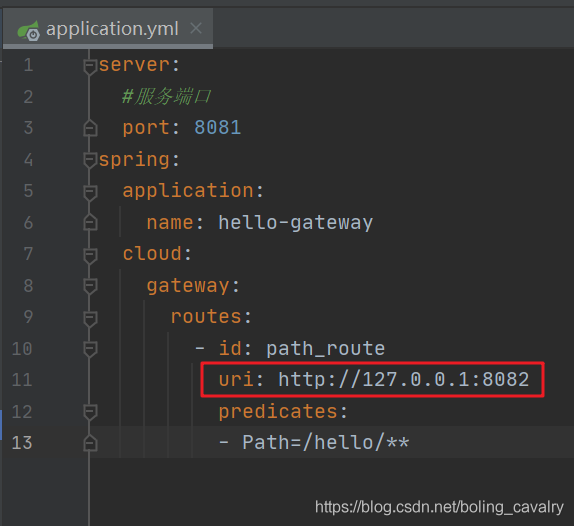
玩过Spring Cloud的您自然看出了问题所在:没有注册发现,确实,这样将地址和端口写死在配置文件中是不合适的,咱们先来解决这个问题;
新增名为gateway-by-loadbalance的子工程,其pom.xml中的依赖情况如下,可见重点是spring-cloud-starter-loadbalancer:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.bolingcavalry</groupId>
<artifactId>common</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId>
<artifactId>reactor-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 路由策略使用lb的方式是,这个依赖一定要有 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-loadbalancer</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--nacos:注册中心-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
启动类的代码省去了(和前文的一样)
配置信息如下,重点是uri的值lb://provider-hello,用了前缀lb:,后面的provider-hello就是在nacos注册的服务名:
server:
#服务端口
port: 8085
spring:
application:
name: gateway-by-loadbalance
cloud:
nacos:
# 注册中心的配置
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
gateway:
routes:
- id: path_route_lb
uri: lb://provider-hello
predicates:
- Path=/lbtest/**
- 单元测试类:
package com.bolingcavalry.gateway;
import com.bolingcavalry.common.Constants;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.reactive.AutoConfigureWebTestClient;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import org.springframework.test.web.reactive.server.WebTestClient;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
@SpringBootTest
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@AutoConfigureWebTestClient
public class HelloTest {
@Autowired
private WebTestClient webClient;
@Test
void testLoadBalance() {
webClient.get()
