hdu 1685 Booksort (IDA*)
Booksort
There is one department in the library, full of bookcases, where still the old way of borrowing is in use. Students can simply walk around there, pick out the books they like and, after registration, take them home for at most three weeks.
Quite often, however, it happens that a student takes a book from the shelf, takes a closer look at it, decides that he does not want to read it, and puts it back. Unfortunately, not all students are very careful with this last step. Although each book has a unique identification code, by which the books are sorted in the bookcase, some students put back the books they have considered at the wrong place. They do put it back onto the right shelf. However, not at the right position on the shelf.
Other students use the unique identification code (which they can find in an online catalogue) to find the books they want to borrow. For them, it is important that the books are really sorted on this code. Also for the librarian, it is important that the books are sorted. It makes it much easier to check if perhaps some books are stolen: not borrowed, but yet missing.
Therefore, every week, the librarian makes a round through the department and sorts the books on every shelf. Sorting one shelf is doable, but still quite some work. The librarian has considered several algorithms for it, and decided that the easiest way for him to sort the books on a shelf, is by sorting by transpositions: as long as the books are not sorted,
take out a block of books (a number of books standing next to each other),
shift another block of books from the left or the right of the resulting ‘hole’, into this hole,
and put back the first block of books into the hole left open by the second block.
One such sequence of steps is called a transposition.
The following picture may clarify the steps of the algorithm, where X denotes the first block of books, and Y denotes the second block.
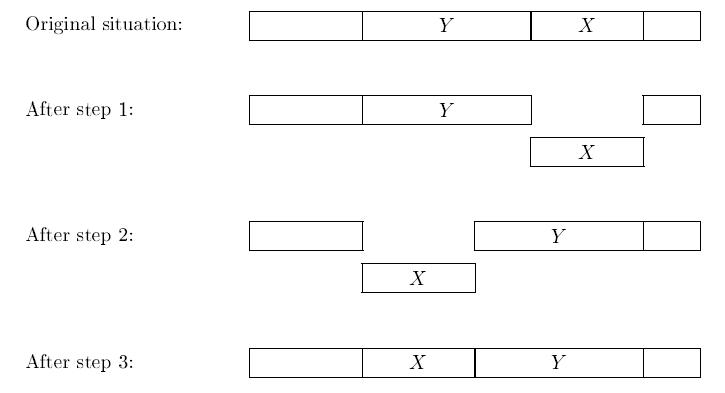
Of course, the librarian wants to minimize the work he has to do. That is, for every bookshelf, he wants to minimize the number of transpositions he must carry out to sort the books. In particular, he wants to know if the books on the shelf can be sorted by at most 4 transpositions. Can you tell him?
One line with one integer n with 1 ≤ n ≤ 15: the number of books on a certain shelf.
One line with the n integers 1, 2, …, n in some order, separated by single spaces: the unique identification codes of the n books in their current order on the shelf.
if the minimal number of transpositions to sort the books on their unique identification codes (in increasing order) is T ≤ 4, then this minimal number T;
if at least 5 transpositions are needed to sort the books, then the message "5 or more".
6
1 3 4 6 2 5
5
5 4 3 2 1
10
6 8 5 3 4 7 2 9 1 10
3
5 or more
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#define maxn 16
using namespace std; int n,m,ans,depth,flag;
int a[maxn]; bool isok()
{
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(a[i]!=i) return false ;
}
return true ;
}
int h()
{
int i,j,t=0;
for(i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
if(a[i]+1!=a[i+1]) t++;
}
return t;
}
void dfs(int d)
{
if(isok())
{
flag=1;
return ;
}
if(flag||(d-1)*3+h()>depth*3) return ; // 实现IDA*
int i,j,k,p;
int tmp[maxn];
for(i=1; i<=n; i++) // 模拟操作
{
for(j=i; j<=n; j++)
{
for(k=1; k<=i-1; k++)
{
memcpy(tmp,a,sizeof(tmp));
for(p=k; p<=i-1; p++)
{
a[p+j-i+1]=tmp[p];
}
for(p=i; p<=j; p++)
{
a[p-i+k]=tmp[p];
}
dfs(d+1);
memcpy(a,tmp,sizeof(tmp));
}
for(k=j+1; k<=n; k++)
{
memcpy(tmp,a,sizeof(tmp));
for(p=j+1; p<=k; p++)
{
a[p-j-1+i]=tmp[p];
}
for(p=i; p<=j; p++)
{
a[p+k-j]=tmp[p];
}
dfs(d+1);
memcpy(a,tmp,sizeof(tmp));
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j,t,flg;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
flg=1;
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
if(a[i]!=i) flg=0;
}
a[0]=0,a[n+1]=n+1;
if(flg)
{
printf("0\n");
continue ;
}
flag=depth=0;
while(!flag)
{
depth++;
dfs(1);
if(depth>=4) break ;
}
if(flag) printf("%d\n",depth);
else printf("5 or more\n");
}
return 0;
}
hdu 1685 Booksort (IDA*)的更多相关文章
- POJ 1077 HDU 1043 Eight (IDA*)
题意就不用再说明了吧......如此经典 之前想用双向广搜.a*来写,但总觉得无力,现在用IDA*感觉其他的解法都弱爆了..............想法活跃,时间,空间消耗很小,给它跪了 启发式搜索关 ...