.uri("/lbtest/str")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.exchange()
// 验证状态
.expectStatus().isOk()
// 验证结果,注意结果是字符串格式
.expectBody(String.class).consumeWith(result -> assertTrue(result.getResponseBody().contains(Constants.LB_PREFIX)));
}
}
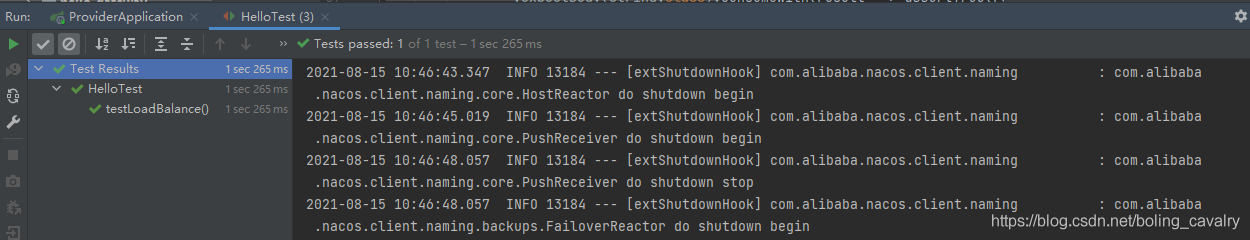
- 运行单元测试,通过,可见上述配置可以通过前缀lb:准确找到服务:
支持在nacos上配置
将所有配置信息写在application.yml中有个问题:不能远程配置,这在应用数量较多的场景就不方便了,好在nacos提供了远程配置的能力,应用启动后可以从nacos取得自己的配置信息,咱们来试试
新增名为gateway-nacos-config的子工程,其pom.xml中的依赖情况如下,请注意里面的中文注释,每指明了每一个依赖的作用:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.bolingcavalry</groupId>
<artifactId>common</artifactId>
<version>${project.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId>
<artifactId>reactor-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用bootstrap.yml的时候,这个依赖一定要有 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 路由策略使用lb的方式是,这个依赖一定要有 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-loadbalancer</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--nacos:配置中心-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--nacos:注册中心-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 本地的配置文件bootstrap.yml,非常简单,就是nacos的地址和远程配置信息:
spring:
application:
name: gateway-nacos-config
cloud:
nacos:
config:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
file-extension: yml
group: DEFAULT_GROUP
- 接下来再nacos增加一个配置文件,操作如下图红框:
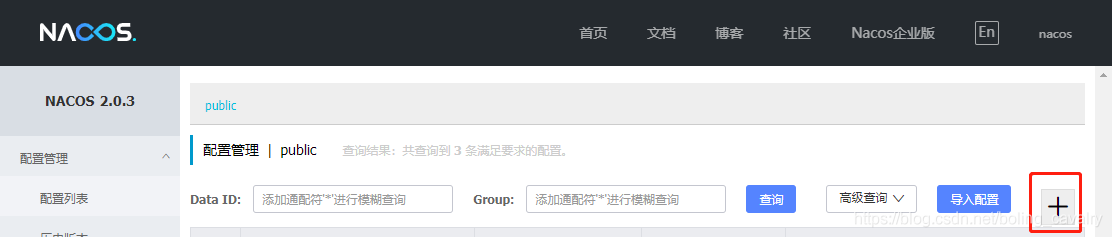
- 增加一个配置,要注意的地方如下(配置信息的文本稍后给出,便于复制):
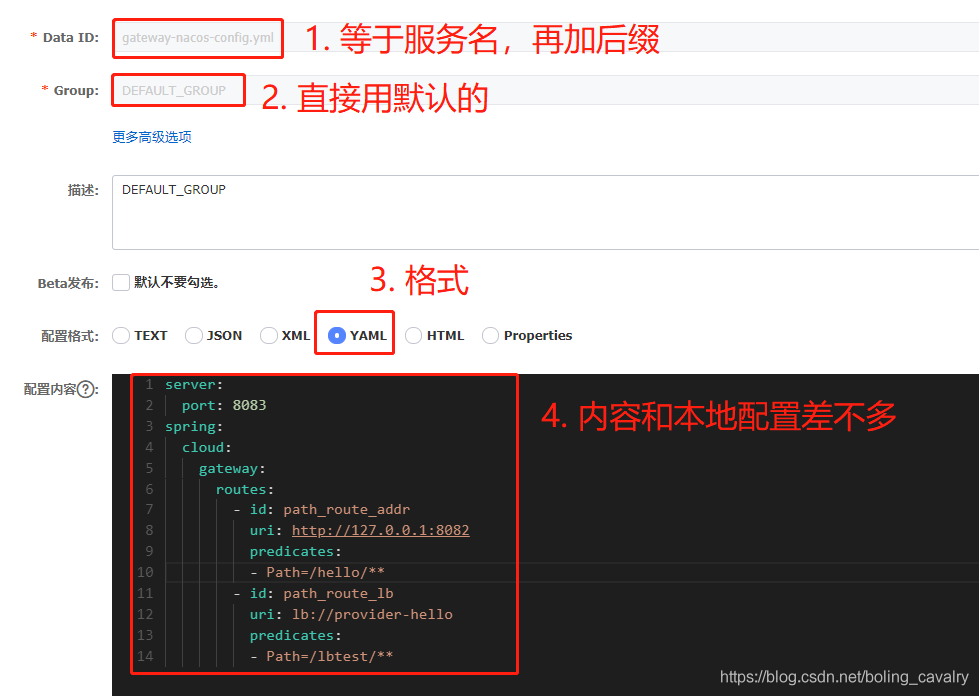
- 上图中完整的配置信息如下:
server:
port: 8083
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: path_route_addr
uri: http://127.0.0.1:8082
predicates:
- Path=/hello/**
- id: path_route_lb
uri: lb://provider-hello
predicates:
- Path=/lbtest/**
- 测试类中的两个测试方法如下所示,和前面没有任何区别:
@Test
void testHelloPredicates() {
webClient.get()
.uri("/hello/str")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.exchange()
// 验证状态
.expectStatus().isOk()
// 验证结果,注意结果是字符串格式
.expectBody(String.class).consumeWith(result -> assertTrue(result.getResponseBody().contains(Constants.HELLO_PREFIX)));
}
@Test
void testLoadBalance() {
webClient.get()
.uri("/lbtest/str")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.exchange()
// 验证状态
.expectStatus().isOk()
// 验证结果,注意结果是字符串格式
.expectBody(String.class).consumeWith(result -> assertTrue(result.getResponseBody().contains(Constants.LB_PREFIX)));
}
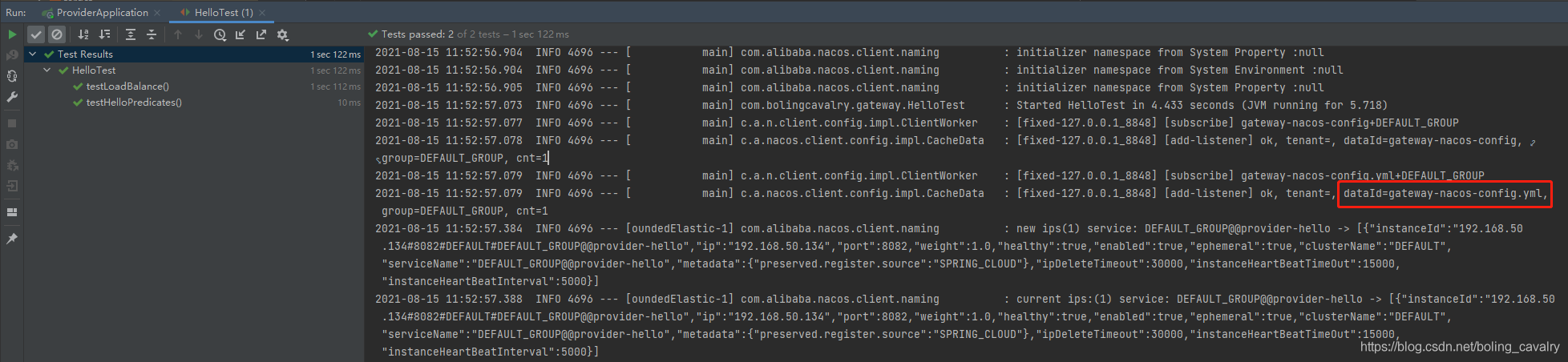
- 运行单元测试类,测试通过,证明从nacos获取配置文件成功:
写代码的方式配置
前面的几个例子,路由信息都是写在配置文件中的,其实还有一种方式:写代码配置路由,能自己写代码来配置,这灵活性就更强了
新增名为gateway-by-code的子工程,其pom.xml文件参照前面工程的即可
接下来的本例的重点,在配置类中增加一个RouteLocator类型的bean,通过以下代码即可增加一个路由:
package com.bolingcavalry.gateway.cofig;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteLocator;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.builder.RouteLocatorBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RouteConfig {
@Bean
public RouteLocator customizeRoute(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder
.routes()
.route(
// 第一个参数是路由的唯一身份
"path_route_lb",
// 第二个参数是个lambda实现,
// 设置了配套条件是按照请求路径匹配,以及转发地址,
// 注意lb://表示这是个服务名,要从