- DNA sequence HDU - 1560(IDA*,迭代加深搜索)
题目大意:有n个DNA序列,构造一个新的序列,使得这n个DNA序列都是它的子序列,然后输出最小长度. 题解:第一次接触IDA*算法,感觉~~好暴力!!思路:维护一个数组pos[i],表示第i个串该匹配 ...
- HDU 2485 Destroying the bus stations (IDA*+ BFS)
传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2485 题意:给你n个点,m条相连的边,问你最少去掉几个点使从1到n最小路径>=k,其中不能去掉1, ...
- HDU 1813 Escape from Tetris (IDA*)
传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1813 题意:给你一个n*n的迷宫,其中0代表有一个人在这个位置,1代表墙,现在要求一个路线,使所有的人通 ...
- POJ3460 Booksort(IDA*)
POJ3460 Booksort 题意:给定一个长度为n的序列,每次可以取出其中的一段数,插入任意一个位置,问最少需要几次操作才能使整个序列变为1~n 思路:IDA*+迭代加深搜索 小技巧:将一段数插 ...
- hdu 2234(IDA*)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2234 思路:IDA*可以搞,借鉴的是大牛的启发式函数h(): 可以考虑把每一行上的数转化成相同的,或者 ...
- hdu 1667(IDA*)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1667 思路:大牛说是IDA*的入门题=.=构造h()=8-max(1,2,3); max(1,2,3 ...
- HDU 1043 & POJ 1077 Eight(康托展开+BFS | IDA*)
Eight Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 30176 Accepted: 13119 Special ...
- HDU 1560 DNA sequence (IDA* 迭代加深 搜索)
题目地址:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1560 BFS题解:http://www.cnblogs.com/crazyapple/p/321810 ...
随机推荐
- myeclipse 'no default proposals' when use 'alt + /'.
solution: Window -> Preferences -> Java -> Editor -> Content Assist -> Advanced in th ...
- 对ajax的hack的分析
先上原文链接:对jQuery ajax请求成功(失败)回调执行前的统一处理(兼容较老版本jQuery) 原文中已经提到了使用场景了,我觉得这非常适合单页面应用,还有backbone应用中.毕竟ajax ...
- 【windows开发实现记事本程序——逻辑篇1】
1. 主要内容 从本节开始介绍windows开发实现记事本程序的逻辑实现部分.本节的主要内容有以下3点: 1. 主窗口定义 -- 主要介绍记事本主界面窗口对应的窗口类及实现方案 2. RichEdi ...
- 【cogs247】售票系统
[问题描述] 某次列车途经C个城市,城市编号依次为1到C,列车上共有S个座位,铁路局规定售出的车票只能是坐票, 即车上所有的旅客都有座.售票系统是由计算机执行的,每一个售票申请包含三个参数,分别用O. ...
- c#中使用ABCpdf处理PDF
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Web;using System.Web.UI ...
- sql批量插入数据之存储过程
-- ============================================= -- Author: jf_ou -- Create date: 2016/03/22 -- Desc ...
- Git 远程仓库的管理和使用
要参与任何一个 Git 项目的协作,必须要了解该如何管理远程仓库.远程仓库是指托管在网络上的项目仓库,可能会有好多个,其中有些你只能读,另外有些可以写.同他人协作开发某 个项目时,需要管理这些远程仓库 ...
- java中加载xml文件方法
this.getclass().getclassloader().getresourceasstream(String file); 可以加载文件,比如xml.
- Android模拟器Genymotion安装向导
Genymotion简述 Genymotion提供Android虚拟环境的工具集.相信很多Android开发者一定受够了速度慢.体验差效率及其地下的官方模拟器了.如果你没有物理机器,又不想忍受官方模拟 ...
- Unity3d在安卓android的更新(APK覆盖)
其实这并没什么技术难点,也不是完美的热更新方案,只能说是退而求其次的一个方法. 起因主要是因为公司几个U3D项目在立项之初都没有能做好热更新的规化,导致现在要去做U3D的热更新非常难,并且项目已处于中 ...