r -> r.path("/lbtest/**").uri("lb://provider-hello")
)
.build();
}
}
- 上述代码只配置了一个路由,还有一个在配置文件中,这样就能验证代码和配置文件能不能同时生效了:
server:
#服务端口
port: 8084
spring:
application:
name: gateway-by-code
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
# nacos服务地址
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
gateway:
routes:
- id: path_route_addr
uri: http://127.0.0.1:8082
predicates:
- Path=/hello/**
测试类和之前工程的一模一样,就不占用篇幅了,依旧是两个测试方法testHelloPredicates和testLoadBalance
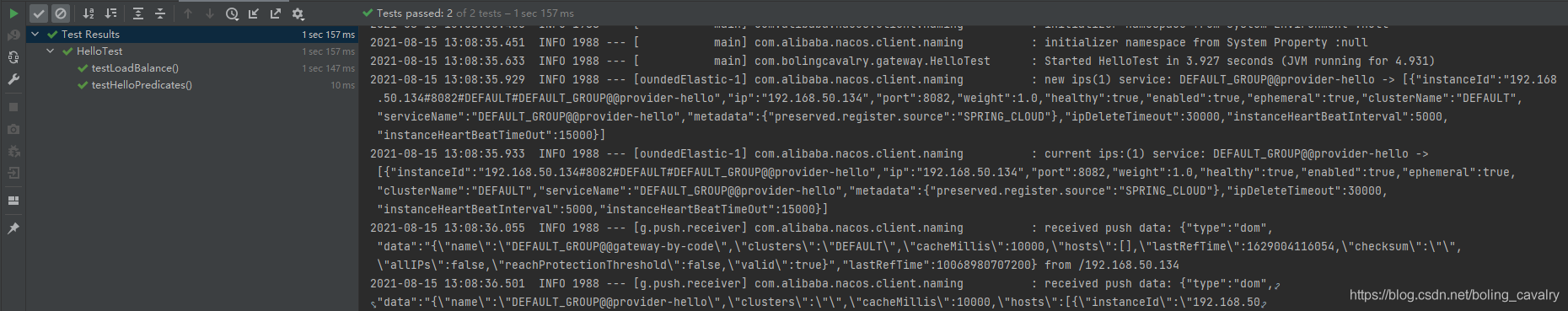
执行单元测试可以顺利通过,证明代码配置路由没有问题:
- 至此,负载均衡、nacos配置、代码配置的实例咱们都尝试过了,它们合起来会给实际生存环境的配置带来很大的方便,希望能够给您一些参考
缺陷和解决之道
- 上述配置方式虽多,但有一个共同的问题:每当配置变动后,Gateway应用需要重启才能生效,这在请求不间断的生产环境是难以接受的
- 为了让最新的路由配置能在Gateway应用不重启的前提下生效,接下来的文章咱们一起去探索动态路由是如何实现的
你不孤单,欣宸原创一路相伴
欢迎关注公众号:程序员欣宸
微信搜索「程序员欣宸」,我是欣宸,期待与您一同畅游Java世界...
https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos
Spring Cloud Gateway实战之二:更多路由配置方式的更多相关文章
- Spring Cloud Gateway实战之三:动态路由
欢迎访问我的GitHub https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos 内容:所有原创文章分类汇总及配套源码,涉及Java.Docker.Kubernetes.DevOPS ...
- Spring Cloud Gateway实战之一:初探
欢迎访问我的GitHub 这里分类和汇总了欣宸的全部原创(含配套源码):https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos 关于<Spring Cloud Gateway实 ...
- Spring Cloud Gateway实战之四:内置predicate小结
欢迎访问我的GitHub https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos 内容:所有原创文章分类汇总及配套源码,涉及Java.Docker.Kubernetes.DevOPS ...
- Spring Cloud Gateway实战之五:内置filter
欢迎访问我的GitHub https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos 内容:所有原创文章分类汇总及配套源码,涉及Java.Docker.Kubernetes.DevOPS ...
- Spring Cloud gateway 网关服务二 断言、过滤器
微服务当前这么火爆的程度,如果不能学会一种微服务框架技术.怎么能升职加薪,增加简历的筹码?spring cloud 和 Dubbo 需要单独学习.说没有时间?没有精力?要学俩个框架?而Spring C ...
- Spring Cloud Gateway(七):路由谓词工厂WeightRoutePredicateFactory
本文基于 spring cloud gateway 2.0.1 接上文 5.基于路由权重(weigth)的谓词工厂 Spring Cloud Gateway 提供了基于路由权重的断言工厂,配置时指定分 ...
- Spring Cloud Gateway(六):路由谓词工厂 RoutePredicateFactory
本文基于 spring cloud gateway 2.0.1 1.简介 Spring Cloud Gateway 创建 Route 对象时, 使用 RoutePredicateFactory 创建 ...
- Spring Cloud Gateway(五):路由定位器 RouteLocator
本文基于 spring cloud gateway 2.0.1 1.简介 直接 获取 路 由 的 方法 是 通过 RouteLocator 接口 获取. 同样, 该 顶 级 接口 有多 个 实现 类, ...
- Spring Cloud Gateway(四):路由定义定位器 RouteDefinitionLocator
本文基于 spring cloud gateway 2.0.1 1.简介 RouteDefinitionLocator 是路由定义定位器的顶级接口,它的主要作用就是读取路由的配置信息(org.spri ...
随机推荐
- javascript 比较版本号大小 字符串
* 不用系统比较大小的函数 // 不考虑字母 function s2i(s) { return s.split('').reduce(function(a, c) { var code = c.cha ...
- Jmeter导出测试报告
测试数据概述 jemter导出数据 另存为导出csv文件 命令行导出 测试报告的作用: 反馈结果 复现问题,所以需要写明测试场景.数据
- Markdown 编写技巧汇总(一)
编写文档,有很多格式选择,也有不同平台选择.下面就自己接触到的MarkDown编写文档的各种技巧做简单梳理,供自己参阅,也希望帮到网友. [1]添加空格 ① 这种写法比较老土,但是,很实用!注意都 ...
- Python:raschii库计算任意阶数Stokes波
Stokes五阶波 最近发现一个很有用的Stokes波计算Python库,raschii官方说明,可以计算任意阶数,不同水深下的Stokes波,简单做了下测试,测试结果与脚本如下 Python 脚本 ...
- mysql从零开始之MySQL UPDATE 更新
MySQL UPDATE 更新 如果我们需要修改或更新 MySQL 中的数据,我们可以使用 SQL UPDATE 命令来操作. 语法 以下是 UPDATE 命令修改 MySQL 数据表数据的通用 SQ ...
- Python - poetry(1)包管理利器的入门介绍
Python 虚拟环境详解 https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/p/15266382.html poetry 官方介绍 github:https://github.com/p ...
- The Data Way Vol.2 | 做个『单纯』的程序员还真不简单
关于「The Data Way」 「The Data Way」是由 SphereEx 公司出品的一档播客节目.这里有开源.数据.技术的故事,同时我们关注开发者的工作日常,也讨论开发者的生活日常:我们聚 ...
- pure-ftpd管理FTP服务器,创建文件夹可以,但上传下载文件不行
两种原因 1.因为pure-ftpd的防火墙端口问题 # Port range for passive connections replies. - for firewalling. PassiveP ...
- ubuntu16.04安装klee
ubuntu16.04安装klee(基于llvm 3.8)教程 前言 查阅了很多资料,踩了不少的坑,总的来说,这个应该是比较完善的基于llvm3.8和ubuntu16.04的安装教程,至少我自己按照这 ...
- 这样学BAT必面之软件设计原则,还不会就是我的问题
学习设计原则是学习设计模式的基础.在实际开发过程中,并不要求所有代码都遵循设计原则,我们要考虑人力.时间.成本.质量,不能刻意追求完美,但要在适当的场景遵循设计原则,这体现的是一种平衡取舍,可以帮助我 ...
